Professional Documents
Culture Documents
b2 Summary Mind Maps
b2 Summary Mind Maps
Uploaded by
api-228548823Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 1 A & P Check PointsDocument11 pagesChapter 1 A & P Check PointsRobin Wilfong89% (9)
- SYMBIOGENESIS A New Principle of EvolutionDocument240 pagesSYMBIOGENESIS A New Principle of Evolutionaaguilard100% (3)
- CSEC Biology ManualDocument132 pagesCSEC Biology ManualChelsea FrancisNo ratings yet
- BIO103.13 Course Outline CAK Spring 2021Document5 pagesBIO103.13 Course Outline CAK Spring 2021Samiul Hasan PrantoNo ratings yet
- SACE Stage 1 Biology Test Revision/Summary QuestionsDocument1 pageSACE Stage 1 Biology Test Revision/Summary QuestionsNhi HinNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Study Guide For 2022 Without EcologyDocument8 pagesMid Term Study Guide For 2022 Without EcologyAniya HarriottNo ratings yet
- 8th Class Science NotesDocument23 pages8th Class Science NotesMehreen RashidNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Jan Mock Revision ListDocument9 pagesYear 11 Jan Mock Revision Listbseddon6969No ratings yet
- BIOL-121 Exam 1 Study GuideDocument3 pagesBIOL-121 Exam 1 Study GuidemaydelinNo ratings yet
- 1.basic Principles of Human PhysiologyDocument94 pages1.basic Principles of Human PhysiologyBobyAnugrah50% (2)
- GBIO 106 Final Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesGBIO 106 Final Exam ReviewDauntlessNo ratings yet
- 12th Bio Important ALPDocument15 pages12th Bio Important ALPAdnan RafiqNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Part 1 - Lecture 1, 2 and 3Document2 pagesQuestion Bank Part 1 - Lecture 1, 2 and 3anandswarupNo ratings yet
- Life Process: Join Free Learning Group - For Easy Access To Video Lectures and AssessmentDocument4 pagesLife Process: Join Free Learning Group - For Easy Access To Video Lectures and AssessmentarunimaNo ratings yet
- Pixl Knowledge Test Answers - Aqa b2 Additional Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017Document17 pagesPixl Knowledge Test Answers - Aqa b2 Additional Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017api-342297566No ratings yet
- GCE - O Level BiologyDocument25 pagesGCE - O Level BiologyWayne WeeNo ratings yet
- 6e39fa66 - 1 16667079390929 2452Document11 pages6e39fa66 - 1 16667079390929 2452markelsaify2007No ratings yet
- Xi Bio PDocument4 pagesXi Bio PVirendra SinghNo ratings yet
- BIO 101 Exit Exam Study GuideDocument3 pagesBIO 101 Exit Exam Study GuideOlaide Seun Akintade100% (1)
- "We Heal As One": Department of EducationDocument11 pages"We Heal As One": Department of EducationJonathan YambaoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PDocument25 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PSyrine Myles Sullivan100% (2)
- Envi Prelim Module No.3Document11 pagesEnvi Prelim Module No.3Philip Christian RoxasNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY (Theory) : Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsDocument21 pagesBIOLOGY (Theory) : Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsWajahat AliNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Revision List For StudentsDocument3 pagesYear 10 Revision List For StudentsSankarshan DahiyaNo ratings yet
- SBI3U0 Exam Review 2023 PDFDocument3 pagesSBI3U0 Exam Review 2023 PDFartkid234566No ratings yet
- Principles of Biology I Class Assignment-1 Due Date: Lecture 7Document5 pagesPrinciples of Biology I Class Assignment-1 Due Date: Lecture 7Ainaya Hanifa Nur AisyaNo ratings yet
- Unit OutlineDocument3 pagesUnit Outlineapi-212901753No ratings yet
- Study Guide For FinalDocument2 pagesStudy Guide For Finalkwrrm99r8fNo ratings yet
- SCU BIOL18 Midterm Study GuideDocument3 pagesSCU BIOL18 Midterm Study GuidePaige RichardsNo ratings yet
- Gen. Bio. Q4 M1 Janine Joy M. Arroyo 11 STEM ADocument19 pagesGen. Bio. Q4 M1 Janine Joy M. Arroyo 11 STEM Abm5755768No ratings yet
- Target Paper X BiologyDocument3 pagesTarget Paper X BiologyMeer UmarNo ratings yet
- 10th Bio Guess 2023 PTBDocument8 pages10th Bio Guess 2023 PTBashfaq4985No ratings yet
- CH 1-20 Reading Guide and VocabularyDocument81 pagesCH 1-20 Reading Guide and VocabularyCrystal VillelaNo ratings yet
- b2 Summary Notes - Sets 1-5Document31 pagesb2 Summary Notes - Sets 1-5api-320022467No ratings yet
- 2.1 1. List All The Things You Should An Should Not Do in Biological DrawingsDocument2 pages2.1 1. List All The Things You Should An Should Not Do in Biological DrawingsCherry T CYNo ratings yet
- State Test Study Guide 2019Document25 pagesState Test Study Guide 2019All about derreonnnNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PDocument26 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PTipsy MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Good Hand Written Notes Chapter WiseDocument8 pagesGood Hand Written Notes Chapter Wisesantunaskar948No ratings yet
- Cell Division With GameDocument52 pagesCell Division With GameLeanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Module BIO IIDocument7 pagesModule BIO IIBrandon DacanayNo ratings yet
- 1a. Characteristics of Life 2023 - Copy-1Document4 pages1a. Characteristics of Life 2023 - Copy-1llekhanya-1No ratings yet
- Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Test Bank instant download all chapterDocument37 pagesBiology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Test Bank instant download all chapterbelicepandor100% (4)
- Q1 Science 9 (Biology)Document3 pagesQ1 Science 9 (Biology)Łuci MattiasNo ratings yet
- 16 Quarter 1 Module 16-Introduction-To-Cellular-RespirationDocument21 pages16 Quarter 1 Module 16-Introduction-To-Cellular-RespirationBRYAN ZAFENo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Test Bank Full ChapterDocument37 pagesInstant Download PDF Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Test Bank Full Chapterhickenthess100% (5)
- 100 Sawal BioDocument4 pages100 Sawal BiorajivNo ratings yet
- 2015 Fall Semester Test Biology Study Guide: Fromunit 1 (Answer On Your Own Paper)Document8 pages2015 Fall Semester Test Biology Study Guide: Fromunit 1 (Answer On Your Own Paper)beckid75No ratings yet
- CH.5 LIFE PROCESSES NOTES ANSKEY CompleteDocument25 pagesCH.5 LIFE PROCESSES NOTES ANSKEY Completemananahuja0987No ratings yet
- Cell Division: Origin of CellsDocument9 pagesCell Division: Origin of CellselizabethNo ratings yet
- Lucknow Public School Sample Paper-Ii Biology Class - XiDocument3 pagesLucknow Public School Sample Paper-Ii Biology Class - XiNishant singhNo ratings yet
- Fall Semester Review 2020Document5 pagesFall Semester Review 2020api-521781723No ratings yet
- Dewan Aminul Islam BME Assignment1Document12 pagesDewan Aminul Islam BME Assignment1Towsif Muhtadi KhanNo ratings yet
- Biochem IntroductionDocument317 pagesBiochem IntroductionTrisha DicangNo ratings yet
- Life Science Exam Review-May 2015 2Document7 pagesLife Science Exam Review-May 2015 2api-233757247No ratings yet
- Biology 10-12 Revised Edition 2-1Document101 pagesBiology 10-12 Revised Edition 2-1Daniel FulirwaNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Semester I Final Exam Study Guide - Bio23Document4 pagesKami Export - Semester I Final Exam Study Guide - Bio23Ryan FungNo ratings yet
- WS - Life Processes-ImpDocument8 pagesWS - Life Processes-ImpAISHA AMAL ANDIKATTILASSLAM ANDIKATTILNo ratings yet
- Textbook The Evolution of Molecular Biology The Search For The Secrets of Life 1St Edition Kensal E Van Holde Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook The Evolution of Molecular Biology The Search For The Secrets of Life 1St Edition Kensal E Van Holde Ebook All Chapter PDFjulia.lee522100% (4)
- GENERAL BI0LOGY 1 Cell Cycle Mitosis & MeiosisDocument12 pagesGENERAL BI0LOGY 1 Cell Cycle Mitosis & MeiosisPercival RiegoNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-StudyGuide EDITEDDocument5 pagesChapter1-StudyGuide EDITEDdaddy 'oNo ratings yet
- Biochem Introduction A PDFDocument107 pagesBiochem Introduction A PDFDaevy Toribio AmdosNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - The People Behind The Science - K. Cullen (2006) WW PDFDocument193 pagesChemistry - The People Behind The Science - K. Cullen (2006) WW PDFThe Dangerous One100% (1)
- CucumberDocument76 pagesCucumberБойка Родопска100% (3)
- Biology WaecDocument37 pagesBiology WaecPascal JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Nucleus: Structure Function The Nucleus Controls and Regulates The Activities of The CellDocument13 pagesNucleus: Structure Function The Nucleus Controls and Regulates The Activities of The CellAndres ValleNo ratings yet
- Investigation of The Factors Affecting PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesInvestigation of The Factors Affecting PhotosynthesisAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Fix Kelas XiDocument7 pagesBahasa Inggris Fix Kelas Xirinto lamere0% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/32Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/32Saleha ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Notes Biology A Level PRDocument30 pagesToaz - Info Notes Biology A Level PRThoon Nadi NaiNo ratings yet
- Alison Smith, Michael Witty-Heme, Chlorophyll, and Bilins - Methods and Protocols (2001)Document351 pagesAlison Smith, Michael Witty-Heme, Chlorophyll, and Bilins - Methods and Protocols (2001)Andres CastilloNo ratings yet
- BETCK105E Mod3AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument27 pagesBETCK105E Mod3AzDOCUMENTS - inVELUANBALAGANNo ratings yet
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument74 pagesGaseous ExchangeMartina BugejaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 1010 Section A Term Test #1 2010 Summer: Good Luck!!!Document8 pagesBIOL 1010 Section A Term Test #1 2010 Summer: Good Luck!!!Haris HarahapNo ratings yet
- The Biophysics of PhotosynthesisDocument465 pagesThe Biophysics of Photosynthesisunknown159No ratings yet
- Causes of Salinity PDFDocument20 pagesCauses of Salinity PDFhaimiljoshi_84970418No ratings yet
- Gardening Indoors With CO2 1997Document50 pagesGardening Indoors With CO2 1997Darwin100% (1)
- 17 Photosynth 2 10 10 05Document19 pages17 Photosynth 2 10 10 05Kima MadNo ratings yet
- QAAC-CourseSpecification - BIOLS 320 S1 2023-2024Document11 pagesQAAC-CourseSpecification - BIOLS 320 S1 2023-2024fatima.alzahrNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science NotesDocument4 pagesNutrition in Plants Class 7 Science Notesshravandownload100% (1)
- Taylor Grino - Biology 101 Chapter 7 Colorful Case StudyDocument5 pagesTaylor Grino - Biology 101 Chapter 7 Colorful Case StudyTaylor GrinoNo ratings yet
- Mark Marlatt - Photosynthesis Lab and Report Track D - 5261224Document8 pagesMark Marlatt - Photosynthesis Lab and Report Track D - 5261224api-544304176No ratings yet
- Handy PEA+ Manual EmailDocument87 pagesHandy PEA+ Manual EmailAdgroup NghiaNo ratings yet
- Leaf Area Meter-WriteupDocument3 pagesLeaf Area Meter-WriteupSreya P SNo ratings yet
- Remed Pat B.ingDocument11 pagesRemed Pat B.ingMuhamad RaihanNo ratings yet
- Bio Quiz BeeDocument2 pagesBio Quiz BeeRuchi Briam James LagitnayNo ratings yet
- Plant Stress PhysiologyDocument14 pagesPlant Stress Physiologyaqsa nazNo ratings yet
- RPH SC Form 2Document50 pagesRPH SC Form 2lccjane8504No ratings yet
- Edexcel A2 Biology Revision NotesDocument79 pagesEdexcel A2 Biology Revision NotesAasiya SultanaNo ratings yet
- Bal Bharati Public School, GRH Marg SESSION: 2021-2022 Class Vii Science Nutrition in Plants Lesson Plan - 2Document4 pagesBal Bharati Public School, GRH Marg SESSION: 2021-2022 Class Vii Science Nutrition in Plants Lesson Plan - 2Pooja guptaNo ratings yet
b2 Summary Mind Maps
b2 Summary Mind Maps
Uploaded by
api-228548823Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
b2 Summary Mind Maps
b2 Summary Mind Maps
Uploaded by
api-228548823Copyright:
Available Formats
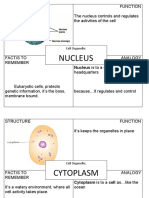
B2 REVISION CHAPTER 1 CELLS, TISSUES & ORGANS
KEY WORDS:
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Cell membrane
Mitochondria
Ribosome
Chloroplast
Vacuole
Specialised
Diffusion
Concentration
gradient
Multicellular
Tissue
Organ
Organ system
ASSESSMENT:
What do plant cells have that animal
cells do not?
What is the function of:
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Chloroplasts
Cell Wall
Sketch and label a plant and an
animal cell;
Draw and label 2 specialised cells. Explain their structure is adapted to suit their
function
Use pictures and words to describe the three ways substances
can move in and out of cells
Diffusion
What is a tissue?
What is an organ?
What is an organ system?
B2 REVISION CHAPTER 2 ORGANISMS IN THE ENVIRONMENT
KEY WORDS:
Photosynthesis
Glucose
Limiting factors
Quadrat
Sample size
Range
Mean
Median
Mode
Transect
Reproducible
Valid
Variables
ASSESSMENT:
What is the equation for
photosynthesis
Where in the plant does it occur?
How are leaves adapted to
perform photosynthesis?
Explain how light, CO
2
and temperature are limiting factors of
photosynthesis
Explain how plants use glucose for
the following:
Respiration
Transport
Storage
How do we measure the distribution of organisms?
How do we know this data is accurate?
How doe the follow factors affect organisms in their
environment?
Temperature:
Light:
Water:
CO
2
and O
2
:
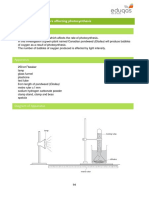
B2 REVISION CHAPTER 3 ENZYMES
KEY WORDS:
Catalysts
Enzyme
Active site
Denatured
Digested
Carbohydrase
Amylase
Protease
Lipase
Bile
Emulsifiers
Biological
detergents
ASSESSMENT:
What are enzymes made from?
What do enzymes do?
How do they work? (explain &
draw the lock & key mechanism
What effect does temperature
have on enzyme activity
What effect does pH have on
enzyme activity
What are the 3 groups of enzymes in digestion? What is
their substrate and what do they break them down into?
1)
2)
3)
Why is the stomach acidic?
What is bile, what does it do and how does it do it?
Describe 3 industrial uses for
enzymes
How can we speed up digestion?
Changing the pH:
Altering the surface area:
B2 REVISION CHAPTER 4 ENERGY FROM RESPIRATION
KEY WORDS:
Aerobic respiration
Mitochondria
Glycogen
Anaerobic respiration
Oxygen debt
ASSESSMENT:
What is the formula for aerobic respiration?
What is the role of
mitochondria in respiration?
Why do organisms respire?
A student pedalled an exercise cycle at constant speed for 5 minutes.
The students heart rate was recorded at one-minute intervals during the
exercise and also during recovery.
Describe the effect exercise has on the heart:
A students breathing was monitored before and after vigorous exercise.
The student breathed in and out through a special apparatus. The graphs
show the changes in the volume of air inside the apparatus. Each time the
student breathed in, the line on the graph dropped. Each time the
student breathed out, the line went up.
Describe the effect of exercise has on breathing:
What is anaerobic respiration?
How does it cause muscle fatigue?
What is oxygen debt?
B2 REVISION CHAPTER 5 SIMPLE INHERITANCE
KEY WORDS:
Alleles
Mitosis
Meiosis
Stem cells
Therapeutic
cloning
Mendel
DNA finger
printing
Chromosomes
Dominant
Recessive
Polydactyly
Cystic fibrosis
ASSESSMENT:
What are stem cells?
State 2 uses of stem cells:
State 2 problems with stem cell
research:
Chromosomes are made of long strands
of what?
Small sections of this are called what?
What do genes code for?
What is DNA fingerprinting?
What is mitosis and why is it needed?
What is differentiation?
How does it differ in plants and
animals?
What is meiosis?
Why is it important?
How does it help generate variation?
How many chromosomes in a) gamete and b) somatic cell?
What is an allele?
What does a) dominant; and b) recessive mean?
What is Cystic Fibrosis and what causes it?
Draw the punnet's square for 2 CF carriers
How do these fossils support the theory of
evolution
B2 REVISION CHAPTER 6 OLD & NEW SPECIES
KEY WORDS:
Fossils
Extinction
Geographical isolation
Endemic
Speciation
ASSESSMENT:
What are fossils?
How are they formed?
What can we learn from
fossils?
Why do we describe
fossil records as
incomplete?
What is extinction?
Describe how
environmental change leads to extinction
organisms can cause extinction
Describe how new species can evolve through geographical
isolation:
Higher: include info on speciation
What caused the
extinction of the
dinosaurs?
You might also like
- Chapter 1 A & P Check PointsDocument11 pagesChapter 1 A & P Check PointsRobin Wilfong89% (9)
- SYMBIOGENESIS A New Principle of EvolutionDocument240 pagesSYMBIOGENESIS A New Principle of Evolutionaaguilard100% (3)
- CSEC Biology ManualDocument132 pagesCSEC Biology ManualChelsea FrancisNo ratings yet
- BIO103.13 Course Outline CAK Spring 2021Document5 pagesBIO103.13 Course Outline CAK Spring 2021Samiul Hasan PrantoNo ratings yet
- SACE Stage 1 Biology Test Revision/Summary QuestionsDocument1 pageSACE Stage 1 Biology Test Revision/Summary QuestionsNhi HinNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Study Guide For 2022 Without EcologyDocument8 pagesMid Term Study Guide For 2022 Without EcologyAniya HarriottNo ratings yet
- 8th Class Science NotesDocument23 pages8th Class Science NotesMehreen RashidNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Jan Mock Revision ListDocument9 pagesYear 11 Jan Mock Revision Listbseddon6969No ratings yet
- BIOL-121 Exam 1 Study GuideDocument3 pagesBIOL-121 Exam 1 Study GuidemaydelinNo ratings yet
- 1.basic Principles of Human PhysiologyDocument94 pages1.basic Principles of Human PhysiologyBobyAnugrah50% (2)
- GBIO 106 Final Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesGBIO 106 Final Exam ReviewDauntlessNo ratings yet
- 12th Bio Important ALPDocument15 pages12th Bio Important ALPAdnan RafiqNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Part 1 - Lecture 1, 2 and 3Document2 pagesQuestion Bank Part 1 - Lecture 1, 2 and 3anandswarupNo ratings yet
- Life Process: Join Free Learning Group - For Easy Access To Video Lectures and AssessmentDocument4 pagesLife Process: Join Free Learning Group - For Easy Access To Video Lectures and AssessmentarunimaNo ratings yet
- Pixl Knowledge Test Answers - Aqa b2 Additional Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017Document17 pagesPixl Knowledge Test Answers - Aqa b2 Additional Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017api-342297566No ratings yet
- GCE - O Level BiologyDocument25 pagesGCE - O Level BiologyWayne WeeNo ratings yet
- 6e39fa66 - 1 16667079390929 2452Document11 pages6e39fa66 - 1 16667079390929 2452markelsaify2007No ratings yet
- Xi Bio PDocument4 pagesXi Bio PVirendra SinghNo ratings yet
- BIO 101 Exit Exam Study GuideDocument3 pagesBIO 101 Exit Exam Study GuideOlaide Seun Akintade100% (1)
- "We Heal As One": Department of EducationDocument11 pages"We Heal As One": Department of EducationJonathan YambaoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PDocument25 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PSyrine Myles Sullivan100% (2)
- Envi Prelim Module No.3Document11 pagesEnvi Prelim Module No.3Philip Christian RoxasNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY (Theory) : Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsDocument21 pagesBIOLOGY (Theory) : Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsWajahat AliNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Revision List For StudentsDocument3 pagesYear 10 Revision List For StudentsSankarshan DahiyaNo ratings yet
- SBI3U0 Exam Review 2023 PDFDocument3 pagesSBI3U0 Exam Review 2023 PDFartkid234566No ratings yet
- Principles of Biology I Class Assignment-1 Due Date: Lecture 7Document5 pagesPrinciples of Biology I Class Assignment-1 Due Date: Lecture 7Ainaya Hanifa Nur AisyaNo ratings yet
- Unit OutlineDocument3 pagesUnit Outlineapi-212901753No ratings yet
- Study Guide For FinalDocument2 pagesStudy Guide For Finalkwrrm99r8fNo ratings yet
- SCU BIOL18 Midterm Study GuideDocument3 pagesSCU BIOL18 Midterm Study GuidePaige RichardsNo ratings yet
- Gen. Bio. Q4 M1 Janine Joy M. Arroyo 11 STEM ADocument19 pagesGen. Bio. Q4 M1 Janine Joy M. Arroyo 11 STEM Abm5755768No ratings yet
- Target Paper X BiologyDocument3 pagesTarget Paper X BiologyMeer UmarNo ratings yet
- 10th Bio Guess 2023 PTBDocument8 pages10th Bio Guess 2023 PTBashfaq4985No ratings yet
- CH 1-20 Reading Guide and VocabularyDocument81 pagesCH 1-20 Reading Guide and VocabularyCrystal VillelaNo ratings yet
- b2 Summary Notes - Sets 1-5Document31 pagesb2 Summary Notes - Sets 1-5api-320022467No ratings yet
- 2.1 1. List All The Things You Should An Should Not Do in Biological DrawingsDocument2 pages2.1 1. List All The Things You Should An Should Not Do in Biological DrawingsCherry T CYNo ratings yet
- State Test Study Guide 2019Document25 pagesState Test Study Guide 2019All about derreonnnNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PDocument26 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PTipsy MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Good Hand Written Notes Chapter WiseDocument8 pagesGood Hand Written Notes Chapter Wisesantunaskar948No ratings yet
- Cell Division With GameDocument52 pagesCell Division With GameLeanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Module BIO IIDocument7 pagesModule BIO IIBrandon DacanayNo ratings yet
- 1a. Characteristics of Life 2023 - Copy-1Document4 pages1a. Characteristics of Life 2023 - Copy-1llekhanya-1No ratings yet
- Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Test Bank instant download all chapterDocument37 pagesBiology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Test Bank instant download all chapterbelicepandor100% (4)
- Q1 Science 9 (Biology)Document3 pagesQ1 Science 9 (Biology)Łuci MattiasNo ratings yet
- 16 Quarter 1 Module 16-Introduction-To-Cellular-RespirationDocument21 pages16 Quarter 1 Module 16-Introduction-To-Cellular-RespirationBRYAN ZAFENo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Test Bank Full ChapterDocument37 pagesInstant Download PDF Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Test Bank Full Chapterhickenthess100% (5)
- 100 Sawal BioDocument4 pages100 Sawal BiorajivNo ratings yet
- 2015 Fall Semester Test Biology Study Guide: Fromunit 1 (Answer On Your Own Paper)Document8 pages2015 Fall Semester Test Biology Study Guide: Fromunit 1 (Answer On Your Own Paper)beckid75No ratings yet
- CH.5 LIFE PROCESSES NOTES ANSKEY CompleteDocument25 pagesCH.5 LIFE PROCESSES NOTES ANSKEY Completemananahuja0987No ratings yet
- Cell Division: Origin of CellsDocument9 pagesCell Division: Origin of CellselizabethNo ratings yet
- Lucknow Public School Sample Paper-Ii Biology Class - XiDocument3 pagesLucknow Public School Sample Paper-Ii Biology Class - XiNishant singhNo ratings yet
- Fall Semester Review 2020Document5 pagesFall Semester Review 2020api-521781723No ratings yet
- Dewan Aminul Islam BME Assignment1Document12 pagesDewan Aminul Islam BME Assignment1Towsif Muhtadi KhanNo ratings yet
- Biochem IntroductionDocument317 pagesBiochem IntroductionTrisha DicangNo ratings yet
- Life Science Exam Review-May 2015 2Document7 pagesLife Science Exam Review-May 2015 2api-233757247No ratings yet
- Biology 10-12 Revised Edition 2-1Document101 pagesBiology 10-12 Revised Edition 2-1Daniel FulirwaNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Semester I Final Exam Study Guide - Bio23Document4 pagesKami Export - Semester I Final Exam Study Guide - Bio23Ryan FungNo ratings yet
- WS - Life Processes-ImpDocument8 pagesWS - Life Processes-ImpAISHA AMAL ANDIKATTILASSLAM ANDIKATTILNo ratings yet
- Textbook The Evolution of Molecular Biology The Search For The Secrets of Life 1St Edition Kensal E Van Holde Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook The Evolution of Molecular Biology The Search For The Secrets of Life 1St Edition Kensal E Van Holde Ebook All Chapter PDFjulia.lee522100% (4)
- GENERAL BI0LOGY 1 Cell Cycle Mitosis & MeiosisDocument12 pagesGENERAL BI0LOGY 1 Cell Cycle Mitosis & MeiosisPercival RiegoNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-StudyGuide EDITEDDocument5 pagesChapter1-StudyGuide EDITEDdaddy 'oNo ratings yet
- Biochem Introduction A PDFDocument107 pagesBiochem Introduction A PDFDaevy Toribio AmdosNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - The People Behind The Science - K. Cullen (2006) WW PDFDocument193 pagesChemistry - The People Behind The Science - K. Cullen (2006) WW PDFThe Dangerous One100% (1)
- CucumberDocument76 pagesCucumberБойка Родопска100% (3)
- Biology WaecDocument37 pagesBiology WaecPascal JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Nucleus: Structure Function The Nucleus Controls and Regulates The Activities of The CellDocument13 pagesNucleus: Structure Function The Nucleus Controls and Regulates The Activities of The CellAndres ValleNo ratings yet
- Investigation of The Factors Affecting PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesInvestigation of The Factors Affecting PhotosynthesisAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Fix Kelas XiDocument7 pagesBahasa Inggris Fix Kelas Xirinto lamere0% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/32Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/32Saleha ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Notes Biology A Level PRDocument30 pagesToaz - Info Notes Biology A Level PRThoon Nadi NaiNo ratings yet
- Alison Smith, Michael Witty-Heme, Chlorophyll, and Bilins - Methods and Protocols (2001)Document351 pagesAlison Smith, Michael Witty-Heme, Chlorophyll, and Bilins - Methods and Protocols (2001)Andres CastilloNo ratings yet
- BETCK105E Mod3AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument27 pagesBETCK105E Mod3AzDOCUMENTS - inVELUANBALAGANNo ratings yet
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument74 pagesGaseous ExchangeMartina BugejaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 1010 Section A Term Test #1 2010 Summer: Good Luck!!!Document8 pagesBIOL 1010 Section A Term Test #1 2010 Summer: Good Luck!!!Haris HarahapNo ratings yet
- The Biophysics of PhotosynthesisDocument465 pagesThe Biophysics of Photosynthesisunknown159No ratings yet
- Causes of Salinity PDFDocument20 pagesCauses of Salinity PDFhaimiljoshi_84970418No ratings yet
- Gardening Indoors With CO2 1997Document50 pagesGardening Indoors With CO2 1997Darwin100% (1)
- 17 Photosynth 2 10 10 05Document19 pages17 Photosynth 2 10 10 05Kima MadNo ratings yet
- QAAC-CourseSpecification - BIOLS 320 S1 2023-2024Document11 pagesQAAC-CourseSpecification - BIOLS 320 S1 2023-2024fatima.alzahrNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science NotesDocument4 pagesNutrition in Plants Class 7 Science Notesshravandownload100% (1)
- Taylor Grino - Biology 101 Chapter 7 Colorful Case StudyDocument5 pagesTaylor Grino - Biology 101 Chapter 7 Colorful Case StudyTaylor GrinoNo ratings yet
- Mark Marlatt - Photosynthesis Lab and Report Track D - 5261224Document8 pagesMark Marlatt - Photosynthesis Lab and Report Track D - 5261224api-544304176No ratings yet
- Handy PEA+ Manual EmailDocument87 pagesHandy PEA+ Manual EmailAdgroup NghiaNo ratings yet
- Leaf Area Meter-WriteupDocument3 pagesLeaf Area Meter-WriteupSreya P SNo ratings yet
- Remed Pat B.ingDocument11 pagesRemed Pat B.ingMuhamad RaihanNo ratings yet
- Bio Quiz BeeDocument2 pagesBio Quiz BeeRuchi Briam James LagitnayNo ratings yet
- Plant Stress PhysiologyDocument14 pagesPlant Stress Physiologyaqsa nazNo ratings yet
- RPH SC Form 2Document50 pagesRPH SC Form 2lccjane8504No ratings yet
- Edexcel A2 Biology Revision NotesDocument79 pagesEdexcel A2 Biology Revision NotesAasiya SultanaNo ratings yet
- Bal Bharati Public School, GRH Marg SESSION: 2021-2022 Class Vii Science Nutrition in Plants Lesson Plan - 2Document4 pagesBal Bharati Public School, GRH Marg SESSION: 2021-2022 Class Vii Science Nutrition in Plants Lesson Plan - 2Pooja guptaNo ratings yet