Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grob Basic Electronics: Direct-Current Meters
Grob Basic Electronics: Direct-Current Meters
Uploaded by
Rebecca Elliott0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views8 pagesThis chapter discusses different types of direct current (DC) meters, including moving-coil meters, voltmeters, ohmmeters, and multimeters. It explains that moving-coil meters measure current by the proportional deflection of a coil, voltmeters use a high-resistance multiplier to measure potential differences, and ohmmeters use an internal battery to measure resistance inversely proportional to current flow. The chapter also covers meter shunts, which extend the current measurement range, and different meter types like analog, VOM, and digital multimeters.
Original Description:
DC Meters
Original Title
DC Meters
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis chapter discusses different types of direct current (DC) meters, including moving-coil meters, voltmeters, ohmmeters, and multimeters. It explains that moving-coil meters measure current by the proportional deflection of a coil, voltmeters use a high-resistance multiplier to measure potential differences, and ohmmeters use an internal battery to measure resistance inversely proportional to current flow. The chapter also covers meter shunts, which extend the current measurement range, and different meter types like analog, VOM, and digital multimeters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views8 pagesGrob Basic Electronics: Direct-Current Meters
Grob Basic Electronics: Direct-Current Meters
Uploaded by
Rebecca ElliottThis chapter discusses different types of direct current (DC) meters, including moving-coil meters, voltmeters, ohmmeters, and multimeters. It explains that moving-coil meters measure current by the proportional deflection of a coil, voltmeters use a high-resistance multiplier to measure potential differences, and ohmmeters use an internal battery to measure resistance inversely proportional to current flow. The chapter also covers meter shunts, which extend the current measurement range, and different meter types like analog, VOM, and digital multimeters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
1
Grob Basic Electronics
Chapter 8
DIRECT-CURRENT METERS
2
Topics Covered in Chapter 8
Moving-coil meter
Measuring current
Voltmeters
Ohmmeters
Multimeters
Meter applications
Checking continuity with an ohmmeter
3
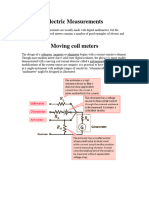
Direct Current Meters
Direct current in a moving-coil meter
deflects the coin in proportion to the amount
of current.
The current meter must be connected in
series with the circuit where the current is
to be measured.
The dc current meter must be connected
with the correct polarity.
4
Meter Shunts
Meter shunts are low-value resistors that are
connected in parallel with the meter
movement.
Meter shunts extend the range of currents
that can be read with the same meter
movement.
5
Voltmeters
A voltmeter uses a high-resistance
multiplier in series with the meter
movement.
The voltmeter is connected across two
points to measure their difference in
potential.
The dc voltmeter must be connected with
the correct polarity.
6
Ohmmeters
An ohmmeter consists of an internal battery
in series with the meter movement.
Current from the internal battery flows
through the resistance being measured,
producing a deflection that is:
Proportional to the current flow
and
Inversely proportional to the amount of
resistance being measured.
7
Types of Meters
Analog, or moving-coil meter:
Uses a pointer to indicate values of current,
voltage, or resistance on a printed scale.
Volt-Ohm-Milliammeter (VOM):
Allows all three kinds of measurements on a
single scale or readout.
Digital multimeter:
Uses a numerical readout instead of a pointer
and printed scale.
8
End of Chapter 8
You might also like
- Ammeter PDFDocument5 pagesAmmeter PDFPromo EltNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Current DividersDocument6 pagesVoltage and Current DividersRebecca ElliottNo ratings yet
- Intrumentation Unit LL (2.7)Document3 pagesIntrumentation Unit LL (2.7)gurungpg143No ratings yet
- 3.3. Ohmmeters: Ohmmeter Working PrincipleDocument3 pages3.3. Ohmmeters: Ohmmeter Working PrincipleEveNo ratings yet
- What Is An OhmmeterDocument4 pagesWhat Is An OhmmeterballDISCOVERIES PHballDISCOVERIESNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Instrumentation ProjectDocument9 pagesSensors and Instrumentation ProjectSai Sandeep RayanuthalaNo ratings yet
- Ammeter, Voltmeter, DC Motor, Electric Generator, UPSDocument13 pagesAmmeter, Voltmeter, DC Motor, Electric Generator, UPSatiqurrehman0074No ratings yet
- Objectives: Lab 1-Introduction To Basic Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDocument7 pagesObjectives: Lab 1-Introduction To Basic Electrical Measuring Instrumentsßirũk Bmt100% (1)
- Unit 09 InstrumentsDocument24 pagesUnit 09 Instrumentsrose ann balaoroNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Measuring InstrumentsDocument24 pagesUnit 9 Measuring InstrumentsjeffmathNo ratings yet
- CIRCUITS 1 - Lab Experiment #02Document5 pagesCIRCUITS 1 - Lab Experiment #02jeryl generalaoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Voltage: Chapter Review QuestionsDocument16 pagesPressure Voltage: Chapter Review QuestionsPrakash Chandran CNo ratings yet
- OhmmeterDocument2 pagesOhmmetervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Question: Discuss in Detail About The Current and Voltage Measurement Instruments. AlsoDocument7 pagesQuestion: Discuss in Detail About The Current and Voltage Measurement Instruments. AlsoSanjana chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Ohmmeter: Design Evolution Precision Ohmmeters See Also References External LinksDocument3 pagesOhmmeter: Design Evolution Precision Ohmmeters See Also References External LinksMadhusudanan AshokNo ratings yet
- VoltmeterDocument5 pagesVoltmeterhumaid15No ratings yet
- BEE LAB MANUAL FINAL1st SemesterDocument38 pagesBEE LAB MANUAL FINAL1st SemesterSaif KhanNo ratings yet
- Moving Coil Meters: Voltmeter Ammeter OhmmeterDocument5 pagesMoving Coil Meters: Voltmeter Ammeter OhmmeterAtique KhanNo ratings yet
- AC & DC MetersDocument2 pagesAC & DC Metersk85yfbwhynNo ratings yet
- Nothing Special 4Document25 pagesNothing Special 4Jester SubiaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Question EE101-Experiment 1Document4 pagesAnswers To Question EE101-Experiment 1Grace Reyes0% (1)
- ElectricalDocument6 pagesElectrical3re0oooNo ratings yet
- غۆڤاندDocument7 pagesغۆڤاندavdfdfdfNo ratings yet
- Current Voltage MeasurementDocument35 pagesCurrent Voltage MeasurementAaqib AliNo ratings yet
- A Multimeter Is An Electronic InstrumentDocument43 pagesA Multimeter Is An Electronic InstrumentSyachrial Yusuf100% (1)
- Methodology Statement For Power Meter p1Document1 pageMethodology Statement For Power Meter p1Charlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- How To Use A Multimeter - The Quick Guide To Accurately Measure ElectricalDocument17 pagesHow To Use A Multimeter - The Quick Guide To Accurately Measure Electricalalex ortizNo ratings yet
- Measuring InsstrumentsDocument11 pagesMeasuring Insstrumentsamit singhNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Q&ADocument6 pagesInstrumentation Q&AcloudNo ratings yet
- Instrument MeasurementDocument6 pagesInstrument MeasurementMarlon Desacula IINo ratings yet
- Multi MeterDocument8 pagesMulti Meterneha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Electrical Instruments and MeasurementsDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Electrical Instruments and Measurementszxufra lumanglasNo ratings yet
- Measurement of CurrentDocument3 pagesMeasurement of CurrentAnkur MathurNo ratings yet
- Electricity Equipment LAB: Lulav Saeed Sadiq Electricity and ElectronicDocument7 pagesElectricity Equipment LAB: Lulav Saeed Sadiq Electricity and ElectronicLulav BarwaryNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Electrical Measuring Instruments Objectives:: Voltmeter AmmeterDocument5 pagesUnit 2: Electrical Measuring Instruments Objectives:: Voltmeter AmmeterMark MagcalasNo ratings yet
- Multimeter - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 pagesMultimeter - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediad_richard_dNo ratings yet
- GMM 3 and 2 CHAPTER 13 Common Test Equipment and Logical ToubleshootingDocument32 pagesGMM 3 and 2 CHAPTER 13 Common Test Equipment and Logical ToubleshootingAbeyu AssefaNo ratings yet
- Basic Instrument Tools & Tackle Introduction: 28 October 2019 Instrumentation and Control 1Document65 pagesBasic Instrument Tools & Tackle Introduction: 28 October 2019 Instrumentation and Control 1Mochammad Maulana SuwardoNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Measurement Et-314Document57 pagesInstrumentation and Measurement Et-314ammarshahzad501No ratings yet
- Fluke Type 73 Digital MultimeterDocument7 pagesFluke Type 73 Digital MultimeterAbiyot AderieNo ratings yet
- Basic Assignment (20116433013)Document7 pagesBasic Assignment (20116433013)Tonmoy RafiNo ratings yet
- Model Answer For ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTDocument20 pagesModel Answer For ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTazhar3303No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Electromagnetic Variables - Part 1Document34 pagesLecture 3 Electromagnetic Variables - Part 1châu nguyễn ngọcNo ratings yet
- William M Belville - The Complete Guide To Using A Multimeter - Mastering The Basics and Functions of A Multimeter-Amazon Digital Services LLC - KDP (2023) - 2Document76 pagesWilliam M Belville - The Complete Guide To Using A Multimeter - Mastering The Basics and Functions of A Multimeter-Amazon Digital Services LLC - KDP (2023) - 2sayid khalif100% (2)
- Expirement 1 - Fundamental Electrical MeasurementsDocument8 pagesExpirement 1 - Fundamental Electrical MeasurementsJhajha AlboniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Transducers and Measuring Instruments: Current and Voltage MeasurementDocument30 pagesChapter-3 Transducers and Measuring Instruments: Current and Voltage MeasurementYab TadNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements, Types of Electrical Instruments & Different Types of Voltmeter and AmeterDocument9 pagesElectrical Measurements, Types of Electrical Instruments & Different Types of Voltmeter and AmeterIzhar Jiskani50% (2)
- Intro To Circuits Lab #1: Anatomy of A BreadboardDocument5 pagesIntro To Circuits Lab #1: Anatomy of A BreadboardNishat AhamadNo ratings yet
- VoltmeterDocument2 pagesVoltmetervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Instituto Politécnico Nacional: Practice: 1 "Use of Ohmmeter, Voltmeter and Ammeter in Measurements D.C"Document11 pagesInstituto Politécnico Nacional: Practice: 1 "Use of Ohmmeter, Voltmeter and Ammeter in Measurements D.C"José Emmanuel Martínez CerónNo ratings yet
- Measurement ElectricityDocument4 pagesMeasurement ElectricityMd HamzaNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 3: Use Measuring Instruments: Ammeter, Voltmeter, and WattmeterDocument4 pagesPractical No. 3: Use Measuring Instruments: Ammeter, Voltmeter, and Wattmeter166CMYashvardhan Shinde100% (1)
- LU1.2.Use Basic Electric MetersDocument23 pagesLU1.2.Use Basic Electric Metersnguemaabraham1No ratings yet
- Defence University College of Engineering: Departement of Electrical Power TechnologyDocument105 pagesDefence University College of Engineering: Departement of Electrical Power Technologychibssa alemayehuNo ratings yet
- VoltmeterDocument6 pagesVoltmeterAndi DelimaNo ratings yet
- Ammeter VoltmeterDocument17 pagesAmmeter Voltmeterfarihakanwal2021No ratings yet
- How To Use A Digital Multimeter The Quick Guide To Learn How To Use A Digital Multimeter To Measure Voltage, Current and More Correctly, Diagnose and Fix Anything ElectronicDocument44 pagesHow To Use A Digital Multimeter The Quick Guide To Learn How To Use A Digital Multimeter To Measure Voltage, Current and More Correctly, Diagnose and Fix Anything ElectronicamseraucNo ratings yet
- Nothing Special 1Document2 pagesNothing Special 1Jester SubiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Elect Measurements-MetersDocument23 pagesChapter 06 Elect Measurements-MetersRobinsNo ratings yet
- AmmeterDocument5 pagesAmmeterGilberto ManhattanNo ratings yet
- Grob Basic Electronics: CapacitanceDocument8 pagesGrob Basic Electronics: CapacitanceRebecca ElliottNo ratings yet
- ComputationsDocument29 pagesComputationsRebecca ElliottNo ratings yet
- Contact Details:: We Can HELP!Document2 pagesContact Details:: We Can HELP!Rebecca ElliottNo ratings yet
- Grob Basic Electronics: Alternating Current CircuitsDocument11 pagesGrob Basic Electronics: Alternating Current CircuitsRebecca ElliottNo ratings yet
- Ect ReviewerDocument165 pagesEct ReviewerKayerzzzNo ratings yet
- Alternating Voltage and CurrentDocument12 pagesAlternating Voltage and CurrentRebecca ElliottNo ratings yet
- 20 Cellular Radio: QuestionsDocument2 pages20 Cellular Radio: QuestionsRebecca ElliottNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 CISCO Packet Tracer Name: - Section: - Professor: - DateDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 CISCO Packet Tracer Name: - Section: - Professor: - DateRebecca ElliottNo ratings yet
- 4 Angle Modulation: QUESTIONS:ANSWERS:What Do You Call of The General Term That Includes Frequencyand PhaseDocument2 pages4 Angle Modulation: QUESTIONS:ANSWERS:What Do You Call of The General Term That Includes Frequencyand PhaseRebecca ElliottNo ratings yet