Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Homework 1
Homework 1
Uploaded by
Adrian Hurtado de Mendoza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views2 pagesThis document contains 5 homework problems for an Aerospace Engineering course on Aerodynamics and Aeroelasticity. The problems cover topics like calculating the location of the center of pressure for a flat plate in supersonic flow, determining lift and drag coefficients from given normal and axial force coefficients, calculating test conditions to match scale model and full-scale lift and drag coefficients, relating lift per unit span to pressure distributions on wind tunnel walls, and calculating various aerodynamic properties for a supersonic flat plate given pressure and shear stress distributions.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 5 homework problems for an Aerospace Engineering course on Aerodynamics and Aeroelasticity. The problems cover topics like calculating the location of the center of pressure for a flat plate in supersonic flow, determining lift and drag coefficients from given normal and axial force coefficients, calculating test conditions to match scale model and full-scale lift and drag coefficients, relating lift per unit span to pressure distributions on wind tunnel walls, and calculating various aerodynamic properties for a supersonic flat plate given pressure and shear stress distributions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views2 pagesHomework 1
Homework 1
Uploaded by
Adrian Hurtado de MendozaThis document contains 5 homework problems for an Aerospace Engineering course on Aerodynamics and Aeroelasticity. The problems cover topics like calculating the location of the center of pressure for a flat plate in supersonic flow, determining lift and drag coefficients from given normal and axial force coefficients, calculating test conditions to match scale model and full-scale lift and drag coefficients, relating lift per unit span to pressure distributions on wind tunnel walls, and calculating various aerodynamic properties for a supersonic flat plate given pressure and shear stress distributions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Universidad Europea de Madrid
Aerospace Engineering program
Aerodynamics and Aeroelasticity
Homework 1
Due May 13
Problem 1
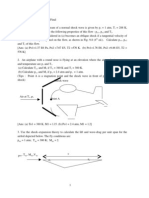
Consider an infinitely thin ftat plate of chord c at an angle of attack in a supersonic flow.
The pressures on the upper and lower surfaces are different but constant over each
surface; i.e., Pu(s) = c1 and p1(s) = c2 , where c1 and c2 are constants and c2 > c 1.
Ignoring the shear stress, calculate the location of the center of pressure.
Problem 2
Consider an airfoil at 12 angle of attack. The normal and axial force coefficients are 1.2
and 0.03, respectively. Calculate the lift and drag coefficients.
Problem 3
Consider a Lear jet flying at a velocity of 250m/s and altitude of 10km, where the density
and temperature are 0.414 kg/m
3
and 223K, respectively. Consider also a one-fifth scale
model of the Lear jet being tested in a wind tunnel in the laboratory. The pressure in the
test section of the wind tunnel is 1 atm. Calculate the necessary velocity, temperature, and
density of the airflow in the wind-tunnel test section such that the lift and drag coefficients
are the same for the wind-tunnel model and the actual airplane in flight. Note: The relation
among pressure, density, and temperature is given by the equation of state.
Problem 4
Consider an airfoil in a wind tunnel (i.e., a wing that spans the entire test section).Prove
that the lift per unit span can be obtained from the pressure distributions on the top and
bottom walls of the wind tunnel (i .e., from the pressure distributions on the walls above
and below the airfoil).
Problem 5
Consider an infinitely thin flat plate with a 1m chord at an angle of attack of 10 in a
supersonic flow. The pressure and shear stress distributions on the upper and lower
surfaces are given by P
u
= 4 x l0
4
(x - 1)
2
+ 5.4 x 10
4
, and P
l
= 2 x 10
4
(x - 1)
2
+ 1.73 x 10
5
,
u
= 288x
-0.2
, and
l
= 73lx
-02
respectively, where x is the distance from the leading edge
in meters and p and are in Newton per square meter. Calculate the normal and axial
forces, the lift and drag, moments about the leading edge, and moments about the quarter
chord, all per unit span. Also, calculate the location of the center of pressure.
You might also like
- Fundamental of Aerodynamic 5th EdDocument14 pagesFundamental of Aerodynamic 5th EdabcNo ratings yet
- Transonic Report DEN 302Document17 pagesTransonic Report DEN 302get_moin50% (2)
- Homework 1Document2 pagesHomework 1Fernando AguayoNo ratings yet
- ME2135-2 Lab Manual (Flow Over An Airfoil)Document19 pagesME2135-2 Lab Manual (Flow Over An Airfoil)meowyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 External ConvectionDocument68 pagesChapter 4 External Convectionpvr2k1No ratings yet
- Airflow Through Mine OpeningDocument6 pagesAirflow Through Mine Openingersunilsingh1No ratings yet
- Perf2 30dec2016Document23 pagesPerf2 30dec2016Keerthi M50% (2)
- HW 2Document2 pagesHW 2Abhimanyu JamwalNo ratings yet
- Problems Set AerodynamicsDocument2 pagesProblems Set Aerodynamics700tyNo ratings yet
- Flow Past An Aerofoil Lab ManualDocument12 pagesFlow Past An Aerofoil Lab ManualLaw Zhan HongNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics ProblemsDocument8 pagesAerodynamics ProblemsPramod GowdaNo ratings yet
- Aero Test2 PDFDocument3 pagesAero Test2 PDFkmssaileshNo ratings yet
- M (A O.g074) - Assuming That The Coefficient of Friction Between The Tires and TheDocument1 pageM (A O.g074) - Assuming That The Coefficient of Friction Between The Tires and ThevibhubhatNo ratings yet
- AE342-Aerodynamics II - RevisionDocument89 pagesAE342-Aerodynamics II - RevisionHus FernandoNo ratings yet
- P 303 AnsDocument4 pagesP 303 AnsDiptoNo ratings yet
- Aerody Practice ProbDocument2 pagesAerody Practice Probmadjeaudrei.romeroNo ratings yet
- MMME2007 Spring 2018-2019 QuestionsDocument9 pagesMMME2007 Spring 2018-2019 QuestionsJonathan AngNo ratings yet
- FlowLabEOC2e CH11Document5 pagesFlowLabEOC2e CH11Anonymous ncBe0B9bNo ratings yet
- Problems Chapter 2 Introduction To Aircraft Technology Use: G 9.81 M/S 1 Atm. 101325 N/M R 287 J/KGK For AirDocument3 pagesProblems Chapter 2 Introduction To Aircraft Technology Use: G 9.81 M/S 1 Atm. 101325 N/M R 287 J/KGK For AirKynn VargasNo ratings yet
- Pressure Distribution, Lift and Drag On An Airfoil: MECH 345: Mechanics of Fluids I Experiment #4Document4 pagesPressure Distribution, Lift and Drag On An Airfoil: MECH 345: Mechanics of Fluids I Experiment #4Js SmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter1 QuestionsRiyad Mohammed0% (1)
- Redifined Approach For The Modeling of Sky DivingDocument14 pagesRedifined Approach For The Modeling of Sky Divingvarun varma100% (1)
- Tfe1 2023Document3 pagesTfe1 2023Radha BhojNo ratings yet
- Effect of Inclination of Impinging Jets On Flow and Heat Transfer CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesEffect of Inclination of Impinging Jets On Flow and Heat Transfer CharacteristicsInternational Journal of Science and Engineering InvestigationsNo ratings yet
- AE 301 - Aerodynamics I - Spring 2015 Problem Set 2: Assigned: Friday, January 23, 2015 Due: Friday, January 30, 2015Document2 pagesAE 301 - Aerodynamics I - Spring 2015 Problem Set 2: Assigned: Friday, January 23, 2015 Due: Friday, January 30, 2015TheTannedFishNo ratings yet
- 1 1 1 O, 1 O, 2 2 TH O, 1 O, 2 2Document4 pages1 1 1 O, 1 O, 2 2 TH O, 1 O, 2 2TimBarberNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet and Assignment IIDocument11 pagesWork Sheet and Assignment IIAb AnNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics I (Review Questionnaire)Document15 pagesAerodynamics I (Review Questionnaire)Christian DimasNo ratings yet
- CHB1 Assignment2Document2 pagesCHB1 Assignment2anhspidermenNo ratings yet
- Practical Lab # 8. Finding Pressure Distribution Over An Aerofoil at Different Velocity and AnglesDocument3 pagesPractical Lab # 8. Finding Pressure Distribution Over An Aerofoil at Different Velocity and Anglesamanuelfitsum589No ratings yet
- 1920SEM1 ExamDocument9 pages1920SEM1 ExamBenedict ChinNo ratings yet
- Exam of Experimental Methods: International Master of Turbulence and SMI Master Lille 2016-2017Document2 pagesExam of Experimental Methods: International Master of Turbulence and SMI Master Lille 2016-2017Smiron VargheseNo ratings yet
- Studio Classroom ProblemsDocument5 pagesStudio Classroom ProblemsIliasMajdiNo ratings yet
- Fluids Systems Practical File: Course OutcomesDocument29 pagesFluids Systems Practical File: Course Outcomes2K18/ME/192 SANCHIT DHASMANANo ratings yet
- ME564 Assignment 1Document9 pagesME564 Assignment 1johnsucceedNo ratings yet
- PRINT AndersonDocument7 pagesPRINT AndersonCed Sison100% (1)
- Problem Sheet 3Document2 pagesProblem Sheet 3balochfrahan.2003No ratings yet
- Basic AerodynamicsDocument43 pagesBasic AerodynamicsSagar LEMONIACNo ratings yet
- Ass - 1 (2021-22)Document3 pagesAss - 1 (2021-22)Nishith KumarNo ratings yet
- 1718SEM1Document6 pages1718SEM1Benedict ChinNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023 Fall AE305 PH-1: Res. Asst. Burak ÇİFTCİOĞLU 02.11.2022Document8 pages2022-2023 Fall AE305 PH-1: Res. Asst. Burak ÇİFTCİOĞLU 02.11.2022Mehmet AliNo ratings yet
- Assignment B 1Document4 pagesAssignment B 1José A. Montiel QuirósNo ratings yet
- Kelompok - 03 - Modul - 1 - Laporan - IPE - 2023Document13 pagesKelompok - 03 - Modul - 1 - Laporan - IPE - 2023ac3.evfrezNo ratings yet
- EXP6Document6 pagesEXP6MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Problems-Convection 1Document2 pagesProblems-Convection 1Ira Octavia100% (1)
- 19AEE301 CA3 4 QP 2023Document3 pages19AEE301 CA3 4 QP 2023gnsvaravishwas03No ratings yet
- Lab 4Document13 pagesLab 4Dilshad S FaisalNo ratings yet
- AerodynamicsDocument5 pagesAerodynamicsmohamedelamari04No ratings yet
- AERO2358 Review of Key Concepts 2015Document39 pagesAERO2358 Review of Key Concepts 2015chuhaininh123No ratings yet
- Assignment Reg 2013 Tuesday1Document2 pagesAssignment Reg 2013 Tuesday1Abubakar AdeniNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Airway Resistance - IntroductionDocument11 pages5.1 Airway Resistance - IntroductionDeepakKattimaniNo ratings yet
- Wind Tunnel Experiments Procedure in UPMDocument5 pagesWind Tunnel Experiments Procedure in UPMMohd AnuarNo ratings yet
- FMDocument4 pagesFMvishalNo ratings yet
- Lect 01 Introduction02Document21 pagesLect 01 Introduction02Salman KhalilNo ratings yet
- Problem 1Document3 pagesProblem 1Alfredo Gonzalez SoteloNo ratings yet
- Convection Tutorial Sheet 3Document4 pagesConvection Tutorial Sheet 3Charlotte BNo ratings yet
- Convection Tutorial Sheet 3Document4 pagesConvection Tutorial Sheet 3Charlotte BNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 3 - External Forced Convection - WatermarkDocument2 pagesProblem Sheet 3 - External Forced Convection - WatermarkUzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Noorul Islam College of Engineering, KumaracoilDocument37 pagesNoorul Islam College of Engineering, KumaracoilJames PraveenNo ratings yet