Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GoF - Patterns
GoF - Patterns
Uploaded by
hdksromeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleFrom EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- RESTful API Design - Best Practices in API Design with REST: API-University Series, #3From EverandRESTful API Design - Best Practices in API Design with REST: API-University Series, #3Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Becoming Telebirr AgentDocument147 pagesBecoming Telebirr AgentSami91% (34)
- Microservices Patterns: With examples in JavaFrom EverandMicroservices Patterns: With examples in JavaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- System Design Interview - An Insider's GuideDocument103 pagesSystem Design Interview - An Insider's GuideОлег Шванн90% (10)
- Design Pattern CheatsheetDocument2 pagesDesign Pattern Cheatsheeta_anastassov100% (16)
- Coding Interview-LeetcodeDocument181 pagesCoding Interview-LeetcodeAkshit Sharma80% (5)
- Gang of Four Design Patterns 4.0 PDFDocument86 pagesGang of Four Design Patterns 4.0 PDFEli_Hux100% (6)
- Software Design Patterns Made SimpleDocument31 pagesSoftware Design Patterns Made SimpleAnoop Madhusudanan100% (13)
- Re Factoring and Design PatternsDocument783 pagesRe Factoring and Design PatternsEvans Krypton Sowah100% (6)
- Software Architecture For Developers PDFDocument133 pagesSoftware Architecture For Developers PDFAdha Mashur Sajiah78% (9)
- Architectural PatternsDocument458 pagesArchitectural PatternsGaby Sandoval100% (11)
- Architectural Patterns - Uncover Essential Patterns in The Most Indispensable Realm of Enterprise Architecture PDFDocument458 pagesArchitectural Patterns - Uncover Essential Patterns in The Most Indispensable Realm of Enterprise Architecture PDFRishi Rai100% (6)
- Domain Driven Design : How to Easily Implement Domain Driven Design - A Quick & Simple GuideFrom EverandDomain Driven Design : How to Easily Implement Domain Driven Design - A Quick & Simple GuideRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Getting started with Spring Framework: A Hands-on Guide to Begin Developing Applications Using Spring FrameworkFrom EverandGetting started with Spring Framework: A Hands-on Guide to Begin Developing Applications Using Spring FrameworkRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Cloud Native Patterns: Designing change-tolerant softwareFrom EverandCloud Native Patterns: Designing change-tolerant softwareRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- UML Quick Reference CardDocument1 pageUML Quick Reference Cardallen.bang100% (6)
- Coding InterviewDocument109 pagesCoding InterviewAshok Obuli100% (4)
- Grok System Design InterviewDocument163 pagesGrok System Design InterviewCarlos Rojas100% (3)
- Microservices Architecture Handbook: Non-Programmer's Guide for Building MicroservicesFrom EverandMicroservices Architecture Handbook: Non-Programmer's Guide for Building MicroservicesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- MySQL Quick Reference SheetDocument2 pagesMySQL Quick Reference SheetSneetsher Crispy100% (5)
- CSS Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCSS Cheat Sheetesommer99% (77)
- Unix Commands Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageUnix Commands Cheat Sheet PDFRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Java Script 2Document121 pagesJava Script 2Sneetsher Crispy100% (2)
- Jharkhand General Knowledge (Objective Question)Document8 pagesJharkhand General Knowledge (Objective Question)Gunjan86% (28)
- ISM CPSM Exam-SpecificationsDocument7 pagesISM CPSM Exam-SpecificationsmsajanjNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Finance For ManagersDocument322 pagesAccounting and Finance For ManagersPrasanna Aravindan100% (5)
- UML Reference CardDocument2 pagesUML Reference CardSneetsher Crispy100% (10)
- Clean Code Cheat Sheet V1.3Document1 pageClean Code Cheat Sheet V1.3Peter Saddington100% (7)
- Engineering Managers Guide Design PatternsDocument28 pagesEngineering Managers Guide Design Patternstompacheco-1100% (7)
- Software Architecture PatternsDocument55 pagesSoftware Architecture Patternseggie545100% (15)
- Design Patterns Difference FAQS Compiled-1Document8 pagesDesign Patterns Difference FAQS Compiled-1Umar Ali100% (1)
- Cracking System Design Interview Like A Pro - A 10 DayDocument199 pagesCracking System Design Interview Like A Pro - A 10 Daybrian50% (8)
- 140 Google Interview QuestionsDocument6 pages140 Google Interview QuestionsstephanehaddadNo ratings yet
- Design PatternsDocument7 pagesDesign Patternstongaboardi2363No ratings yet
- Visualising Software ArchitectureDocument198 pagesVisualising Software ArchitectureLaure Kamalandua100% (5)
- Software Architecture Interview QuestionsDocument219 pagesSoftware Architecture Interview QuestionsHemant Patil86% (7)
- CleanCodeHandbook v1.0.1Document100 pagesCleanCodeHandbook v1.0.1spanishsauce100% (2)
- Design Patterns Interview QuestionsDocument13 pagesDesign Patterns Interview QuestionsGopinath100% (2)
- Domain Driven Design - Step by StepDocument20 pagesDomain Driven Design - Step by Stepossus3r70% (10)
- 278 Software Architecture Design ModelsDocument310 pages278 Software Architecture Design Modelstrans50% (2)
- An Insiders Guide To Ace System Design in - Maurice JaysonDocument60 pagesAn Insiders Guide To Ace System Design in - Maurice JaysonAkriti Jain100% (1)
- How To Build Microservices: Top 10 Hacks To Modeling, Integrating & Deploying MicroservicesFrom EverandHow To Build Microservices: Top 10 Hacks To Modeling, Integrating & Deploying MicroservicesNo ratings yet
- Cracking Microservices Interview: Learn Advance Concepts, Patterns, Best Practices, NFRs, Frameworks, Tools and DevOpsFrom EverandCracking Microservices Interview: Learn Advance Concepts, Patterns, Best Practices, NFRs, Frameworks, Tools and DevOpsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Coder Habits: The #39# Habits of the Professional ProgrammerFrom EverandThe Coder Habits: The #39# Habits of the Professional ProgrammerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mastering JavaScript Design Patterns - Second EditionFrom EverandMastering JavaScript Design Patterns - Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Good Code, Bad Code: Think like a software engineerFrom EverandGood Code, Bad Code: Think like a software engineerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- PostScript Quick ReferenceDocument2 pagesPostScript Quick ReferenceSneetsher CrispyNo ratings yet
- SVN RefDocument2 pagesSVN Refanon-247901100% (1)
- STL Quick ReferenceDocument8 pagesSTL Quick ReferenceSneetsher Crispy100% (3)
- Octave Reference CardDocument3 pagesOctave Reference CardSneetsher CrispyNo ratings yet
- RSS Cheat SheetDocument1 pageRSS Cheat SheetSneetsher CrispyNo ratings yet
- X86 AssemblyDocument123 pagesX86 AssemblySneetsher Crispy97% (39)
- Subversion Cheat Sheet v1 For SVNDocument1 pageSubversion Cheat Sheet v1 For SVNGabriel GaheteNo ratings yet
- Emacs Quick ReferenceDocument3 pagesEmacs Quick ReferenceSneetsher Crispy100% (1)
- RGB Color Hex Cheat Sheet v1Document1 pageRGB Color Hex Cheat Sheet v1Sneetsher Crispy100% (4)
- MySQL. Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMySQL. Cheat Sheetjorgekf13No ratings yet
- PHP Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePHP Cheat Sheetanon-280494100% (4)
- PHP Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePHP Cheat Sheetwarezisgr8No ratings yet
- XML Path Language 1 0Document2 pagesXML Path Language 1 0Sneetsher Crispy100% (1)
- HTML Character Entities Cheat SheetDocument1 pageHTML Character Entities Cheat SheetcormissNo ratings yet
- HTML Cheat Sheet v1 PDFDocument1 pageHTML Cheat Sheet v1 PDFallmanahNo ratings yet
- Javascript Cheat SheetDocument1 pageJavascript Cheat Sheetdanielle leigh100% (4)
- Gimp Quick Reference Card v.1.0Document1 pageGimp Quick Reference Card v.1.0Sneetsher CrispyNo ratings yet
- stmp3500 Reference SCH RevbDocument15 pagesstmp3500 Reference SCH RevbSneetsher Crispy100% (1)
- Cascading Style Sheets 1.0Document2 pagesCascading Style Sheets 1.0Ivana JakimovskaNo ratings yet
- Chuleta CssDocument1 pageChuleta CssoscarlopgaNo ratings yet
- Mysql Quick SheetDocument2 pagesMysql Quick Sheetibrahim-bn-yah-ya-9183No ratings yet
- Vi Quick ReferenceDocument1 pageVi Quick ReferenceSneetsher Crispy100% (6)
- The Identification of Common RocksDocument18 pagesThe Identification of Common RocksSneetsher Crispy100% (7)
- CISCO in ArabicDocument214 pagesCISCO in ArabicSneetsher Crispy100% (5)
- OHSAS 18001 Work Instruction and SOPsDocument5 pagesOHSAS 18001 Work Instruction and SOPsAlina Walace0% (1)
- Ict Dos and DontsDocument5 pagesIct Dos and DontsLouwellaEredianoIbabaoNo ratings yet
- NLC English 7 Enhancement LP v.1Document85 pagesNLC English 7 Enhancement LP v.1patric maturan100% (1)
- Digital NativesDocument10 pagesDigital NativesJonathan Blanco Sa RiyadhNo ratings yet
- Archer T5E (UN) - 1.0 Datasheet PDFDocument4 pagesArcher T5E (UN) - 1.0 Datasheet PDFeeerakeshNo ratings yet
- The Current WarDocument1 pageThe Current WarkanuvietNo ratings yet
- Primus Overview Catalogue ANGDocument8 pagesPrimus Overview Catalogue ANGpesumasinad0% (1)
- OPM Costing Fundamentals - ActualDocument21 pagesOPM Costing Fundamentals - Actualkhaled_ghrbia100% (1)
- Niir Mumbai Companies Directory Database XLSX Excel Format 5th EditionDocument2 pagesNiir Mumbai Companies Directory Database XLSX Excel Format 5th Editionphone25hire phone25hireNo ratings yet
- Debug Tacacs CiscoDocument5 pagesDebug Tacacs CiscodeztrocxeNo ratings yet
- PragmaticsDocument10 pagesPragmaticsDisya RusmadinantiNo ratings yet
- Present Etac Dep Psis PDFDocument96 pagesPresent Etac Dep Psis PDFRobiahZakariaNo ratings yet
- OtooDocument11 pagesOtooStefania DavidNo ratings yet
- TC-42X1 Part 1Document50 pagesTC-42X1 Part 1Pedro SandovalNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide For Growing Plants Hydroponically by J Benton Jones JR B00hznqitmDocument5 pagesComplete Guide For Growing Plants Hydroponically by J Benton Jones JR B00hznqitmnagesh dolasNo ratings yet
- Normalized Impedance and Admittance Coordinates: Name Title Dwg. NoDocument1 pageNormalized Impedance and Admittance Coordinates: Name Title Dwg. NoJayeng WidiatmokoNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Ingenieria en Control Moderna OGATADocument240 pagesSolucionario Ingenieria en Control Moderna OGATAanandpj444471% (7)
- GRP 3 Keesha & Marie Faye Abdellah Power Point FINALDocument10 pagesGRP 3 Keesha & Marie Faye Abdellah Power Point FINALevangelo22656No ratings yet
- Case CX TrainingDocument20 pagesCase CX Traininghoward100% (27)
- Lacerte Jennifer ResumeDocument1 pageLacerte Jennifer Resumejennifer_lacerteNo ratings yet
- Course Registration SystemDocument11 pagesCourse Registration Systemananthprasad91100% (3)
- H11L1Document6 pagesH11L1Silvio QuerzoliNo ratings yet
- Class 12 CS ProjectDocument27 pagesClass 12 CS ProjectKs100% (3)
- The Secret SharerDocument3 pagesThe Secret ShareranbarasiNo ratings yet
- Essay On Flood in PakistanDocument6 pagesEssay On Flood in Pakistanjvscmacaf100% (2)
- SADP User Manual (V2.0)Document10 pagesSADP User Manual (V2.0)tehixazNo ratings yet
GoF - Patterns
GoF - Patterns
Uploaded by
hdksromeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GoF - Patterns
GoF - Patterns
Uploaded by
hdksromeCopyright:
Available Formats
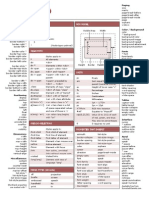
+visitElementA(in a : ConcreteElementA)
+visitElementB(in b : ConcreteElementB)
interface
Visitor
+visitElementA(in a : ConcreteElementA)
+visitElementB(in b : ConcreteElementB)
ConcreteVisitor
+accept(in v : Visitor)
interface
Element
+accept(in v : Visitor)
ConcreteElementA
+accept(in v : Visitor)
ConcreteElementB
Client
Visitor
Type: Behavioral
What it is:
Represent an operation to be
performed on the elements of an
object structure. Lets you define a
new operation without changing
the classes of the elements on
which it operates.
+templateMethod()
#subMethod()
AbstractClass
+subMethod()
ConcreteClass
Template Method
Type: Behavioral
What it is:
Define the skeleton of an algorithm in an
operation, deferring some steps to subclasses.
Lets subclasses redefine certain steps
of an algorithm without changing the
algorithm's structure.
+execute()
ConcreteStrategyB
+execute()
interface
Strategy
Context
+execute()
ConcreteStrategyA
Strategy
Type: Behavioral
What it is:
Define a family of algorithms,
encapsulate each one, and make them
interchangeable. Lets the algorithm vary
independently from
clients that use it.
+handle()
ConcreteState1
+handle()
interface
State
+request()
Context
+handle()
ConcreteState2
State
Type: Behavioral
What it is:
Allow an object to alter its behavior when
its internal state changes. The object will
appear to change its class.
-subjectState
ConcreteSubject
+update()
-observerState
ConcreteObserver
+update()
interface
Observer
notifies
observes
+attach(in o : Observer)
+detach(in o : Observer)
+notify()
interface
Subject Observer
Type: Behavioral
What it is:
Define a one-to-many dependency between
objects so that when one object changes
state, all its dependents are notified and
updated automatically.
-state
Memento
+setMemento(in m : Memento)
+createMemento()
-state
Originator
Caretaker
Memento
Type: Behavioral
What it is:
Without violating encapsulation, capture
and externalize an object's internal state
so that the object can be restored to this
state later.
Abstract Factory C
Adapter S
Bridge S
Builder C
Chain of Responsibility B
Command B
Composite S
Decorator S
Facade S
Factory Method C
Flyweight S
Interpreter B
Iterator B
Mediator B
Memento B
Prototype C
Proxy S
Observer B
Singleton C
State B
Strategy B
Template Method B
Visitor B
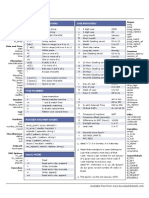
Chain of Responsibility
+handleRequest()
interface
Handler
+handleRequest()
ConcreteHandler1
+handleRequest()
ConcreteHandler2
Client
successor
Type: Behavioral
What it is:
Avoid coupling the sender of a request to
its receiver by giving more than one object
a chance to handle the request. Chain the
receiving objects and pass the request
along the chain until an object handles it.
+execute()
ConcreteCommand
Client
+action()
Receiver
Invoker Command
Type: Behavioral
What it is:
Encapsulate a request as an object,
thereby letting you parameterize clients
with different requests, queue or log
requests, and support undoable operations.
+interpret()
interface
AbstractExpression
+interpret() : Context
TerminalExpression
Client
Context
+interpret() : Context
NonterminalExpression
Interpreter
Type: Behavioral
What it is:
Given a language, define a representation
for its grammar along with an interpreter
that uses the representation to interpret
sentences in the language.
+createIterator()
interface
Aggregate
+createIterator() : Context
ConcreteAggregate
+next()
interface
Iterator
+next() : Context
ConcreteIterator
Iterator
Type: Behavioral
What it is:
Provide a way to access the elements of
an aggregate object sequentially without
exposing its underlying representation.
Client
Mediator
ConcreteMediator ConcreteColleague
interface
Colleague
informs
updates
Mediator
Type: Behavioral
What it is:
Define an object that encapsulates how a
set of objects interact. Promotes loose
coupling by keeping objects from referring
to each other explicitly and it lets you vary
their interactions independently.
Copyright 2007 Jason S. McDonald
http://www.McDonaldLand.info
Gamma, Erich; Helm, Richard; Johnson, Ralph; Vlissides, John (1995). Design Patterns: Elements of
Reusable Object-Oriented Software. Reading, Massachusetts: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc..
+execute()
Command
Facade
Complex system
Adapter
Type: Structural
What it is:
Convert the interface of a class into
another interface clients expect. Lets
classes work together that couldn't
otherwise because of incompatible
interfaces.
+adaptedOperation()
Adaptee
+operation()
interface
Adapter
+operation()
-adaptee
ConcreteAdapter
Client
+operationImpl()
interface
Implementor
+operation()
Abstraction
+operationImpl()
ConcreteImplementorA
+operationImpl()
ConcreteImplementorB
Bridge
Type: Structural
What it is:
Decouple an abstraction from its
implementation so that the two can vary
independently.
+operation()
Leaf
+operation()
+add(in c : Composite)
+remove(in c : Composite)
+getChild(in i : int)
Composite
+operation()
+add(in c : Composite)
+remove(in c : Composite)
+getChild(in i : int)
interface
Component
children
Composite
Type: Structural
What it is:
Compose objects into tree structures to
represent part-whole hierarchies. Lets
clients treat individual objects and
compositions of objects uniformly.
+operation()
ConcreteComponent
+operation()
Decorator
+operation()
interface
Component
+operation()
+addedBehavior()
-addedState
ConcreteDecorator
Decorator
Type: Structural
What it is:
Attach additional responsibilities to an
object dynamically. Provide a flexible
alternative to sub-classing for extending
functionality.
Facade
Type: Structural
What it is:
Provide a unified interface to a set of
interfaces in a subsystem. Defines a high-
level interface that makes the subsystem
easier to use.
Flyweight
Type: Structural
What it is:
Use sharing to support large numbers of
fine grained objects efficiently.
+request()
RealSubject
+request()
Proxy
+request()
interface
Subject
Client
represents
Proxy
Type: Structural
What it is:
Provide a surrogate or placeholder for
another object to control access to it.
+static instance()
+SingletonOperation()
-static uniqueInstance
-singletonData
Singleton
Singleton
Type: Creational
What it is:
Ensure a class only has one instance and
provide a global point of access to it.
+clone()
ConcretePrototype2
+clone()
interface
Prototype
Client
+clone()
ConcretePrototype1
Prototype
Type: Creational
What it is:
Specify the kinds of objects to create
using a prototypical instance, and
create new objects by copying this
prototype.
interface
Product
ConcreteProduct
+factoryMethod()
ConcreteCreator
+factoryMethod()
+anOperation()
Creator Factory Method
Type: Creational
What it is:
Define an interface for creating an
object, but let subclasses decide which
class to instantiate. Lets a class defer
instantiation to subclasses.
+buildPart()
interface
Builder
+buildPart()
+getResult()
ConcreteBuilder
+construct()
Director
Builder
Type: Creational
What it is:
Separate the construction of a
complex object from its representing
so that the same construction
process can create different
representations.
interface
AbstractProduct
ConcreteProduct
+createProductA()
+createProductB()
interface
AbstractFactory
+createProductA()
+createProductB()
ConcreteFactory
Client
Abstract Factory
Type: Creational
What it is:
Provides an interface for creating
families of related or dependent
objects without specifying their
concrete class.
+operation(in extrinsicState)
-intrinsicState
ConcreteFlyweight
+operation(in extrinsicState)
-allState
UnsharedConcreteFlyweight
+operation(in extrinsicState)
interface
Flyweight
+getFlyweight(in key)
FlyweightFactory
Client
Copyright 2007 Jason S. McDonald
http://www.McDonaldLand.info
Gamma, Erich; Helm, Richard; Johnson, Ralph; Vlissides, John (1995). Design Patterns: Elements of
Reusable Object-Oriented Software. Reading, Massachusetts: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc..
You might also like
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleFrom EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- RESTful API Design - Best Practices in API Design with REST: API-University Series, #3From EverandRESTful API Design - Best Practices in API Design with REST: API-University Series, #3Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Becoming Telebirr AgentDocument147 pagesBecoming Telebirr AgentSami91% (34)
- Microservices Patterns: With examples in JavaFrom EverandMicroservices Patterns: With examples in JavaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- System Design Interview - An Insider's GuideDocument103 pagesSystem Design Interview - An Insider's GuideОлег Шванн90% (10)
- Design Pattern CheatsheetDocument2 pagesDesign Pattern Cheatsheeta_anastassov100% (16)
- Coding Interview-LeetcodeDocument181 pagesCoding Interview-LeetcodeAkshit Sharma80% (5)
- Gang of Four Design Patterns 4.0 PDFDocument86 pagesGang of Four Design Patterns 4.0 PDFEli_Hux100% (6)
- Software Design Patterns Made SimpleDocument31 pagesSoftware Design Patterns Made SimpleAnoop Madhusudanan100% (13)
- Re Factoring and Design PatternsDocument783 pagesRe Factoring and Design PatternsEvans Krypton Sowah100% (6)
- Software Architecture For Developers PDFDocument133 pagesSoftware Architecture For Developers PDFAdha Mashur Sajiah78% (9)
- Architectural PatternsDocument458 pagesArchitectural PatternsGaby Sandoval100% (11)
- Architectural Patterns - Uncover Essential Patterns in The Most Indispensable Realm of Enterprise Architecture PDFDocument458 pagesArchitectural Patterns - Uncover Essential Patterns in The Most Indispensable Realm of Enterprise Architecture PDFRishi Rai100% (6)
- Domain Driven Design : How to Easily Implement Domain Driven Design - A Quick & Simple GuideFrom EverandDomain Driven Design : How to Easily Implement Domain Driven Design - A Quick & Simple GuideRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Getting started with Spring Framework: A Hands-on Guide to Begin Developing Applications Using Spring FrameworkFrom EverandGetting started with Spring Framework: A Hands-on Guide to Begin Developing Applications Using Spring FrameworkRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Cloud Native Patterns: Designing change-tolerant softwareFrom EverandCloud Native Patterns: Designing change-tolerant softwareRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- UML Quick Reference CardDocument1 pageUML Quick Reference Cardallen.bang100% (6)
- Coding InterviewDocument109 pagesCoding InterviewAshok Obuli100% (4)
- Grok System Design InterviewDocument163 pagesGrok System Design InterviewCarlos Rojas100% (3)
- Microservices Architecture Handbook: Non-Programmer's Guide for Building MicroservicesFrom EverandMicroservices Architecture Handbook: Non-Programmer's Guide for Building MicroservicesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- MySQL Quick Reference SheetDocument2 pagesMySQL Quick Reference SheetSneetsher Crispy100% (5)
- CSS Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCSS Cheat Sheetesommer99% (77)
- Unix Commands Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageUnix Commands Cheat Sheet PDFRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Java Script 2Document121 pagesJava Script 2Sneetsher Crispy100% (2)
- Jharkhand General Knowledge (Objective Question)Document8 pagesJharkhand General Knowledge (Objective Question)Gunjan86% (28)
- ISM CPSM Exam-SpecificationsDocument7 pagesISM CPSM Exam-SpecificationsmsajanjNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Finance For ManagersDocument322 pagesAccounting and Finance For ManagersPrasanna Aravindan100% (5)
- UML Reference CardDocument2 pagesUML Reference CardSneetsher Crispy100% (10)
- Clean Code Cheat Sheet V1.3Document1 pageClean Code Cheat Sheet V1.3Peter Saddington100% (7)
- Engineering Managers Guide Design PatternsDocument28 pagesEngineering Managers Guide Design Patternstompacheco-1100% (7)
- Software Architecture PatternsDocument55 pagesSoftware Architecture Patternseggie545100% (15)
- Design Patterns Difference FAQS Compiled-1Document8 pagesDesign Patterns Difference FAQS Compiled-1Umar Ali100% (1)
- Cracking System Design Interview Like A Pro - A 10 DayDocument199 pagesCracking System Design Interview Like A Pro - A 10 Daybrian50% (8)
- 140 Google Interview QuestionsDocument6 pages140 Google Interview QuestionsstephanehaddadNo ratings yet
- Design PatternsDocument7 pagesDesign Patternstongaboardi2363No ratings yet
- Visualising Software ArchitectureDocument198 pagesVisualising Software ArchitectureLaure Kamalandua100% (5)
- Software Architecture Interview QuestionsDocument219 pagesSoftware Architecture Interview QuestionsHemant Patil86% (7)
- CleanCodeHandbook v1.0.1Document100 pagesCleanCodeHandbook v1.0.1spanishsauce100% (2)
- Design Patterns Interview QuestionsDocument13 pagesDesign Patterns Interview QuestionsGopinath100% (2)
- Domain Driven Design - Step by StepDocument20 pagesDomain Driven Design - Step by Stepossus3r70% (10)
- 278 Software Architecture Design ModelsDocument310 pages278 Software Architecture Design Modelstrans50% (2)
- An Insiders Guide To Ace System Design in - Maurice JaysonDocument60 pagesAn Insiders Guide To Ace System Design in - Maurice JaysonAkriti Jain100% (1)
- How To Build Microservices: Top 10 Hacks To Modeling, Integrating & Deploying MicroservicesFrom EverandHow To Build Microservices: Top 10 Hacks To Modeling, Integrating & Deploying MicroservicesNo ratings yet
- Cracking Microservices Interview: Learn Advance Concepts, Patterns, Best Practices, NFRs, Frameworks, Tools and DevOpsFrom EverandCracking Microservices Interview: Learn Advance Concepts, Patterns, Best Practices, NFRs, Frameworks, Tools and DevOpsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Coder Habits: The #39# Habits of the Professional ProgrammerFrom EverandThe Coder Habits: The #39# Habits of the Professional ProgrammerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mastering JavaScript Design Patterns - Second EditionFrom EverandMastering JavaScript Design Patterns - Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Good Code, Bad Code: Think like a software engineerFrom EverandGood Code, Bad Code: Think like a software engineerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- PostScript Quick ReferenceDocument2 pagesPostScript Quick ReferenceSneetsher CrispyNo ratings yet
- SVN RefDocument2 pagesSVN Refanon-247901100% (1)
- STL Quick ReferenceDocument8 pagesSTL Quick ReferenceSneetsher Crispy100% (3)
- Octave Reference CardDocument3 pagesOctave Reference CardSneetsher CrispyNo ratings yet
- RSS Cheat SheetDocument1 pageRSS Cheat SheetSneetsher CrispyNo ratings yet
- X86 AssemblyDocument123 pagesX86 AssemblySneetsher Crispy97% (39)
- Subversion Cheat Sheet v1 For SVNDocument1 pageSubversion Cheat Sheet v1 For SVNGabriel GaheteNo ratings yet
- Emacs Quick ReferenceDocument3 pagesEmacs Quick ReferenceSneetsher Crispy100% (1)
- RGB Color Hex Cheat Sheet v1Document1 pageRGB Color Hex Cheat Sheet v1Sneetsher Crispy100% (4)
- MySQL. Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMySQL. Cheat Sheetjorgekf13No ratings yet
- PHP Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePHP Cheat Sheetanon-280494100% (4)
- PHP Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePHP Cheat Sheetwarezisgr8No ratings yet
- XML Path Language 1 0Document2 pagesXML Path Language 1 0Sneetsher Crispy100% (1)
- HTML Character Entities Cheat SheetDocument1 pageHTML Character Entities Cheat SheetcormissNo ratings yet
- HTML Cheat Sheet v1 PDFDocument1 pageHTML Cheat Sheet v1 PDFallmanahNo ratings yet
- Javascript Cheat SheetDocument1 pageJavascript Cheat Sheetdanielle leigh100% (4)
- Gimp Quick Reference Card v.1.0Document1 pageGimp Quick Reference Card v.1.0Sneetsher CrispyNo ratings yet
- stmp3500 Reference SCH RevbDocument15 pagesstmp3500 Reference SCH RevbSneetsher Crispy100% (1)
- Cascading Style Sheets 1.0Document2 pagesCascading Style Sheets 1.0Ivana JakimovskaNo ratings yet
- Chuleta CssDocument1 pageChuleta CssoscarlopgaNo ratings yet
- Mysql Quick SheetDocument2 pagesMysql Quick Sheetibrahim-bn-yah-ya-9183No ratings yet
- Vi Quick ReferenceDocument1 pageVi Quick ReferenceSneetsher Crispy100% (6)
- The Identification of Common RocksDocument18 pagesThe Identification of Common RocksSneetsher Crispy100% (7)
- CISCO in ArabicDocument214 pagesCISCO in ArabicSneetsher Crispy100% (5)
- OHSAS 18001 Work Instruction and SOPsDocument5 pagesOHSAS 18001 Work Instruction and SOPsAlina Walace0% (1)
- Ict Dos and DontsDocument5 pagesIct Dos and DontsLouwellaEredianoIbabaoNo ratings yet
- NLC English 7 Enhancement LP v.1Document85 pagesNLC English 7 Enhancement LP v.1patric maturan100% (1)
- Digital NativesDocument10 pagesDigital NativesJonathan Blanco Sa RiyadhNo ratings yet
- Archer T5E (UN) - 1.0 Datasheet PDFDocument4 pagesArcher T5E (UN) - 1.0 Datasheet PDFeeerakeshNo ratings yet
- The Current WarDocument1 pageThe Current WarkanuvietNo ratings yet
- Primus Overview Catalogue ANGDocument8 pagesPrimus Overview Catalogue ANGpesumasinad0% (1)
- OPM Costing Fundamentals - ActualDocument21 pagesOPM Costing Fundamentals - Actualkhaled_ghrbia100% (1)
- Niir Mumbai Companies Directory Database XLSX Excel Format 5th EditionDocument2 pagesNiir Mumbai Companies Directory Database XLSX Excel Format 5th Editionphone25hire phone25hireNo ratings yet
- Debug Tacacs CiscoDocument5 pagesDebug Tacacs CiscodeztrocxeNo ratings yet
- PragmaticsDocument10 pagesPragmaticsDisya RusmadinantiNo ratings yet
- Present Etac Dep Psis PDFDocument96 pagesPresent Etac Dep Psis PDFRobiahZakariaNo ratings yet
- OtooDocument11 pagesOtooStefania DavidNo ratings yet
- TC-42X1 Part 1Document50 pagesTC-42X1 Part 1Pedro SandovalNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide For Growing Plants Hydroponically by J Benton Jones JR B00hznqitmDocument5 pagesComplete Guide For Growing Plants Hydroponically by J Benton Jones JR B00hznqitmnagesh dolasNo ratings yet
- Normalized Impedance and Admittance Coordinates: Name Title Dwg. NoDocument1 pageNormalized Impedance and Admittance Coordinates: Name Title Dwg. NoJayeng WidiatmokoNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Ingenieria en Control Moderna OGATADocument240 pagesSolucionario Ingenieria en Control Moderna OGATAanandpj444471% (7)
- GRP 3 Keesha & Marie Faye Abdellah Power Point FINALDocument10 pagesGRP 3 Keesha & Marie Faye Abdellah Power Point FINALevangelo22656No ratings yet
- Case CX TrainingDocument20 pagesCase CX Traininghoward100% (27)
- Lacerte Jennifer ResumeDocument1 pageLacerte Jennifer Resumejennifer_lacerteNo ratings yet
- Course Registration SystemDocument11 pagesCourse Registration Systemananthprasad91100% (3)
- H11L1Document6 pagesH11L1Silvio QuerzoliNo ratings yet
- Class 12 CS ProjectDocument27 pagesClass 12 CS ProjectKs100% (3)
- The Secret SharerDocument3 pagesThe Secret ShareranbarasiNo ratings yet
- Essay On Flood in PakistanDocument6 pagesEssay On Flood in Pakistanjvscmacaf100% (2)
- SADP User Manual (V2.0)Document10 pagesSADP User Manual (V2.0)tehixazNo ratings yet