Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Computer Interaction
Human Computer Interaction
Uploaded by
Baraveli KakuniCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Mercer Functional Organization DesignDocument2 pagesMercer Functional Organization DesignnafizNo ratings yet
- Cathodic Protection Design Calculation PDFDocument27 pagesCathodic Protection Design Calculation PDFRini PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- LOGframeDocument83 pagesLOGframeAnonymous Xb3zHioNo ratings yet
- Cs3724 ActivityDocument11 pagesCs3724 ActivityShyr R PalmNo ratings yet
- Projectmanagement IPTDocument9 pagesProjectmanagement IPTAnsh GanneNo ratings yet
- Human-Computer InteractionDocument4 pagesHuman-Computer Interactionrem cartNo ratings yet
- GuidelinesDocument41 pagesGuidelinesHaidee VenturilloNo ratings yet
- Project Formulation: Ing. J. Mauricio Espinoza September 19th, 2015Document38 pagesProject Formulation: Ing. J. Mauricio Espinoza September 19th, 2015Victor Pinillos RosasNo ratings yet
- HCI Lecture 5: Conceptual Models: Task AnalysisDocument4 pagesHCI Lecture 5: Conceptual Models: Task AnalysisSadıkNo ratings yet
- Argaw ECWC Presentation Oct 21.21Document172 pagesArgaw ECWC Presentation Oct 21.21AbirhamNo ratings yet
- 4-Human Centred-Process-21Document14 pages4-Human Centred-Process-21Yuyun JoeNo ratings yet
- People and Technology Development PhaseDocument24 pagesPeople and Technology Development PhaseAGUSTIANNo ratings yet
- DS-Honeywell-HMIWeb Graphic Best PracticesDocument52 pagesDS-Honeywell-HMIWeb Graphic Best Practicessyed muffassirNo ratings yet
- Practicing What We Preach: Usage-Centered Approaches To Designing Effective DeliverablesDocument28 pagesPracticing What We Preach: Usage-Centered Approaches To Designing Effective DeliverablesRicoo ChowNo ratings yet
- SPM Notes As Per Syllabus FinalDocument236 pagesSPM Notes As Per Syllabus FinalShilpa ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Performance Management and KPIDocument46 pagesPerformance Management and KPIJonas Onstrup HansenNo ratings yet
- HCI - Lecture 3Document28 pagesHCI - Lecture 3MD.HASIBUL HASAN, 180041104No ratings yet
- Toward Enterprise Agile Scalability: Pat ReedDocument42 pagesToward Enterprise Agile Scalability: Pat ReedJason Oz100% (1)
- 4 - Interaction StylesDocument71 pages4 - Interaction Stylesfmp5wqx8wnNo ratings yet
- 1.chapter The InteractionDocument28 pages1.chapter The InteractionHarshdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- OOAD LecturesDocument104 pagesOOAD LecturesFarhan AkramNo ratings yet
- Log Framework Tool TemplateDocument3 pagesLog Framework Tool TemplateMasterHomerNo ratings yet
- Design Principles and GuidelinesDocument39 pagesDesign Principles and GuidelinesBaraa AbeadNo ratings yet
- STIM5013 IT For Manager: Topic Eight Information Systems DevelopmentDocument61 pagesSTIM5013 IT For Manager: Topic Eight Information Systems DevelopmentNurliyana MaludinNo ratings yet
- Planning Types and ProcessDocument22 pagesPlanning Types and ProcessRajuNo ratings yet
- HCI L03 (En)Document75 pagesHCI L03 (En)minhNo ratings yet
- HCI Lecture Evaluation Part-IDocument54 pagesHCI Lecture Evaluation Part-INAFEESA IQBALNo ratings yet
- 1-Value Engineering Methodology in Construction by Mr. Fadi ElayacheDocument46 pages1-Value Engineering Methodology in Construction by Mr. Fadi ElayacheMohamed AsharNo ratings yet
- Affordances SlideDocument23 pagesAffordances SlideErnesto GiacopelloNo ratings yet
- Design and Planning FPDocument36 pagesDesign and Planning FPAkhmad KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Outline: - Ethnography, Participatory (Cooperative) DesignDocument31 pagesOutline: - Ethnography, Participatory (Cooperative) DesignjohhnNo ratings yet
- Mastering The Case InterviewDocument42 pagesMastering The Case InterviewGoldy BhowmikNo ratings yet
- KPI S and Performance Management GCDocument34 pagesKPI S and Performance Management GCLeonardo Medici100% (5)
- 03 - Construction Project Management-IIIDocument66 pages03 - Construction Project Management-IIIdharanya sivabalanNo ratings yet
- Marinier Laird Ace 2006 PresentationDocument25 pagesMarinier Laird Ace 2006 PresentationHadrianus Handoko SaputroNo ratings yet
- 10 - Communications Management - 12Document24 pages10 - Communications Management - 12Anonymous j19GEvKNNo ratings yet
- Oracle - BI - Positioning NewDocument26 pagesOracle - BI - Positioning NewFabian ZeaNo ratings yet
- Design Process and Prototyping Chapter 3 - Part 2: Sub-TopicDocument36 pagesDesign Process and Prototyping Chapter 3 - Part 2: Sub-TopicSandra Suriya A/l JayasuriNo ratings yet
- HCIN Finals ReviewerDocument27 pagesHCIN Finals Reviewererror55No ratings yet
- W 3 Developing Business Strategy-CompressedDocument44 pagesW 3 Developing Business Strategy-CompressedWie WyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 An Overview of Project PlanningDocument34 pagesChapter-2 An Overview of Project Planningadarsh rajNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Project Devt & MGTDocument35 pagesFundamentals of Project Devt & MGTJerico TorresNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 14 HCI:: Models of Interaction Some Terms of InteractionDocument8 pagesLecture # 14 HCI:: Models of Interaction Some Terms of InteractionharisNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Interaction Design and HCIDocument30 pagesChapter Five: Interaction Design and HCIWudneh AderawNo ratings yet
- Planning Slides - MOWUDDocument66 pagesPlanning Slides - MOWUDAlex ShiferawNo ratings yet
- Social Project ManagementDocument39 pagesSocial Project Managementfiki admpublikNo ratings yet
- Addressing Factors That Restrict Success of KM ProgramsDocument16 pagesAddressing Factors That Restrict Success of KM ProgramsankitvermaNo ratings yet
- Management Information System Pak DonnyDocument18 pagesManagement Information System Pak DonnyagneswahyuNo ratings yet
- How To Becoming-a-Successful-Business-AnalystDocument72 pagesHow To Becoming-a-Successful-Business-AnalystBiznis 360No ratings yet
- CFI L3 TryitNowDocument4 pagesCFI L3 TryitNowRagab HashimNo ratings yet
- Design Principles and GuidelineDocument44 pagesDesign Principles and Guidelinemaneka bandaraNo ratings yet
- Notes Me 112 Concepts in Engineering Design Unit 3Document23 pagesNotes Me 112 Concepts in Engineering Design Unit 3rkNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgDEBNIdHrZ5SbB nbC5i3Llm3utg YGem 4fZMsXVIMrz-qwRHPD82-7u7 p5s1fvKH85952b5I1ROneIc6TneVFhaG3JDWNUjFRsTn843JCG yAHPLU5OU0N9oXDaJNiJ5zF1PpDocument18 pagesACFrOgDEBNIdHrZ5SbB nbC5i3Llm3utg YGem 4fZMsXVIMrz-qwRHPD82-7u7 p5s1fvKH85952b5I1ROneIc6TneVFhaG3JDWNUjFRsTn843JCG yAHPLU5OU0N9oXDaJNiJ5zF1PponyebuchiannabelNo ratings yet
- Ux DesignDocument1 pageUx DesignKalai ArasanNo ratings yet
- Module 05. CPI Roles and ResponsibilitiesDocument20 pagesModule 05. CPI Roles and Responsibilitiestaghavi1347No ratings yet
- IISE 2021 - Product and Service InnovationDocument50 pagesIISE 2021 - Product and Service InnovationIntan Putri Maharani SinagaNo ratings yet
- UI/UX Presentation11Document42 pagesUI/UX Presentation11Rohit BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Basics Organisation Hierarchies and Behaviour 2. Responsibility CentresDocument20 pagesBasics Organisation Hierarchies and Behaviour 2. Responsibility CentresSharvari OkeNo ratings yet
- Include A Description of Each Metric and The Reason That The Team Has Chosen This Measure For The ProjectDocument31 pagesInclude A Description of Each Metric and The Reason That The Team Has Chosen This Measure For The ProjectNimalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Strategic ImplementationDocument14 pagesChapter 6 - Strategic ImplementationTú ÂnNo ratings yet
- Bulk SMS Application FormDocument5 pagesBulk SMS Application FormBaraveli KakuniNo ratings yet
- Apiit LankaDocument16 pagesApiit LankaBaraveli KakuniNo ratings yet
- APU Appeal FormDocument1 pageAPU Appeal FormBaraveli KakuniNo ratings yet
- The Sleepy SalonDocument4 pagesThe Sleepy SalonBaraveli KakuniNo ratings yet
- Academic LibrariesDocument98 pagesAcademic LibrariesBaraveli KakuniNo ratings yet
- Cost Estimation: Size-Related Metrics and Function-Related MetricsDocument6 pagesCost Estimation: Size-Related Metrics and Function-Related MetricsBaraveli KakuniNo ratings yet
- Flyer Sewage Sludge DryingDocument6 pagesFlyer Sewage Sludge Dryingkosmc123No ratings yet
- IEC Motor Protection Book 3Document4 pagesIEC Motor Protection Book 3sajid munirNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Mainstreaming DRR and CCA in The Comprehensive Development PlanDocument35 pagesGuidelines On Mainstreaming DRR and CCA in The Comprehensive Development PlanRey Jan Sly100% (6)
- 4925B Dual MosfetDocument8 pages4925B Dual MosfetRaj ChoudharyNo ratings yet
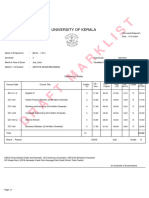
- Draft Marklist: University of KeralaDocument1 pageDraft Marklist: University of Keralamuraliadithya4No ratings yet
- Handout - Intro To CANVADocument6 pagesHandout - Intro To CANVAArnel BoholstNo ratings yet
- Effects of Packaging DesignDocument12 pagesEffects of Packaging Designkimmelody oliquiano0% (1)
- DMFDocument29 pagesDMFFree Escort ServiceNo ratings yet
- Internal Controls ITGCs Part 1 Introduction To ITGCs HandoutDocument3 pagesInternal Controls ITGCs Part 1 Introduction To ITGCs Handoutcharm.lopezz12No ratings yet
- Technical Manual Gear Hub Systems: EnglishDocument84 pagesTechnical Manual Gear Hub Systems: EnglishЕвгений ЕвсеевNo ratings yet
- Owner'S Manual: F50D T50D F60D T60DDocument80 pagesOwner'S Manual: F50D T50D F60D T60Deduardo garciaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Scanning and Industry Analysis: Group 1Document42 pagesEnvironmental Scanning and Industry Analysis: Group 1Virlaine JameroNo ratings yet
- Computer Forensics Investigation - A Case Study PDFDocument3 pagesComputer Forensics Investigation - A Case Study PDFTefeNo ratings yet
- Nasir Et Al. 2019 - Forecasting Cryptocurrency Returns and Volume Using Search EnginesDocument13 pagesNasir Et Al. 2019 - Forecasting Cryptocurrency Returns and Volume Using Search Enginesdaniel.finn24No ratings yet
- 9a. Failure TheoriesDocument3 pages9a. Failure TheoriesadnandjNo ratings yet
- 20 CSR Social Impact El PDFDocument23 pages20 CSR Social Impact El PDFsuggestionboxNo ratings yet
- Government e Marketplace (GeM) - 10.01.2024Document9 pagesGovernment e Marketplace (GeM) - 10.01.2024SSPOS DHULENo ratings yet
- Volume 28, Issue 1, 2008/2009Document17 pagesVolume 28, Issue 1, 2008/2009LawLibNENo ratings yet
- FIrst Discoveries Workbook Unit 5Document6 pagesFIrst Discoveries Workbook Unit 5Felipe Herrera ZentenoNo ratings yet
- Resume Abhijit Khairnar (Opex)Document2 pagesResume Abhijit Khairnar (Opex)Patel MiteshNo ratings yet
- Path SensitizationDocument4 pagesPath SensitizationTarun SinghNo ratings yet
- Linked ListDocument35 pagesLinked ListVijay JayNo ratings yet
- 2023 08 Commitment LetterDocument1 page2023 08 Commitment LetterBrian irunguNo ratings yet
- Uspat 4203107 PDFDocument19 pagesUspat 4203107 PDFPaulo MoraisNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument56 pagesUntitledsolomon kpayehNo ratings yet
- PSM QuizDocument89 pagesPSM QuizAbdul Wasay100% (1)
- JM's Hot Bread: Business PlanDocument7 pagesJM's Hot Bread: Business PlanJomari minozaNo ratings yet
- Invoice - 77075555Document1 pageInvoice - 77075555Shubham ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Ziad CV UpdateDocument2 pagesZiad CV UpdateGeorges Abi JaoudeNo ratings yet
Human Computer Interaction
Human Computer Interaction
Uploaded by
Baraveli KakuniCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Computer Interaction
Human Computer Interaction
Uploaded by
Baraveli KakuniCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Problem scenarios
summative
evaluation
Information scenarios
claims about
current
practice
analysis of
stakeholders,
field studies
Usability specifications
Activity
scenarios
Interaction scenarios
iterative
analysis of
usability
claims and
re-design
metaphors,
information
technology,
HCI theory,
guidelines
formative
evaluation
DESIGN
ANALYZE
PROTOTYPE & EVALUATE
Normans Stages of Action
A different look at design
2
Stages of Action
What makes something difficult to do?
What are you trying to do?
What ways can you achieve it?
How do you execute one of those ways?
What happened as a result?
Action
Start with goal (goal formation)
You have to do something (execution)
Check to see that goal is made
(evaluation)
3
Four parts
Goal
What is done to world
The world itself
Check on the world
Not that easy
Real tasks are imprecisely defined
Get to work, get some food
Goals do not state what to do
Intentions: lower level statements of what
is to be done
Still not enough: too vague
4
Execution
Three stages
Intention
Action sequence
Execution
Evaluation
Three stages
Perceiving what happened
Interpreting it
Evaluating (did what happened match
what we wanted?)
5
7 Stages of Action
Forming the goal
Forming the intention
Specifying an action
Executing the action
Perceiving state of world
Interpreting state of world
Evaluating the outcome
Activity design
Interaction design
Information design
Notes
Only approximate model
Stages are not discrete
Not in sequence
Some activities satisfied by single actions
Continual feedback
Results of one activity feed goals of
another
6
Execution
Action plan
System
goal
Last months
budget... ?
Interpretation
Perception
Making
sense
GULF OF
EVALUATION
GULF OF
EXECUTION
Stages of Action in HCI
focus of
information
design
focus of
interaction
design
What are Gulfs?
The distance between the mental
representations of the person and the
physical components and states of the
environment
Illustrates difficulty in deriving
relationships between mental intentions
and interpretations and the physical
actions and states
7
Going from users task concept to system concept:
the cognitive distance between two models
Mental model held by users tells them what to do
This must make connection with designers model that
is conveyed and supported by the user interface
The closer the match, the easier to find and
pursue a relevant goal
Example: Gulf of Execution
cognitive distance
Execution
Action plan
System
goal
Last months
budget... ?
Interpretation
Perception
Making
sense
GULF OF
EVALUATION
GULF OF
EXECUTION
Stages of Action in HCI
focus of
information
design
focus of
interaction
design
8
Suggesting Goals to the User
Menu titles, folder names, application names, ...
Decreasing the distance via direct manipulation:
UI controls appear as physical analogs of real objects;
their affordances suggest interaction goals
Key ideas are visual representation, immediate and
continuing feedback, and simple reversibility
Visual or auditory UI elements sometimes lead to
opportunistic selection of goals
Interesting object or message intrudes on a task
Or user is paused, choosing among things to do;
especially common among novice users
Gulf of Evaluation
Reflects amount of effort that a person
exerts to interpret physical state of a
system
Small gulf when system provides state
information in a form that is easy to
get, easy to interpret, and matches the
thinking
9
Execution
Action plan
System
goal
Last months
budget... ?
Interpretation
Perception
Making
sense
GULF OF
EVALUATION
GULF OF
EXECUTION
Stages of Action in HCI
focus of
information
design
focus of
interaction
design
About Gulfs
Present in all interfaces
Most are unremarkable and invisible
Users blame themselves or decide they
are incapable
Water faucets, temperature controls, stove
tops, etc.
Sewing machines, washing machines,
digital watches
10
Design Aids
Each stage requires special design
strategies
Simple questions
How easily can one:
Determine function of device?
Tell possible actions? System in
desired state?
Determine Mapping? Mapping?
Perform action? What state is
system in?
Design Advice
Visibility: can user tell state of system and
alternatives for action?
Good conceptual model: consistency in
presentation of operations and results
Good mappings: relationships between
actions and results, between controls and
effects, system state and what we see are all
clear
Feedback: full and continuous feedback on
results of actions
11
SBD: From Activity to
Interaction
Activity Design
Information Design
Interaction Design
metaphors and
information
technology
opportunities
and
constraints
ongoing
analysis of
usage
scenarios and
claims
7 Stages and SBD
Activity Design
Information Design
Interaction Design
metaphors and
information
technology
opportunities
and
constraints
ongoing
analysis of
usage
scenarios and
claims
Forming the Goal
Perceiving world
Interpreting world
Evaluating outcome
Forming the intention
Specifying an action
Executing the action
12
Coming up
Information design
Interaction design
Prototyping
Evaluation
You might also like
- Mercer Functional Organization DesignDocument2 pagesMercer Functional Organization DesignnafizNo ratings yet
- Cathodic Protection Design Calculation PDFDocument27 pagesCathodic Protection Design Calculation PDFRini PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- LOGframeDocument83 pagesLOGframeAnonymous Xb3zHioNo ratings yet
- Cs3724 ActivityDocument11 pagesCs3724 ActivityShyr R PalmNo ratings yet
- Projectmanagement IPTDocument9 pagesProjectmanagement IPTAnsh GanneNo ratings yet
- Human-Computer InteractionDocument4 pagesHuman-Computer Interactionrem cartNo ratings yet
- GuidelinesDocument41 pagesGuidelinesHaidee VenturilloNo ratings yet
- Project Formulation: Ing. J. Mauricio Espinoza September 19th, 2015Document38 pagesProject Formulation: Ing. J. Mauricio Espinoza September 19th, 2015Victor Pinillos RosasNo ratings yet
- HCI Lecture 5: Conceptual Models: Task AnalysisDocument4 pagesHCI Lecture 5: Conceptual Models: Task AnalysisSadıkNo ratings yet
- Argaw ECWC Presentation Oct 21.21Document172 pagesArgaw ECWC Presentation Oct 21.21AbirhamNo ratings yet
- 4-Human Centred-Process-21Document14 pages4-Human Centred-Process-21Yuyun JoeNo ratings yet
- People and Technology Development PhaseDocument24 pagesPeople and Technology Development PhaseAGUSTIANNo ratings yet
- DS-Honeywell-HMIWeb Graphic Best PracticesDocument52 pagesDS-Honeywell-HMIWeb Graphic Best Practicessyed muffassirNo ratings yet
- Practicing What We Preach: Usage-Centered Approaches To Designing Effective DeliverablesDocument28 pagesPracticing What We Preach: Usage-Centered Approaches To Designing Effective DeliverablesRicoo ChowNo ratings yet
- SPM Notes As Per Syllabus FinalDocument236 pagesSPM Notes As Per Syllabus FinalShilpa ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Performance Management and KPIDocument46 pagesPerformance Management and KPIJonas Onstrup HansenNo ratings yet
- HCI - Lecture 3Document28 pagesHCI - Lecture 3MD.HASIBUL HASAN, 180041104No ratings yet
- Toward Enterprise Agile Scalability: Pat ReedDocument42 pagesToward Enterprise Agile Scalability: Pat ReedJason Oz100% (1)
- 4 - Interaction StylesDocument71 pages4 - Interaction Stylesfmp5wqx8wnNo ratings yet
- 1.chapter The InteractionDocument28 pages1.chapter The InteractionHarshdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- OOAD LecturesDocument104 pagesOOAD LecturesFarhan AkramNo ratings yet
- Log Framework Tool TemplateDocument3 pagesLog Framework Tool TemplateMasterHomerNo ratings yet
- Design Principles and GuidelinesDocument39 pagesDesign Principles and GuidelinesBaraa AbeadNo ratings yet
- STIM5013 IT For Manager: Topic Eight Information Systems DevelopmentDocument61 pagesSTIM5013 IT For Manager: Topic Eight Information Systems DevelopmentNurliyana MaludinNo ratings yet
- Planning Types and ProcessDocument22 pagesPlanning Types and ProcessRajuNo ratings yet
- HCI L03 (En)Document75 pagesHCI L03 (En)minhNo ratings yet
- HCI Lecture Evaluation Part-IDocument54 pagesHCI Lecture Evaluation Part-INAFEESA IQBALNo ratings yet
- 1-Value Engineering Methodology in Construction by Mr. Fadi ElayacheDocument46 pages1-Value Engineering Methodology in Construction by Mr. Fadi ElayacheMohamed AsharNo ratings yet
- Affordances SlideDocument23 pagesAffordances SlideErnesto GiacopelloNo ratings yet
- Design and Planning FPDocument36 pagesDesign and Planning FPAkhmad KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Outline: - Ethnography, Participatory (Cooperative) DesignDocument31 pagesOutline: - Ethnography, Participatory (Cooperative) DesignjohhnNo ratings yet
- Mastering The Case InterviewDocument42 pagesMastering The Case InterviewGoldy BhowmikNo ratings yet
- KPI S and Performance Management GCDocument34 pagesKPI S and Performance Management GCLeonardo Medici100% (5)
- 03 - Construction Project Management-IIIDocument66 pages03 - Construction Project Management-IIIdharanya sivabalanNo ratings yet
- Marinier Laird Ace 2006 PresentationDocument25 pagesMarinier Laird Ace 2006 PresentationHadrianus Handoko SaputroNo ratings yet
- 10 - Communications Management - 12Document24 pages10 - Communications Management - 12Anonymous j19GEvKNNo ratings yet
- Oracle - BI - Positioning NewDocument26 pagesOracle - BI - Positioning NewFabian ZeaNo ratings yet
- Design Process and Prototyping Chapter 3 - Part 2: Sub-TopicDocument36 pagesDesign Process and Prototyping Chapter 3 - Part 2: Sub-TopicSandra Suriya A/l JayasuriNo ratings yet
- HCIN Finals ReviewerDocument27 pagesHCIN Finals Reviewererror55No ratings yet
- W 3 Developing Business Strategy-CompressedDocument44 pagesW 3 Developing Business Strategy-CompressedWie WyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 An Overview of Project PlanningDocument34 pagesChapter-2 An Overview of Project Planningadarsh rajNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Project Devt & MGTDocument35 pagesFundamentals of Project Devt & MGTJerico TorresNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 14 HCI:: Models of Interaction Some Terms of InteractionDocument8 pagesLecture # 14 HCI:: Models of Interaction Some Terms of InteractionharisNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Interaction Design and HCIDocument30 pagesChapter Five: Interaction Design and HCIWudneh AderawNo ratings yet
- Planning Slides - MOWUDDocument66 pagesPlanning Slides - MOWUDAlex ShiferawNo ratings yet
- Social Project ManagementDocument39 pagesSocial Project Managementfiki admpublikNo ratings yet
- Addressing Factors That Restrict Success of KM ProgramsDocument16 pagesAddressing Factors That Restrict Success of KM ProgramsankitvermaNo ratings yet
- Management Information System Pak DonnyDocument18 pagesManagement Information System Pak DonnyagneswahyuNo ratings yet
- How To Becoming-a-Successful-Business-AnalystDocument72 pagesHow To Becoming-a-Successful-Business-AnalystBiznis 360No ratings yet
- CFI L3 TryitNowDocument4 pagesCFI L3 TryitNowRagab HashimNo ratings yet
- Design Principles and GuidelineDocument44 pagesDesign Principles and Guidelinemaneka bandaraNo ratings yet
- Notes Me 112 Concepts in Engineering Design Unit 3Document23 pagesNotes Me 112 Concepts in Engineering Design Unit 3rkNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgDEBNIdHrZ5SbB nbC5i3Llm3utg YGem 4fZMsXVIMrz-qwRHPD82-7u7 p5s1fvKH85952b5I1ROneIc6TneVFhaG3JDWNUjFRsTn843JCG yAHPLU5OU0N9oXDaJNiJ5zF1PpDocument18 pagesACFrOgDEBNIdHrZ5SbB nbC5i3Llm3utg YGem 4fZMsXVIMrz-qwRHPD82-7u7 p5s1fvKH85952b5I1ROneIc6TneVFhaG3JDWNUjFRsTn843JCG yAHPLU5OU0N9oXDaJNiJ5zF1PponyebuchiannabelNo ratings yet
- Ux DesignDocument1 pageUx DesignKalai ArasanNo ratings yet
- Module 05. CPI Roles and ResponsibilitiesDocument20 pagesModule 05. CPI Roles and Responsibilitiestaghavi1347No ratings yet
- IISE 2021 - Product and Service InnovationDocument50 pagesIISE 2021 - Product and Service InnovationIntan Putri Maharani SinagaNo ratings yet
- UI/UX Presentation11Document42 pagesUI/UX Presentation11Rohit BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Basics Organisation Hierarchies and Behaviour 2. Responsibility CentresDocument20 pagesBasics Organisation Hierarchies and Behaviour 2. Responsibility CentresSharvari OkeNo ratings yet
- Include A Description of Each Metric and The Reason That The Team Has Chosen This Measure For The ProjectDocument31 pagesInclude A Description of Each Metric and The Reason That The Team Has Chosen This Measure For The ProjectNimalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Strategic ImplementationDocument14 pagesChapter 6 - Strategic ImplementationTú ÂnNo ratings yet
- Bulk SMS Application FormDocument5 pagesBulk SMS Application FormBaraveli KakuniNo ratings yet
- Apiit LankaDocument16 pagesApiit LankaBaraveli KakuniNo ratings yet
- APU Appeal FormDocument1 pageAPU Appeal FormBaraveli KakuniNo ratings yet
- The Sleepy SalonDocument4 pagesThe Sleepy SalonBaraveli KakuniNo ratings yet
- Academic LibrariesDocument98 pagesAcademic LibrariesBaraveli KakuniNo ratings yet
- Cost Estimation: Size-Related Metrics and Function-Related MetricsDocument6 pagesCost Estimation: Size-Related Metrics and Function-Related MetricsBaraveli KakuniNo ratings yet
- Flyer Sewage Sludge DryingDocument6 pagesFlyer Sewage Sludge Dryingkosmc123No ratings yet
- IEC Motor Protection Book 3Document4 pagesIEC Motor Protection Book 3sajid munirNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Mainstreaming DRR and CCA in The Comprehensive Development PlanDocument35 pagesGuidelines On Mainstreaming DRR and CCA in The Comprehensive Development PlanRey Jan Sly100% (6)
- 4925B Dual MosfetDocument8 pages4925B Dual MosfetRaj ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Draft Marklist: University of KeralaDocument1 pageDraft Marklist: University of Keralamuraliadithya4No ratings yet
- Handout - Intro To CANVADocument6 pagesHandout - Intro To CANVAArnel BoholstNo ratings yet
- Effects of Packaging DesignDocument12 pagesEffects of Packaging Designkimmelody oliquiano0% (1)
- DMFDocument29 pagesDMFFree Escort ServiceNo ratings yet
- Internal Controls ITGCs Part 1 Introduction To ITGCs HandoutDocument3 pagesInternal Controls ITGCs Part 1 Introduction To ITGCs Handoutcharm.lopezz12No ratings yet
- Technical Manual Gear Hub Systems: EnglishDocument84 pagesTechnical Manual Gear Hub Systems: EnglishЕвгений ЕвсеевNo ratings yet
- Owner'S Manual: F50D T50D F60D T60DDocument80 pagesOwner'S Manual: F50D T50D F60D T60Deduardo garciaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Scanning and Industry Analysis: Group 1Document42 pagesEnvironmental Scanning and Industry Analysis: Group 1Virlaine JameroNo ratings yet
- Computer Forensics Investigation - A Case Study PDFDocument3 pagesComputer Forensics Investigation - A Case Study PDFTefeNo ratings yet
- Nasir Et Al. 2019 - Forecasting Cryptocurrency Returns and Volume Using Search EnginesDocument13 pagesNasir Et Al. 2019 - Forecasting Cryptocurrency Returns and Volume Using Search Enginesdaniel.finn24No ratings yet
- 9a. Failure TheoriesDocument3 pages9a. Failure TheoriesadnandjNo ratings yet
- 20 CSR Social Impact El PDFDocument23 pages20 CSR Social Impact El PDFsuggestionboxNo ratings yet
- Government e Marketplace (GeM) - 10.01.2024Document9 pagesGovernment e Marketplace (GeM) - 10.01.2024SSPOS DHULENo ratings yet
- Volume 28, Issue 1, 2008/2009Document17 pagesVolume 28, Issue 1, 2008/2009LawLibNENo ratings yet
- FIrst Discoveries Workbook Unit 5Document6 pagesFIrst Discoveries Workbook Unit 5Felipe Herrera ZentenoNo ratings yet
- Resume Abhijit Khairnar (Opex)Document2 pagesResume Abhijit Khairnar (Opex)Patel MiteshNo ratings yet
- Path SensitizationDocument4 pagesPath SensitizationTarun SinghNo ratings yet
- Linked ListDocument35 pagesLinked ListVijay JayNo ratings yet
- 2023 08 Commitment LetterDocument1 page2023 08 Commitment LetterBrian irunguNo ratings yet
- Uspat 4203107 PDFDocument19 pagesUspat 4203107 PDFPaulo MoraisNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument56 pagesUntitledsolomon kpayehNo ratings yet
- PSM QuizDocument89 pagesPSM QuizAbdul Wasay100% (1)
- JM's Hot Bread: Business PlanDocument7 pagesJM's Hot Bread: Business PlanJomari minozaNo ratings yet
- Invoice - 77075555Document1 pageInvoice - 77075555Shubham ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Ziad CV UpdateDocument2 pagesZiad CV UpdateGeorges Abi JaoudeNo ratings yet