Professional Documents
Culture Documents
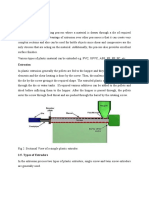
Extrusion Molding Methods
Extrusion Molding Methods
Uploaded by
Himesh Desai0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views24 pagesExtrusion molding methods of polymer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentExtrusion molding methods of polymer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views24 pagesExtrusion Molding Methods
Extrusion Molding Methods
Uploaded by
Himesh DesaiExtrusion molding methods of polymer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 24
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
1
Extrusion Processes
Extrusion of plastics, like injection molding, is a
relatively simple concept, but the design and
application of extruders is a complex field
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
2
Melt Extrusion, Single Screw Extruders
The work horse of melt extrusion is the single
screw extruder
In injection molding the purpose
of the screw extruder is simply
to obtain a melt, a dedicated
extrusion machine works on the
same principle but also must
mix, homogenize and melt the
material
Higher back pressures may be
generated in single screw
extrusion machines compared to
injection molding machines and
the screws may be longer for
better mixing
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
3
Single Screw Extruder
(Plastics Extrusion Technology, 2
nd
ed pg 23)
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
4
The Extrusion Screw
In combination with the barrel, the purpose of the screw is
to convey solid material to the melt zone, melt, mix and
pump material to the die in an efficient manner
The screw design and length of screw will depend on the polymer
being processed as well as the application
Text pg 169
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
5
Melt Considerations in Extrusion Screws
Increasing the capacity by pumping more material
through the screw can be done by increasing the length of
the screw and or flight dept, but this only helps to a point
For hard to melt materials or to increase melt homogeneity,
a second or third flight may be added to a screw in order to
prevent unmelted material from reaching the die
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
6
Mixing Considerations in Extrusion Screws
While melting and pumping as much polymer to
the die as possible is important, mixing material in
compounding applications is equally important;
there are many ways of achieving good mixing
Pins may be placed in strategic placed in the metering
section of a screw
Fluted sections at the end of the screw help to both mix
and melt left over solid polymer
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
7
Pin Arrangements and Fluted Sections
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
8
Twin Screw Extruders
Twin screw extruders are used to process heat sensitive
and shear sensitive materials and may provide intensive
mixing by kneading
PVC is the highest volume material processed by twin screw extruders
There are two types of screw extruders, co-rotating and
counter-rotating screw extruders
The screws in co-rotating extruders turn in the same direction
The screws in counter rotating extruders turn in opposite directions
For either class of extruder, the flights may or may not be
intermeshing
Intermeshing extruders work on a different principle than singlescrew
extruders; material is pumped by forward action of the root of one screw
against the flights of the other
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
9
Twin Screw Extruder Melt Flow
Co-rotating intermeshing extruders are the most common
twin screw extruder type
In this case the root of one screw is wiped by the crests of theadjacent
screw flights
The material follows a figure 8 patterns
Residence time is short and shearing is low
Provides very accurate process control
Counter rotating intermeshing extruders are the next most
common type
Material in this case is moved as a unit volume between the screws
and barrel
Spacers, disk rings and other flow interrupters may be used to
disrupt the characteristic encapsulated flow
Higher material volumes may be extruded in this configuration
This type of extruder evolved from pumping machines
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
10
Material Flow Around Twin Screws
Plastic extrusion
technology handbook pg57
11
Die Swell
When polymer exits the die of the extruder it will swell,
this action is referred to as die swell
Die swell occurs because the sudden release of pressure causes the polymer
chains to relax; remember, polymers are viscoelastic and displaytime
dependent stress relaxation
Go to http://www.pct.edu/prep/ex.htmand click on the die swell animation
to view a cartoon of the concept
High shear rates (and thus compression at the die) followedby
sudden release of pressure is the main factor responsible for
die swell; shear rate and pressure can be influenced by
Increasing the output rate
Decreasing die orifice dimension
Reducing the melt temperature
Increasing molar mass (molecular weight), chain branching
Decreasing the die L/D ratio
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
12
Effects of Die Swell on Profile Shapes
Text pg 172
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
13
Post Forming of Profiles
To avoid the necessity of
having a complex die orifice for
complex shapes, post forming
may be accomplished on basic
shapes
This is essentially a
thermoforming process where
the still warm extrudate is
shaped and drawn through a
series of plates, shoes, rollers or
dies to form the final shape
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
14
Extrusion Shapes
For melt extrusion the extrusion machine will be similar
for all cases, the die and application being differentiating
facets
The shape of the extruded section will depend on the die
orifice shape (and die swell, of course); the type of shape
produced is divided into several categories
Sheet (more than 0.25 mm thick)
Film (less or equal to 0.25 mm thick)
Blown, film casting, calendering
Filament
Blow molding
Wire insulation
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
15
Sheet Extrusion
ASTM has defined sheet as being more than 0.25
mm thick
Sheet is extruded by cast extrusion, which simply
refers to sheets being extruded through a
horizontal die
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
16
T-Shaped Sheet Die
Plastics extrusion
technology handbook
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
17
Coat Hanger Sheet Die
Plastics extrusion
technology handbook
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
18
Cut Away Coat Hanger Sheet Die View
(Shown is a Flex-Lip adjustableprelandreplacing the restrictor-bar)
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
19
Film Extrusion
ASTM has defined film as being equal to or less than 0.25
mm in thickness
Film can be extruded in a similar manner as sheet in a
process referred to as slot casting
In this case, the film is drawn from the die onto chilled rollers that quickly
quench the material
The blown film process extrudes a tube of material and
pinches of the end while simultaneously blowing the tube
into a thin walled balloon
Click on the download button at
http://www.glad.com.au/student_main.aspto get product
propaganda but also some interesting info. on how Glad
Wrap and garbage bags are made at Glad
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
20
Blow Molding
The basic principle of blow molding is simple; a hollow molten
preform or tube is placed in a female mold and inflated to
conform to the shape of the mold
Two different varieties of blow molding
Injection blow molding is a two step process where a blank
preform is first molded, it is then transferred to the mold cavity
where it is blown into shape
The advantages of injection molding are good control of
wall thickness, no bottom pinch off line, no scrap; the
main disadvantage is requiring two molds and transfer
time to the mold after performing
Extrusion blow molding a molten tube (parison) is
extruded, without pre-forming, the bottom of the parison is
pinched of by the mold and air is used to blow it into shape
The main disadvantage of this method is the less
controllable wall thickness, though some basic control is
possible
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
21
Injection Blow Molding
parison
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
22
Extrusion Blow Molding
The wall thickness of
extruded parisons may be
controlled by the use of a
variable orifice die
This type of die can
continuously change the
orifice tube width and is
typically computer
controlled
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
23
Variations on Blow Molding
Injection and extrusion blow molding are the basic
methods by which blow molded products are made, there
are many variations on these concepts to make the process
faster, and more efficient
Merry go round like mold arrays may be used to continuously
mold without having to waiting for cooling before molding again
Multilayered containers can be made by co-extrusion
Used extensively in food storage containers, high strength bags
Sheet blow molding can be accomplished by heating two separate
sheets, clamping them together in a mold and blowing to shape
Different color sides can be produced but high scrap rates are
prevalent
3/17/2004
Extrusion Molding Methods, Tech 140
Credit: A. Lopez
24
Resources and References
As with injection molding there is a great quantity of literature on
extrusion and extrusion processes, following are just some references
Levy and Carley, eds.. Plastics Extrusion Technology Handbook, 2
nd
Ed.. New
York, First Printing, 1989.
Rosato, Domic and Donald, et al, eds.. Plastics Engineering Manufacturing and
Data Book, Vol. 1. Boston, Kluwer Academic Pub., 2001.
Birley, Arthur; Haworth, Barry; Batchelor, J im. Physics of Plastics, Processing,
Properties and Materials Engineering. New York, Oxford Press, 1992. (Presents
more of a materials engineering view of processing)
SPE extrusion division on line at http://www.extdiv4spe.org/
The Plastics Resources for Educators Program.
http://www.pct.edu/prep/core.htm- great descriptions and animations of
processes. Review animations for extrusion and injection.
You might also like
- Injection Molding NotesDocument23 pagesInjection Molding NotesK_Amey50% (2)
- Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers - Volume I: Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers, #1From EverandPlastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers - Volume I: Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Samsung KS1A - AA41-00131H - CB21F52TS 5Q0765 TDA9381 LA7840 D2499 TDA8943-44Document4 pagesSamsung KS1A - AA41-00131H - CB21F52TS 5Q0765 TDA9381 LA7840 D2499 TDA8943-44Hartono Prayitno86% (7)
- Office 2013 Product KeyDocument2 pagesOffice 2013 Product KeyHartono Prayitno75% (4)
- The Blow Molding ProcessDocument4 pagesThe Blow Molding Processabi lashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Extrusion-Based Processes (Part 1)Document45 pagesChapter 13 - Extrusion-Based Processes (Part 1)hirenpatNo ratings yet
- Polymers PPT PDFDocument47 pagesPolymers PPT PDFShivani RajeevNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Single Screw Extrusion: Table of ContentsDocument6 pagesAn Introduction To Single Screw Extrusion: Table of ContentsKuzhaliNo ratings yet
- Plastic Processes - FINALDocument48 pagesPlastic Processes - FINALswap dNo ratings yet
- Module V - Blow and Transfer Molding ProcessesDocument17 pagesModule V - Blow and Transfer Molding ProcessesAntonius PrakosaNo ratings yet
- Injection Permanent Molding and Extrution Machine: Case StudyDocument7 pagesInjection Permanent Molding and Extrution Machine: Case StudyBrown MeshNo ratings yet
- Plastics ExtrusionDocument9 pagesPlastics ExtrusionFITIWINo ratings yet
- Polymer Extrusion Experimental Report: April 2018Document9 pagesPolymer Extrusion Experimental Report: April 2018Mehmet Sarı100% (1)
- High Speed Blow Molding MachineDocument64 pagesHigh Speed Blow Molding MachineSandip LadNo ratings yet
- Blow MouldingDocument40 pagesBlow MouldingDINO FANNo ratings yet
- Processing of Plastics PDFDocument61 pagesProcessing of Plastics PDFCh Talha0% (1)
- Manual Injectie Mase PlasticeDocument7 pagesManual Injectie Mase PlasticeRadu Sorin MarinescuNo ratings yet
- Cavity Mold Cooling Construction DesignDocument141 pagesCavity Mold Cooling Construction DesignJayson Serato50% (2)
- Blow - M.Document40 pagesBlow - M.Kagehiza Aghna IlmaNo ratings yet
- Basic of Mould DesignDocument79 pagesBasic of Mould DesignKamal Krishna Kashyap100% (4)
- Topics Covered: Processing of PlasticsDocument30 pagesTopics Covered: Processing of PlasticsParthiban DhakshnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Polymer Notes 2014 Parts 8-11 PDFDocument42 pagesPolymer Notes 2014 Parts 8-11 PDFRadhiNo ratings yet
- Injection MouldingDocument7 pagesInjection MouldingAzizol WahabNo ratings yet
- Plastic Injection Molding: Akash Deep.B.N 1SJ03ME121Document20 pagesPlastic Injection Molding: Akash Deep.B.N 1SJ03ME121Maheesaras0% (1)
- Technical Report 1 - Sdb24103 (Sept 2022) Mohd Iqmal HafizDocument15 pagesTechnical Report 1 - Sdb24103 (Sept 2022) Mohd Iqmal HafiziqmalNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes: International Islamic University IslamabadDocument44 pagesManufacturing Processes: International Islamic University IslamabadHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document32 pagesGroup 1GemedaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes: International Islamic University IslamabadDocument44 pagesManufacturing Processes: International Islamic University IslamabadMuhammad Qasim SajidNo ratings yet
- Compression MoldingDocument17 pagesCompression MoldingGordon YapNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument23 pagesSeminar Reportbijithbigb0% (1)
- Injection Blow MouldingDocument22 pagesInjection Blow MouldingPRANJAL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Extrusion Blow MoldingDocument23 pagesExtrusion Blow MoldingBeshoy NadyNo ratings yet
- Extrusion and Injection Molding of PolymersDocument6 pagesExtrusion and Injection Molding of PolymersazamtoorNo ratings yet
- Injection Molding Machine SnopsisDocument6 pagesInjection Molding Machine Snopsisrajinder kutaalNo ratings yet
- Forming & Shaping Processes For Plastics: Manufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222Document41 pagesForming & Shaping Processes For Plastics: Manufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222shahnawaz875No ratings yet
- Compression Molding Is A Method ofDocument4 pagesCompression Molding Is A Method ofsathishpantaloonNo ratings yet
- Mt1 Unit 5 NotesDocument11 pagesMt1 Unit 5 NotesvelavansuNo ratings yet
- CH 13Document102 pagesCH 13Alex BjNo ratings yet
- Injection Moulding ProcessDocument11 pagesInjection Moulding ProcessDhileepan KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- 1.polymer ProcessingDocument23 pages1.polymer Processingafia rahmanNo ratings yet
- Ch13 1 PolymerMelt&ExtrusionDocument32 pagesCh13 1 PolymerMelt&ExtrusionPrabhu MechNo ratings yet
- Plastic Injection Moulding Study GuideDocument5 pagesPlastic Injection Moulding Study GuideChirag PatelNo ratings yet
- UnitVI Injection - Compressiona ND Blow MoldingDocument48 pagesUnitVI Injection - Compressiona ND Blow Moldingharrywilson.harish77No ratings yet
- Fundamental of Manufacturing by Groover Cahpter 13Document125 pagesFundamental of Manufacturing by Groover Cahpter 13ali kingNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode in Effet AnalysisDocument14 pagesFailure Mode in Effet AnalysisBharat DograNo ratings yet
- I/ Reading 1 1. What Is Plastic Injection Molding?Document5 pagesI/ Reading 1 1. What Is Plastic Injection Molding?Hieu Nguyen TrungNo ratings yet
- Tool Design & Applications Injection MoldingDocument24 pagesTool Design & Applications Injection MoldingpvmrtpvmrtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document25 pagesChapter 7GemedaNo ratings yet
- Polymer Processing HandoutDocument68 pagesPolymer Processing HandoutibraheemNo ratings yet
- Polymer Processing Operation: "Sheet Extruding Machine"Document9 pagesPolymer Processing Operation: "Sheet Extruding Machine"zarqullah javaidNo ratings yet
- Blow Moulding by HammahDocument28 pagesBlow Moulding by HammahAdnan JavedNo ratings yet
- Extrusion Die DesignDocument17 pagesExtrusion Die Designkkatarn327No ratings yet
- Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers - Volume III: Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers, #3From EverandPlastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers - Volume III: Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers, #3No ratings yet
- Interacademic Collaboration Involving Higher Education Institutions in Tlaxcala and Puebla, Mexico. Presented in Collaboration with Université Clermont Auvergne (France): Case Studies of Collaborative, Multidisciplinary Applications.From EverandInteracademic Collaboration Involving Higher Education Institutions in Tlaxcala and Puebla, Mexico. Presented in Collaboration with Université Clermont Auvergne (France): Case Studies of Collaborative, Multidisciplinary Applications.No ratings yet
- Extrusion Dies for Plastics and Rubber: Design and Engineering ComputationsFrom EverandExtrusion Dies for Plastics and Rubber: Design and Engineering ComputationsNo ratings yet
- Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers - Volume II: Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers, #2From EverandPlastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers - Volume II: Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers, #2No ratings yet
- 5HP18Document39 pages5HP18Leonard67% (3)
- In Situ: BurningDocument23 pagesIn Situ: BurningHartono PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- The Future For Biomass Pyrolysis and Gasification: Status, Opportunities and Policies For EuropeDocument30 pagesThe Future For Biomass Pyrolysis and Gasification: Status, Opportunities and Policies For EuropeHartono PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Waste Tyres Into Carbon Black and Their Utilization As AdsorbentDocument5 pagesConversion of Waste Tyres Into Carbon Black and Their Utilization As AdsorbentHartono PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- Suitability of Tyre Pyrolysis Oil (Tpo) As An Alternative Fuel For Internal Combustion EngineDocument5 pagesSuitability of Tyre Pyrolysis Oil (Tpo) As An Alternative Fuel For Internal Combustion EngineHartono PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- 23 F Borsodi Full Paper IpcDocument9 pages23 F Borsodi Full Paper IpcHartono PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- 04 Edwards 1Document17 pages04 Edwards 1Hartono PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- Investigations of The Scaling Criteria For A Mild Combustion BurnerDocument9 pagesInvestigations of The Scaling Criteria For A Mild Combustion BurnerHartono PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Production From Biomass Wastes by Hydrothermal GasificationDocument15 pagesHydrogen Production From Biomass Wastes by Hydrothermal GasificationHartono PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- Absorptive and Swelling Properties of Clay-Water SystemDocument8 pagesAbsorptive and Swelling Properties of Clay-Water SystemHartono PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Orifice Meter FinalDocument7 pagesCalibration of Orifice Meter FinalHartono PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- 8697 BulDocument4 pages8697 BulHartono PrayitnoNo ratings yet