Professional Documents
Culture Documents
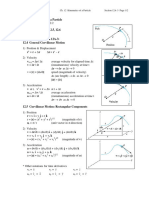
Average Acceleration (A) (V Instantaneous Acceleration/ Acceleration (A) DV / DT
Average Acceleration (A) (V Instantaneous Acceleration/ Acceleration (A) DV / DT
Uploaded by
Dan McOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Average Acceleration (A) (V Instantaneous Acceleration/ Acceleration (A) DV / DT
Average Acceleration (A) (V Instantaneous Acceleration/ Acceleration (A) DV / DT
Uploaded by
Dan McCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
5) Acceleration
Acceleration: The rate at which somethings velocity is changing at a given instant; always length
/ time
2
o Average Acceleration (aavg) = (v2 v1)/(t2 t1) = v/t
o Instantaneous Acceleration/ Acceleration (a) = dv / dt
Combine this with v = (dx / dt) and you get a = (d / dt)(dx / dt) = (d
2
x / dt
2
)
Acceleration is the second derivative of position x(t) with respect to time
o g units of acceleration: 1g= 9.8 m/s
2
2.6) Constant Acceleration: A Special Case (Properties Specially Derived for Constant or Approx. Constant
Acceleration)
Can rewrite (v2 v1)/(t2 t1) = v/t as a = aavg = (v v0)/(t 0) *v0 is the velocity at t = 0*
o v = v0 + at
Likewise, rewrite vavg = x/t = (x2 x1)/(t2 t1) as vavg = (x x0)/(t 0) * x0 is the position at t = 0
o vavg = (v0 + v)/2 -> vavg = v0 + (at)/2 -> (Substitute that into x = x0 x + x0 + (at
2
)/2
o
You might also like
- Motion in One DimensionDocument12 pagesMotion in One DimensionShinji50% (2)
- Physics Formulas and Symbols: Physics I Symbol FormulaDocument5 pagesPhysics Formulas and Symbols: Physics I Symbol Formulakaparthy100% (10)
- Chemistry Chapter 10 Study GuideDocument2 pagesChemistry Chapter 10 Study GuideDan McNo ratings yet
- CH 12 A1 NoteDocument2 pagesCH 12 A1 NoteSam RajibNo ratings yet
- CH 12 A3 NoteDocument2 pagesCH 12 A3 NoteSam RajibNo ratings yet
- Kinematics in 1DDocument5 pagesKinematics in 1Dnandinidevip17No ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document12 pagesAssignment 3mechanical engNo ratings yet
- CH 12 B1 NoteDocument2 pagesCH 12 B1 Noteh rajabNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument35 pagesProjectile Motionapi-285179261No ratings yet
- PE2113-Chapter 12 - Dynamics - Draft1Document115 pagesPE2113-Chapter 12 - Dynamics - Draft1Mohammed AlkhalifaNo ratings yet
- Dissipation Function PDFDocument1 pageDissipation Function PDFRafael DalmauNo ratings yet
- Dissipation Function PDFDocument1 pageDissipation Function PDFRafael DalmauNo ratings yet
- CH - 2 p1 DynaDocument11 pagesCH - 2 p1 DynaFikadu BelaynehNo ratings yet
- Che 323 Note Heat ConductionDocument5 pagesChe 323 Note Heat ConductionifiokNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: Lesson OutcomesDocument7 pagesDynamics: Lesson OutcomesNaqib NordinNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional Motion and Gravity: That Means There Is An AccelerationDocument31 pagesOne Dimensional Motion and Gravity: That Means There Is An AccelerationshahzreenNo ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument2 pagesEquation SheetKao LimNo ratings yet
- Basics About DifferentiationDocument2 pagesBasics About DifferentiationVivienne LovegoodNo ratings yet
- Dinamica - Presentacion 2Document24 pagesDinamica - Presentacion 2Jhonny CarbonóNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Equation SheetDocument2 pagesDynamics Equation SheeterpuhlNo ratings yet
- MET 304 Engineering AnalysisDocument31 pagesMET 304 Engineering AnalysisOscar WangNo ratings yet
- 1.3 KinematicsDocument12 pages1.3 KinematicseltytanNo ratings yet
- Acceleration ArmDocument21 pagesAcceleration ArmSean Angel PascuaNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 and 2 Formulas PDFDocument5 pagesPhysics 1 and 2 Formulas PDFPuebloNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Line: Fundamentals of Physics 10th EditionDocument24 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line: Fundamentals of Physics 10th EditionvefomNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of A Particle: Particle Motion Along A Curved PathDocument60 pagesKinematics of A Particle: Particle Motion Along A Curved PathtomodachiNo ratings yet
- Refers To Section 9.4 in Your Text: Tuesday Jan 11Document8 pagesRefers To Section 9.4 in Your Text: Tuesday Jan 11mike_tzoneNo ratings yet
- Projeto NewtonianoDocument3 pagesProjeto NewtonianoAndré Luis GhellereNo ratings yet
- APPM 211 Week 1, Lesson1-Part 1Document19 pagesAPPM 211 Week 1, Lesson1-Part 1ruanhattingh037No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2Prince AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Curvilinear MotionDocument52 pages1.3 Curvilinear MotionKaren MenesesNo ratings yet
- Quantity: (Uniform Acceleration)Document5 pagesQuantity: (Uniform Acceleration)Anoni AnonNo ratings yet
- Dynamics PPT 1Document13 pagesDynamics PPT 1qurriyatus zahroNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Rectilinear Kinematics: CONTINUOUS MOTION (Sections 12.1 - 12.2)Document15 pagesIntroduction & Rectilinear Kinematics: CONTINUOUS MOTION (Sections 12.1 - 12.2)Mohamed DamraNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PDFDocument10 pagesUnit 3 PDFChrollo LuciferNo ratings yet
- Curvilinear Motion: Rectangular Components Projectiles (Sections 12.4-12.6)Document34 pagesCurvilinear Motion: Rectangular Components Projectiles (Sections 12.4-12.6)Mohamed DamraNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Senior High School Physics: Lech Jedral 2006Document32 pagesProjectile Motion Senior High School Physics: Lech Jedral 2006kentNo ratings yet
- Solucionario 1Document24 pagesSolucionario 1Heriberto CanoNo ratings yet
- Sheet Mumber 1 Mechanical Eng Kirkuk UniversityDocument12 pagesSheet Mumber 1 Mechanical Eng Kirkuk UniversityMostafa HamawandyNo ratings yet
- Appendix A-Historic Intro of CalculusDocument8 pagesAppendix A-Historic Intro of CalculusPiyush DaveNo ratings yet
- 12.1) Introduction & Rectilinear Kinematics: Continuous MotionDocument13 pages12.1) Introduction & Rectilinear Kinematics: Continuous MotionSalim Bin AgilNo ratings yet
- Solution Exam 23-8Document2 pagesSolution Exam 23-8gamer gamingNo ratings yet
- Solutions 1.8-Page 89 Problem 2: e V T V e X T XDocument8 pagesSolutions 1.8-Page 89 Problem 2: e V T V e X T Xukel de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument32 pagesProjectile MotionIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasTanisha JainNo ratings yet
- projectile motion STA 2012Document32 pagesprojectile motion STA 2012KLINTH JERALD PINLACNo ratings yet
- CMCH 02Document19 pagesCMCH 02cychan410No ratings yet
- Physics 107 Homework Assignment #1Document4 pagesPhysics 107 Homework Assignment #1Prichebelle Gerona GrafiaNo ratings yet
- Chap 4. Time-dependent Method of Fermi's Golden Rule 2π ¯ h - U - δ (E − E ± ¯hω) Molecular systems: - mi = - i, νi → - ki = - f, ν i · · · - electrons, nucleiiDocument21 pagesChap 4. Time-dependent Method of Fermi's Golden Rule 2π ¯ h - U - δ (E − E ± ¯hω) Molecular systems: - mi = - i, νi → - ki = - f, ν i · · · - electrons, nucleiiAzhar MahmoodNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument11 pagesPhysicsEthylNo ratings yet
- Chương 2Document65 pagesChương 2Le Nguyen Thu HaNo ratings yet
- MECHANICS PHYSICS A NOTES 1&2 Dim RevDocument14 pagesMECHANICS PHYSICS A NOTES 1&2 Dim Revokumuenock000No ratings yet
- 2022+Projectile+Motion+2022+Edited Converted Converted CompressedDocument89 pages2022+Projectile+Motion+2022+Edited Converted Converted CompressedAlthea Joy Castor SobretodoNo ratings yet
- LandingDocument3 pagesLandingAna AnaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Equations Study Guide DALDocument4 pagesKinematics Equations Study Guide DALmayettevillamero17No ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 25.: VDV Adx K VDX X V DX VDV KDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 25.: VDV Adx K VDX X V DX VDV KMario MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 25.: VDV Adx K VDX X V DX VDV KDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 25.: VDV Adx K VDX X V DX VDV KLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Logical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeFrom EverandLogical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeNo ratings yet
- 351lecture9 12 16Document11 pages351lecture9 12 16Dan McNo ratings yet
- The General Motors BankruptcyDocument2 pagesThe General Motors BankruptcyDan McNo ratings yet
- Che 342 Practice Prob ViDocument3 pagesChe 342 Practice Prob ViDan McNo ratings yet
- Fluorescence KineticsDocument10 pagesFluorescence KineticsDan McNo ratings yet
- 2016 Che 151 Homework 1Document2 pages2016 Che 151 Homework 1Dan McNo ratings yet
- Che 342 Practice Set VDocument2 pagesChe 342 Practice Set VDan McNo ratings yet
- Che 142: Separation Process Principles: Il Iv Il Iv I IDocument4 pagesChe 142: Separation Process Principles: Il Iv Il Iv I IDan McNo ratings yet
- 151lecture3 24 15Document6 pages151lecture3 24 15Dan McNo ratings yet
- Che 342 PracticesetiiiDocument3 pagesChe 342 PracticesetiiiDan Mc100% (1)
- HW 02Document4 pagesHW 02Tabitha HowardNo ratings yet
- Che 342 PracticesetiiiDocument3 pagesChe 342 PracticesetiiiDan Mc100% (1)
- ENGSC 2333 - ThermodynamicsDocument47 pagesENGSC 2333 - ThermodynamicsDan McNo ratings yet
- Che 342 Practice Set I IDocument4 pagesChe 342 Practice Set I IDan McNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Set 1 - Three Heat Transfer TechniquesDocument4 pagesPractice Problem Set 1 - Three Heat Transfer TechniquesDan Mc0% (1)
- Delegation: Process by Which A Manager Assigns Authority To Subordinates WhoDocument1 pageDelegation: Process by Which A Manager Assigns Authority To Subordinates WhoDan McNo ratings yet
- Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy Are Both Utilized To Analyze Many Molecules in The Solid, Liquid, and Gaseous StatesDocument1 pageInfrared and Raman Spectroscopy Are Both Utilized To Analyze Many Molecules in The Solid, Liquid, and Gaseous StatesDan McNo ratings yet
- Conquest of IrelandDocument6 pagesConquest of IrelandDan McNo ratings yet
- Bio102 Problem Set 3 Revised Last FigureDocument3 pagesBio102 Problem Set 3 Revised Last FigureDan McNo ratings yet
- Education & Philosophy in UtopiaDocument1 pageEducation & Philosophy in UtopiaDan McNo ratings yet
- Conquest of IrelandDocument6 pagesConquest of IrelandDan McNo ratings yet
- Education & Philosophy in UtopiaDocument1 pageEducation & Philosophy in UtopiaDan McNo ratings yet