Professional Documents
Culture Documents
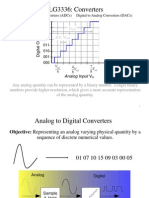
EEE C364/INSTR C364 Analog Electronics ADC
EEE C364/INSTR C364 Analog Electronics ADC
Uploaded by
Angad SehdevOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EEE C364/INSTR C364 Analog Electronics ADC
EEE C364/INSTR C364 Analog Electronics ADC
Uploaded by
Angad SehdevCopyright:
Available Formats
EEE C364/INSTR C364
Analog Electronics
ADC
Lecture 32
19-04-2012
Uses only two values of resistors
Overcomes the limitations of Binary
weighted DAC
OPAMP is connected in inverting mode
Each digital input is applied through R-2R
network and V
r
R-2R LADDER TYPE DAC
R-2R ladder D/A converter
Charge redistribution architecture
Redistribution switch
C
1
= C
2
= C
S
2
is used to recharge C
1
to V
r
if i
th
bit is 1
S
3
is used to recharge C
1
to 0 if i
th
bit is 0
C2 isinitially discharged using S
4
before the beginning
of the conversion
( )
3
3
2
2
1
1
2 2 2
8 4 2 2
2 4
2 4 2
2 /
2
+ + = + + =
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
+ =
+
=
=
b b b V
V V V
V
V V
V
V V V V
V
V
V
r
r r r
r
r r
out
r r r r
out
r
out
Charge redistribution architecture
Example: 101
V
out
= 0
( )
3 2 1
12 2 . 0 2 . 1
8
0
2 2
0
4
0
4 2
0 2 /
2
+ + = + + =
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
+ =
+
=
=
r
r r
r
r
out
r r
out
r
out
V
V V
V
V
V
V V
V
V
V
V
r
V
r
/2
V
out
= V
r
/2
oV
V
out
= (V
r
/4+Vr)/2 V
out
= V
r
/4
Pipelined DAC architecture
Block diagram of commercial D/A converters
Performance characteristics of D/A converters
1. Resolution --- V
r
/2
N
2. Accuracy
3. Offset error
4. Gain error
(a) Differential non-linearity (DNL) error
(b) Integral nonlinearity (INL) error
5. Settling time
6. Dynamic range
7. Power supply rejection ratio
8. Drift
You might also like
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
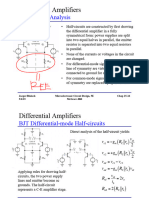
- Differential Amplifier Using BJTDocument11 pagesDifferential Amplifier Using BJTAssini HussainNo ratings yet
- Matrix Formulation of The LppsDocument13 pagesMatrix Formulation of The LppsAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- ADC Pipeline LectureDocument29 pagesADC Pipeline LectureInJune YeoNo ratings yet
- Lec 11 Sequential Logic CircuitsDocument49 pagesLec 11 Sequential Logic CircuitsDeependra NigamNo ratings yet
- EC303Document21 pagesEC303api-3853441No ratings yet
- 1V 10-Bit Successive Approximation ADC For Low Power Biomedical ApplicationsDocument4 pages1V 10-Bit Successive Approximation ADC For Low Power Biomedical ApplicationsSounakDuttaNo ratings yet
- CukonverterDocument30 pagesCukonverterPowersavvyNo ratings yet
- Designing of Combinational Logic Gates in Cmos: G.Susmitha Roll No:06Document49 pagesDesigning of Combinational Logic Gates in Cmos: G.Susmitha Roll No:06kumarbsnspNo ratings yet
- SAR Cyclic and Integrating ADCsDocument50 pagesSAR Cyclic and Integrating ADCsAlberto DanNo ratings yet
- A/D & D/A ConvertersDocument16 pagesA/D & D/A Convertersgeet_battaNo ratings yet
- Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design PerspectiveDocument78 pagesDigital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspectiveapi-127299018No ratings yet
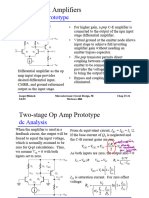
- Lecture 3 - Small Signal Analysis (2 SPP PDFDocument47 pagesLecture 3 - Small Signal Analysis (2 SPP PDFAids Sumalde100% (2)
- Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design PerspectiveDocument78 pagesDigital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspectiveدانشجویان فوق لیسانس الکترونیک 91 سیرجانNo ratings yet
- Lab 11 DAC and ADC Full PackageDocument5 pagesLab 11 DAC and ADC Full PackageLoveWorldCanadaNo ratings yet
- BJT Diff AmplifierDocument15 pagesBJT Diff AmplifierAdrià Amézaga SàrriesNo ratings yet
- BI Technologies R2R Resistor Ladder NetworksDocument6 pagesBI Technologies R2R Resistor Ladder NetworksChethan JayasimhaNo ratings yet
- Fardapaper Controller Design For Cuk Converter Using Model Order ReductionDocument5 pagesFardapaper Controller Design For Cuk Converter Using Model Order Reductionmohamed rafeNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Ch15 NotesDocument18 pagesWeek 3 Ch15 NotesDesan ScientistNo ratings yet
- Lab 5: Digital To Analog and Analog To Digital Converter: Telecommunication Electronics Laboratory Exercise 5Document7 pagesLab 5: Digital To Analog and Analog To Digital Converter: Telecommunication Electronics Laboratory Exercise 5Nilesh BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Adc ConversionDocument20 pagesAdc Conversionhemantec100% (1)
- EE42 100 Wb-Lecture19 080713-FDocument37 pagesEE42 100 Wb-Lecture19 080713-FozanistzNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier - PDF 2Document10 pagesFull Wave Rectifier - PDF 2Gulshan KataraNo ratings yet
- 3EJ4 Set 07 Mixed Signal MJDDocument45 pages3EJ4 Set 07 Mixed Signal MJDSoroush AkNo ratings yet
- DelayDocument31 pagesDelayvarun186No ratings yet
- Analog To Digital & Digital To Analog ConvertersDocument66 pagesAnalog To Digital & Digital To Analog ConvertersSai Krishna Kodali100% (1)
- Bakir Chapter6 7Document66 pagesBakir Chapter6 7mehtajay1993No ratings yet
- PowerSupply VoltageMultipliersDocument1 pagePowerSupply VoltageMultipliersleardpanNo ratings yet
- DAC AnalysisDocument19 pagesDAC Analysisమురళీధర్ ఆది ఆంధ్రుడుNo ratings yet
- L-19 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document12 pagesL-19 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)umi_ktkNo ratings yet
- Final 190416 Solution PDFDocument22 pagesFinal 190416 Solution PDFYoujung KimNo ratings yet
- Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design PerspectiveDocument113 pagesDigital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspectiveapi-127299018No ratings yet
- Lab Manual EC II Format 2Document53 pagesLab Manual EC II Format 2nishavs100% (1)
- EC303Document19 pagesEC303api-3853441No ratings yet
- Measurement of Capacitance de Sauty's BridgeDocument30 pagesMeasurement of Capacitance de Sauty's BridgeRajaa HusseinNo ratings yet
- Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design PerspectiveDocument84 pagesDigital Integrated Circuits: A Design PerspectivedurraizaliNo ratings yet
- DACDocument28 pagesDACRohith Mohan100% (1)
- Flash ADCDocument15 pagesFlash ADCJagadeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 ADCDocument8 pagesUnit-5 ADCDr. M Kiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Analog-to-Digital and Digital-to-Analog ConversionsDocument20 pagesAnalog-to-Digital and Digital-to-Analog ConversionsArif HassanNo ratings yet
- Switched Capacitor 2898320923Document36 pagesSwitched Capacitor 2898320923pardeep184No ratings yet
- Week 4 Ch15 NotesDocument10 pagesWeek 4 Ch15 NotesDesan ScientistNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 BDocument22 pagesChapter 6 BSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase Diode Bridge RectifierDocument54 pages3-Phase Diode Bridge RectifierHimanshu Gupta50% (2)
- Digital To Analog ConvertersDocument13 pagesDigital To Analog ConvertersPasha ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Logic Circuits ProjectDocument13 pagesAdvanced Logic Circuits ProjectLymen LagumbayNo ratings yet
- NTS Past Electrical Engineering Question On RLC Time ConstantDocument3 pagesNTS Past Electrical Engineering Question On RLC Time ConstantHamza IzharNo ratings yet
- Application of ABCDDocument15 pagesApplication of ABCDSantanu Nath50% (4)
- Euler's PathDocument10 pagesEuler's PathSatish Kumar0% (1)
- Atlcee2 2018Document23 pagesAtlcee2 2018Matheus BordinNo ratings yet
- EC304Document17 pagesEC304api-3853441No ratings yet
- A 15-b - Msample/s Digitally Self-Calibrated Pipeline ADC: Hae-Seung Lee, andDocument9 pagesA 15-b - Msample/s Digitally Self-Calibrated Pipeline ADC: Hae-Seung Lee, andSilpa VelagaletiNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 ADCDocument54 pagesUnit-3 ADCPrassun PrasadNo ratings yet
- Devices and Circuits Ii: Lecture GoalsDocument3 pagesDevices and Circuits Ii: Lecture GoalsMạnh Cường TrầnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document90 pagesChapter 12Deepak SubramaniNo ratings yet
- ECE 6130/4130: Advance VLSI Systems: Combinational Logic Styles: Part-II Dynamic Logic Other StylesDocument26 pagesECE 6130/4130: Advance VLSI Systems: Combinational Logic Styles: Part-II Dynamic Logic Other StylesRupesh ParabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document63 pagesChapter 2Mohammad ja'farNo ratings yet
- Low Power CMOS AD ConvertersDocument53 pagesLow Power CMOS AD ConvertersguitarfridoNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Analog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13From EverandAnalog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Duality Theorems Finding The Dual Optimal Solution From The Primal Optimal TableauDocument25 pagesDuality Theorems Finding The Dual Optimal Solution From The Primal Optimal TableauAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- Some Problems Illustrating The Principles of DualityDocument22 pagesSome Problems Illustrating The Principles of DualityAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- In This Presentation We Illustrate The Ideas Developed in The Previous Presentation With Two More ProblemsDocument21 pagesIn This Presentation We Illustrate The Ideas Developed in The Previous Presentation With Two More ProblemsAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- Determination of Starting Basic Feasible SolutionDocument12 pagesDetermination of Starting Basic Feasible SolutionAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- Iterative Computations of The Transportation AlgorithmDocument35 pagesIterative Computations of The Transportation AlgorithmAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- 18 Sensi 1Document24 pages18 Sensi 1Potnuru VinayNo ratings yet
- Problem 10 Problem Set 10.3A Page 414: Maximize Z y y y Subject To y +y + +y C, y 0Document35 pagesProblem 10 Problem Set 10.3A Page 414: Maximize Z y y y Subject To y +y + +y C, y 0Angad SehdevNo ratings yet
- Hillier and Lieberman Problem 14.4-2 Page 746Document27 pagesHillier and Lieberman Problem 14.4-2 Page 746Potnuru VinayNo ratings yet
- Deterministic Dynamic Programming: To The NextDocument52 pagesDeterministic Dynamic Programming: To The NextAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- PERT NetworksDocument10 pagesPERT NetworksAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Solution of Lpps - Simplex MethodDocument26 pagesAlgebraic Solution of Lpps - Simplex MethodAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- Classical Optimization Theory Quadratic Forms: Let Be A N-VectorDocument48 pagesClassical Optimization Theory Quadratic Forms: Let Be A N-VectorAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- Quadratic ProgrammingDocument38 pagesQuadratic ProgrammingAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- Infosys AR 16 PDFDocument218 pagesInfosys AR 16 PDFAngad Sehdev0% (1)
- Ib Handout Fin C 451 - Mgts C 473Document3 pagesIb Handout Fin C 451 - Mgts C 473Angad SehdevNo ratings yet
- Infosys AR 12 PDFDocument110 pagesInfosys AR 12 PDFAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- EEE C364/INSTR C364 Analog Electronics ADCDocument11 pagesEEE C364/INSTR C364 Analog Electronics ADCAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- EEE C364/INSTR C364 Analog Electronics Integrated Circuit Power AmplifiersDocument12 pagesEEE C364/INSTR C364 Analog Electronics Integrated Circuit Power AmplifiersAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- EEE C364/INSTR C364 Analog Electronics Integrated Circuit Power AmplifiersDocument16 pagesEEE C364/INSTR C364 Analog Electronics Integrated Circuit Power AmplifiersAngad SehdevNo ratings yet