Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reflexes
Reflexes
Uploaded by
Suganthi LakshminarayananOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reflexes
Reflexes
Uploaded by
Suganthi LakshminarayananCopyright:
Available Formats
A Presentation on
Reflex
History
Reflex mechanisms are of course still being
extensively studied in the central nervous system
(CNS).
First of which dates back to 1949, when D. P. C.
Lloyd published an article in J. Gen. Physiol, on
monosynaptic reflex.
Reflex is discovered by Marshall Hall , so he is
known as Father of reflex action .
Pavlov is known as Father of conditional reflexes.
Introduction
What is reflex action ?
A reflex action is an automatic response to a certain
situation or stimulus.
Involuntary action is carried out unconsciously
(without our thinking about it) an example of this
could be regulation of heat , heart beat . It is
controlled by hypothalamus.
Voluntary action is something our decide to do within
our conscious mind, this could something like food
searching, protection from enemies , etc. It is
controlled by cerebrum .
TYPES OF ACTION
Action
Involuntary
autonomic
reflex
voluntary
Kinds of reflex
Tonic reflex they are slow , long lasting
adjustments which maintain muscular tone ,posture
and equilibrium.
Phasic reflex they are rapid short lived adjustments
as seen in flexure response.
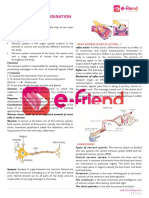
Basic Organization of a Reflex Arc
Path of Reflex arc
Reflex Arc
1-Monosynaptic
2-Polysynaptic
e.g. Stretch Reflex
e.g. Withdrawal Reflex
Types of reflex action
Unconditioned Reflex:It was discovered by Marshall
in 1883 . An automatic instinctive unlearned reaction
to a stimulus. An instinctive reflex not dependent on
previous learning or experience.
Examples-instinct behavior ,nest formation ,
migration , reproduction in specific weather .
Conditioned Reflex: It was first discovered by Pavlov.
A learned response performed by a trained animal to
a signal that was previously associated with an event
of consequence for that animal.
Examples-cycling , dancing , singing ,etc.
Examples of Reflexes:
Flexor reflex (Withdrawal, "hot stove")
31 Oct. 2012
Reflexes.ppt
12
1. receptors sense pain
2. sensory impulse to
spinal cord
3. synapse to association
neuron, synapse to motor
neurons (polysynaptic)
4. motor neurons to flexor
muscles to
5. withdraw offended
body part from stimulus
13
1. Muscle spindles sense
stretch of muscle,
2. Increase rate of sensory
impulses to spinal cord
3. One synapse to motor
neuron(monosynaptic)
4. Motor neurons
stimulate muscle to
5. Contract & restore
tension.
Stretch Reflex (Knee jerk)
Other examples
Blinking reflex of eye Sometimes when an object
comes in front of our eyes, eyelids close.
Scratch reflex- when we put a drop of acetic acid on one
leg of a frog, it tries to remove it from other leg, even
after its brain is removed.
Yawning When level of carbon dioxide increases in our
blood we remove it by Yawning.
Coughing When there comes a foreign particle in
trachea, air comes with great intensity from our lungs so
that this particle can come out with it.
Sneezing- It is same as above, but air comes out from
nose instead of mouth.
References
1. Dr. S.M. Saxena: R.P. unified Ramprashad & sons
publication.
2. Www.en.wikipedia.org.
3. Dr. Ramesh Gupta: Modern Zoology. Prakash
Publication.
4. H.N. Baijal: Zoology Arun prakashan.
You might also like
- Philosophy 3 m-3 QuizeDocument2 pagesPhilosophy 3 m-3 QuizeJoey ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Group 6 Nerves and ReflexesDocument5 pagesLab Report Group 6 Nerves and ReflexesKristina Esta50% (2)
- Ratification Page: Human". Which Made byDocument8 pagesRatification Page: Human". Which Made byNur Fahmi UtamiNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN ANFISMAN - Unit 4Document14 pagesLAPORAN ANFISMAN - Unit 4Rezki Asya NurNo ratings yet
- Conditioning Po KnjigiDocument58 pagesConditioning Po KnjigiMelita BezjakNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument29 pagesScience NotesADITYA KUMARNo ratings yet
- Reflex Arc and ReflexesIonutDocument16 pagesReflex Arc and ReflexesIonutClaudius AndreiaNo ratings yet
- Tulip Series English GuideDocument11 pagesTulip Series English GuideUrwah hassanNo ratings yet
- Approval Sheet: Name: Mujahidah Reg - No: 071404184 Group: IV (Fourth)Document19 pagesApproval Sheet: Name: Mujahidah Reg - No: 071404184 Group: IV (Fourth)Mujahidah UjhaNo ratings yet
- DATE: - Experiment: 01 ObjectsDocument8 pagesDATE: - Experiment: 01 ObjectsMuhammad BashirNo ratings yet
- Raymhee - Behaviorism Research PaperDocument7 pagesRaymhee - Behaviorism Research Paperneil ryan ruizNo ratings yet
- Theories of Learning Chapter 1 - What Is Learning?Document36 pagesTheories of Learning Chapter 1 - What Is Learning?Good HeartNo ratings yet
- Ivan Pavlov's - Classical ConditioningDocument34 pagesIvan Pavlov's - Classical ConditioningJosh PoloNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document10 pagesModule 6Antonette ArmaNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument8 pagesControl and CoordinationAkash DuttaNo ratings yet
- LearningDocument8 pagesLearningAnonymous Dk7NHaTZIONo ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument37 pagesReflexesSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Biopsych Reviewer - FinalsDocument8 pagesBiopsych Reviewer - FinalsNathaniel DimateraNo ratings yet
- Laprak 1 FixDocument11 pagesLaprak 1 FixTakery Chiko KeikoNo ratings yet
- Lab 03 Reflexes Referred PainDocument14 pagesLab 03 Reflexes Referred PainViraj TatikondaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Brain Sensory Receptors Central Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesSpinal Cord Brain Sensory Receptors Central Nervous Systemmohitnet1327No ratings yet
- BehaviorismDocument21 pagesBehaviorismIqbal Haziq100% (2)
- Learning and Memory NotesDocument12 pagesLearning and Memory Notesjincalizo3No ratings yet
- Chart Showing The Classification of Human Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesChart Showing The Classification of Human Nervous Systemamala raviNo ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument7 pagesReflexesShaine Dominique SantosNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument11 pagesControl and CoordinationJit AggNo ratings yet
- Jeanne Erika Asio - Activity 4 (Lab Report) PDFDocument29 pagesJeanne Erika Asio - Activity 4 (Lab Report) PDFJeanne AsioNo ratings yet
- Chapter SummariesDocument4 pagesChapter Summariesdemet ulkuNo ratings yet
- 7.reflex Regulation of Physiological Function PDFDocument2 pages7.reflex Regulation of Physiological Function PDFNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- Spinal ReflexDocument10 pagesSpinal ReflexFata HalaniNo ratings yet
- Controll and Coordination: Animals Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesControll and Coordination: Animals Nervous SystemNAVAS E VNo ratings yet
- 6 Reflex ActionDocument19 pages6 Reflex Actionsanjay jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Psych 261 Module 1 Lecture NotesDocument26 pagesPsych 261 Module 1 Lecture NotesMahum GanatraNo ratings yet
- Chapter Summary Chapter 12 Learning and MemoryDocument6 pagesChapter Summary Chapter 12 Learning and MemoryAlyNo ratings yet
- LearningDocument20 pagesLearningmcmquinitNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination - Class XDocument5 pagesControl and Coordination - Class XMonika Mehan89% (19)
- Bio Grade 12 U5 and Answer For Unit 4Document22 pagesBio Grade 12 U5 and Answer For Unit 4HUIXUNNo ratings yet
- Reflex MovementDocument24 pagesReflex MovementMuqeet76No ratings yet
- Social PsychologyDocument6 pagesSocial PsychologyRaxNo ratings yet
- Activity 4Document15 pagesActivity 4Jeanne AsioNo ratings yet
- Function: Voluntary and Involuntary Responses - AvivaDocument6 pagesFunction: Voluntary and Involuntary Responses - AvivaBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Spinal FrogDocument9 pagesSpinal FrogLutfia NirwanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 CH 8 RGDocument38 pagesUnit 6 CH 8 RGapi-343457547No ratings yet
- Refleks Spinal (Revised)Document11 pagesRefleks Spinal (Revised)Anang Yanuar RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Bio 122 FR 11 - Reflex Action in FrogsDocument8 pagesBio 122 FR 11 - Reflex Action in FrogsLance CarandangNo ratings yet
- Proprioceptive Pathway: ObjectivesDocument17 pagesProprioceptive Pathway: ObjectivesHuyền ĐinhNo ratings yet
- 2.voluntary Body Movements: o o o o o o o o o o o o o o oDocument5 pages2.voluntary Body Movements: o o o o o o o o o o o o o o oCasey HachilesNo ratings yet
- Control Coordination FinalDocument27 pagesControl Coordination Finalabiarju0208No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Stimuli and ResponsesDocument19 pagesChapter 1 - Stimuli and ResponsesFlorence EweNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument10 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentRazi BaigNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination CL XDocument7 pagesControl and Coordination CL XMukul BanoulaNo ratings yet
- Higher Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesHigher Functions of The Nervous SystemPatterson MachariaNo ratings yet
- Reflexes.... Group 1Document28 pagesReflexes.... Group 1King kakaNo ratings yet
- Safari - Feb 21, 2024 at 12:08 PM 2Document1 pageSafari - Feb 21, 2024 at 12:08 PM 2syansyncNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination 2019 PDFDocument8 pagesControl and Coordination 2019 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Class X - Biology Control and Coordination Intext: Questionsp.119Document8 pagesClass X - Biology Control and Coordination Intext: Questionsp.119VijiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Bio4Er NotesDocument72 pagesUnit 5 Bio4Er NoteskgpunithaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Learning and MemoryDocument60 pagesUnit 4: Learning and MemoryPuna Ram GhimireNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument19 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismekosaputrobbppbatuNo ratings yet
- Valence Bond Theory: Hybridization: o o o o o oDocument12 pagesValence Bond Theory: Hybridization: o o o o o oGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Plant ChromatographyDocument17 pagesPlant ChromatographyYujin SeoNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Silk WormDocument13 pagesLife Cycle of Silk WormSuganthi LakshminarayananNo ratings yet
- ProtochordateDocument1 pageProtochordateSuganthi LakshminarayananNo ratings yet
- Ya Kundendu Tushaara Haara DhavalaaDocument1 pageYa Kundendu Tushaara Haara DhavalaaSuganthi LakshminarayananNo ratings yet
- Internet in 21th CenturyDocument2 pagesInternet in 21th CenturySuganthi LakshminarayananNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Honey BeeDocument15 pagesLife Cycle of Honey BeeSuganthi LakshminarayananNo ratings yet
- Hormone and Animal BehavioursDocument22 pagesHormone and Animal BehavioursSuganthi LakshminarayananNo ratings yet