Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Life Processes Revision Guide
Life Processes Revision Guide
Uploaded by
api-2556233020 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
250 views2 pagesOriginal Title
life processes revision guide
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
250 views2 pagesLife Processes Revision Guide
Life Processes Revision Guide
Uploaded by
api-255623302Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Life Processes Revision Guide
Movement To find nutrients and
to reproduce
Respiration Release energy to
carry out life processes
Sensitivity To sense which
direction to move, changes and
adapt to them
Growth To be able to reproduce
Reproduction To keep the
species from becoming extinct
Excretion To remove toxins
from the body eg: C0
2
from blood
cells
Nutrition To help carry out life
processes eg: respiration
Control of internal condition To
keep chemical reactions on going
eg: body temperature, water
content, sugar level etc.
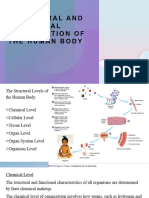
Organization (Cell, Tissues,
Organs, Organs Systems
Cell is the smallest functioning
part of an LO eg: White Blood
Cell
Tissue A group of the same
cells that work together to
complete a job eg: Muscle
Tissue
Organ A group of tissues that
work together to complete a job
eg: Heart
Organ System A group of
organs working together to
complete a job eg: respiratory
system
Jobs
Nucleus controls the activities of
the cell
Cell Membrane Controls the
movement of substances in and
out if the cell (selectively
permeable)
Ribosomes Need to make
proteins
Cytoplasm This fills cells and
organelles are found in it.
Substances are dissolved in it.
Mitochondria - This is where aerobic respiration takes place
Chloroplast Contains a green pigment, chlorophyll, which
absorbs light energy to make glucose during photosynthesis
Vacuole Contains cell sap, mixture of sugars and ions
Cell Wall A thick structure made from cellulose, freely
permeable
Cell Wall, permanent vacuole, chloroplasts are
NOT found in ANIMAL CELLS!
You might also like
- Human and Social Biology Study GuideDocument14 pagesHuman and Social Biology Study GuideThompson Ta Ta Jevon82% (11)
- HSB Section A Living OrganismDocument7 pagesHSB Section A Living OrganismliltrashNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Pre LimDocument13 pagesAnaphy Pre LimKyle M. BayangosNo ratings yet
- What A Middle School 7 Grade Science Student Should Know: About ProtistsDocument3 pagesWhat A Middle School 7 Grade Science Student Should Know: About Protistsapi-300685908No ratings yet
- A p2 Lesson 1Document10 pagesA p2 Lesson 1api-257062466No ratings yet
- Introduction To Animal PhysiologyDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Animal PhysiologyJoachim “Jayrz” MwambireNo ratings yet
- Human Biology 1Document14 pagesHuman Biology 1Arwa AhmedNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONALOrganization of The Human BodyDocument16 pagesFUNCTIONALOrganization of The Human BodyAuliya AlfaNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Biology - Unit 2 Summary NotesDocument4 pagesAQA GCSE Biology - Unit 2 Summary NotesRajashree MuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology DDocument127 pagesAnatomy & Physiology DJhae Zharie Delasan PanosoNo ratings yet
- AnapehDocument25 pagesAnapehKayNo ratings yet
- (W2) Intro To H A P PDocument3 pages(W2) Intro To H A P PFRANCES DEANNE ALABADONo ratings yet
- The Human Body - An IntroductionDocument10 pagesThe Human Body - An IntroductionAkanksha ChoutiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerAnn Fenelope AniscoNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms in Anatomy and Physiology - AssignmentDocument4 pagesDefinition of Terms in Anatomy and Physiology - Assignmentcriselda desistoNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology/Cell Physiology: Jump ToDocument29 pagesHuman Physiology/Cell Physiology: Jump ToPrincess SaniaNo ratings yet
- 2 Structural and Functional Organization, Necessary Life Functions & HomeostasisDocument37 pages2 Structural and Functional Organization, Necessary Life Functions & HomeostasisCamille Marie UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissuesDocument18 pagesCell and Tissuesalvin jr ayugatNo ratings yet
- Four Systems For Happy YogaDocument109 pagesFour Systems For Happy YogaAwanish PandeyNo ratings yet
- Study Guide HomeostasisDocument5 pagesStudy Guide Homeostasisgmanb5100% (1)
- Study Guide For Science Periodic 2 Term 2 6 Grade Life Science-Sections 1.1, 1.2, & 1.3Document7 pagesStudy Guide For Science Periodic 2 Term 2 6 Grade Life Science-Sections 1.1, 1.2, & 1.3api-270387817No ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 7Document5 pagesLesson Proper For Week 7Merlyn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 35 Nervous System: Notes 35.1 Human Body SystemsDocument11 pagesBio Chapter 35 Nervous System: Notes 35.1 Human Body SystemsLeah100% (1)
- Chapter 2 BotanyDocument6 pagesChapter 2 BotanyLebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology/Cell Physiology: From Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open World Jump ToDocument25 pagesHuman Physiology/Cell Physiology: From Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open World Jump ToUsman SherifNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument5 pagesBiology NotesBruce ZhouNo ratings yet
- C1Document256 pagesC1azfdin100% (4)
- HAPP Human-Body-Orienation-Reviewer-lecDocument5 pagesHAPP Human-Body-Orienation-Reviewer-lecDenize Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3Al Cris BarroNo ratings yet
- Bio and H.BioDocument175 pagesBio and H.BioXX OniiSan XXNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ChuchuDocument2 pagesEarth and Life ChuchuAndrew TanecaNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissueDocument10 pagesCell and TissueCarl SantosNo ratings yet
- Introduction of AnatomyDocument71 pagesIntroduction of AnatomyPrasannaa BaleNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument8 pagesCellsNusaybah GhanyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Notes Online NotesDocument92 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Notes Online NotesSharique KhanNo ratings yet
- B1 Cells (Summary Notes)Document3 pagesB1 Cells (Summary Notes)noraNo ratings yet
- Lecture BZE Life-HomeostasisDocument10 pagesLecture BZE Life-Homeostasiscarolinebrongelcopti24No ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDump Acc 2100% (1)
- Cells and Tissues: Gross CellularDocument10 pagesCells and Tissues: Gross Cellularsasa sasadzeNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 2 Form 1Document23 pagesScience Chapter 2 Form 1Kelvin0% (1)
- Biology ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiology ReviewerflowenceNo ratings yet
- Chap 7 PDFDocument4 pagesChap 7 PDFQuốc HuyNo ratings yet
- Bio 10 Master Study Guide Part 1Document9 pagesBio 10 Master Study Guide Part 1leonor.estimaNo ratings yet
- Biology Capsule For SSC CGL by StudyIQDocument73 pagesBiology Capsule For SSC CGL by StudyIQstudyiq83% (6)
- Introduction To Body Chemistry: Processes That Characterise LifeDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Body Chemistry: Processes That Characterise LifeLeo OrtegaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Revision BookDocument65 pagesIGCSE Revision BookTANDON Aditya0% (1)
- Life Process NotesDocument15 pagesLife Process NotesYumna KulsumNo ratings yet
- Topic: Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesTopic: Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRustin John ReaNo ratings yet
- Ana&Physio 1 - The Human Body - An OrientationDocument59 pagesAna&Physio 1 - The Human Body - An OrientationShery Han Bint HindawiNo ratings yet
- Cells & TissuesDocument8 pagesCells & Tissuessanjay6969No ratings yet
- Hapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument29 pagesHapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeShu85No ratings yet
- 10 Major System of Responsible For Body FunctionDocument27 pages10 Major System of Responsible For Body Functionقى قىNo ratings yet
- CU-Bio 106 Lecture Notes-2021Document24 pagesCU-Bio 106 Lecture Notes-2021Platon S PlakarNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument8 pagesBiology NoteskatebelikovcullenNo ratings yet
- Theory of Special CreationDocument9 pagesTheory of Special Creationnico peregrinoNo ratings yet
- Notes For Biology Form OneDocument8 pagesNotes For Biology Form Onelopem clarysonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Human Body: Notes: From Atoms To OrganismsDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - The Human Body: Notes: From Atoms To OrganismsIssa AvenaNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument8 pagesReviewerJean Loraine MirandaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument85 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationIsmail ZueNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Igcse Biology Respiration, Lungs & Smoking Revision GuideDocument2 pagesIgcse Biology Respiration, Lungs & Smoking Revision Guideapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Igcse Biology Digestion Revision GuideDocument3 pagesIgcse Biology Digestion Revision Guideapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Shell Revision Guide Problem of Evil and SufferingDocument2 pagesShell Revision Guide Problem of Evil and Sufferingapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Igcse Physics Forces MovementDocument6 pagesIgcse Physics Forces Movementapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Igcse Revision Guide AstronomyDocument1 pageIgcse Revision Guide Astronomyapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Math Number Revision GuideDocument9 pagesMath Number Revision Guideapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Bonding Revision GuidesDocument1 pageBonding Revision Guidesapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Igcse Physics Forces MovementDocument6 pagesIgcse Physics Forces Movementapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Igcse Unit - C Forces Movement Shapeand MomentumDocument3 pagesIgcse Unit - C Forces Movement Shapeand Momentumapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Igcse Biology Cell StructureDocument2 pagesIgcse Biology Cell Structureapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Igcse Revision GuideDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Igcse Revision Guideapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Variety of Living OrganismsDocument4 pagesVariety of Living Organismsapi-255623302No ratings yet