Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LVEDP Table
LVEDP Table
Uploaded by
hollyu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
87 views3 pagesThe document summarizes potential discrepancies between left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) and other hemodynamic measurements in various cardiac conditions. It lists conditions that can lead to underestimation or overestimation of LVEDP and explains the underlying causes, such as increased pulmonary pressures from pulmonary hypertension or obstruction of blood flow from valvular diseases.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes potential discrepancies between left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) and other hemodynamic measurements in various cardiac conditions. It lists conditions that can lead to underestimation or overestimation of LVEDP and explains the underlying causes, such as increased pulmonary pressures from pulmonary hypertension or obstruction of blood flow from valvular diseases.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
87 views3 pagesLVEDP Table
LVEDP Table
Uploaded by
hollyuThe document summarizes potential discrepancies between left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) and other hemodynamic measurements in various cardiac conditions. It lists conditions that can lead to underestimation or overestimation of LVEDP and explains the underlying causes, such as increased pulmonary pressures from pulmonary hypertension or obstruction of blood flow from valvular diseases.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
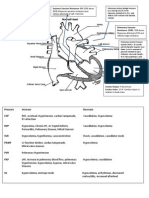
TABLE 30–7.
Underestimation of Left Ventricular End-Diastolic Pressure
SITE OF
CONDITION CAUSE OF DISCREPANCY
DISCREPANCY
Decreased left ventricular
Mean LAP<LVEDP Increased end-diastolic a wave
compliance
Mitral valve closure prior to end-
Aortic regurgitation LAP a wave<LVEDP
diastole
Bidirectional runoff for pulmonary
Pulmonic regurgitation PADP<LVEDP
artery flow
Right bundle branch block PADP<LVEDP Delayed pulmonic valve opening
Decreased pulmonary Obstruction of pulmonary blood
PAWP<LVEDP
vascular bed flow
TABLE 30–8. Overestimation of Left Ventricular End-Diastolic Pressure
SITE OF
CONDITION CAUSE OF DISCREPANCY
DISCREPANCY
Positive end-expiratory Mean PAWP>Mean Creation of lung zone 1 or 2 or
pressure LAP pericardial pressure changes
Pul arterial HTN PADP>Mean PAWP pulmonary vascular resistance
Pulmonary veno- Mean PAWP>Mean Obstruction to flow in large pulmonary
occlusive disease LAP veins
Mitral stenosis Mean LAP>LVEDP Obstruction to flow across mitral valve
Retrograde systolic v wave raises mean
Mitral regurgitation Mean LAP>LVEDP
atrial pressure
Ventricular septal Antegrade systolic v wave raises mean
Mean LAP>LVEDP
defect atrial pressure
TABLE 30–8. Overestimation of Left Ventricular End-Diastolic Pressure
SITE OF
CONDITION CAUSE OF DISCREPANCY
DISCREPANCY
PADP>Mean Short diastole creates pulmonary
Tachycardia
LAP>LVEDP vascular and mitral valve gradients
You might also like
- (SVR) Measures Systemic Resistance and Reflects Afterload of Left Ventricle Average Perfusion of A Cardiac CycleDocument1 page(SVR) Measures Systemic Resistance and Reflects Afterload of Left Ventricle Average Perfusion of A Cardiac Cyclesarah_stover_1100% (4)
- Valvular Heart Disease: Hakim AlkatiriDocument84 pagesValvular Heart Disease: Hakim AlkatiriFNo ratings yet
- Exam 1reference SheetDocument2 pagesExam 1reference SheetAndrea Norton100% (1)
- Rosenberg Circulatory Assist DevicesDocument61 pagesRosenberg Circulatory Assist DevicesMilisha Albro100% (1)
- Pulmonary Artery Catheters and Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument32 pagesPulmonary Artery Catheters and Hemodynamic Monitoringjpsahni100% (1)
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument33 pagesHemodynamic MonitoringISICLE GTNo ratings yet
- Mitral StenosisDocument37 pagesMitral StenosisInsan IlmanNo ratings yet
- Zoom Final PA CathetherDocument45 pagesZoom Final PA Cathetherhasanafridi.mechNo ratings yet
- Comparing LVEDP Vs PCWP JAMA Cardio.2018Document2 pagesComparing LVEDP Vs PCWP JAMA Cardio.2018Sajjad HussainNo ratings yet
- Mitral Stenosis For Beginners: Pratap Sagar TiwariDocument23 pagesMitral Stenosis For Beginners: Pratap Sagar TiwariMituran IshwarNo ratings yet
- Foreward Failure: Cardiac OutputDocument1 pageForeward Failure: Cardiac Outputmaria ngongoNo ratings yet
- Duct Dependent Lesions - PPSXDocument41 pagesDuct Dependent Lesions - PPSXSindujaNo ratings yet
- 16 57 1 Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection IDocument38 pages16 57 1 Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection Iwiyay34652ceoshubcomNo ratings yet
- LVAD InfoDocument2 pagesLVAD InfoCPNo ratings yet
- Clinical Hemodynamic Correlation in Mitral StenosisDocument82 pagesClinical Hemodynamic Correlation in Mitral StenosisHristo MateevNo ratings yet
- MS MR As ArDocument21 pagesMS MR As ArTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Jantung KatupDocument35 pagesPenyakit Jantung Katupdwi ariskaNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DiseasesDocument86 pagesValvular Heart DiseasesParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamics 090529201710 Phpapp01Document73 pagesHemodynamics 090529201710 Phpapp01Michael Ian Redito100% (3)
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument6 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseSamah KhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle JVPDocument70 pagesCardiac Cycle JVPAstrid PramudyaaNo ratings yet
- 28 Valvular Heart Disease DR - YusraDocument46 pages28 Valvular Heart Disease DR - YusraSurya ArhNo ratings yet
- Swan Ganz FinalDocument36 pagesSwan Ganz FinalDanial HassanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Hypertension: Kazemi - Toba, M.D. Birjand University of Medical Sciences 24 Ordibeheshte 1390Document58 pagesPulmonary Hypertension: Kazemi - Toba, M.D. Birjand University of Medical Sciences 24 Ordibeheshte 1390Devashish VermaNo ratings yet
- Cardio 2020 MedantaDocument454 pagesCardio 2020 Medantadoc339No ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument7 pagesHeart FailureLovely CacapitNo ratings yet
- Valvular UpdateDocument44 pagesValvular UpdateUlmi FadillahNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease: Etiology PathophysiologyDocument34 pagesValvular Heart Disease: Etiology PathophysiologyensiNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock: DR M. Durand Anesthesia Department II CHU GrenobleDocument36 pagesCardiogenic Shock: DR M. Durand Anesthesia Department II CHU GrenobleÁdrian LupasNo ratings yet
- CHD Fetal CirculationDocument31 pagesCHD Fetal CirculationNandita ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema: Prepared By: South West Education CommitteeDocument65 pagesPulmonary Edema: Prepared By: South West Education CommitteedanradulescuNo ratings yet
- CCC Nurs 235 - Pediatric & Maternity NursingFinal Study GuideDocument13 pagesCCC Nurs 235 - Pediatric & Maternity NursingFinal Study GuideHeidi HeffelfingerNo ratings yet
- Mitral Regurgitation: MedicineDocument7 pagesMitral Regurgitation: Medicineapi-3829364No ratings yet
- Jugular Venous Pressure: DR - Sameer Ambar JNMC & Kles Hospital BelgaumDocument35 pagesJugular Venous Pressure: DR - Sameer Ambar JNMC & Kles Hospital BelgaumAyu Rahmi AMyNo ratings yet
- Pleno Minggu 3 Blok 3.2Document57 pagesPleno Minggu 3 Blok 3.2ima_nekonayagiNo ratings yet
- Type of Shock Signs/Symptoms RA CVP PCWP/ Lvedp SVR HR Co Etiology Treatment HypovolemicDocument1 pageType of Shock Signs/Symptoms RA CVP PCWP/ Lvedp SVR HR Co Etiology Treatment Hypovolemicri2323No ratings yet
- Penyakit KatupDocument31 pagesPenyakit KatupAdinda Suci MaghfiraNo ratings yet
- Mitral Stenosis Mitral RegurgitationDocument66 pagesMitral Stenosis Mitral RegurgitationMarshellaTriPradilagaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Hypertension in Intensive Care UnitDocument52 pagesPulmonary Hypertension in Intensive Care UnitsarsalNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasesDocument7 pagesAcyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasesAlvin De LunaNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument32 pagesValvular Heart DiseasefallenczarNo ratings yet
- Woc Gagal JantungDocument1 pageWoc Gagal JantungAhdya Islaha WidyaputriNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument10 pagesValvular Heart DiseaseEzyan SyaminNo ratings yet
- Valvular 2005Document32 pagesValvular 2005rajeeNo ratings yet
- CCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Cardiac Part 3Document18 pagesCCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Cardiac Part 3Giovanni MictilNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Heart FailureDocument39 pagesDrugs For Heart FailureOngKahYeeNo ratings yet
- Falla Ventriculo DerechoDocument6 pagesFalla Ventriculo DerechoMartin M.V.No ratings yet
- Cyanosis in The NewbornDocument32 pagesCyanosis in The Newbornimma_2014No ratings yet
- Bedside Assessment of Left Atrial Pressure in Critical Care: A Multifaceted Gem Emma Maria Bowcock and Anthony McleanDocument16 pagesBedside Assessment of Left Atrial Pressure in Critical Care: A Multifaceted Gem Emma Maria Bowcock and Anthony McleanAlicia LópezNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument41 pagesHemodynamic MonitoringSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Fluid ResponsivenessDocument42 pagesFluid Responsivenessgwhqvmqks5No ratings yet
- Management of Pulmonary EdemaDocument42 pagesManagement of Pulmonary Edemaademato4real576No ratings yet
- Pericardial Disease: Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1Document5 pagesPericardial Disease: Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1Shaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Fluid ResponsivenessDocument27 pagesFluid ResponsivenessBiko Adji S. RahardjoNo ratings yet
- Aortic Stenosis BY ISRARDocument50 pagesAortic Stenosis BY ISRARAkramNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease-2Document57 pagesCongenital Heart Disease-2Deepika LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Failure March 2016Document61 pagesHemodynamic Failure March 2016Adriana VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument73 pagesValvular Heart Diseaseindia2puppy100% (5)
- CCRN CardiacDocument39 pagesCCRN CardiacMike100% (5)
- ANESTHESIA Monitors LeafleTDocument4 pagesANESTHESIA Monitors LeafleThollyuNo ratings yet
- ANESTHESIA-Pediatrics Airway SyndromesDocument12 pagesANESTHESIA-Pediatrics Airway SyndromeshollyuNo ratings yet
- Final Anesthesia Reviw Flash CardsDocument217 pagesFinal Anesthesia Reviw Flash Cardsaljuhanita100% (1)
- POVN - Postoperative Nausea and VomitingDocument2 pagesPOVN - Postoperative Nausea and VomitinghollyuNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument1 pageStrokehollyuNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument1 pageSystemic Lupus ErythematosushollyuNo ratings yet
- Causes: Head Injuries, Intracranial Tumors, Pulmonary Infections, Small CellDocument2 pagesCauses: Head Injuries, Intracranial Tumors, Pulmonary Infections, Small CellhollyuNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument2 pagesShockhollyuNo ratings yet
- Post Ton BleedDocument1 pagePost Ton BleedhollyuNo ratings yet