Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Periodic Function: T F L T F
Periodic Function: T F L T F
Uploaded by
David WhiteOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Periodic Function: T F L T F
Periodic Function: T F L T F
Uploaded by
David WhiteCopyright:
Available Formats
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
1
PERIODIC FUNCTION
If its function values repeat at regular intervals of the independent variable.
Definition
If function f is define for every x and its properties is
) ( ) 2 ( t f L t f = +
then f is a periodic function.
period
Functions Period
x sin 2
x cos 2
nx sin
n
2
nx cos
n
2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 1
Sketch the graph of . x y sin =
Solution
y
x
2
Amplitude
x y sin =
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
2
Example 2
Sketch the graph of
). ( ) (
, 0 , sin ) (
+ =
< =
t g t g
t t t g
Solution
g(t)
t
0 2 3 4
1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 3
Sketch the graph of
) 2 ( ) (
. 2 , 2
, 0 ,
) (
+ =
<
<
=
t f t f
t t
t t
t f
Solution
f(t)
t
0 2 4 6
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 4
Define analytically the periodic function.
f(t)
t
4 10 13
3
3
Solution
) 13 ( ) (
. 13 10 , 3
, 10 4 , 7
, 4 0 , 4 / 3
) (
+ =
< <
< <
< <
=
t f t f
t
t t
t t
t f
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
3
Example 5
Sketch the graph of
) 2 ( ) (
. 2 , 0
, 0 , sin 2
) (
+ =
< <
< <
=
t f t f
t
t t
t f
Solution
f(t)
t
2
2 3 4
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 6
Sketch the graph of
) 9 ( ) (
. 9 7 , 0
, 7 4 , 5
, 4 0 , 3
) (
+ =
< <
< <
< <
=
t f t f
t
t
t
t f
Solution
f(t)
t
3
5
4 7 9
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
4
HARMONICS
Definition
A function f(x) expressed as a series of a number of different sine components.
Types
1. First harmonic or fundamental
- Largest period
- x A y sin
1
=
2. Second harmonic
- x A y 2 sin
2
=
3. Third harmonic
- x A y 3 sin
3
=
Generally
nx A y
n
sin =
where
- n : n-th harmonic
-
n
A : Amplitude
-
n
2
: Period
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
5
ODD & EVEN FUNCTION ON
Even Functions Even Functions
- If ) ( ) ( x f x f =
- Symmetrical about the y-axis.
Odd Functions
- If ) ( ) ( x f x f =
- Symmetrical about the origin.
Products Of Odd And Even Functions
- (even) (even) = (even)
- (odd) (odd) = (even)
- (even) (odd) = (odd)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 1
Show that is an even function.
2
) ( t t f =
Solution
2
) ( ) ( t t f = ) (
2
t f t = =
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 2
Show that is an odd function.
3
4 ) ( x x f =
Solution
3
) ( 4 ) ( x x f = ) ( 4
3
x f x = =
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 3
State whether the following functions are odd, even, or neither.
(a) x x cos
3
(b) x x 3 cos 2 cos
(c) nx xsin
Solution
(a) (odd) (even) = (odd)
(b) (even) (even) = (even)
(c) (odd) (odd) = (even)
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
6
Example 4
State whether the following functions are odd, even, or neither.
(a)
2 2
(b)
2 2
(c)
2
1
0 2 4 2 4
_ _
Solution
(a) even function
(b) odd function
(c) neither
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
7
FOURIER SERIES
Represent a period function in terms of sinus and/or cosines of different
frequencies.
Two basic theorem :
- dx x f dx x f ) ( ) ( =
- ) ( ) ( x f x f
dx
d
dx
d
=
) (x f of period 2
- write down as ) 2 ( ) ( + = x f x f
We may find the Fourier series of a function with period over periodic intervals
other than 2 .
Therefore in generally :
of period ) (x f L 2 , then ) 2 ( ) ( L x f x f + =
Each cycle is completed in L 2 seconds.
The frequency f hertz given by
L
f
2
1
= .
If the angular velocity radians per second, is defined by f 2 = , then
L 2
2
=
L
=
Definition
=
+ + =
1 1
0
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
nx b nx a a x f
where and are Fourier coefficients.
n
a a ,
0 n
b
In generally
=
+ + =
1 1
0
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
x
L
n
b x
L
n
a a x f
In Long Notation
L + + + = x a x a a x f 2 cos cos
2
1
) (
2 1 0
L + + + x b x b 2 sin sin
2 1
where
x b x a sin cos
1 1
+ : 1
st
harmonic
x b x a 2 sin 2 cos
2 2
+ : 2
nd
harmonic
nx b nx a
n n
sin cos + : n-th harmonic
period
2L
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
8
FOURIER COEFFICIENTS (FULL RANGE)
Fourier Series of Period 2 Fourier Series of Period 2L
Periodic
Function
) 2 ( ) (
. 0 ), (
, 0 ), (
) (
2
1
+ =
<
<
=
x f x f
x x f
x x f
x f
) 2 ( ) (
. 0 ), (
, 0 ), (
) (
2
1
L x f x f
L x x f
x L x f
x f
+ =
<
<
=
0
a
dx x f a ) (
1
0
=
L
L
dx x f
L
a ) (
1
0
n
a
nxdx x f a
n
cos ) (
1
=
L
L
n
xdx n x f
L
a cos ) (
1
=
L
L
dx x
L
n
x f
L
cos ) (
1
F
o
u
r
i
e
r
C
o
e
f
f
i
c
i
e
n
t
s
n
b
nxdx x f b
n
sin ) (
1
=
L
L
n
xdx n x f
L
b sin ) (
1
=
L
L
dx x
L
n
x f
L
sin ) (
1
in each case K , 3 , 2 , 1 = n
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 1
Obtain a Fourier series to represent the following periodic function.
). 2 ( ) (
. 0 , 3
, 0 , 0
) (
+ =
<
<
=
x f x f
x x
x
x f
Solution
= L
=
=
dx x f
dx x f
L
a
L
L
) (
1
) (
1
0
2
3
0
2
3 1
2
3 1
3 ) 0 (
1
2
0
2
0
0
+ =
x
xdx dx
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
9
= =
nxdx x f nxdx x f
L
a
L
L
n
cos ) (
1
cos ) (
1
+ =
0
0
cos 3 cos ) 0 (
1
nxdx x nxdx
Integration by tabular method!
Sign
dx du /
dv
+
3x
nx cos
3
nx
n
sin
1
0
nx
n
cos
1
2
) 1 (cos
3
) 1 (
3
0 cos
3
sin
3 1
cos
3
sin
3 1
2
2 2
0
2
=
+ =
+ =
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
nx
n
nx
n
x
= =
nxdx x f nxdx x f
L
b
L
L
n
sin ) (
1
sin ) (
1
+ =
0
0
sin 3 sin ) 0 (
1
nxdx x nxdx
Integration by tabular method!
Sign
dx du /
dv
+
3x
nx sin
3
nx
n
cos
1
0
nx
n
sin
1
2
) (cos
3
0 0 sin
3
cos
3 1
sin
3
cos
3 1
2
0
2
n
n
n
n
n
n
nx
n
nx
n
x
=
+ =
+ =
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
10
) 1 (cos
3
2
=
n
n
a
n
: K , 5 , 3 , 1 = n
= =
2 2
1 6
) 1 1 (
3
n n
a
n
: K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n 0 ) 1 1 (
3
2
= =
n
a
n
) (cos
3
n
n
b
n
=
: K , 5 , 3 , 1 = n
=
n n
b
n
1
3 ) 1 (
3
: K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n
= =
n n
b
n
1
3 ) 1 (
3
So Fourier series is
=
+ + =
1 1
0
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
nx b nx a a x f
=
+
=
+
+ +
+ + =
1
1
1
2
sin
) 1 ( 3
) 1 2 (
) 1 2 cos( 6
4
3
3 sin
3
1
2 sin
2
1
sin 3 3 cos
9
1
cos
6
4
3
n
n
n
n
nx
n
x n
x x x x x
L L
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 2
Given
). 2 ( ) (
. 0 , sin
, 0 , 0
) (
+ =
<
<
=
x f x f
x x
x
x f
(a) Sketch the graph of f(x) over 3 3 x .
(b) Then, find the Fourier series.
Solution
3 2 2 3
x
f(x)
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
11
dx x f a ) (
1
0
[ ]
[ ]
2
) 1 ( ) 1 (
1
cos
1
sin ) 0 (
1
0
0
0
=
=
=
+ =
x
xdx dx
nxdx x f a
n
cos ) (
1
+ =
dx nx x dx nx
0
0
cos sin cos ) 0 (
1
[ ]
[ ]
+
+
+
+
+
=
+
+
+
=
+ =
+ + =
1
1
1
1
1
) 1 cos(
1
) 1 cos(
2
1
1
) 1 cos(
1
) 1 cos(
2
1
) 1 sin( ) 1 sin(
2
1
) sin( ) sin(
2
1
0
1
0
0
0
n n n
n
n
n
n
x n
n
x n
dx x n x n
dx x nx x nx
] ) sin( ) [sin(
sin cos
2
1
x b a x b a
bx ax
+ =
Trigonometric Identity
Valid only for being non-zero. So we need to look at separate case when . ) 1 ( n 1 = n
K , 7 , 5 , 3 = n : 0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
=
+
+
+
+
=
n n n n
a
n
K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n :
+
+
+
=
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
n n n n
a
n
+
=
1
1 2
1
4
2
1
1
2
1
2
2
1
2
2
n
n
n n
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
12
1 = n ; xdx x a cos sin
1
0
1
0 ) 1 1 (
4
1
2 cos
2
1
2
1
2 sin
2
1
0
0
= =
=
=
x
xdx
nxdx x f b
n
sin ) (
1
[ ]
+
+
+
+
=
+ =
+ =
1
) 1 sin(
1
) 1 sin(
2
1
1
) 1 sin(
1
) 1 sin(
2
1
) 1 cos( ) 1 cos(
2
1
sin sin sin ) 0 (
1
0
0
0
n
n
n
n
n
x n
n
x n
dx x n x n
dx nx x nxdx
Trigonometric Identity
] ) cos( ) [cos(
sin sin
2
1
x b a x b a
bx ax
+ =
Similar with .
n
a
Valid only for being non-zero. So we need to look at separate case when . ) 1 ( n 1 = n
K , 7 , 5 , 3 = n : ( ) 0 0 0
2
1
= =
n
b
K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n : 0 ) 0 0 (
2
1
= =
n
b
1 = n : xdx x b sin sin
1
0
1
2
1
) 0 0 0 (
2
1
2
2 sin
2
1
) 2 cos 1 (
2
1
0
0
=
+ =
=
=
x
x
dx x
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
13
So Fourier series is
=
+ + =
1 1
0
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
nx b nx a a x f
+ + + =
+ =
=
L x x x
nx
n
x
even n
4 cos
15
1
2 cos
3
1 2
sin
2
1 1
2 cos
1
1 2
sin
2
1 1
2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 3
Sketch the following function.
). 2 ( ) (
. 1 0 ,
, 0 1 , 0
) (
+ =
<
<
=
x f x f
x x
x
x f
Then, find the Fourier series.
Solution
2 1 1 2 3
x
f(x)
=
=
1
1
0
) (
1
1
) (
1
dx x f
dx x f
L
a
L
L
2
1
2
0
1
0
2
1
0
0
1
=
=
+ =
x
dx x dx
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
14
=
L
L
n
dx x
L
n
x f
L
a
cos ) (
1
+ =
1
0
0
1
1
cos
1
cos 0
1
1
dx x
n
x dx x
n
Integration by tabular method!
Sign
dx du /
dv
+
x
x n cos
1
x n
n
sin
1
0
x n
n
cos
1
2 2
) 1 (cos
1
1
0
cos sin
cos sin
2 2
2 2 2 2
1
0
2 2
=
+ =
+ =
n
n
n n
n
n
n
n
x n
n
x n x
=
L
L
n
dx x
L
n
x f
L
b
sin ) (
1
+ =
1
0
0
1
1
sin
1
sin 0
1
1
dx x
n
x dx x
n
Integration by tabular method!
Sign
dx du /
dv
+
x
x n sin
1
x n
n
cos
1
0
x n
n
sin
1
2 2
) (cos
1
0 0
sin cos
sin cos
2 2
1
0
2 2
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
x n
n
x n x
=
+
=
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
15
) 1 (cos
1
2 2
=
n
n
a
n
: K , 5 , 3 , 1 = n
= =
2 2 2 2
1 2
) 1 1 (
1
n n
a
n
: K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n 0 ) 1 1 (
1
2 2
= =
n
a
n
) (cos
1
n
n
b
n
=
: K , 5 , 3 , 1 = n
= =
n n
b
n
1 1
) 1 (
1
: K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n
= =
n
b
n
1 1
) 1 (
1
So the Fourier series,
=
+ + =
1 1
0
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
x
L
n
b x
L
n
a a x f
=
+
=
+
+ +
+ + + =
1
1
1
2 2
2
sin
) 1 (
1
) 1 2 (
) 1 2 cos( 2
4
1
3
3 sin
2
2 sin
sin
1
25
5 cos
9
3 cos
cos
2
4
1
n
n
n
n
x n
n
x n
x x
x
x x
x
L L
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
16
FOURIER COEFFICIENTS (ODD AND EVEN FUNCTIONS)
Fourier Series of Period 2 Fourier Series of Period 2L
0
a
0
0
) (
2
dx x f a
=
L
dx x f
L
a
0
0
) (
2
n
a
0
cos ) (
2
nxdx x f a
n
=
=
L
L
n
dx x
L
n
x f
L
dx x n x f
L
a
0
0
cos ) (
2
cos ) (
2
E
v
e
n
F
u
n
c
t
i
o
n
s
n
b
0 0
0
a
0 0
n
a
0 0
F
o
u
r
i
e
r
C
o
e
f
f
i
c
i
e
n
t
s
O
d
d
F
u
n
c
t
i
o
n
s
n
b
0
sin ) (
2
nxdx x f b
n
=
L
n
xdx n x f
L
b
0
sin ) (
2
=
L
dx x
L
n
x f
L
0
sin ) (
2
in each case K , 3 , 2 , 1 = n
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 1
Given a periodic function
). 2 ( ) (
. 0 , 5
, 0 , 5
) (
+ =
<
<
=
x f x f
x
x
x f
(a) Sketch the graph of f(x).
(b) Determine whether f(x) is an even, odd or neither function.
(c) Show that ) cos 1 (
10
n
n
b
n
= .
(d) Obtain the Fourier series.
(e) Calculate the sum of the series
L +
5
1
3
1
1
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
17
Solution
(a)
x
f(x)
2 2
5
5
(b) The given function is an odd function.
(c)
=
L
n
dx x
L
n
x f
L
b
0
sin ) (
2
) cos 1 (
10
cos
5 2
sin 5
2
0
0
n
n
nx
n
dx nx
=
=
=
(d) Since f(x) is an odd function,
0
0
= =
n
a a .
) cos 1 (
10
n
n
b
n
=
: K , 5 , 3 , 1 = n [ ]
= =
n n
b
n
1 20
) 1 ( 1
10
: K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n [ ] 0 1 1
10
= =
n
b
n
So the Fourier series,
+ + + =
+ + =
1
1 1
0
1 2
) 1 2 sin( 20
5 sin
5
1
3 sin
3
1
sin
20
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
n
n
x n
x x x
nx b nx a a x f
L
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
18
(e) When
2
= x ; 5 ) (
2
=
f
Thus,
L
L
+ =
+ + + =
=
+
=
5
1
3
1
1
4
) 1 (
5
1
) 1 (
3
1
1
20
1 2
) 1 ( 20
5
1 2
) 1 2 sin( 20
) (
1
1
1
2
2
n
n
n
n
n
n
f
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 2
A periodic function defined as
) 2 ( ) (
0 4 4
0 4 4
) (
+ =
< +
< +
=
x f x f
x x
x x
x f
(a) Sketch the graph of the function.
(b) Determine whether the function is an even odd or neither function.
(c) Then, find the Fourier series.
(d) By choosing an appropriate values for x, deduce the sum of the infinite series
L + + + +
49
1
25
1
9
1
1
Solution
(a)
x
f(x)
2 2
4
(b) The given function is an even function.
(c) Since the function is an even function, 0 =
n
b .
+ =
0
0
) 4 4 (
2
dx x a
4 4
2
4 2
0
2
=
+ = x x
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
19
+ =
0
cos ) 4 4 (
2
nxdx x a
n
Sign
dx du /
dv
+
4 4 + x
nx cos
4
nx
n
sin
1
0
nx
n
cos
1
2
) cos 1 (
8
cos
4
sin
1
) 4 4 (
2
2
0
2
n
n
nx
n
nx
n
x
=
+
=
K , 5 , 3 , 1 = n : [ ]
= =
2 2
1 16
) 1 ( 1
8
n n
a
n
K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n : [ ] 0 1 1
8
2
= =
n
a
n
So the Fourier series,
+ =
+ + + + =
+ + =
1
2
1 1
0
) 1 2 (
) 1 2 cos( 16
2
5 cos
25
1
3 cos
9
1
cos
16
2
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
n
n
x n
x x x
nx b nx a a x f
L
(d) When
0 = x ; 4 4 ) 0 ( 4 ) 0 ( = + = f
Thus,
L + + + + =
+ =
+ =
=
49
1
25
1
9
1
1
8
) 1 2 (
1 16
2 4
) 1 2 (
) 0 )( 1 2 cos( 16
2 ) 0 (
2
1
2
1
2
n
n
n
n
n
f
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
20
Example 3
Find the Fourier series for the function defined by
2
4 ) ( x x f = , 2 2 x
Solution
This is an even function, so
0 =
n
b
=
L
L
dx x f
L
a ) (
1
0
3
16
3
16
16
2
1
3
8
8
3
8
8
2
1
3
4
2
1
) 4 (
2
1
2
2
3
2
2
2
=
=
=
x
x
dx x
OR
=
L
dx x f
L
a
0
0
) (
2
3
16
0
3
8
8
3
4
) 4 (
2
2
2
0
3
2
0
2
=
=
=
x
x
dx x
=
L
n
dx x
L
n
x f
L
a
0
cos ) (
2
=
2
0
2
cos ) 4 (
2
2
dx x
L
n
x
Integration by tabular method!
Sign
dx du /
dv
+
2
4 x
x
n
2
cos
x 2
x
n
n 2
sin
2
+
2
x
n
n 2
cos
4
2 2
0
x
n
n 2
sin
8
3 3
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
21
) (cos
16
0 0 0 sin
16
cos
16
0
2
sin
) 2 ( 8
2
cos
) 2 ( 4
2
sin
) 4 ( 2
2 2
3 3 2 2
2
0
3 3 2 2
2
n
n
n
n
n
n
x
n
n
x
n
n
x
x
n
n
x
=
+ =
=
K , 5 , 3 , 1 = n :
=
2 2 2 2
1 16
) 1 (
16
n n
a
n
K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n :
=
2 2 2 2
1 16
) 1 (
16
n n
a
n
So the Fourier series,
+ + =
+ =
+ + =
=
+
=
L x x x
x
n
n
x
L
n
b x
L
n
a a x f
n
n
n
n
n
n
2
3
cos
9
1
cos
4
1
2
cos
16
3
8
2
cos
) 1 ( 16
3
8
sin cos
2
1
) (
2
1
2
1
2
1 1
0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FOURIER SERIES FOR HALF RANGE SERIES
The given function over only half of the range.
Can be extend as an
1. Odd function half-range sine series
2. Even function half-range cosine series
3. Neither function half-range series
The Fourier coefficients,
n
a a ,
0
and
n
b for half range series are same as the
Fourier coefficients for odd and even functions.
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
22
Example
Given
) 2 ( ) (
0 , 2 ) (
+ =
< < =
x f x f
x x x f
y
x
2
Solution
(a) Half-range cosine series
cosine terms
0
a
n
a
0 =
n
b
y
x
2
(b) Half-range sine series
sine terms
0
0
= a
0 =
n
a
n
b
y
x
2
(c) Half-range series
cosine terms
sine terms
0
a
n
a
n
b
y
x
2
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
23
Example 1
A function is defined by ) (x f
). 2 ( ) (
. , 3
, 0 , 0
) (
2
2
+ =
< <
<
=
x f x f
x
x
x f
y
x
3
2
Represent the function as
(a) half-range sine series,
(b) half-range cosine series.
Solution
(a) Half-range sine series is an odd function
y
x
3
2
3
So 0
0
= =
n
a a
0
sin ) (
2
nxdx x f b
n
+ =
2
cos cos
6
cos
3 2
sin 3 sin 0
2
2 /
2 /
2 /
0
n
n
n
nx
n
nxdx nxdx
: K , 5 , 3 , 1 = n
= =
n n
b
n
1 6
) 0 1 (
6
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
24
Because of the
2
n
, we need to look at alternate even values of . n
= n 2, 6, 10, :
=
n n
b
n
2 6
)) 1 ( 1 (
6
= n 4, 8, 12, : 0 ) 1 1 (
6
=
=
n
b
n
So the half-range Fourier sine series,
=
+ + =
1 1
0
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
nx b nx a a x f
+ + + =
+ + + =
L
L
5
5 sin
3
3 sin
2 sin sin
6
5
5 sin
3
3 sin
2
2 sin 2
sin
6
x x
x x
x x x
x
(b) Half-range cosine series is an even function
y
x
3
2
So 0 =
n
b
0
0
) (
2
dx x f a
[ ]
3
2
3
3
2
3
2
3 0
2
2
2
2 /
0
=
=
=
+ =
x
dx dx
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
25
0
cos ) (
2
nxdx x f a
n
+ =
2
sin sin
6
sin
3 2
cos 3 cos 0
2
2 /
2 /
2 /
0
n
n
n
nx
n
nxdx nxdx
K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n : 0 ) 0 0 (
6
= =
n
a
n
Because of the
2
n
, we need to look at alternate odd values of n.
= n 1, 5, 9, , :
= =
n n
a
n
1 6
) 1 0 (
6
= n 3, 7, 11, :
= =
n n
a
n
1 6
)) 1 ( 0 (
6
So the half-range Fourier cosine series,
+ =
+ + + =
1
1 2
) 1 2 cos(
) 1 (
6
2
3
5
5 cos
3
3 cos
cos
6
2
3
) (
n
n
n
x n
x x
x x f
L
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 2
Find the half-range Fourier cosine and sine series for
x x f = ) ( , < x 0 .
Solution
(a) Half-range cosine series
y
x
2 2
So . 0 =
n
b
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
26
0
0
) (
2
dx x f a
=
=
0
2
0
2
2
2
x
xdx
0
cos
2
nxdx x a
n
) 1 (cos
2
) 1 (
1
0 cos
1
sin
2
cos
1
sin
2
2
2 2
0
2
=
+ =
+ =
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
nx
n
nx
n
x
K , 5 , 3 , 1 = n ;
= =
2 2
1 4
) 1 1 (
2
n n
a
n
K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n ; 0 ) 1 1 (
2
2
= =
n
a
n
So the half-range Fourier cosine series,
+ + + =
+ + =
1
2
1 1
0
) 1 2 (
) 1 2 cos( 4
2
25
5 cos
9
3 cos
cos
4
2
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
n
n
x n
x x
x
nx b nx a a x f
L
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
27
(b) Half-range sine series
y
x
2 2
So 0
0
= =
n
a a
0
sin
2
nxdx x b
n
) (cos
2
0 0
sin cos 2
sin cos 2
2
0
2
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
nx
n
x n x
=
=
: K , 5 , 3 , 1 = n
= =
n n
b
n
1
2 ) 1 (
2
: K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n
= =
n n
b
n
1
2 ) 1 (
2
So the half-range Fourier cosine series,
=
+ + =
1 1
0
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
nx b nx a a x f
n
nx
x x x
x
x x x x
n
sin
) 1 ( 2
4
4 sin
3
3 sin
2
2 sin
sin 2
4 sin
4
2
3 sin
3
2
2 sin sin 2
1
+
=
+ + =
+ + =
L
L
n 1 =
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
28
Example 3
Determine a half-range Fourier cosine series for
x x f 2 ) ( = , < x 0 .
Solution
Cosine series is an even series, so 0 =
n
b
0
0
) (
2
dx x f a [ ]
2
2
2
2
0
2
0
= = =
x xdx
0
cos 2
2
nxdx x a
n
) 1 (cos
4
) 1 (
1
0 cos
1
sin
4
cos
1
sin
4
2
2 2
0
2
=
+ =
+ =
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
nx
n
nx
n
x
K , 5 , 3 , 1 = n :
= =
2 2
1 8
) 1 1 (
4
n n
a
n
K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n : 0 ) 1 1 (
4
2
= =
n
a
n
So the half-range Fourier cosine series,
=
+ + =
1 1
0
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
nx b nx a a x f
+ + + =
1 n
2
) 1 2 (
) 1 2 cos( 8
25
5 cos
9
3 cos
cos
8
n
x n
x x
x
L
SRI / Series / Fourier Series
29
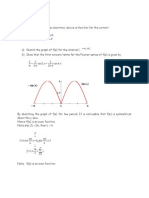
Example 4
Find the half-range Fourier sine series for
2
) ( x x f = , 1 0 < x .
Solution
Half-range sine series is an odd function, so 0
0
= =
n
a a
y
x
2 1 1 2
=
=
1
0
2
0
1
sin
1
2
sin ) (
2
dx x
n
x
dx x
L
n
x f
L
b
L
n
Sign
dx du /
dv
+
2
x
x n sin
x 2
x n
n
cos
1
+
2
x n
n
sin
1
2 2
0
x n
n
cos
1
3 3
+ +
+ +
=
) 1 (cos
2 cos
2
2 cos 2 cos
2
2
0 0
cos 2 sin 2 cos
2
cos 2 sin 2 cos
2
3 3
3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3 2 2
1
0
3 3 2 2
2
n
n n
n
n n
n
n
n
n n
n
n
n
n
n
n
x n
n
x n x
n
x n x
K , 5 , 3 , 1 = n :
= =
2 3 3 3
4 1 2 8 2
n n n n
b
n
K , 6 , 4 , 2 = n :
=
n n n
b
n
1 2
) 1 1 (
2 1
2
3 3
So the half-range Fourier sine series,
=
+ + =
1 1
0
sin cos
2
1
) (
n
n
n
n
x n b x n a a x f
= L
3
3 sin
3
4
3
1
2
2 sin
sin
4
1
2
2 3 2
x x
x
You might also like
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 pagesAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Process Control-Thomas E MarlinDocument1,026 pagesProcess Control-Thomas E MarlinDhini Cibilz80% (10)
- Rayleigh Ritz MethodDocument7 pagesRayleigh Ritz Methodrameshbabu_197963% (8)
- MA1505 Tutorial Solution 1Document6 pagesMA1505 Tutorial Solution 1Bilguun BatboldNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Helicopter Landing GearDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Helicopter Landing GearMihaela NastaseNo ratings yet
- As Further Mathematics - CP1 - Vectors MSDocument12 pagesAs Further Mathematics - CP1 - Vectors MSjimNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics 1 - Tut SheetsDocument3 pagesApplied Mathematics 1 - Tut SheetsRajiv MishraNo ratings yet
- EE - 210 - Exam 3 - Spring - 2008Document26 pagesEE - 210 - Exam 3 - Spring - 2008doomachaleyNo ratings yet
- Answers 2009-10Document19 pagesAnswers 2009-10Yoga RasiahNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1) - Home Work: Q 8: Determine The Fourier Series Up To and Including The Third Harmonic For The FunctionDocument5 pagesSheet (1) - Home Work: Q 8: Determine The Fourier Series Up To and Including The Third Harmonic For The FunctionZayn AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument31 pagesFourier SeriesSachi DhanandamNo ratings yet
- Formula MatematiceDocument4 pagesFormula MatematiceAnonymous eWnwHDNo ratings yet
- Calculus Made Ridiculusly EasyDocument250 pagesCalculus Made Ridiculusly Easyiamsandesh91% (11)
- Chapter 5 Fourier Analysis: 5-1 Fourier Series of A Periodical FunctionDocument20 pagesChapter 5 Fourier Analysis: 5-1 Fourier Series of A Periodical FunctionVienNgocQuangNo ratings yet
- Exam - 2011 10 28Document5 pagesExam - 2011 10 28lieth-4No ratings yet
- (A) If F (X) and G (X) Have Period P, Show That H (X) Af (X) + BG (X) (A, B, Constant)Document15 pages(A) If F (X) and G (X) Have Period P, Show That H (X) Af (X) + BG (X) (A, B, Constant)Heather JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Formula For TPDEDocument11 pagesFormula For TPDEGowtham Raj100% (2)
- Fourier SeriesDocument81 pagesFourier SeriesBunty PereraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Council Exam Mathematics C101 Solutions To Exam Paper 2004Document2 pagesEngineering Council Exam Mathematics C101 Solutions To Exam Paper 2004cataiceNo ratings yet
- Ux VX : Função Derivada Da Função Fórmulas de IntegraçãoDocument2 pagesUx VX : Função Derivada Da Função Fórmulas de IntegraçãoJosierBaiottoNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions PDFDocument10 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions PDFJiung WeiNo ratings yet
- Estabilidad Interna y Entrada-Salida de Sistemas Continuos: Udec - DieDocument10 pagesEstabilidad Interna y Entrada-Salida de Sistemas Continuos: Udec - DieagustinpinochetNo ratings yet
- Circular FunctionsDocument44 pagesCircular Functionsrica_marquezNo ratings yet
- Formula2 (1) UpdatedDocument3 pagesFormula2 (1) UpdatedAmm RoehNo ratings yet
- Gevorderde SysteemidentificatieDocument243 pagesGevorderde SysteemidentificatiefonsverbiestNo ratings yet
- (A305) Otomatik Kontrol Ders Notu (Slayt)Document27 pages(A305) Otomatik Kontrol Ders Notu (Slayt)Mücahit Ezel100% (1)
- Calculus BookletDocument6 pagesCalculus Bookletangie81No ratings yet
- Maths FormulaDocument4 pagesMaths Formulamickey_disney93No ratings yet
- 2010 AJC Paper 1solDocument6 pages2010 AJC Paper 1solnothingtodo1992No ratings yet
- Chapter 4XDocument96 pagesChapter 4XAndrei FirteNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis of Plate With HoleDocument8 pagesStress Analysis of Plate With Holeketu009100% (1)
- 7 7 7 7 Topic Topic Topic Topic: Laplace Transforms Laplace Transforms Laplace Transforms Laplace TransformsDocument10 pages7 7 7 7 Topic Topic Topic Topic: Laplace Transforms Laplace Transforms Laplace Transforms Laplace TransformsManpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1) - Home Work: Q 8: Determine The Fourier Series Up To and Including The Third Harmonic For The FunctionDocument5 pagesSheet (1) - Home Work: Q 8: Determine The Fourier Series Up To and Including The Third Harmonic For The FunctionZayn AhmedNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document52 pagesCH 06Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- SOV ConductionDocument47 pagesSOV ConductionRanadip AcharyaNo ratings yet
- תקשורת ספרתית- הרצאה 6 - מסננת מתואמת, איפנון בסיסDocument40 pagesתקשורת ספרתית- הרצאה 6 - מסננת מתואמת, איפנון בסיסRonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 - Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument12 pagesLesson 12 - Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsAlexander PiniliNo ratings yet
- Text Book: Barrante, 3rd, 2004.: Applied Mathematics For Physical ChemistryDocument38 pagesText Book: Barrante, 3rd, 2004.: Applied Mathematics For Physical ChemistryTzung-Ying YangNo ratings yet
- Problem TPDEDocument8 pagesProblem TPDEGowtham RajNo ratings yet
- Random Process in Analog Communication SystemsDocument91 pagesRandom Process in Analog Communication SystemsEkaveera Gouribhatla100% (1)
- AIEEE MathsDocument3 pagesAIEEE MathsSk SharukhNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument27 pagesMathematicsneilmehta87No ratings yet
- VAR Models: Gloria González-RiveraDocument32 pagesVAR Models: Gloria González-RiveraVinko ZaninovićNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- Chpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewDocument56 pagesChpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewKrishna MyakalaNo ratings yet
- FEM Prof NotesDocument96 pagesFEM Prof NotesTahir BashirNo ratings yet
- Integration E.G.Document11 pagesIntegration E.G.azzyhiscoxNo ratings yet
- Revision FourierDocument19 pagesRevision FourierHazim NaharNo ratings yet
- Double Integrals: A y X F Da y X FDocument31 pagesDouble Integrals: A y X F Da y X FsaperuddinNo ratings yet
- Mat Sup 03062011 A B TM SolDocument5 pagesMat Sup 03062011 A B TM SolVictor MartinezNo ratings yet
- Four Series Unit IDocument32 pagesFour Series Unit IkausikraamNo ratings yet
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument26 pagesFourier SeriesPurushothamanNo ratings yet
- 01b-Fourier Series RevisionDocument37 pages01b-Fourier Series RevisionGeorges YoussefNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sweet Baby Dresses in Crochet: 4 Dresses in Sizes Newborn to 24 Months, with Matching AccessoriesFrom EverandSweet Baby Dresses in Crochet: 4 Dresses in Sizes Newborn to 24 Months, with Matching AccessoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- SNDEY11FDocument580 pagesSNDEY11FAbhishek PatraNo ratings yet
- A Nearly Uniform Traffic Flow Example: Figure 70-2 Characteristics Along Which The Density Is ConstantDocument12 pagesA Nearly Uniform Traffic Flow Example: Figure 70-2 Characteristics Along Which The Density Is ConstantnegurrasNo ratings yet
- (MATH1013) (2016) (F) Midterm Wsuab 41338Document9 pages(MATH1013) (2016) (F) Midterm Wsuab 41338陳希程No ratings yet
- Mathematics Book List Prakash Rajpurohit's BlogDocument2 pagesMathematics Book List Prakash Rajpurohit's BlogdkdhirajNo ratings yet
- University TechnologyDocument16 pagesUniversity TechnologyAleksandarBukvaNo ratings yet
- Module 4: Dynamic Programming: Design and Analysis of Algorithms 21CS42Document105 pagesModule 4: Dynamic Programming: Design and Analysis of Algorithms 21CS42Prajwal OconnerNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics-Lec8-Divergence Theorem, Energy and Electric PotentialDocument15 pagesElectromagnetics-Lec8-Divergence Theorem, Energy and Electric PotentialNerlisa NadadoNo ratings yet
- 10.lesson Plan in Trigonometric RatiosDocument7 pages10.lesson Plan in Trigonometric RatiosAeron TamaniNo ratings yet
- Epsilon DeltaDocument4 pagesEpsilon DeltasprokonoinoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Simultaneous Linear Equations: Fall, 202XDocument7 pagesChapter 6: Simultaneous Linear Equations: Fall, 202X이수민No ratings yet
- MUSA Final Numec 5 SETS PDFDocument123 pagesMUSA Final Numec 5 SETS PDFAlbert Chong100% (1)
- Desmos Heart Equation - Google SearchDocument1 pageDesmos Heart Equation - Google SearchHarry JohnsonNo ratings yet
- NPTEL Basics of FEM - I Week 4 SolutionsDocument18 pagesNPTEL Basics of FEM - I Week 4 SolutionsVISMAY KG MechNo ratings yet
- Regression Weights: (Group Number 1 - Default Model)Document96 pagesRegression Weights: (Group Number 1 - Default Model)Alifa Nasyahta RosianaNo ratings yet
- Vector Norms: X. X Is Denoted As Kxk. X RDocument8 pagesVector Norms: X. X Is Denoted As Kxk. X Rap021No ratings yet
- Math 21 Samplex For FinalsDocument2 pagesMath 21 Samplex For Finalsvectorredz10No ratings yet
- 4th International Conference On Numerical Ship HydrodynamicsDocument570 pages4th International Conference On Numerical Ship HydrodynamicsTahsin Tezdogan100% (1)
- Exercise - Binary Integer ProgrammingDocument3 pagesExercise - Binary Integer ProgrammingSergio Alexander GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic SequencesDocument3 pagesArithmetic SequencestuvvacNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Time Reversal and Linear Equalization in DCDocument3 pagesRelationship Between Time Reversal and Linear Equalization in DCMohamed BGcityNo ratings yet
- Geometric Reference System - Ch. Jekeli PDFDocument209 pagesGeometric Reference System - Ch. Jekeli PDFkyuNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Analytical Mechanics 2010Document62 pagesAn Introduction To Analytical Mechanics 2010antoniolamadeuNo ratings yet
- Prob DBDocument3 pagesProb DBSandyArevaloNo ratings yet
- Solving Systems of Fractional Differential EquatioDocument11 pagesSolving Systems of Fractional Differential EquatioamonateeyNo ratings yet
- The Heat EquationDocument13 pagesThe Heat EquationRahulNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Harmonic and Other SequenceDocument24 pagesWeek 6 - Harmonic and Other SequenceJeff LacasandileNo ratings yet