Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is RNA?: DNA Structure
What Is RNA?: DNA Structure
Uploaded by
rockingtwo07Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is RNA?: DNA Structure
What Is RNA?: DNA Structure
Uploaded by
rockingtwo07Copyright:
Available Formats
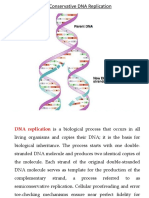
DNA structure
DNA is usually a double-helix and has two strands running in opposite directions. (There are
some examples of viral DNA which are single-stranded). ach chain is a polymer of subunits
called nucleotides (hence the name polynucleotide).
ach strand has a bac!bone made up of (deoxy-ribose) sugar molecules lin!ed together by
phosphate groups. The "# $ of a sugar molecule is connected through a phosphate group to the %#
$ of the next sugar. This lin!age is also called "#-%# phosphodiester lin!age. All DNA strands are
read from the %# to the "# end where the %# end terminates in a phosphate group and the "# end
terminates in a sugar molecule.
What is RNA?
Ribonucleic acid, or RNA is one of the three major biological macromolecules that are essential for all
known forms of life (along with DNA and proteins). A central tenant of molecular biology states that the
flow of genetic information in a cell is from DNA through RNA to proteins !DNA makes RNA makes
protein". #roteins are the workhorses of the cell$ they play leading roles in the cell as en%ymes, as
structural components, and in cell signaling, to name just a few. DNA(deo&yribonucleic acid) is
considered the !blueprint" of the cell$ it carries all of the genetic information re'uired for the cell to grow, to
take in nutrients, and to propagate. RNA(in this role(is the !DNA photocopy" of the cell. )hen the cell
needs to produce a certain protein, it acti*ates the protein+s gene(the portion of DNA that codes for that
protein(and produces multiple copies of that piece of DNA in the form of messenger RNA, or mRNA. ,he
multiple copies of mRNA are then used to translate the genetic code into protein through the action of the
cell+s protein manufacturing machinery, the ribosomes. ,hus, RNA e&pands the 'uantity of a gi*en protein
that can be made at one time from one gi*en gene, and it pro*ides an important control point for
regulating when and how much protein gets made.
-or many years RNA was belie*ed to ha*e only three major roles in the cell(as a DNA photocopy
(mRNA), as a coupler between the genetic code and the protein building blocks (tRNA), and as a
structural component of ribosomes (rRNA). .n recent years, howe*er, we ha*e begun to reali%e that the
roles adopted by RNA are much broader and much more interesting. )e now know that RNA can also act
as en%ymes (called ribo%ymes) to speed chemical reactions. .n a number of clinically important *iruses
RNA, rather than DNA, carries the *iral genetic information. RNA also plays an important role in
regulating cellular processes(from cell di*ision, differentiation and growth to cell aging and death. Defects
in certain RNAs or the regulation of RNAs ha*e been implicated in a number of important human
diseases, including heart disease, some cancers, stroke and many others.
You might also like
- Virology Assignment0Document11 pagesVirology Assignment0Affan sageNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure: What Is RNA?Document3 pagesDNA Structure: What Is RNA?rockingtwo07No ratings yet
- Dna - Rna: DNA Is The Genetic Material of All Cellular OrganismsDocument6 pagesDna - Rna: DNA Is The Genetic Material of All Cellular Organismsmirza putraNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Rna World Biotech ProjectDocument18 pagesNucleic Acids Rna World Biotech ProjectSakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- RNA Ribonucleic Acid (English Pronunciation: /raɪbɵ - Nju Kleɪ - Ɨk Æsɪd/), or RNA, Is One of The Three MajorDocument1 pageRNA Ribonucleic Acid (English Pronunciation: /raɪbɵ - Nju Kleɪ - Ɨk Æsɪd/), or RNA, Is One of The Three MajorPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines 363 P. Casal ST., Quiapo, ManilaDocument6 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines 363 P. Casal ST., Quiapo, ManilaGellene GarciaNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure: What Is RNA?Document5 pagesDNA Structure: What Is RNA?rockingtwo07No ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument3 pagesGenetic CodeAngelica PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Genes As DnaDocument16 pagesResearch Paper Genes As DnaMarrell UnajanNo ratings yet
- Def of Terms & Res LocaleDocument7 pagesDef of Terms & Res LocaleAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Auto Saved)Document7 pagesGenetics Auto Saved)natseeaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Genetic Disorder?Document11 pagesWhat Is A Genetic Disorder?Jemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- Concept of Central DogmaDocument1 pageConcept of Central DogmaIsmaël BikomamangaNo ratings yet
- Heredity Inheritance and Variations PDFDocument56 pagesHeredity Inheritance and Variations PDFNoean LargoNo ratings yet
- Gift RNADocument13 pagesGift RNAPeter DindahNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids OnlineDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids OnlineIsabel DizonNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument25 pagesTranscriptionYamunaa ElencovanNo ratings yet
- Dna & RnaDocument11 pagesDna & Rnabelal.hassan3No ratings yet
- DNA Structure: What Is RNA?Document3 pagesDNA Structure: What Is RNA?rockingtwo07No ratings yet
- Semi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDocument13 pagesSemi-Conservative DNA ReplicationMohd JunaidNo ratings yet
- Week 15 Lecture 560B On LineDocument9 pagesWeek 15 Lecture 560B On LineTheNourishedSproutNo ratings yet
- What Are The Key Differences Between DNA and RNADocument5 pagesWhat Are The Key Differences Between DNA and RNAGloriel PateñoNo ratings yet
- In Our Cells: From Microscopes To MoleculesDocument9 pagesIn Our Cells: From Microscopes To Moleculesshamu081No ratings yet
- Lesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2Document7 pagesLesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2almafebe caselNo ratings yet
- Chemical Structure of RNADocument7 pagesChemical Structure of RNARoger EfrainNo ratings yet
- Compare The Structure and Functions of DNA and RNADocument2 pagesCompare The Structure and Functions of DNA and RNAQwec CiahcNo ratings yet
- Ribosome and Protein Synthesis: By: Delfi Zurita NIM: RSA1C411009Document16 pagesRibosome and Protein Synthesis: By: Delfi Zurita NIM: RSA1C411009Atikatul MutmainahNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering 3Document32 pagesGenetic Engineering 3shrouqNo ratings yet
- How Cells Work CompilationDocument18 pagesHow Cells Work CompilationJocelyn Diaz AbangNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Store, Transmit and Help Express Hereditary InformationDocument6 pagesNucleic Acids Store, Transmit and Help Express Hereditary InformationDanielle GuerraNo ratings yet
- Coursenotesdomain 4 InformationDocument29 pagesCoursenotesdomain 4 Informationapi-300668314No ratings yet
- Rna World: GENETICS/Molecular Basis of Inheritance /BIBATSU SALAM / /page No.29Document3 pagesRna World: GENETICS/Molecular Basis of Inheritance /BIBATSU SALAM / /page No.29Salty ChipsNo ratings yet
- 26.01 DNA-Dependent Synthesis of RNADocument26 pages26.01 DNA-Dependent Synthesis of RNAUttam BhuniaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Mutations Science Presentation in Blue Orange Flat Graphic StyleDocument30 pagesGenetic Mutations Science Presentation in Blue Orange Flat Graphic StylechrishhhaaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Genetic: I. Organization of Genetic Information-General Concept - A. Deoxyribonucleid Acid (DNA)Document62 pagesBacterial Genetic: I. Organization of Genetic Information-General Concept - A. Deoxyribonucleid Acid (DNA)wijayantiNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Genetics: Genetic Elements Such As Plasmids or Bacteriophages (BacterialDocument14 pagesBacterial Genetics: Genetic Elements Such As Plasmids or Bacteriophages (Bacterialعلي الكوافيNo ratings yet
- 1 The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument6 pages1 The Central Dogma of Molecular Biologydeladestianiaji2490100% (1)
- Resume 293-305Document8 pagesResume 293-305Amirah NviNo ratings yet
- Full Genetics From Genes To Genomes 6Th Edition Hartwell Solutions Manual Online PDF All ChapterDocument58 pagesFull Genetics From Genes To Genomes 6Th Edition Hartwell Solutions Manual Online PDF All Chapterdaniaakonkani100% (6)
- 230 GeneticCodeRNAandProteinSynthesis PDFDocument22 pages230 GeneticCodeRNAandProteinSynthesis PDFSubhecchha BaidyaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ReportDocument15 pagesNucleic Acid Reportmumu memeNo ratings yet
- Mukesh's Biology Project TranscriptionDocument33 pagesMukesh's Biology Project TranscriptionM.S.Mukesh Kumar X-ANo ratings yet
- Genetic InformationDocument7 pagesGenetic Informationsheryladhiambo046No ratings yet
- Q3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisDocument65 pagesQ3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Biotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 5 Role of DNA RNA and Protein in The Transmission of Hereditary Traits 3Document14 pagesBiotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 5 Role of DNA RNA and Protein in The Transmission of Hereditary Traits 3Aileen Ocampo100% (1)
- Synthesis of ProtiensDocument10 pagesSynthesis of ProtiensJeth JuradoNo ratings yet
- Biology InformationDocument6 pagesBiology InformationIgnacio LeonNo ratings yet
- Rotein Ynthesis: Big PictureDocument3 pagesRotein Ynthesis: Big PicturehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- GQA-Science10 Q3 Wk4-5 Protein-Synthesis GQA - LRQADocument14 pagesGQA-Science10 Q3 Wk4-5 Protein-Synthesis GQA - LRQALevi AckermanNo ratings yet
- DNA To RNA Activity NinthDocument4 pagesDNA To RNA Activity NinthDeiby PovedaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument7 pagesScienceRonald Alexandrei TropelNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument24 pagesBiology ProjectAnant KumarNo ratings yet
- AC Dogma CentralDocument3 pagesAC Dogma CentralsdsomosaNo ratings yet
- Heredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA InformationDocument45 pagesHeredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA Informationkath chandriaNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic Reticulum and RibosomesDocument16 pagesEndoplasmic Reticulum and RibosomesRis habhNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Genetics From Genes To Genomes 6th Edition Hartwell Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument58 pages(Download PDF) Genetics From Genes To Genomes 6th Edition Hartwell Solutions Manual Full Chapteriqbalydallys100% (10)
- 2009 SolutionsDocument21 pages2009 SolutionsSonal Power UnlimitdNo ratings yet
- ESCI 2nd QTRDocument8 pagesESCI 2nd QTRBye Not thisNo ratings yet
- 05-02-Genetika MikroorganismeDocument48 pages05-02-Genetika MikroorganismeKinad DanikNo ratings yet
- Nobel Prize in Chemistry Eric Betzig William Moerner Stefan Hell Optical Microscopy Nano DimensionDocument1 pageNobel Prize in Chemistry Eric Betzig William Moerner Stefan Hell Optical Microscopy Nano Dimensionrockingtwo07No ratings yet
- William Moerner Optical Microscopy Nano Dimension: Nobel Prize in Chemistry Eric Betzig Stefan HellDocument1 pageWilliam Moerner Optical Microscopy Nano Dimension: Nobel Prize in Chemistry Eric Betzig Stefan Hellrockingtwo07No ratings yet
- On October 8, 2014, The Was Awarded To, and For "The Development of Super-Resolved Fluorescence Microscopy," Which Brings " Into The "Document1 pageOn October 8, 2014, The Was Awarded To, and For "The Development of Super-Resolved Fluorescence Microscopy," Which Brings " Into The "rockingtwo07No ratings yet
- Centrifugation: HistoryDocument3 pagesCentrifugation: Historyrockingtwo07No ratings yet
- CentrifugationDocument2 pagesCentrifugationrockingtwo07100% (1)
- CentrifugationDocument3 pagesCentrifugationrockingtwo07No ratings yet
- CentrifugationDocument2 pagesCentrifugationrockingtwo07No ratings yet
- Centrifugation Centrifugation Is A Process That Involves The Use of The Centrifugal Force For TheDocument1 pageCentrifugation Centrifugation Is A Process That Involves The Use of The Centrifugal Force For Therockingtwo07No ratings yet
- Centrifugation Centrifugation Is A Process That Involves The Use of The Centrifugal Force For TheDocument1 pageCentrifugation Centrifugation Is A Process That Involves The Use of The Centrifugal Force For Therockingtwo07No ratings yet
- Chromatography How Does It Work? Like Magic!: The Figure Below Will Help You To Follow Along in Our DiscussionDocument2 pagesChromatography How Does It Work? Like Magic!: The Figure Below Will Help You To Follow Along in Our Discussionrockingtwo07No ratings yet