Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GSM Network Basics: Power System of A Typical Bts Site
GSM Network Basics: Power System of A Typical Bts Site
Uploaded by
Sameer SulemanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Excitation SystemDocument13 pagesExcitation SystemKVVNo ratings yet
- GP Power System OverviewDocument36 pagesGP Power System OverviewMd.Bellal HossainNo ratings yet
- Electrical Estimation & Costing - 18EE822 2022-23: Mrs - Tarakeshwari V, Asst. Professor Department of EEE, SJBITDocument27 pagesElectrical Estimation & Costing - 18EE822 2022-23: Mrs - Tarakeshwari V, Asst. Professor Department of EEE, SJBITabbgowdaNo ratings yet
- Practical 2Document7 pagesPractical 2Sunny DograNo ratings yet
- BTS 2000 Conference Paper IEEE IAS PCI Conference 2004Document11 pagesBTS 2000 Conference Paper IEEE IAS PCI Conference 2004kvramanan_1No ratings yet
- Fast Bus Transfer Systems For Critical Process ContinuityDocument11 pagesFast Bus Transfer Systems For Critical Process ContinuityamdatiNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basics of MTDC SystemsDocument24 pagesIntroduction and Basics of MTDC SystemsmadhanNo ratings yet
- SMPSDocument10 pagesSMPSASPIRER63No ratings yet
- BSNL (Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited) : A Presentation OnDocument25 pagesBSNL (Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited) : A Presentation OnMahesh Kumar NigamNo ratings yet
- Chaper 10 System Design and Integration of Grid-Tied SystemsDocument21 pagesChaper 10 System Design and Integration of Grid-Tied SystemsSabri BouloumaNo ratings yet
- Static Excitation System-AMTECHDocument24 pagesStatic Excitation System-AMTECHsssduduNo ratings yet
- Technical Comparison of On-Line vs. Line-Interactive UPS DesignsDocument14 pagesTechnical Comparison of On-Line vs. Line-Interactive UPS Designsdrpiratheepan4274No ratings yet
- Tribhuvan UniversityDocument14 pagesTribhuvan UniversitySudhakar ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Uninterruptible Power For Modern Data Processing: White Paper: Tw0051Document16 pagesOptimizing Uninterruptible Power For Modern Data Processing: White Paper: Tw0051Hüthâifâ AbdérahmânNo ratings yet
- Manakula Vinayagar Institute of TechnologyDocument16 pagesManakula Vinayagar Institute of TechnologyAbdul AsifNo ratings yet
- 120109arti - Rai StatcomDocument5 pages120109arti - Rai StatcomjobNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Strongly Supports Electronic Power System by Excellent Power System Analysis TechnologyDocument1 pageHitachi Strongly Supports Electronic Power System by Excellent Power System Analysis TechnologygopiNo ratings yet
- ABB Generations - 20 Onboard DC GridDocument6 pagesABB Generations - 20 Onboard DC Gridashishdce7643No ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters: AbstractDocument8 pagesHVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters: AbstractVelu SamyNo ratings yet
- Grid Station Report of Internship at IESCO: 2.4.1.2.3. Auto TransformersDocument5 pagesGrid Station Report of Internship at IESCO: 2.4.1.2.3. Auto TransformersMuhammad Asif IqbalNo ratings yet
- PRS Little Barford - RevADocument2 pagesPRS Little Barford - RevAxolraxNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Improvement of Distribution System Using D-STATCOMDocument11 pagesPower Quality Improvement of Distribution System Using D-STATCOMShashankNo ratings yet
- AC Auxiliary Systems in Power Substations Design Requirements and EquipmentDocument13 pagesAC Auxiliary Systems in Power Substations Design Requirements and EquipmentAleksandarNo ratings yet
- Electrical High Rise BuildingDocument11 pagesElectrical High Rise BuildingAstha Goyal100% (1)
- DC Standby Systems: Iorw Iorw IorwDocument3 pagesDC Standby Systems: Iorw Iorw IorwManuel CardozoNo ratings yet
- Tsewg tp19Document24 pagesTsewg tp197xz77bmvqfNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Transducers & PLC: SyllabusDocument29 pagesModule 1-Transducers & PLC: SyllabusRaja G VNo ratings yet
- Static Transfer Switch Design by NoelDocument4 pagesStatic Transfer Switch Design by Noeldarshan chirkeNo ratings yet
- Bi-Directional Battery Management SystemDocument28 pagesBi-Directional Battery Management SystemAjit NarwalNo ratings yet
- NetSure 501 DatasheetDocument2 pagesNetSure 501 DatasheetAnnBlissNo ratings yet
- A Cascaded Converter-Based Statcom With Energy StorageDocument6 pagesA Cascaded Converter-Based Statcom With Energy Storageamayac814No ratings yet
- Role of Power Electronic Devices and Applications in Aerospace TechnologyDocument7 pagesRole of Power Electronic Devices and Applications in Aerospace TechnologyAbhishek KhotNo ratings yet
- High Efficiency Bi-Directional DC-DC Converter For Charge Balancing Control of EV Application-Specific Battery StringsDocument6 pagesHigh Efficiency Bi-Directional DC-DC Converter For Charge Balancing Control of EV Application-Specific Battery StringsLE-225 Moulali ShaikNo ratings yet
- Ijest10 02 12 227Document7 pagesIjest10 02 12 227Aroma AamirNo ratings yet
- Estudio Tecnico-Despliegue Data Center 73-EndDocument107 pagesEstudio Tecnico-Despliegue Data Center 73-EndRei AmyNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics For Renewable Energy SystemsDocument33 pagesPower Electronics For Renewable Energy SystemssrilakshmisiriNo ratings yet
- Estudo CapacitorDocument9 pagesEstudo Capacitorsajo1000No ratings yet
- Applied Sciences: Development of A Loss Minimization Based Operation Strategy For Embedded BTB VSC HVDCDocument19 pagesApplied Sciences: Development of A Loss Minimization Based Operation Strategy For Embedded BTB VSC HVDChumudsaidNo ratings yet
- AC Auxiliary Systems in Power SubstDocument16 pagesAC Auxiliary Systems in Power SubstNepoliyanNo ratings yet
- V4i3 1616 PDFDocument6 pagesV4i3 1616 PDFjoy 11No ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument2 pagesPower ElectronicsG VigneshNo ratings yet
- Smart Grid Storage Management SystemDocument4 pagesSmart Grid Storage Management SystemjuevesNo ratings yet
- Battery Sizing Basics1Document7 pagesBattery Sizing Basics1وليد موسىNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter: Akshay R MishraDocument10 pagesDC-DC Converter: Akshay R MishraAugust mishraNo ratings yet
- Computer Power Supplies CHT 113Document5 pagesComputer Power Supplies CHT 113PythiusNo ratings yet
- DC BattryDocument36 pagesDC Battryelsayed abdemagiedNo ratings yet
- Protection System of Hybrid Insulated Sub-StationDocument8 pagesProtection System of Hybrid Insulated Sub-Stationshoaib faseehNo ratings yet
- (2010) Control Strategy of A Multi-Port, Grid Connected, Direct-DCDocument5 pages(2010) Control Strategy of A Multi-Port, Grid Connected, Direct-DCabc1231234454252452342No ratings yet
- Electronics Assignment: by S.rudhraprakash 09lm55 Dme (SW)Document4 pagesElectronics Assignment: by S.rudhraprakash 09lm55 Dme (SW)rvikneshNo ratings yet
- Application For Industrial Power SupplyDocument5 pagesApplication For Industrial Power SupplySunghoonie KangNo ratings yet
- Regulated Power Supply-Block Diagram, Circuit Diagram, WorkingDocument17 pagesRegulated Power Supply-Block Diagram, Circuit Diagram, WorkingsridharparthipanNo ratings yet
- STATCOMDocument5 pagesSTATCOMVenkateshNo ratings yet
- Eltek Middle East (System Training) : by Mahmood SheikhDocument47 pagesEltek Middle East (System Training) : by Mahmood Sheikhsamad_omidvar6292No ratings yet
- Methods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesFrom EverandMethods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Basics: Wcdma TechnologyDocument2 pagesGSM Network Basics: Wcdma TechnologySameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- Site Master S325D: Cable and Antenna Analyzer, 250 MHZ To 2500 MHZDocument12 pagesSite Master S325D: Cable and Antenna Analyzer, 250 MHZ To 2500 MHZSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- Tower & AntennaDocument3 pagesTower & AntennaSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM IdentitiesDocument3 pagesGSM IdentitiesSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Basics: Transmission PlanningDocument4 pagesGSM Network Basics: Transmission PlanningSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM Network BasicsDocument2 pagesGSM Network BasicsSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Basics: Mobile Originating CallDocument2 pagesGSM Network Basics: Mobile Originating CallSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM CellDocument2 pagesGSM CellSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Basics: Authentication Process of A SubscriberDocument2 pagesGSM Network Basics: Authentication Process of A SubscriberSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
GSM Network Basics: Power System of A Typical Bts Site
GSM Network Basics: Power System of A Typical Bts Site
Uploaded by
Sameer SulemanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GSM Network Basics: Power System of A Typical Bts Site
GSM Network Basics: Power System of A Typical Bts Site
Uploaded by
Sameer SulemanCopyright:
Available Formats
8/2/13 Power System
gsmbasics.awardspace.info/power.htm 1/1
GSM Network Basics
An Introduction to GSM Networks
POWER SYSTEM OF A TYPICAL BTS SITE
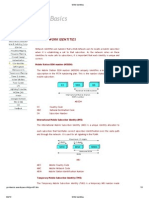
The following figure shows the Power System of a typical BTS site.
Power System of a typical BTS site
A typical BTS site has a 2 way power supply, CEB and Generator power. The ATS
(Automatic Transfer switch) is there to select the power source. The rectifier converts
the AC supply voltage to a DC voltage of -48V. The battery bank is there to supply the
power during an emergency case that is when both the CEB and Generator power fails.
The HRC (High Rupture Capacity Fuses) prevents the equipment from voltage spikes.
The BTS and modems operate in -48V DC. The rectifier unit converts the AC supply
into -48V DC. Battery bank is used as a back-up power at a mains failure. The
manufactures provide battery cells, the rack and other necessary components for every
battery bank.
Home | BSS | NSS | GSM Cell | Transmission Planning | Tower & Antenna | Power System | WCDMA | SS7
Chathuranga Perera,
Electrical Engineer
Ceylon Electricity Board
You might also like
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Excitation SystemDocument13 pagesExcitation SystemKVVNo ratings yet
- GP Power System OverviewDocument36 pagesGP Power System OverviewMd.Bellal HossainNo ratings yet
- Electrical Estimation & Costing - 18EE822 2022-23: Mrs - Tarakeshwari V, Asst. Professor Department of EEE, SJBITDocument27 pagesElectrical Estimation & Costing - 18EE822 2022-23: Mrs - Tarakeshwari V, Asst. Professor Department of EEE, SJBITabbgowdaNo ratings yet
- Practical 2Document7 pagesPractical 2Sunny DograNo ratings yet
- BTS 2000 Conference Paper IEEE IAS PCI Conference 2004Document11 pagesBTS 2000 Conference Paper IEEE IAS PCI Conference 2004kvramanan_1No ratings yet
- Fast Bus Transfer Systems For Critical Process ContinuityDocument11 pagesFast Bus Transfer Systems For Critical Process ContinuityamdatiNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basics of MTDC SystemsDocument24 pagesIntroduction and Basics of MTDC SystemsmadhanNo ratings yet
- SMPSDocument10 pagesSMPSASPIRER63No ratings yet
- BSNL (Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited) : A Presentation OnDocument25 pagesBSNL (Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited) : A Presentation OnMahesh Kumar NigamNo ratings yet
- Chaper 10 System Design and Integration of Grid-Tied SystemsDocument21 pagesChaper 10 System Design and Integration of Grid-Tied SystemsSabri BouloumaNo ratings yet
- Static Excitation System-AMTECHDocument24 pagesStatic Excitation System-AMTECHsssduduNo ratings yet
- Technical Comparison of On-Line vs. Line-Interactive UPS DesignsDocument14 pagesTechnical Comparison of On-Line vs. Line-Interactive UPS Designsdrpiratheepan4274No ratings yet
- Tribhuvan UniversityDocument14 pagesTribhuvan UniversitySudhakar ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Uninterruptible Power For Modern Data Processing: White Paper: Tw0051Document16 pagesOptimizing Uninterruptible Power For Modern Data Processing: White Paper: Tw0051Hüthâifâ AbdérahmânNo ratings yet
- Manakula Vinayagar Institute of TechnologyDocument16 pagesManakula Vinayagar Institute of TechnologyAbdul AsifNo ratings yet
- 120109arti - Rai StatcomDocument5 pages120109arti - Rai StatcomjobNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Strongly Supports Electronic Power System by Excellent Power System Analysis TechnologyDocument1 pageHitachi Strongly Supports Electronic Power System by Excellent Power System Analysis TechnologygopiNo ratings yet
- ABB Generations - 20 Onboard DC GridDocument6 pagesABB Generations - 20 Onboard DC Gridashishdce7643No ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters: AbstractDocument8 pagesHVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters: AbstractVelu SamyNo ratings yet
- Grid Station Report of Internship at IESCO: 2.4.1.2.3. Auto TransformersDocument5 pagesGrid Station Report of Internship at IESCO: 2.4.1.2.3. Auto TransformersMuhammad Asif IqbalNo ratings yet
- PRS Little Barford - RevADocument2 pagesPRS Little Barford - RevAxolraxNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Improvement of Distribution System Using D-STATCOMDocument11 pagesPower Quality Improvement of Distribution System Using D-STATCOMShashankNo ratings yet
- AC Auxiliary Systems in Power Substations Design Requirements and EquipmentDocument13 pagesAC Auxiliary Systems in Power Substations Design Requirements and EquipmentAleksandarNo ratings yet
- Electrical High Rise BuildingDocument11 pagesElectrical High Rise BuildingAstha Goyal100% (1)
- DC Standby Systems: Iorw Iorw IorwDocument3 pagesDC Standby Systems: Iorw Iorw IorwManuel CardozoNo ratings yet
- Tsewg tp19Document24 pagesTsewg tp197xz77bmvqfNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Transducers & PLC: SyllabusDocument29 pagesModule 1-Transducers & PLC: SyllabusRaja G VNo ratings yet
- Static Transfer Switch Design by NoelDocument4 pagesStatic Transfer Switch Design by Noeldarshan chirkeNo ratings yet
- Bi-Directional Battery Management SystemDocument28 pagesBi-Directional Battery Management SystemAjit NarwalNo ratings yet
- NetSure 501 DatasheetDocument2 pagesNetSure 501 DatasheetAnnBlissNo ratings yet
- A Cascaded Converter-Based Statcom With Energy StorageDocument6 pagesA Cascaded Converter-Based Statcom With Energy Storageamayac814No ratings yet
- Role of Power Electronic Devices and Applications in Aerospace TechnologyDocument7 pagesRole of Power Electronic Devices and Applications in Aerospace TechnologyAbhishek KhotNo ratings yet
- High Efficiency Bi-Directional DC-DC Converter For Charge Balancing Control of EV Application-Specific Battery StringsDocument6 pagesHigh Efficiency Bi-Directional DC-DC Converter For Charge Balancing Control of EV Application-Specific Battery StringsLE-225 Moulali ShaikNo ratings yet
- Ijest10 02 12 227Document7 pagesIjest10 02 12 227Aroma AamirNo ratings yet
- Estudio Tecnico-Despliegue Data Center 73-EndDocument107 pagesEstudio Tecnico-Despliegue Data Center 73-EndRei AmyNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics For Renewable Energy SystemsDocument33 pagesPower Electronics For Renewable Energy SystemssrilakshmisiriNo ratings yet
- Estudo CapacitorDocument9 pagesEstudo Capacitorsajo1000No ratings yet
- Applied Sciences: Development of A Loss Minimization Based Operation Strategy For Embedded BTB VSC HVDCDocument19 pagesApplied Sciences: Development of A Loss Minimization Based Operation Strategy For Embedded BTB VSC HVDChumudsaidNo ratings yet
- AC Auxiliary Systems in Power SubstDocument16 pagesAC Auxiliary Systems in Power SubstNepoliyanNo ratings yet
- V4i3 1616 PDFDocument6 pagesV4i3 1616 PDFjoy 11No ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument2 pagesPower ElectronicsG VigneshNo ratings yet
- Smart Grid Storage Management SystemDocument4 pagesSmart Grid Storage Management SystemjuevesNo ratings yet
- Battery Sizing Basics1Document7 pagesBattery Sizing Basics1وليد موسىNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter: Akshay R MishraDocument10 pagesDC-DC Converter: Akshay R MishraAugust mishraNo ratings yet
- Computer Power Supplies CHT 113Document5 pagesComputer Power Supplies CHT 113PythiusNo ratings yet
- DC BattryDocument36 pagesDC Battryelsayed abdemagiedNo ratings yet
- Protection System of Hybrid Insulated Sub-StationDocument8 pagesProtection System of Hybrid Insulated Sub-Stationshoaib faseehNo ratings yet
- (2010) Control Strategy of A Multi-Port, Grid Connected, Direct-DCDocument5 pages(2010) Control Strategy of A Multi-Port, Grid Connected, Direct-DCabc1231234454252452342No ratings yet
- Electronics Assignment: by S.rudhraprakash 09lm55 Dme (SW)Document4 pagesElectronics Assignment: by S.rudhraprakash 09lm55 Dme (SW)rvikneshNo ratings yet
- Application For Industrial Power SupplyDocument5 pagesApplication For Industrial Power SupplySunghoonie KangNo ratings yet
- Regulated Power Supply-Block Diagram, Circuit Diagram, WorkingDocument17 pagesRegulated Power Supply-Block Diagram, Circuit Diagram, WorkingsridharparthipanNo ratings yet
- STATCOMDocument5 pagesSTATCOMVenkateshNo ratings yet
- Eltek Middle East (System Training) : by Mahmood SheikhDocument47 pagesEltek Middle East (System Training) : by Mahmood Sheikhsamad_omidvar6292No ratings yet
- Methods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesFrom EverandMethods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Basics: Wcdma TechnologyDocument2 pagesGSM Network Basics: Wcdma TechnologySameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- Site Master S325D: Cable and Antenna Analyzer, 250 MHZ To 2500 MHZDocument12 pagesSite Master S325D: Cable and Antenna Analyzer, 250 MHZ To 2500 MHZSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- Tower & AntennaDocument3 pagesTower & AntennaSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM IdentitiesDocument3 pagesGSM IdentitiesSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Basics: Transmission PlanningDocument4 pagesGSM Network Basics: Transmission PlanningSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM Network BasicsDocument2 pagesGSM Network BasicsSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Basics: Mobile Originating CallDocument2 pagesGSM Network Basics: Mobile Originating CallSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM CellDocument2 pagesGSM CellSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Basics: Authentication Process of A SubscriberDocument2 pagesGSM Network Basics: Authentication Process of A SubscriberSameer SulemanNo ratings yet