Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Urinary System by Carmelita Chavez
Urinary System by Carmelita Chavez
Uploaded by
tankmpOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Urinary System by Carmelita Chavez
Urinary System by Carmelita Chavez
Uploaded by
tankmpCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9
Urinary System
By; Carmelita Chavez
The urinary system or genitourinary system is a
combination of two kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra,
and nephrons that work together to produce, store, and
eliminate urine.
Sometimes if one or more of the organs are not
working people can develop illnesses and diseases.
To detect if someone has an illness there are
diagnostic procedures which can include laboratory
tests.
Some abbreviations that represent illnesses and
diagnostic procedures are: BNO, Cath, CC, EU, and
UTI.
(Im going to explain in detail BNO, Cath, CC, EU, and
UTI.)
Blockage of the bladder outlet. Often caused by
an enlarged prostate gland in males.
Is a condition where the neck of the bladder does
not open completely during voiding.
BNO occurs mostly in 50 year old males frequently
after being diagnose with prostate or had previous
history of bladder stones.
Also, BNO occurs due to previous history of
bladder tumors, pelvic tumors, or urethral scar
tissue.
BNO symptoms in male are abdominal pain, slow
urine flow, frequency, urgency, incontinence, and
incomplete emptying when voiding.
If BNO if is not detected in the early stage it can
develop into bladder cancer.
The urology or physician might recommend some
laboratory tests to determine the cause of BNO.
Those laboratory tests include cystoscopy (x-ray
to look inside urethral,) urinalysis (to look for urine
infection,) and uroflowmetry (to know how fast
urine flows.)
Treatment for BNO is a Foley Catherer which is a
tube inserted into the bladder or surgery.
Catheterization is the insertion of a tube through the
urethra and into the urinary bladder purpose of
withdrawing urine or insertion dye.
There are different types of catheters such as; Foley,
Robinson, Coude, irrigation, and external Texas.
Catheterization is use for people that are going to have
surgery, or people that cant use a bedpan.
Intermittent catheterization is performed four times a
day for patients with urinary incontinence.
Nonintermittent catheterization it remains inserted till
patients can control his/her bladder.
Complications of catheterization can include
incontinence, trauma to bladder, and infections that
can cause fever and inflammation.
Is a urine sample obtained after cleaning off
the urinary opening and catching or collecting
a urine sample in midstream (halfway through
the urination process to minimize
contamination from the genitalia.
Is a typical urine test where a nurse ore
physician gives the patient a cup where
patient has to put his or her urine.
Is called clean catch for the reason that
before patient can urinate in the cup there are
steps to follow.
First step for a patient prior to this test is to wash
or wipe genital area with a kit that the doctor might
give that would include cleansing solution and
sterile wipes.
Women should wash between vagina lips.
Patient should let genital area dry.
Patient should urinate a little in the toilet then
urinate in the cup or container.
All of this is to prevent bacteria into getting into the
urine test.
Results of this test can indicate excessive amount
of red blood cells, white blood cells, protein, and
kidney or bladder infection.
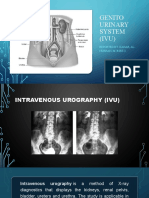
Injection dye into the bloodstream and then taking an
x-ray to trace the action of the kidney as it excretes the
dye.
The dye that is used for this test is called iodine-base
contrast.
This test evaluate the kidneys, urinary tract and
bladder. Medicine is given through IV.
This test detects tumors in the upper urinary tract,
bladder cancer, blood in the urine, and pain.
At the end of the exam patient has to urinate to
eliminate the dye and follow a diet with a lot of fluids.
As the dye is injected patient might feel a burning
sensation, headaches, nausea, and vomiting.
The dye might cause an allergic reaction to the patient.
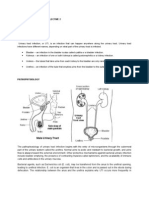
Infection, usually from bacteria, of any organ of the
urinary system. Most often begins with cystitis and may
ascend into the ureters and kidneys. Most common in
women because of their shorter urethra.
Escherichia coli is the most common agent for
infection.
Urine contains salts and waste products that kill
bacteria but once bacteria multiplies in the bladder or
kidney it might cause UTI.
Symptoms of UTI are; pain and burning when urinate,
feeling to urinate frequently and not a lot of urine
comes out, bloated stomach, urine has bad odor, pain
in one side under the ribs, fevers, chills, nausea, and
vomiting.
Drink a lot of water 6-8 cups of 8oz every
day.
Drink cranberry juice
Urinate often
Women should urinate after intercourse to
prevent UTI.
If diagnose with UTI Take full dose of
antibiotics to kill bacteria to prevent future
UTIs.
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/00
2238.htm
http://health.nytimes.com/health/guides/test/urine-
culture-clean-catch/overview.html
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/00
3782.htm
http://www.northvistahospital.com/adam/Health%2
0Illustrated%20Encyclopedia/1/003782/
http://health.yahoo.com/urinary-overview/urinary-
tract-infections-in-teens-and-adults-topic-
overview/healthwise--hw57228.html
You might also like
- CVS Examination ChecklistDocument3 pagesCVS Examination Checklisttankmp100% (3)
- Steam Tracing With MS ExcelDocument14 pagesSteam Tracing With MS ExcelRaul Bautista100% (2)
- The Woman Speaks To The Man Who Has Employed Her SonDocument3 pagesThe Woman Speaks To The Man Who Has Employed Her SonSerena SulawammotNo ratings yet
- What Causes Urinary Retention?Document4 pagesWhat Causes Urinary Retention?darkz_andreaslimNo ratings yet
- NUR209 WK7 Group Handout Case Study Assessment of Urinary Tract Infection Patient ProfileDocument4 pagesNUR209 WK7 Group Handout Case Study Assessment of Urinary Tract Infection Patient Profileania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Care of Patient With Pulmonary EmbolismDocument19 pagesCare of Patient With Pulmonary Embolismtankmp100% (1)
- 4 Corners Gold Rush Lesson PlanDocument3 pages4 Corners Gold Rush Lesson Planapi-267003013No ratings yet
- Project Report On RTS Juice PlantDocument7 pagesProject Report On RTS Juice PlantEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- LG 55ea9800Document102 pagesLG 55ea9800CadwillNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease Naplex QuestionsDocument3 pagesInfectious Disease Naplex QuestionsSARANYA0% (1)
- UTI in AdultsDocument4 pagesUTI in Adultsjoan_padilla2000No ratings yet
- 5 Common Uts DiseasesDocument9 pages5 Common Uts DiseasesJeremiah NayosanNo ratings yet
- Management Bladder IncontinanceDocument14 pagesManagement Bladder IncontinancepaswordnyalupaNo ratings yet
- Article For Patient EducationDocument4 pagesArticle For Patient EducationZaveri Hemant GirishkumarNo ratings yet
- CystosDocument17 pagesCystosMichael Angelo PangiliganNo ratings yet
- جراحة نظري الفصل الثاني فاينلDocument29 pagesجراحة نظري الفصل الثاني فاينلali1ccrNo ratings yet
- Arianna Mabunga BSN-3B Urinary Diversion DeffinitionDocument5 pagesArianna Mabunga BSN-3B Urinary Diversion DeffinitionArianna Jasmine Mabunga0% (1)
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) : A Guide For WomenDocument2 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (UTI) : A Guide For WomenBily ManNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection UTI and Dementia FactsheetDocument10 pagesUrinary Tract Infection UTI and Dementia FactsheettoobaziNo ratings yet
- FAQs Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract InfectionDocument1 pageFAQs Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract InfectioncateterdoblejotaNo ratings yet
- What Is A CystosDocument4 pagesWhat Is A CystosStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Genito Urinary System (Ivu)Document12 pagesGenito Urinary System (Ivu)KATE NICHOLE MANDAPNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument10 pagesUrinary Tract Infectionjaah diazNo ratings yet
- Cystoscopy - Mayo ClinicDocument7 pagesCystoscopy - Mayo ClinicSAIFUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Urinary RetentionDocument24 pagesUrinary RetentionMuhammad Amri Kautsar100% (1)
- MedSurg Chapter 66 OutlineDocument7 pagesMedSurg Chapter 66 OutlineJosephine NavarroNo ratings yet
- OverviewDocument3 pagesOverviewAlhaisa BejemilNo ratings yet
- Urology: By:Dishita Sarma Mha 3 SemesterDocument24 pagesUrology: By:Dishita Sarma Mha 3 SemesterDr. NasrumminallahNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument15 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionMASII100% (4)
- Readings: Acute PyelonephritisDocument6 pagesReadings: Acute PyelonephritisMauriceNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument18 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionDaphne ChendunNo ratings yet
- Health Education For Patients With Urinary CathetersDocument2 pagesHealth Education For Patients With Urinary CathetersTriXie SorrillaNo ratings yet
- Cystoscopy WordDocument4 pagesCystoscopy WordMon ManguilinNo ratings yet
- The Test Urine CultureDocument13 pagesThe Test Urine CultureAnonymous 5aoV2RWWAwNo ratings yet
- Investigations of The Urinary System: Group 4Document53 pagesInvestigations of The Urinary System: Group 4YvonneNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Urinary Tract InfectionDocument10 pagesCase Study - Urinary Tract InfectionJiffy198867% (3)
- INCONTINENCE3Document12 pagesINCONTINENCE3allthingali217No ratings yet
- Urinalysis Is A Diagnostic Physical, Chemical, and Microscopic Examination ofDocument4 pagesUrinalysis Is A Diagnostic Physical, Chemical, and Microscopic Examination ofjadeyjadeNo ratings yet
- Female Urinary System: Types of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument6 pagesFemale Urinary System: Types of Urinary Tract InfectionCarmela BedanoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection, (UTI) Is An Infection of One orDocument4 pagesUrinary Tract Infection, (UTI) Is An Infection of One orLorebellNo ratings yet
- Promotion To Maintain EliminationDocument31 pagesPromotion To Maintain EliminationDenise Louise PoNo ratings yet
- RLE Urinary Tract InfectionDocument13 pagesRLE Urinary Tract InfectionAliza AlyyNo ratings yet
- What Causes A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument6 pagesWhat Causes A Urinary Tract InfectionStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Fundamental EliminationDocument27 pagesFundamental Eliminationالموعظة الحسنه chanelNo ratings yet
- vt59.2708-21368446078 - 3195905547377425 - 5588203228225134062 - n.pdfColorful-Aesthetic-Retro-Group-Project - 3Document12 pagesvt59.2708-21368446078 - 3195905547377425 - 5588203228225134062 - n.pdfColorful-Aesthetic-Retro-Group-Project - 3LwhynnNo ratings yet
- Presentation2 URINARYDocument16 pagesPresentation2 URINARYEunice HandigNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Document6 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (UTI)Anonymous iG0DCOfNo ratings yet
- Turbt 2Document80 pagesTurbt 2Windelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Utis Are Very Common, Especially in Women. They Are Usually Confined To The Urethra and BladderDocument4 pagesUtis Are Very Common, Especially in Women. They Are Usually Confined To The Urethra and BladderMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection, Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction: 1) What Is A UTI?Document5 pagesUrinary Tract Infection, Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction: 1) What Is A UTI?varssitha VNo ratings yet
- Incontinentia Urine: HasnawatyDocument12 pagesIncontinentia Urine: HasnawatyafatspNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument4 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsRalph Patrick SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Elective 2 ReportDocument7 pagesElective 2 ReportJem TellainNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument5 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsEben Leonel Albano MaiopueNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection 1Document17 pagesUrinary Tract Infection 1Annie Lou AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Pyelonephritis 508Document8 pagesPyelonephritis 508Dery ZhibharanyNo ratings yet
- Urinary RetentionDocument6 pagesUrinary RetentiongradnurseNo ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence: 2 PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesUrinary Incontinence: 2 PathophysiologyZiedTrikiNo ratings yet
- Uti PathoDocument15 pagesUti PathoEden Astred ObilloNo ratings yet
- Campoli 257 Renal CH 55Document26 pagesCampoli 257 Renal CH 55FeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Concept of EliminationDocument42 pagesConcept of EliminationOpen UserNo ratings yet
- Urinary RetentionDocument6 pagesUrinary Retentionjakenathanielvelasco50% (2)
- Prevention of Infection Associated With Urinary Catheter: DR/ Wafaa MostafaDocument10 pagesPrevention of Infection Associated With Urinary Catheter: DR/ Wafaa Mostafamohamed abdallaNo ratings yet
- Hematuria, (Blood in Urine) A Simple Guide to The Condition, Related Diseases And Use in Diagnosis of DiseasesFrom EverandHematuria, (Blood in Urine) A Simple Guide to The Condition, Related Diseases And Use in Diagnosis of DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- A Simple Guide to Gallbladder Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Gallbladder Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Prostatitis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandProstatitis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Diverticulitis Cure: The Ultimate Diverticulitis Diet: Diverticulitis Recipes: Your Ultimate Diverticulitis CookbookFrom EverandDiverticulitis Cure: The Ultimate Diverticulitis Diet: Diverticulitis Recipes: Your Ultimate Diverticulitis CookbookNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Immune SystemDocument39 pagesDisorders of The Immune SystemTotaAl-mutairiNo ratings yet
- Priciplesofmanagementpptfinal 120924062449 Phpapp02Document16 pagesPriciplesofmanagementpptfinal 120924062449 Phpapp02tankmpNo ratings yet
- What Is Nursing ManagementDocument16 pagesWhat Is Nursing ManagementtankmpNo ratings yet
- Priciplesofmanagementpptfinal 120924062449 Phpapp02Document16 pagesPriciplesofmanagementpptfinal 120924062449 Phpapp02tankmpNo ratings yet
- Chakras: Muladhar ChakraDocument4 pagesChakras: Muladhar ChakratankmpNo ratings yet
- Introduction: - : Conginital Heart DiseaseDocument25 pagesIntroduction: - : Conginital Heart DiseasetankmpNo ratings yet
- LeprosyDocument7 pagesLeprosytankmpNo ratings yet
- Physical ExaminationDocument20 pagesPhysical ExaminationtankmpNo ratings yet
- Role Av Aids in Clinical TeachingDocument16 pagesRole Av Aids in Clinical Teachingtankmp100% (1)
- FEEDS and FEEDING - FEED FORMULATIONDocument55 pagesFEEDS and FEEDING - FEED FORMULATIONJane LabradorNo ratings yet
- SDS Hardener 2750 EN 221004Document10 pagesSDS Hardener 2750 EN 221004juprykaNo ratings yet
- ECA DatabaseDocument22 pagesECA DatabaseRidhwan JamaludinNo ratings yet
- Barcode v1Document31 pagesBarcode v1Desinta OctavianiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document32 pagesLecture 6Nilesh PanchalNo ratings yet
- Analysis On Explanation TextDocument2 pagesAnalysis On Explanation Textasih dwi astutiNo ratings yet
- Early Alt-RAMEC and Facial Mask Protocol in Class III MalocclusionDocument9 pagesEarly Alt-RAMEC and Facial Mask Protocol in Class III MalocclusionNievecillaNeiraNo ratings yet
- Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, IncDocument4 pagesRamon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, IncPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANNo ratings yet
- Vegetarian Meals On College CampusesDocument14 pagesVegetarian Meals On College CampusesVegan FutureNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz Earth Sci 11Document2 pagesLong Quiz Earth Sci 11Jesha mae MagnoNo ratings yet
- SPE 13932 Wettability Part2 AndersonDocument17 pagesSPE 13932 Wettability Part2 AndersonSergio EduardoNo ratings yet
- Welding Procedure Specification Joint Venture: Azzawiya Control System Modernization ProjectDocument4 pagesWelding Procedure Specification Joint Venture: Azzawiya Control System Modernization ProjectwentropremNo ratings yet
- Thesis Van Ende FinalDocument277 pagesThesis Van Ende FinalArtem KravchenkoNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in PharmacyDocument8 pagesArtificial Intelligence in PharmacyMeraNo ratings yet
- Piping SpecificationDocument5 pagesPiping SpecificationShandi Hasnul FarizalNo ratings yet
- Catálogo de Referencias - Power Conversion SystemsDocument60 pagesCatálogo de Referencias - Power Conversion SystemsBENo ratings yet
- Covalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionDocument4 pagesCovalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionJuan Carlos Contreras CherresNo ratings yet
- Material HPLCDocument19 pagesMaterial HPLCIsmil ImamaNo ratings yet
- Dan Sof TG 0122Document30 pagesDan Sof TG 0122Erick Trujillo100% (1)
- 793-P-1C Relay Data SheetDocument6 pages793-P-1C Relay Data SheetsendmebooksNo ratings yet
- 555-Timer AStable and MonostableDocument13 pages555-Timer AStable and MonostableenzuekNo ratings yet
- Conference Meeting ScriptDocument2 pagesConference Meeting ScriptAndrei PrinsesaNo ratings yet
- Beyond FurosemideDocument13 pagesBeyond FurosemideHeath HensleyNo ratings yet
- On Light: Science Holiday Homework Made By-Aish Mishra Class-8 Diamond Roll No.-6Document9 pagesOn Light: Science Holiday Homework Made By-Aish Mishra Class-8 Diamond Roll No.-6Ansh MishraNo ratings yet