Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Raining Project: Buddhika Kumarasinghe Heeshan Gunathilaka
Raining Project: Buddhika Kumarasinghe Heeshan Gunathilaka
Uploaded by
HeeshanGunathilakaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Raining Project: Buddhika Kumarasinghe Heeshan Gunathilaka
Raining Project: Buddhika Kumarasinghe Heeshan Gunathilaka
Uploaded by
HeeshanGunathilakaCopyright:
Available Formats
T RAINING PROJECT
Buddhika Kumarasinghe
Heeshan Gunathilaka
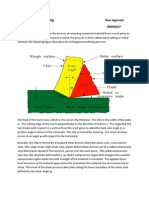
Problem ??
Cracks
Defects
Thickness reduction
Welding
cracks
HAZ
cracks
Welding
cracks
HAZ
cracks
Fixed flange
cracks
Loose flange
cracks
Fixed flange
cracks
Loose flange
cracks
Thickness
reduction
Fixed flange
Longitudinal
cracks
Transverse
cracks
Longitudinal
cracks
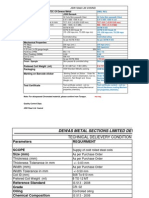
Most defective rim types
Rim type Plate thickness (mm)
Percentage elongation
(Fixed flange forming )
3.00D8 6 38.12%
4.00E9 6 37.24%
4.33R8 6 60.70%
5.00F10 6 37.65%
5.50F10 7 37.65%
5.00S12 7 44.56%
6.50F10 7 37.65%
7.00 15 8 38.84%
8.00 15 8 45.24%
Reasons
THICKNESS
reduction
WELDING cracks
HAZ cracks
Improper welding parameters
Improper welding wire selection
Low after grinding thickness
Improper cooling cycle
Solution
Proper selection of
welding parameters
Welding parameters and plate thickness
Welding parameters and Material
composition
Welding parameters and Mechanical
properties of the plate
Appropriate after grinding thickness
Proper cooling cycle
Proper production
methods
Approach 1:
Identification of the relationship between welding
parameters (current, voltage, and torch speed) and
chemical composition of parent material for defect free
product.
Initial
compositions
Composition after
welding
Heat
(Current voltage time)
Diffusion and
Dilution
AFT = - 3.48 + 0.00538 Current + 0.0003 Voltage
- 0.0033 Speed + 17.7 C% - 1.6 Mn% + 37.7 S%
- 15.6 P% + 0.977 BFT
C%
Mn%
S%
P%
Current, Voltage
and Speed
After
forming
thickness
Thickness (T) (mm) Result
T= 0 A crack
0 < T < 4.7 Repairable due to necking
4.7 T 6.0 Ok
You might also like
- Formulas For Designing Press ToolsDocument21 pagesFormulas For Designing Press ToolsKarthik Gopal86% (35)
- Cutting ToolsDocument25 pagesCutting ToolsjaiswalsiddharthNo ratings yet
- Weld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesFrom EverandWeld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Predictive Modeling of Tool Wear in Hard Turning: Yong Huang Advisor: Prof. Steven Y. LiangDocument20 pagesPredictive Modeling of Tool Wear in Hard Turning: Yong Huang Advisor: Prof. Steven Y. Liangirinuca12No ratings yet
- Answer SheetsDocument7 pagesAnswer Sheetsgirma workuNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Machining - Mechanical ExperimentDocument4 pagesOrthogonal Machining - Mechanical ExperimentRavi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- PEM Self Clinching Floating FastenersDocument2 pagesPEM Self Clinching Floating FastenersAce Industrial SuppliesNo ratings yet
- Resistance Spot Welding Parameters Optimal Selection For Automotive Steel PlateDocument6 pagesResistance Spot Welding Parameters Optimal Selection For Automotive Steel PlateMahmoud SingerNo ratings yet
- Effect PDFDocument9 pagesEffect PDFvichuNo ratings yet
- Trade Test of Welders (For Petron Limay Bataan Project) : Equipments, Materials and ConsumablesDocument2 pagesTrade Test of Welders (For Petron Limay Bataan Project) : Equipments, Materials and ConsumableswalitedisonNo ratings yet
- 25 Mechanical Engineering Interview Questions and Answers - Freshers, ExperiencedDocument3 pages25 Mechanical Engineering Interview Questions and Answers - Freshers, Experiencedmehul kapadiaNo ratings yet
- ESMDocument10 pagesESM47 Bhushan BariNo ratings yet
- Cutting Tool Technology: ME 482 - Manufacturing SystemsDocument25 pagesCutting Tool Technology: ME 482 - Manufacturing SystemsRajesh VermaNo ratings yet
- High Strength Hexagon Bolts (JIS B1186)Document4 pagesHigh Strength Hexagon Bolts (JIS B1186)Mario HanamiciNo ratings yet
- Kyocera Substrates) Electronic Fine CeramicsDocument17 pagesKyocera Substrates) Electronic Fine Ceramicsmanolo_superNo ratings yet
- Friction Stir Welding of Aluminum MMC: Tracy W. Nelson, Dick LederichDocument22 pagesFriction Stir Welding of Aluminum MMC: Tracy W. Nelson, Dick LederichSanthosh Kumar KodhandapaniNo ratings yet
- Cutting Tool Technology: ME 482 - Manufacturing SystemsDocument25 pagesCutting Tool Technology: ME 482 - Manufacturing SystemsPrashant ChouhanNo ratings yet
- MOS COUPLER FOR TcsDocument25 pagesMOS COUPLER FOR TcsRituraj RNo ratings yet
- MDP Report PDFDocument9 pagesMDP Report PDFkanishk maheshwariNo ratings yet
- 2 67 1587472886 2.ijmperdjun20202Document12 pages2 67 1587472886 2.ijmperdjun20202TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Matecconf Imanee2018Document6 pagesMatecconf Imanee2018Irina BesliuNo ratings yet
- SmtdataDocument8 pagesSmtdataDaftDeveloperNo ratings yet
- Distortion in Welding 1111111Document40 pagesDistortion in Welding 1111111wenigma100% (1)
- Cutting Tool Technology: ME 482 - Manufacturing SystemsDocument25 pagesCutting Tool Technology: ME 482 - Manufacturing SystemsLeo RíosNo ratings yet
- Week 6 AE 2024 - NTM and JoiningDocument47 pagesWeek 6 AE 2024 - NTM and JoiningJulian PostmaNo ratings yet
- Welding Recommendation TS890Document2 pagesWelding Recommendation TS890max_powerNo ratings yet
- Cutting Tool Technology: ME 482 - Manufacturing SystemsDocument25 pagesCutting Tool Technology: ME 482 - Manufacturing Systemssrk_ukNo ratings yet
- Revista - Materials Science ForumDocument5 pagesRevista - Materials Science Forum0741005518No ratings yet
- Soldering Joint Criteria: For CHIP-R and MLCCDocument21 pagesSoldering Joint Criteria: For CHIP-R and MLCCAdriano AraujoNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Machining and MetrologyDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank For Machining and MetrologyAbhisheak DineshNo ratings yet
- Welding Balancing Using SysweldDocument1 pageWelding Balancing Using SysweldMukesh JindalNo ratings yet
- Tata Steel Bulb Flats BroDocument11 pagesTata Steel Bulb Flats BroMd. Rafique HassanNo ratings yet
- Theory of Metal Cutting, Metal FormingDocument181 pagesTheory of Metal Cutting, Metal Formingprabhjotbhangal100% (1)
- TR Hank Self-Clinch: Broaching NutsDocument1 pageTR Hank Self-Clinch: Broaching NutsJosko SpehNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Process Parameters in Orthogonal Machining of Ti6Al4V With Tic Coated PCBN Inserts - A Finite Element AnalysisDocument8 pagesExperimental Investigation of Process Parameters in Orthogonal Machining of Ti6Al4V With Tic Coated PCBN Inserts - A Finite Element AnalysisAzaath AzuNo ratings yet
- TIG Welding ProjectDocument42 pagesTIG Welding ProjectAshok KotthapalliNo ratings yet
- Welding Presentation by NoreastDocument78 pagesWelding Presentation by Noreastravi00098No ratings yet
- Hot Rolled Products, Cold Rolled Products, Galvanised Products From Flats, Tata Steel, IndiaDocument4 pagesHot Rolled Products, Cold Rolled Products, Galvanised Products From Flats, Tata Steel, IndiaraajmrkNo ratings yet
- Cf53 DIN 1Document1 pageCf53 DIN 1empty_No ratings yet
- Tube HydraulicsDocument8 pagesTube HydraulicsrijalharunNo ratings yet
- AnglaisDocument10 pagesAnglaisÎb TįHęêēëlNo ratings yet
- Astm A 572m Grade 50Document2 pagesAstm A 572m Grade 50anon_892533596No ratings yet
- Weld Neck Body Flange Design Calculation: HE-CGI, HE-CG, Spiral Wound Gaskets For Heat ExchangersDocument30 pagesWeld Neck Body Flange Design Calculation: HE-CGI, HE-CG, Spiral Wound Gaskets For Heat ExchangersmishtinilNo ratings yet
- Material Removal Process (Metal Machining Process) : Theory of Metal CuttingDocument129 pagesMaterial Removal Process (Metal Machining Process) : Theory of Metal CuttingIjanSahrudinNo ratings yet
- TDC of Dewas Metal: Parameters JSW Remark Product Details Size (MM)Document5 pagesTDC of Dewas Metal: Parameters JSW Remark Product Details Size (MM)anandsharma9No ratings yet
- Hydac Filter TrainingDocument99 pagesHydac Filter TrainingChozim Anank100% (1)
- Jarak Poros 250Document13 pagesJarak Poros 250AnamNo ratings yet
- RF Circuit Fabrication RulesDocument51 pagesRF Circuit Fabrication Rulesazizhamdi100% (1)
- BorgWarner DCTWet ClutchesFrictionMtrls GoldDocument45 pagesBorgWarner DCTWet ClutchesFrictionMtrls Goldddeeff715No ratings yet
- Vitronics PresentDocument54 pagesVitronics PresentCrina100% (1)
- BS en 10219 (Tolerances) Dimensional-TolerancesDocument1 pageBS en 10219 (Tolerances) Dimensional-TolerancesBFEVietnamNo ratings yet
- Lab Evaluation of YSZ Coating Surface and Thermal Analysis For Plasma Sprayed Coated IC Engine PistonDocument35 pagesLab Evaluation of YSZ Coating Surface and Thermal Analysis For Plasma Sprayed Coated IC Engine PistonSurenNo ratings yet
- AluminizedDocument4 pagesAluminizedmarkengineerNo ratings yet
- Joining of Polymer-Metal Hybrid Structures: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandJoining of Polymer-Metal Hybrid Structures: Principles and ApplicationsSergio T. Amancio FilhoNo ratings yet
- Welding Terminology: A Guide to MIG, TIG, Stick, Gas, and Spot Welding TermsFrom EverandWelding Terminology: A Guide to MIG, TIG, Stick, Gas, and Spot Welding TermsNo ratings yet
- REGISTRATION PROCESS NewDocument9 pagesREGISTRATION PROCESS NewHeeshanGunathilakaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Adaptiveness Within Industry Sectors Measurement and Observations 2016 Telecommunications PolicyDocument16 pagesCloud Adaptiveness Within Industry Sectors Measurement and Observations 2016 Telecommunications PolicyHeeshanGunathilakaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Grain SizeDocument5 pagesDetermination of Grain SizeHeeshanGunathilaka100% (2)
- Ball MillDocument3 pagesBall MillHeeshanGunathilakaNo ratings yet