Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Capiz State University
Capiz State University
Uploaded by
Josal Mariano Jacinto0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 page1) Newton's second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
2) Mathematically, this can be expressed as a=F/m, where a is acceleration, F is net force, and m is mass.
3) During free fall near Earth's surface, the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s^2) causes objects to reach the ground at the same time regardless of differences in their mass.
Original Description:
Law of Acceleration
Original Title
Handouts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Newton's second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
2) Mathematically, this can be expressed as a=F/m, where a is acceleration, F is net force, and m is mass.
3) During free fall near Earth's surface, the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s^2) causes objects to reach the ground at the same time regardless of differences in their mass.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageCapiz State University
Capiz State University
Uploaded by
Josal Mariano Jacinto1) Newton's second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
2) Mathematically, this can be expressed as a=F/m, where a is acceleration, F is net force, and m is mass.
3) During free fall near Earth's surface, the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s^2) causes objects to reach the ground at the same time regardless of differences in their mass.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Republic of the Philippines
CAPIZ STATE UNIVERSITY
College of Education
Main Campus, Roxas City
Tel. No. (036) 6214 578 local 118
NEWTONS SECOND LAW OF MOTION : LAW OF ACCELERATION
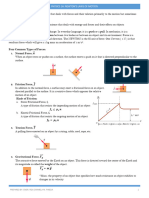
Relationship of Force to Acceleration: At constant mass, the acceleration of an object is
directly proportional to the net force acting on it.
Mathematically it is expressed as:
a=kF
where:
a= acceleration
k= constant mass
F= force acting on an object
Relationship of Mass to Acceleration: The relationship of Acceleration to Mass at constant
force is inversely, proportional. When mass of the object increases then its acceleration decreases
and if the mass decreases then acceleration increases.
a= k(1/m)
where:
a= acceleration
k= force
m= mass
Law of Acceleration: Acceleration is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force
acting on it and is inversely proportional to its mass.
A=F
n
/ M
where:
a= acceleration
F
n
= net force
M= mass
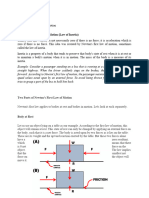
Free Fall and Newtons Second Law of Motion
Both of the books reach the ground at the same time because of the gravity that acts
on its surface. This gravity which is the same for all objects on Earth and is equal to 9.8 m/s
2
causes the books to accelerate and this acceleration is what we called acceleration due to gravity
(ag). This means that when two objects are drop at the same time from the same height these
objects will reach the ground at the same time even if they differ in Mass.
You might also like
- Chapter 7 Basic Physics SEDocument15 pagesChapter 7 Basic Physics SEtsoniffNo ratings yet
- Experiment 101 Newton'S Second Law of Motion AnalysisDocument5 pagesExperiment 101 Newton'S Second Law of Motion AnalysisJerome LangitNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law of Motion and Free FallDocument25 pagesNewton's Second Law of Motion and Free FallScribd-957616100% (2)
- NEWTON's 1st, 2nd & 3rd LawsDocument20 pagesNEWTON's 1st, 2nd & 3rd LawsNorKamilahMakhtarNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document23 pagesGroup 5Gavin avNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Amaljith H Assistant Professor Dept. of Mechanical EngineeringDocument21 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Amaljith H Assistant Professor Dept. of Mechanical EngineeringSijuKalladaNo ratings yet
- Note Applicationas of Newton's Laws and Conservation of MomentumDocument16 pagesNote Applicationas of Newton's Laws and Conservation of MomentumWatr SatNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of MotionDocument28 pagesNewton's Law of MotionJosh JavierNo ratings yet
- 05 PH Newtons LawsDocument22 pages05 PH Newtons Lawsapi-235269401No ratings yet
- PHYSICS HANDOUT Newtons LawDocument6 pagesPHYSICS HANDOUT Newtons LawAlexander DolinNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument24 pagesPhysicsMayra FlorNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To Gravity ForcesDocument28 pagesAcceleration Due To Gravity Forcesfelipee20No ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of Motion1Document6 pagesNewtons Laws of Motion1darlei byerotNo ratings yet
- Phys 1011 - Dynamic NotesDocument10 pagesPhys 1011 - Dynamic Notesnigusayele06No ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesSciencemalaitslasharmanniNo ratings yet
- NSLDocument1 pageNSLfranklin.yin2020No ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law of MotionDocument9 pagesNewton's Second Law of Motionlekshmikrishnan224No ratings yet
- Group-4'S Report: Leader: Chauncey Dale Pequiña Asst - Leader: Kristofer Cruz Sec - Alliah Garcia Jefel EcleoDocument26 pagesGroup-4'S Report: Leader: Chauncey Dale Pequiña Asst - Leader: Kristofer Cruz Sec - Alliah Garcia Jefel EcleoSheralyne Daz PequinaNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law of MotionDocument14 pagesNewtons Law of MotionJohn Irvin M. AbatayNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Unit 9Document2 pagesPhysical Science Unit 9Bluematwo TwoNo ratings yet
- Phys Science ExamDocument1 pagePhys Science Exampaul darrenNo ratings yet
- Newtons 2nd Law Lesson 3Document19 pagesNewtons 2nd Law Lesson 3Aimee Gallego AngoluanNo ratings yet
- LAWS of Motion SCIENCE 8Document14 pagesLAWS of Motion SCIENCE 8Gregg LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 101 - Phys101lDocument4 pagesExperiment 101 - Phys101lthomas melgarNo ratings yet
- The Law of MotionDocument30 pagesThe Law of MotionNurulWardhani11No ratings yet
- Forces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: PreviewDocument24 pagesForces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: Previewnanio_7No ratings yet
- The Laws of MotionDocument15 pagesThe Laws of MotionAmar Poñado BagacinaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Forces in Nature: Force&MotionDocument11 pagesFundamental Forces in Nature: Force&MotionUtku OztekinNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: PreviewDocument23 pagesForces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: PreviewAnonymous m8oCtJBNo ratings yet
- Part 2 - CedricsDocument112 pagesPart 2 - CedricsMaria Loresa TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Newton's First Law: Previous Chapter of StudyDocument5 pagesNewton's First Law: Previous Chapter of StudyIrene QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Newtons Law of MotionDocument52 pagesTopic 4 Newtons Law of Motionalianapaloma77No ratings yet
- Newton'S Laws: Unit Is 4.45 NDocument2 pagesNewton'S Laws: Unit Is 4.45 NGabriel VirayNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Rigid BodiesDocument7 pagesStatistics of Rigid BodiesAphaedes AlcalaNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument11 pagesForceAnastasia LarasatiNo ratings yet
- 7th Lesson Newtons Laws of MotionDocument27 pages7th Lesson Newtons Laws of MotionMRmister123No ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Newton's LawsDocument8 pagesChapter-3 Newton's LawsMd Najmul HudaNo ratings yet
- Ancy C Simon Physical Science Optional Register Number-13971004Document20 pagesAncy C Simon Physical Science Optional Register Number-13971004Mark Jay BongolanNo ratings yet
- PHY101 Lecture Note 2015 - 2016-3-1Document7 pagesPHY101 Lecture Note 2015 - 2016-3-1Kenneth SilvaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Newton2&3Document2 pagesLesson 6 - Newton2&3AliiAmiirNo ratings yet
- Newton LawDocument5 pagesNewton Lawdva222No ratings yet
- U 1 NotesDocument2 pagesU 1 NotesLyndon LiNo ratings yet
- Wk6 GenPhys1 - 0926 30Document8 pagesWk6 GenPhys1 - 0926 30JenRose Gadon SoliguenNo ratings yet
- Contact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesDocument6 pagesContact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesBethlehem CuradaNo ratings yet
- Newton 120 AnswersDocument6 pagesNewton 120 AnswersNovenalista Domitilla FlavianaNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 - Fundamental Physics (Forces)Document6 pagesPhysics 1 - Fundamental Physics (Forces)Claire FabellarNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument43 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionNasr UllahNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three (3) Laws of MotionDocument24 pagesNewton's Three (3) Laws of MotionCabalan O. Charles KevinNo ratings yet
- Physics: First Law (Law of Inertia)Document2 pagesPhysics: First Law (Law of Inertia)Kumanan CultureshockNo ratings yet
- Week 3 and 4 Pt. 2Document13 pagesWeek 3 and 4 Pt. 2Bradley HausNo ratings yet
- CP Physics Ms. MorrisonDocument11 pagesCP Physics Ms. MorrisonDwight StephensonNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law of MotionDocument11 pagesNewton's Third Law of MotionScribd-95761650% (2)
- 3 - DynamicsDocument2 pages3 - DynamicsStephen CamsolNo ratings yet
- Learner Guide 2023Document111 pagesLearner Guide 2023ntandophakzinsNo ratings yet
- Physics Mechanics CHAPTER 2Document7 pagesPhysics Mechanics CHAPTER 2vikingrings.aeNo ratings yet
- Physics: Unit 3 (Forces) Key Notes or IdeasDocument2 pagesPhysics: Unit 3 (Forces) Key Notes or IdeasRana Muhammad UmarNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three Law of MotionDocument3 pagesNewton's Three Law of MotionArlyn Pong Pling PioNo ratings yet
- 0301 Newton's Laws of MotionDocument4 pages0301 Newton's Laws of MotionimfizicsNo ratings yet
- Who Discovered The Three Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesWho Discovered The Three Laws of MotionQUENZELLE JADE LOKINGNo ratings yet
- Origin of Chemical ElementsDocument13 pagesOrigin of Chemical ElementsJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- RizalDocument22 pagesRizalJosal Mariano Jacinto100% (1)
- Activity 1Document1 pageActivity 1Josal Mariano Jacinto100% (1)
- Vicente Andaya Sr. National High School: Daily Lesson Plan in Science 9 August 23,2017Document3 pagesVicente Andaya Sr. National High School: Daily Lesson Plan in Science 9 August 23,2017Josal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- August 24,2017: Daily Lesson Plan in Science 9Document3 pagesAugust 24,2017: Daily Lesson Plan in Science 9Josal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- Vicente Andaya Sr. National High School: I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesVicente Andaya Sr. National High School: I. ObjectivesJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: Vicente Andaya Sr. National High SchoolDocument3 pagesI. Objectives:: Vicente Andaya Sr. National High SchoolJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: Vicente Andaya Sr. National High SchoolDocument3 pagesI. Objectives:: Vicente Andaya Sr. National High SchoolJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- Vicente Andaya Sr. National High School: Daily Lesson Plan in Science 9 August 22,2017Document3 pagesVicente Andaya Sr. National High School: Daily Lesson Plan in Science 9 August 22,2017Josal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: Vicente Andaya Sr. National High SchoolDocument3 pagesI. Objectives:: Vicente Andaya Sr. National High SchoolJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: Sex Chromosomes and Sex DeterminationDocument3 pagesI. Objectives:: Sex Chromosomes and Sex DeterminationJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: July 19,2017Document3 pagesI. Objectives:: July 19,2017Josal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: Vicente Andaya Sr. National High SchoolDocument2 pagesI. Objectives:: Vicente Andaya Sr. National High SchoolJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- First Periodical Test in SCIENCE 9 NAME: - GRADE & SECTIONDocument3 pagesFirst Periodical Test in SCIENCE 9 NAME: - GRADE & SECTIONJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- 7 11 17Document2 pages7 11 17Josal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- Input Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdDocument54 pagesInput Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- Input Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdDocument54 pagesInput Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- L 1 1aDocument1 pageL 1 1aJosal Mariano Jacinto100% (1)
- Lptemplate Phy - SciDocument1 pageLptemplate Phy - SciJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- Input Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdDocument54 pagesInput Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- 7 10 17Document2 pages7 10 17Josal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- Input Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdDocument54 pagesInput Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- Input Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdDocument54 pagesInput Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- Input Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdDocument54 pagesInput Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- Input Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdDocument54 pagesInput Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School IdJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Electronic Class Record: InstructionsDocument80 pagesSenior High School Electronic Class Record: InstructionsJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 12Document3 pagesPhysical Science 12Josal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet