Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enchimento Coluna
Enchimento Coluna
Uploaded by
Juan Canellas Bosch NetoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enchimento Coluna
Enchimento Coluna
Uploaded by
Juan Canellas Bosch NetoCopyright:
Available Formats
Colunas de Pratos
2
Flooding: excessive accumulation of liquids inside the columns
Column operating in spray regime
liquid on the tray in form of drops
As vapor velocity is raised, bulk of these drops are entrained into the tray
above
Liquid accumulates on the tray above instead of flowing to the tray below
3
At higher liquid flow rates, dispersion on the tray is in the form of a
froth
When vapor velocity is raised, froth height increases
To design a sieve tray
1. Calculate the column diameter that prevents flooding
2. Design the tray layout
3. Design the downcomers
4
Downcomers and weirs
control the liquid distribution and flow
5
Weir
Plate
Froth
Phase Contact on a Contacting Tray
Vapor streams (shown
in red) bubble up through
froth. Liquid stream flows
through froth and over weir
The froth conditions can be varied depending on the vapor-liquid
flow regimes to include: spray, froth, emulsion bubble, and cellular foam.
6
Tray Configuration
Three type of tray openings:
Perforation
Valve cap
Bubble cap
slots
cap
riser
plate
plate
cap
leg
plate
Weir
7
Liquid flow shown by blue arrows.
Vapor flow by red arrows.
Weir
Plate
8
Prato Perfurado Prato de vlvula Prato de campnula
(perforation cap) (valve cap) (bubble cap)
9
Sizes the column to prevent flooding caused by excessive
entrainment.
Excessive entrainment can cause a large drop in stage efficiency
liquid that has not been separated is mixed with vapor.
Design Procedure
10
Extractor Sieve Tray
11
12
13
Trayed Columns
14
15
Reboilers
16
Feed Distributors
17
Valve Tray Deck
18
Fouled Bubble Cap Tray
19
Fouling Resistant Design
20
The Real World
21
Coluna de Pratos Coluna de Enchimento
Colunas de Enchimento
22
Enchimento Estruturado
(havendo grandes quedas de presso requer que se
gaste mais energia para que o vapor suba na coluna)
VANTAGENS: eficiente contacto lquido-vapor sem causar quedas de
presso assinalveis
(maior rea interfacial gs-lquido)
Maior eficincia para a mesma altura de coluna
23
Structured Packing Wetted Area
24
Enchimento Aleatrio
25
IMTP
Pall Rings
Structured
26
altura do enchimento
HETP=
n. pratos tericos
1/ 2
V
L
L
G
U
<
U
1/ 2 1/ 2
( )
s G L V V
w C
U U U
1/ 2
s V
F w U
HETP = altura de enchimento necessria para obter a variao de
composio obtida com um andar de equilbrio
1) Parmetro de fluxo <
3) C
G,operacional
= 0.70 u C
G,max
4) Velocidade superficial do gs, w
s
5) Factor F (factor caracterstico do tipo de enchimento)
6) N. de andares tericos/m (= 1/HETP)
Grfico sabendo F e tipo de enchimento 1/HETP HETP
Colunas de Enchimento
2) C
G,max
Grfico sabendo < e tipo de enchimento
Factor de capacidade
27
HETP =
n. pratos tericos
H
3
2
caudal volumtrico gs m /s
m
velocidade superficial gs m/s
c
s
G
A
w
2
2
caudal gs kg/s
m
fluxo gs
kg/(m s )
c
G
A
G
c
2 3
kg m kg
s
m s m
s
G w c u U
p
4
c
c
A
d
S
7) Altura do enchimento, H
8) Dimetro da coluna de enchimento, d
c
a) rea da seco recta da coluna, A
c
b) Dimetro da coluna, d
c
9) Perda de carga na coluna, 'P
Grfico sabendo F e tipo de enchimento 'P/z (mbar/m)
Perda de carga total: 'P = ('P/z) u altura coluna
28
EXEMPLO: Prob. D7 Usando dados do Prob. D5, mas considerando
que a coluna de enchimento, calcular HETP, a altura e o dimetro da
coluna para ao enchimento Mellapack 125.Y (t = 100C, U
L
= 950 kg/m
3
)
1/ 2
V
L
L
G
U
<
U
1) Parmetro de fluxo <
L = 50.1 kmol/h x = 0.84
V = 66.8 y = 0.915
condies no topo da coluna
(onde existem maiores caudais de L e de V)
L,G : caudais mssicos
U : densidades mssicas
G (kg/h) = V (kmol/h) x M (kg/kmol)
L(kg/h) = L (kmol/h) x M (kg/kmol)
1/2
2294.6 1.5
0.03
3066.1 950
<
2) C
G,max
Grfico sabendo < e tipo de enchimento
0.156
3) C
G,operacional
= 0.70 u C
G,max
=0.70x0.156=0.109 m/s
Mellapack 125Y
29
4) Velocidade superficial do gs, w
s
1/ 2 1/ 2
( )
s G L V V
w C
U U U
=0.109 x (950-1.5)
1/2
x1.5
-1/2
=0.109x25.1 = 2.73 m/s
5) Factor F
1/2 1/ 2
2.73 1.5 3.34 u U
s V
F w
6) N. de andares tericos/m (= 1/HETP)
1.2
1/HETP = 1.2 HETP = 1/1.2 = 0.83 m
1.2 andares tericos
por m de enchimento
7) Altura do enchimento, H
HETP =
n. pratos tericos
H
= 6 (resultado Prob. D5)
0.83=
6
H
H = 6 x 0.83 m = 4.98 m
3.34
30
8) Dimetro da coluna de enchimento, d
c
a) rea da seco recta da coluna, A
c
2
3
m kg
2.73 1.5 4.1 kg/(m s)
s
m
Fluxo de gs = = u u c U
V
s
G w
2
2
3066 / 3600 (kg/h)(s/h)
0.21 m
4.1
kg/(m s)
= =
c
c
G
A
G
2
2 2
4
0.21 m 0.52 m
4
= S S
S
c
c
A d
r d A
b) Dimetro da coluna, d
c
31
9) Perda de carga na coluna, 'P
'P/z = 5 (mbar/m)
Perda de carga total:
'P = ('P/z) u altura coluna
= 5 x 4.98 25 mbar
3.34
4.5
You might also like
- Sieve Tray CalculationsDocument4 pagesSieve Tray CalculationsWade Coleman75% (4)
- Experiment 3 Flow Over WeirsDocument20 pagesExperiment 3 Flow Over Weirsfadhilahmad80% (5)
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry Structure and Function 6th Edition by VollhardtDocument13 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry Structure and Function 6th Edition by Vollhardta492222920No ratings yet
- DESIGN OF SIEVE PLATE ColumnDocument5 pagesDESIGN OF SIEVE PLATE ColumnVirendra Bhagat100% (1)
- Lorenzo Rafael - ElementbuilderseDocument5 pagesLorenzo Rafael - Elementbuilderseapi-529491285100% (4)
- Steam SilencerDocument3 pagesSteam SilencerAntonio Perez100% (1)
- Treatment Plant HydraulicsDocument11 pagesTreatment Plant HydraulicsMadhavan DurairajNo ratings yet
- Qpedia Oct14 Heat Transfer Calculations of ThermosyphonDocument5 pagesQpedia Oct14 Heat Transfer Calculations of ThermosyphonHMMSPNo ratings yet
- Drilling Formulae - 9th Edition PDFDocument87 pagesDrilling Formulae - 9th Edition PDFEng Mohamed SaberNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger SpreadsheetDocument2 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchanger SpreadsheetHernan Cardenas Franco100% (1)
- Total Process Engineering ManualDocument260 pagesTotal Process Engineering Manualmusabammadkhan89% (9)
- Bubble Cap DesignDocument18 pagesBubble Cap Designsanjuct0686% (7)
- Determining The Concentration of Protein On Egg Albumin Through Lowry MethodDocument6 pagesDetermining The Concentration of Protein On Egg Albumin Through Lowry MethodMuslimah Anggun100% (5)
- Development of Heat Exchangers For Use As Replacement Plates in Distillation Columns: Proof of Concept and Collection of Design InformationDocument22 pagesDevelopment of Heat Exchangers For Use As Replacement Plates in Distillation Columns: Proof of Concept and Collection of Design Informationkirandevi1981No ratings yet
- Flow of Water by Notch and WeirsDocument17 pagesFlow of Water by Notch and WeirsMuhammad Zulhusni Che RazaliNo ratings yet
- Perancangan MenaraDocument18 pagesPerancangan Menaraogum_07No ratings yet
- List of Experiments of Fluid LabDocument24 pagesList of Experiments of Fluid LabGhufran Ahmed0% (1)
- BallastDocument7 pagesBallastDian ArinaNo ratings yet
- 96 GT 51 JakartaDocument8 pages96 GT 51 JakartaJagdish Singh MehtaNo ratings yet
- ملخص انتاج م 3 هندسة نفطDocument31 pagesملخص انتاج م 3 هندسة نفطlwrsaghqNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Coefficient of Discharge of Given Orifice MeterDocument62 pagesDetermination of The Coefficient of Discharge of Given Orifice MeterPandiya RajanNo ratings yet
- 10.1016/j.petrol.2009.03.001: Journal of Petroleum Science and EngineeringDocument27 pages10.1016/j.petrol.2009.03.001: Journal of Petroleum Science and EngineeringAli Reza VatandoustNo ratings yet
- Pages From HVAC Design Handbook (301 450)Document150 pagesPages From HVAC Design Handbook (301 450)zaffar731No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Book by RK BansalDocument25 pagesFluid Mechanics Book by RK BansalBibhuti BhusanNo ratings yet
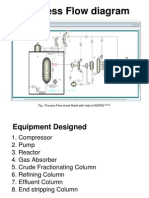
- Process Flow Diagram: Fig: Process Flow Sheet Made With Help of ASPENDocument42 pagesProcess Flow Diagram: Fig: Process Flow Sheet Made With Help of ASPENSwarnim RajNo ratings yet
- Flare KO Drum-3Document35 pagesFlare KO Drum-3nghiemta1892% (13)
- FM Manual PDFDocument37 pagesFM Manual PDFSampathkumar MtechNo ratings yet
- Bahan Tugas 3 Buat EXCEL Perhitungan PompaDocument37 pagesBahan Tugas 3 Buat EXCEL Perhitungan PompaIhsan Wiratama100% (1)
- Lea 1Document7 pagesLea 1vika1301No ratings yet
- Bubble Cap Tray Assignment: CE 428 Spring 2003Document11 pagesBubble Cap Tray Assignment: CE 428 Spring 2003Thọ NguyễnNo ratings yet
- CPE533 Gas Absorption Full Lab ReportDocument30 pagesCPE533 Gas Absorption Full Lab ReportFazsroul83% (12)
- Aerodynamics Lab ManualDocument42 pagesAerodynamics Lab ManualSathya Narayanan100% (2)
- Flow of Water by Notch and WeirsDocument15 pagesFlow of Water by Notch and WeirsCik Tiem Ngagiman93% (29)
- Tappi 0502-17 Papermaker FormulaDocument19 pagesTappi 0502-17 Papermaker FormulaMulyadi Moel86% (21)
- Experiment 1 Centre of Pressure On A Plane SurfaceDocument19 pagesExperiment 1 Centre of Pressure On A Plane SurfacePatrick Camerino DimabuyuNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Lecture Notes - 9Document13 pagesFluid Flow Lecture Notes - 9Lin Xian Xing100% (1)
- Principles of Gas LiftDocument31 pagesPrinciples of Gas LiftYassine Taktak67% (3)
- Discharge CoefficientDocument11 pagesDischarge Coefficientsisai12u2420% (2)
- 236 1Document30 pages236 1anon_836654017No ratings yet
- Losses in Bends FittingsDocument26 pagesLosses in Bends Fittingsdainer08No ratings yet
- 1 - Fluid Mechanics Takehome Project AssignmentDocument4 pages1 - Fluid Mechanics Takehome Project Assignmentazeem sheikhNo ratings yet
- Flow of Water by Notch and WeirsDocument15 pagesFlow of Water by Notch and WeirsAngelica Joyce BenitoNo ratings yet
- Observations and Calculations Table 1. Results of Flow Through Orifice Experiment (Constant Head)Document4 pagesObservations and Calculations Table 1. Results of Flow Through Orifice Experiment (Constant Head)Anonymous yjucdoLNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Pump CalculationDocument4 pagesVacuum Pump Calculationmabj68No ratings yet
- Revamping of Process Plant - S MukherjeeDocument6 pagesRevamping of Process Plant - S Mukherjeesriman1234No ratings yet
- Paper021 MixedFeedINletDevices' PDFDocument11 pagesPaper021 MixedFeedINletDevices' PDFVijay KaleNo ratings yet
- Optimization and Design of Dehydration Unit and NGL ProcessDocument51 pagesOptimization and Design of Dehydration Unit and NGL ProcessHoracio RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CPE533 Gas Absorption Full Lab ReportDocument28 pagesCPE533 Gas Absorption Full Lab ReportKhairul Fathy Ibnu AsrarNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Approach To Water-Hammer AnalysisDocument4 pagesA Simplified Approach To Water-Hammer AnalysisChem.EnggNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column DesignDocument27 pagesDistillation Column Designl7ani100% (9)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersFrom EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Tables; The Elements Of Gagings And The Friction Of Water Flowing In Pipes, Aqueducts, Sewers, Etc., As Determined By The Hazen And Williams Formula And The Flow Of Water Over The Sharp-Edged And Irregular Weirs, And The Quantity DischargedFrom EverandHydraulic Tables; The Elements Of Gagings And The Friction Of Water Flowing In Pipes, Aqueducts, Sewers, Etc., As Determined By The Hazen And Williams Formula And The Flow Of Water Over The Sharp-Edged And Irregular Weirs, And The Quantity DischargedNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in Fluid Mechanics with Sensitivities to Governing VariablesFrom EverandCase Studies in Fluid Mechanics with Sensitivities to Governing VariablesNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods for Simulation and Optimization of Piecewise Deterministic Markov Processes: Application to ReliabilityFrom EverandNumerical Methods for Simulation and Optimization of Piecewise Deterministic Markov Processes: Application to ReliabilityNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics in Channel, Pipe and Aerodynamic Design Geometries 2From EverandFluid Mechanics in Channel, Pipe and Aerodynamic Design Geometries 2No ratings yet
- Interactive Textbook 1 PDF 4 1Document8 pagesInteractive Textbook 1 PDF 4 1api-240094705100% (2)
- 6) ElectrochemistryDocument58 pages6) ElectrochemistrySHANJIDA ALI RIANo ratings yet
- Properties:: Carbonic Acid, (HDocument4 pagesProperties:: Carbonic Acid, (HPRAGYA S BABU AIMLNo ratings yet
- Matthias 2002Document21 pagesMatthias 2002antonio leonNo ratings yet
- BTI1133 Ch33Document39 pagesBTI1133 Ch33ACC SHNo ratings yet
- Unit Test Sample Paper - 2 Grade 12 ChemistryDocument5 pagesUnit Test Sample Paper - 2 Grade 12 Chemistrymilonee lNo ratings yet
- CH 10 HydrogenDocument33 pagesCH 10 HydrogenRobiatuladawiyahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food Freezing - 3Document50 pagesIntroduction To Food Freezing - 3Mahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Formula Sheet (Annotated)Document2 pagesLevel 2 Formula Sheet (Annotated)Lucas Clarke (un gnome)No ratings yet
- Thermal Properties - Temperature 1 QPDocument10 pagesThermal Properties - Temperature 1 QPAnanya GSNo ratings yet
- Gate 2005 CyDocument14 pagesGate 2005 CySumanta- 14No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation Behaving As ParticlesDocument48 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation Behaving As ParticlesLeo YipNo ratings yet
- 634581643032102500Document130 pages634581643032102500DrVenu Madhav KNo ratings yet
- Report 2 - Thermal Conductivity 2.12.15Document9 pagesReport 2 - Thermal Conductivity 2.12.15LegendaryNNo ratings yet
- Growth and Studies of Nickel Chloride Doped Sodium Fluoro Antimonate CrystalsDocument4 pagesGrowth and Studies of Nickel Chloride Doped Sodium Fluoro Antimonate CrystalserpublicationNo ratings yet
- CYANEX® 272 Extractant BrochureDocument16 pagesCYANEX® 272 Extractant BrochureGhina Fatikah Salim100% (2)
- Lecture Pt. 4Document35 pagesLecture Pt. 4zy- SBGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document9 pagesChapter 6Christeena HenryNo ratings yet
- Wrapping SuggestionDocument84 pagesWrapping Suggestionahmed aziziNo ratings yet
- FDG Production-Theory Operations-FDG Synthesis Chemistr1Document25 pagesFDG Production-Theory Operations-FDG Synthesis Chemistr1Cesar Adolfo SanchezNo ratings yet
- Document of Analyst ChemicalDocument3 pagesDocument of Analyst ChemicalHoang BuiNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide To Surface Science & SpectrosDocument200 pagesA Practical Guide To Surface Science & Spectrosyemresimsek100% (1)
- Carnot CycleDocument6 pagesCarnot CyclechillnessNo ratings yet
- F432-007-3-2020 (Hvac) Single PhaseDocument155 pagesF432-007-3-2020 (Hvac) Single PhaseMohamad Afiq Akmal Bin Mohd NizamNo ratings yet
- Effect of Light Intensity On The Rate of PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesEffect of Light Intensity On The Rate of PhotosynthesisCindy Singh100% (2)
- Hexamine PDFDocument86 pagesHexamine PDFmanoranjan singh100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding Sheet Solution3546Document75 pagesChemical Bonding Sheet Solution3546mamtarupa6No ratings yet