Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting
Uploaded by
Phani TripuramalluOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting
Uploaded by
Phani TripuramalluCopyright:
Available Formats
LASER CUTTING
YENDURI UPESH CHANRA(0811607)
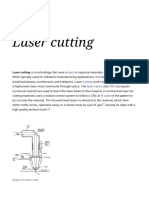
Laser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to cut materials, which is typically used for industrial
manufacturing applications. Laser cutting works by directing the output of a high power laser, by computer, at
the material to be cut. The material then either melts, burns, vaporizes away, or is blown away by a jet of
gas, leaving an edge with a high quality surface finish.
TYPES OF LASERS FOR LASER CUTTING:
Lasing Materials Applications
CO2 Boring,
Cutting/Scribing
LASER GENERATION Engraving
PROCESS
Nd High energy pulses
Stimulating a lasing
,Low repetition speed
material by electrical
discharge or lamps within (1kHz)
a closed container. As the
material is stimulated, it is Boring
reflected internally by
means of a partial mirror, Nd-YAG Very high energy
until it achieves sufficient pulses. Boring
energy. The coherent light ,Engraving ,Trimming
then passes through a lens.
In order to be able to start
cutting from somewhere else than the edge, a pierce is done before every cut.
TYPICAL WORK PIECE MATERIALS
Mild Steel, Titanium, Paper, Wax, Plastics, Wood, Fabrics are typical work piece materials.
SAFETY FACTORS
PERSONAL ENVIRONMENTAL
1. Contact with hot tools and work pieces. 1. Smoke
2. Eye contact with beam radiation can cause damage to eye. 2. Fumes and dust particles
COMPARISON WITH MECHANICAL CUTTING
1.Lack of physical contact
2. Precision
3. There is also a reduced chance of warping the material that is being cut, as laser systems have a small heat-
affected zone.
NOTES & REFERENCES
[1]. Luxon, James T, “Lasers in Manufacturing: an introduction to technology”, 1978.
[2]. Bertolotti, Mario (1999, trans. 2004). The History of the Laser, Institute of
Physics. ISBN 0-750-30911-3
[3]. Siegman, Anthony E. (1986). Lasers, University Science Books. ISBN 0-
935702-11-3
You might also like
- Manufacturing Technology: Unit - IDocument18 pagesManufacturing Technology: Unit - Iapi-271354682100% (1)
- AFL Transmission Distribution CatalogDocument524 pagesAFL Transmission Distribution CatalogAlan ZanzeriNo ratings yet
- SPB 75 Oil Selection and Maintenance - Rev06Document7 pagesSPB 75 Oil Selection and Maintenance - Rev06O mecanicoNo ratings yet
- Purlin LysaghtDocument6 pagesPurlin LysaghtAnonymous MHMqCrzgTNo ratings yet
- Discharge Unit Values BS.5572:1978: Type of Sanitary Fitting Interval Between UseDocument6 pagesDischarge Unit Values BS.5572:1978: Type of Sanitary Fitting Interval Between UseArvensisdesign100% (3)
- Architecture - February 2018Document23 pagesArchitecture - February 2018ArtdataNo ratings yet
- AXS Step Manual en Rev 5Document29 pagesAXS Step Manual en Rev 5Jack NorhyNo ratings yet
- Laser CuttingDocument1 pageLaser CuttingPhani TripuramalluNo ratings yet
- Laser CuttingDocument2 pagesLaser CuttingPhani TripuramalluNo ratings yet
- 18 Applications in Material ProcessingDocument38 pages18 Applications in Material Processingkaushik4208No ratings yet
- Laser CuttingDocument9 pagesLaser Cuttingtoto16161650% (2)
- Laser Cutting - First Principles PaperDocument6 pagesLaser Cutting - First Principles PaperSiddaraju V Hodekal100% (2)
- Laser CuttingDocument8 pagesLaser CuttingSharath KumarNo ratings yet
- LaserCutting RTantraDocument27 pagesLaserCutting RTantraAhmad ZainiNo ratings yet
- Research On Surface Roughness by Laser CDocument5 pagesResearch On Surface Roughness by Laser CfatmirhusejniNo ratings yet
- Laser CuttingDocument25 pagesLaser Cuttingvineeth reddy100% (1)
- Laser Beam WeldingDocument31 pagesLaser Beam WeldingZeel PatelNo ratings yet
- LaserCutting RTantraDocument29 pagesLaserCutting RTantraYandapalli Sai ramNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18 - Laser Materials ProcessingDocument22 pagesLecture 18 - Laser Materials ProcessingGaurav GodseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Cutting Mk4Document37 pagesLecture 4 - Cutting Mk4ryhanwebbadasilvaNo ratings yet
- Laser Processing: Dr. P. KuppanDocument28 pagesLaser Processing: Dr. P. KuppanAbid YusufNo ratings yet
- Laser Systems - The Basics: Generation of A Laser BeamDocument2 pagesLaser Systems - The Basics: Generation of A Laser BeamDjordje KapetanovicNo ratings yet
- Laser CuttingDocument9 pagesLaser CuttingPrabir Kumar PatiNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam WeldingDocument17 pagesLaser Beam WeldingSwati AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Laser Cutting Physics AssignmentDocument5 pagesLaser Cutting Physics Assignmentamithmore5No ratings yet
- Laser CuttingDocument3 pagesLaser CuttingumasreeNo ratings yet
- Lasers Used in Operative Dentistry and EndodonticsDocument28 pagesLasers Used in Operative Dentistry and EndodonticsNingombam Robinson Singh0% (1)
- Lecture 20 - Laser Materials ProcessingDocument29 pagesLecture 20 - Laser Materials ProcessingGaurav GodseNo ratings yet
- Laser Cutting From First Principles To The State of The ArtDocument6 pagesLaser Cutting From First Principles To The State of The ArtJing YinNo ratings yet
- Moderator: Dr. S. Kalpana Presenter: Dr. AnjaliDocument89 pagesModerator: Dr. S. Kalpana Presenter: Dr. Anjaliايه سلام خضير عباس تقنيات البصرياتNo ratings yet
- Laser CuttingDocument9 pagesLaser CuttingBharath vNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 9 Laser Beam MachiningDocument18 pagesLecture - 9 Laser Beam MachiningAbdulrahman goudaNo ratings yet
- Laser Cutting - Wikipedia PDFDocument46 pagesLaser Cutting - Wikipedia PDFSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Laser Cutting + 3D ScaningDocument41 pagesLaser Cutting + 3D ScaningOsama SamyNo ratings yet
- Lasers and Its Application in Periodontal TherapyDocument95 pagesLasers and Its Application in Periodontal TherapyAishwarya PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2013 - @@ - Jun19 - HAZ - Laser Ncutting - PaperDocument6 pages2013 - @@ - Jun19 - HAZ - Laser Ncutting - PaperHarshad PatelNo ratings yet
- Laser Welding 101Document25 pagesLaser Welding 101rakeshkaushikNo ratings yet
- Laser CuttingDocument19 pagesLaser Cuttingtheory of machine fgiet100% (1)
- Module 2 - Laser and Electron BeamDocument53 pagesModule 2 - Laser and Electron BeamVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- Lbm-Sbp-Coep 1 PDFDocument58 pagesLbm-Sbp-Coep 1 PDFtejas chikhlikarNo ratings yet
- Laser Cutting: Navigation SearchDocument11 pagesLaser Cutting: Navigation SearchIjie BladerzNo ratings yet
- Aarya Veer Engineering College 4 TH SemDocument27 pagesAarya Veer Engineering College 4 TH Semd patelNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam MachiningDocument25 pagesLaser Beam MachiningtrimohitNo ratings yet
- 10 NontraditionalDocument8 pages10 Nontraditionalsat_tskNo ratings yet
- Non-Traditional Manufacturing ProcessesDocument8 pagesNon-Traditional Manufacturing Processessantsex111No ratings yet
- Lasers: Inderjeet Kaur Saini Section:G-6001 Roll No.:B-35 Reg - No.:11004846Document17 pagesLasers: Inderjeet Kaur Saini Section:G-6001 Roll No.:B-35 Reg - No.:11004846ashish_hooda22No ratings yet
- AMT Module 4 1Document33 pagesAMT Module 4 1Pranav MgNo ratings yet
- Laser Cutting: Diagram of A Laser CutterDocument9 pagesLaser Cutting: Diagram of A Laser CutterSuraj NagpalNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of Lasers and ApplicationsDocument2 pages3 Types of Lasers and ApplicationsHemlata AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Seminar Paper Laser Cutting: University of Maribor Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringDocument8 pagesSeminar Paper Laser Cutting: University of Maribor Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringPrimož BrglezNo ratings yet
- Lasers in Ophthalmology Part - 1Document53 pagesLasers in Ophthalmology Part - 1bhartiNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam Machining Definition Working Process Principle Advantages Disadvantages Application NotesDocument4 pagesLaser Beam Machining Definition Working Process Principle Advantages Disadvantages Application NotesMD Al-AminNo ratings yet
- D.Palani Kumar, Assistant Prof. / Mech. Engg., Kamaraj College of Engg. & Tech. VirudhunagarDocument28 pagesD.Palani Kumar, Assistant Prof. / Mech. Engg., Kamaraj College of Engg. & Tech. VirudhunagarVinith ArasuNo ratings yet
- MCP 101 Lec - 2Document16 pagesMCP 101 Lec - 228.xie.shayanmajumdarNo ratings yet
- Secenje Laserom WikiDocument13 pagesSecenje Laserom WikiMarko BogosavljevicNo ratings yet
- Dhiraj Kolhe LaserDocument15 pagesDhiraj Kolhe LaserDhiraj KolheNo ratings yet
- Maintenance LaserDocument7 pagesMaintenance LaserRaghunandanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Behavior of Materials UnderDocument17 pagesA Study On Behavior of Materials UnderIlker CetinNo ratings yet
- Laser Marking: Marks Pryor Marking Technology Pvt. LTDDocument9 pagesLaser Marking: Marks Pryor Marking Technology Pvt. LTDhemantNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document33 pagesModule 4Mohammed aslamNo ratings yet
- Laser Cutting - WikipediaDocument13 pagesLaser Cutting - Wikipediakartik sharmaNo ratings yet
- Laser PPT 2Document15 pagesLaser PPT 2Dhiraj KolheNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Optimization of Kerf Taper and Surface Roughness in Laser Cutting of Titanium Alloy SheetDocument1 pageModeling and Optimization of Kerf Taper and Surface Roughness in Laser Cutting of Titanium Alloy SheetTamil ArasanNo ratings yet
- LaserDocument6 pagesLaserhmoa2050No ratings yet
- Copper Electrodeposition for Nanofabrication of Electronics DevicesFrom EverandCopper Electrodeposition for Nanofabrication of Electronics DevicesNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Solid Fuel Handling SystemDocument32 pages2.4 Solid Fuel Handling SystemDangolNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design of A House Home in PakistanDocument2 pagesFoundation Design of A House Home in PakistanRana Mazhar100% (2)
- MOS For Pull Out TestDocument5 pagesMOS For Pull Out TestHasbullah HamzahNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Resource Planning: Presented by MT14IND001 Industrial EngineeringDocument28 pagesManufacturing Resource Planning: Presented by MT14IND001 Industrial Engineeringanam kaziNo ratings yet
- CD-2-mini ProjectDocument86 pagesCD-2-mini ProjectVishakha PatelNo ratings yet
- 7743 - Product Manual VDO Cockpit Vision International1Document272 pages7743 - Product Manual VDO Cockpit Vision International1Anonymous M0OEZEKoGiNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineer: Rahman Ullah S/O Mohammad Ishtiaq KhanDocument6 pagesCivil Engineer: Rahman Ullah S/O Mohammad Ishtiaq KhanAdnan MunirNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Fluid Power-Part 1 Chapter 4: Contamination and FiltrationDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Fluid Power-Part 1 Chapter 4: Contamination and FiltrationWilliam MoscaNo ratings yet
- CSW - Railway - White Paper - ERTMS and CBTC Side by SideDocument4 pagesCSW - Railway - White Paper - ERTMS and CBTC Side by Sidejosemusic23No ratings yet
- Summary: Seismic Performance of Slender Reinforced Concrete Structural WallsDocument87 pagesSummary: Seismic Performance of Slender Reinforced Concrete Structural WallshcastelblancorNo ratings yet
- Conférence AvellanF PDFDocument34 pagesConférence AvellanF PDFceice2013No ratings yet
- Onkar OtariDocument3 pagesOnkar OtariSachin KhotNo ratings yet
- 2002 - The Influence of Fibre Length and Concentration On The Properties of GF RF PP - 5. Injection Molded PPDocument12 pages2002 - The Influence of Fibre Length and Concentration On The Properties of GF RF PP - 5. Injection Molded PPSubramani PichandiNo ratings yet
- MMV 1300 1500 - EnglDocument2 pagesMMV 1300 1500 - EnglEmilian PopaNo ratings yet
- Power Team PE30 ManualDocument6 pagesPower Team PE30 ManualTitanplyNo ratings yet
- Review Paper On Study On Properties of Black Cotton Soil Using Stone Dust and Sisal FiberDocument3 pagesReview Paper On Study On Properties of Black Cotton Soil Using Stone Dust and Sisal FiberEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Tamson-Products PPSXDocument79 pagesTamson-Products PPSXIan JoeNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Catalogue (UreaN46 & DAP 18:46:0)Document7 pagesFertilizer Catalogue (UreaN46 & DAP 18:46:0)Ajay PandeyNo ratings yet
- Mech-Intro 13.0 WS07.1 SStherm PDFDocument14 pagesMech-Intro 13.0 WS07.1 SStherm PDFrustamriyadiNo ratings yet
- Handtalk Using Flex Sensor SusfeDocument18 pagesHandtalk Using Flex Sensor Susfeshubham jatNo ratings yet
- R5410305-Refrigeration & Air ConditioningDocument1 pageR5410305-Refrigeration & Air ConditioningsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Energy Unit Study GuideDocument2 pagesEnergy Unit Study GuideYogi Fathur RahmanNo ratings yet
- FL3100H and FL3101H UV IR and UV Unitized Flame DetectorsDocument2 pagesFL3100H and FL3101H UV IR and UV Unitized Flame DetectorsRomdhoni Widyo BaskoroNo ratings yet
- 203 Super S Inhibited Transformer OilDocument2 pages203 Super S Inhibited Transformer OilHanderson PanjaitanNo ratings yet