Professional Documents
Culture Documents
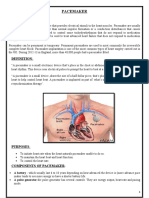
Pacemakers
Pacemakers
Uploaded by
Lisa OktamuvaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pacemakers
Pacemakers
Uploaded by
Lisa OktamuvaCopyright:
Available Formats
Pacemakers 12/04
1-What is a pacemaker?
2- What does intrinsic mean?
3- How exactly do pacemakers work on the heart?
4- What are the parts of a pacemaker?
5- re there different kinds of pacemakers?
!- What is the ad"anta#e of two wires o"er one?
$- How are pacemakers inserted?
%- What do they mean &y trans"eno's( transc'taneo's( and transthoracic?
)- How does the #enerator &ox work?
1*- How lon# do the implanted &atteries last?
11- How m'ch electricity does the pacemaker 'se to act'ally pace the heart?
12- +n ,n#lish( please?
13- What is capt're threshold?
14- Why do paced &eats #enerated &y a "entric'lar wire look like -./s?
15- What does asynchrono's mean( and what does demand mean?
1!- What do those letters0 ..+( 111( etc2 stand for?
1$- What is fail're to capt're?
1%- What is fail're to sense?
1)- How can an implanted pacemaker &e repro#rammed?
2*- What is the ma#net thin#?
21- What are some reasons for placin# a permanent pacemaker?
22- What is an +/1?
23- /an +/13s also f'nction as pacemakers?
24- What pro&lems do +/13s ha"e?
25- How do yo' stop an +/1 from shockin# the patient incorrectly?
2!- /an yo' shock a patient with a pacemaker?
2$- What is external cardiac pacin#?
2%- Who was 4oll( anyhow?
2)- What else do + need to know a&o't r'nnin# the external pacemaker?
3*- How do + know if capt're has &een achie"ed?
31- What3s the tricky part?
32- 1oes external pacin# h'rt?
33- How lon# can a person stay on the external pacemaker?
34- How does the 4oll #o into demand mode?
35- ny other 4oll tricks?
3!- /an yo' do /-5 with the external pacer in place?
3$- How effecti"e is the 4oll?
Pacemakers
1. What is a pacemaker?
pacemaker is an electronic de"ice that pro"ides an electrical si#nal to make the heart &eat
when it3s own( &'ilt-in pacemakers fail2 6he anatomical( &'ilt-in pacemakers pro"ide what3s
called the intrinsic rhythm( and they can &e disr'pted &y "ario's conditions 7 ischemia for
example( or &y an 8+2
2. What does intrinsic mean?
+ntrinsic means &'ilt in2 +n this sit'ation( it means0 comin# from the patient3s own &'ilt-in(
nat'ral pacemakers 0 the 9 or . nodes: or sometimes from lower down in the "entricles2
3. How exactl do pacemakers work on the heart?
6he pacemaker essentially does two thin#s 0 it senses the patient3s own rhythm 'sin# a
sensin# circ'it( and it sends o't electrical si#nals 'sin# an o'tp't circ'it2 +f the patient3s
intrinsic rhythm &ecomes too slow or #oes away completely( the electronic pacemaker senses
that( and starts sendin# o't si#nals alon# the wires leadin# from the control &ox to the heart
m'scle2 6he si#nals( if they3re capt'rin# properly( pro"ide a re#'lar electrical stim'l's(
makin# the heart contract at a rate fast eno'#h to maintain the patient3s &lood press're2
Here3s the &ox( implanted2
How many pacin# wires?
http0;;www2&orleyrectory2com;myessays;pacemaker2htm
4. What are the parts o! a pacemaker?
6he pacemaker &ox itself is called the p'lse #enerator 7 the #enerator is connected to
either one or two wires( which carry the electrical si#nals to the heart m'scle2 -ermanent
pacin# #enerators are implanted in the chest 'nder the skin 7 nowadays they3re "ery small 7
and the wires leadin# to the heart are threaded thro'#h the s'&cla"ian "ein2
2
". #re there di!!erent kinds o! pacemakers?
-acemakers can &e either temporary or permanent2 6he
temporary pacemakers that we see in the 8+/< are
made 'p of a control &ox and one sin#le o'tp't wire
leadin# to the inner wall of the 5. =th's called a
"entric'lar wire( or .-wire>( and pro"ide simple rate
control &y pacin# the "entricles2 -ermanent pacemakers
come in se"eral fla"ors( &'t the main difference &etween
them is that some ha"e only one wire leadin# to the 5.(
and some ha"e two 7 one to the ri#ht atri'm =5>( and
another one to the 5.2 pacin# system that paces &oth
the 5 and the 5. is called an atrio"entric'lar pacer(
and paces &oth ri#ht heart cham&ers in se?'ence2 6he
si#nal affects the left-side cham&ers and stim'lates them
to contract as well2 6he si#nal from the wire #enerates a
"is'al si#nal on the ,@A that looks like( and is called a
spike2
Here3s an example of a temporary( external( sin#le-wire
pacin# &ox2 6he wire has two pole connections( so one pair of
connectors0 sin#le wire &ox2
http0;;www2pacemedicalinc2com;45432htm
Here3s a nice example of sin#le-wire pacin#( with spikes comin# at a rate in the $*3s2 6he
reason we can tell that there3s only one wire #oin# is simply that there3s only one spike2 6wo-
wire systems #enerate two spikes2
How many spikes this time?
3
,"ery&ody see the two spikes?
6he arrows aren3t perfect 7 &'t
clearly there are two pacin#
f'nctions #oin# on here0 the first
spike is #eneratin# atrial kick( and
the second is kickin# the
"entricles0 two spikes( two wires2
6hese spikes #o &oth 'p
and down in front of the
B593s( which yo' see
sometimes 7 a normal
"ariant2
6wo sets of connectors0 two wires2 9o what kind of &ox is this?
http0;;www2oscor2com;defa'lt2asp?owc;tempC2*pacin#2aspDmain
$. What is the ad%anta&e o! two wires o%er one?
+f yo' pace the "entricle alone( the patient doesn3t #et the atrial kick 7 the p'sh of the atria
into the "entricles2 6his can act'ally add 2*-25C to the cardiac o'tp't( and impro"e the
&lood press're accordin#ly2 nice example of this was a patient we saw recently who had a
temporary .-wire in place2 When she was paced at a rate of $*( she only #ot a &lood
press're of a&o't %5( systolic2 E't when the pacer rate was t'rned down( her intrinsic rate
took o"er at a&o't a rate of !* 7 sin's rhythm( which meant that she started #ettin# her atrial
kick a#ain 7 and her &lood press're rose( e"en with the slower rate( to a&o't 1*52 lso a nice
example of how the fastest rate will capt're0 first the wire( then the intrinsic one2
$. How are pacemakers inserted?
temporary pacin# wire is threaded thro'#h an introd'cer placed in a central line site(
's'ally the ri#ht internal F'#'lar or s'&cla"ian2 =6he ri#ht +G is the strai#htest shot down into
the 5.( which is where yo' want yo'r temporary wire to #o2> Howadays we rarely 'se
trans"eno's wire insertion at the &edside 7 we apply the transc'taneo's pacer( or 4oll
instead2 Ince in a #reat while a transthoracic wire placement is attempted( 's'ally at the end
of a code when nothin# else is workin#J
'. What do the mean ( trans%eno)s* transc)taneo)s* and transthoracic?
6rans"eno's means that the pacin# wire is threaded down the F'#'lar "ein thro'#h an
introd'cer =the same as a - line introd'cer>2 6he introd'cer is p't in first( like any central
neck +. line( and the wire is passed thro'#h it( like a - line is( 'ntil it makes contact with the
inner wall of the 5.2 6hen the wire is attached to a #enerator &ox( and the heart is paced
'sin# the wire2 We hardly e"er do this at the &edside anymore( since the comin# of the 4oll
external pacer2
4
6ransc'taneo's pacin# means 'sin# external pacin# pads connected to a de"ice like the 4oll
machine( or one of the defi&rillators that has external pacin# a&ility2
6ransthoracic pacin# means 'sin# wires inserted either d'rin# cardiac s'r#ery 7 small wires
that sit on the o'ter wall of the heart 7 epicardial wires( that lead o't of the chest( to a
control &ox - or doin# a mane'"er that in"ol"es p'shin# a pacin# wire into the 5. 'p thro'#h
the chest wall( s'&xiphoid( d'rin# a code2 +3"e only e"er seen this tried once and it didn3t
work2 ccordin# to a we& so'rce that we looked at( the proced're isn3t "ery pop'lar( can
create a whole slew of nasty complications( and 's'ally isn3t any 'se anyhow2
+. How does the &enerator (ox work?
6he #enerator &ox consists of a small comp'teriKed chip controller that3s r'n &y a &attery2
6he &ox senses and paces thro'#h the same set of wires that lead to the endocardi'm2
,. How lon& does the (atter last?
s + 'nderstand it( implanta&le pacers 'se lithi'm &atteries that last anywhere from ! to 1*
years2 6he &attery in a temporary pacin# &ox is a re#'lar hardware-store type )-"olt &attery2
10. How m)ch electricit does the pacemaker )se to act)all pace the heart?
6he o'tp't of the pacemaker is meas'red in two ways0 si#nal amplit'de( and p'lse width2
11. -n .n&lish* please?
9i#nal amplit'de means how m'ch F'ice the &ox p'ts o't thro'#h the wire with e"ery p'lse2
6his is meas'red in milliamperes( and is called 8 7 there3s a twisty dial to control the 8 on
the front of the temporary pacer &ox2 -'lse width means how lon# each p'lse lasts2 6he
electrical p'lse has to &e stron# eno'#h( and last lon# eno'#h( to capt're the myocardi'm2
12. What is capt)re threshold?
/apt're threshold is the minim'm amo'nt of electricity that the &ox has to emit to pace the
heart 7 as a&o"e( it3s meas'red in milliamps( and the twisty kno& is t'rned 'p 'ntil the heart is
paced 1**C - then t'rned down a#ain 'ntil the minim'm is determined2
13. Wh do paced (eats &enerated ( a %entric)lar wire look like P/0s?
6he reason that -./s look wide and &iKarre is &eca'se they ori#inate down at the &ottom
of the heart( at the opposite end from where they 's'ally come - the path of depolariKation is
&ackwards as a res'lt2 6hink of the normal lead ++ si#nal( #oin# from northwest to so'theast0
Ire#on to Llorida2 paced si#nal is #oin# &ackwards( 'pwards =retro#rade> - the re"erse
of the normal B59 wa"eform2 9ince the "-wire #enerates a rhythm &y emittin# electricity from
a wire whose tip is em&edded in the wall of the 5.( the deflection follows the same path as a
-./ 7 so it looks like one2
5
Here3s the two-wire pacin# strip a#ain0 one wire is in the ri#ht atri'm( and the other3s in the
ri#ht "entricle2 With two wires( the "entric'lar path is still &ackwards( F'st as with one 7 makes
sense( ri#ht?
14. What does asnchrono)s mean* and what does demand mean?
temporary control &ox can &et set to r'n - F'st r'n - at a fixed rate( i#norin# any si#nals that
the patient3s heart may &e makin# =asynchrono's>: or it can &e set to pace only if the intrinsic
heart rate #ets too slow =pacin# on demand>2 Heedless to say( yo' wo'ld 'se the first way
of pacin# only if the patient3s heart rate was either m'ch too slow( as may happen if the
patient wipes o't some of her cond'ction system &y infarct( or if the rhythm F'st isn3t there( as
in asystole( may&e for the same reason2 6here3s a second twisty dial that controls how
sensiti"e the &ox will &e to the patient 7 for f'll control( yo' wo'ld t'rn it all the way 'ntil the
control kno&3s arrow pointer was all the way towards the word asynchrono's2 +nsensiti"e2
6ake the pacin# #enerator o't of the emer#ency pacin# tackle &ox a few times( and #et
familiar with it2
Here3s the strip we looked at on pa#e 32 6his is fixed-rate pacin#2 Hot necessarily
asynchrono's( &'t this is what it wo'ld look like0
6his same dial can also &e t'rned in the other direction( away from asynchrono's 7 this
increases the sensiti"ity of the &ox( so that it will start sensin# the patient3s own rate2 +f yo'
want the &ox to start pacin# the patient only when the intrinsic rate #ets too slow 7 on
demand( then yo' adF'st the sensiti"ity of the &ox so that it can see the patient3s rhythm2
6his will inhi&it the &ox from firin# when it sees intrinsic &eats2 6he cardiolo#y people are
's'ally responsi&le for these settin#s( &'t the idea is pretty simple0 it3s &etter if the patient3s
own rhythm controls the heart( especially if all yo' ha"e is a .-wire =no atrial kick with only a
"-wire( remem&er> 7 &'t if it slows down &elow a certain point( the &ox will wake 'p and take
o"er2 6he intrinsic rhythm stops or slows( and the inter"al is lon# eno'#h for the pacer to t'rn
on2
5emem&er that the wire has to #enerate a rate that3s fast eno'#h to make an ade?'ate &lood
press're2 +f the demand rate is set so that the &ox only kicks in at a rate of !*( that may not
&e eno'#h( especially if yo'3re only workin# with the one wire2
6
1". What do those letters1 //-* 222* etc.* stand !or?
We really only see two kinds of pacemakers in the 8+/< 7 sin#le "-wire pacin# ='s'ally
temporary wires placed for &radycardias and the like>( and permanently implanted -.
pacers2 9in#le "-wire systems are called ..+ pacers( and the -. pacers are called 1112
6he first letter stands for the cham&er that is paced( the second letter is for the cham&er that
is sensed( and the third letter stands for the response the pacer makes to a sensed intrinsic
&eat2 9o a ..+-mode pacer paces the 5.( senses the 5.( and is +nhi&ited from firin# if it
senses an intrinsic &eat2 111 pacers pace &oth cham&ers =1 stands for d'al>( they sense
&oth cham&ers( and each of the two wires is inhi&ited &y an intrinsic &eat2
6his can prod'ce a "ery cool res'lt0 a patient may #enerate her own --wa"es( &'t fail to
cond'ct them 7 may&e she has a fritKed-o't . node2 6he -wire will &e inhi&ited &y the
patient3s -3s( &'t the "-wire will sense( and follow them2 9o the patient will &e in a sin's
rhythm( with "-pacin#( and will &e a&le to increase and decrease heart rate in a normal way
in response to exercise( and the like2 ,xcellentM
1$. What is !ail)re to capt)re?
Here the idea is that the pacin# &ox sends an imp'lse to the heart at the ri#ht time( &'t the
heart doesn3t respond2 6he &ox is sensin# that the intrinsic heart rate is too slow( &'t the
o'tp't si#nal isn3t makin# the myocardi'm respond2 No' see this on a rhythm strip when there
are clear pacin# spikes comin# from the &ox 7 at the ri#ht time after either an intrinsic &eat or
a paced one 7 &'t they3re not followed &y a B59 response2 6here can &e all sorts of reasons
for this0 &roken wires( pacemaker &ox fail're( acidosis( alkalosis( &ad connection to an
external pacin# &ox( &attery fail're( the moon in .ir#oJ this can &e serio's if the patient is
dependin# on the pacemaker to maintain a &lood press're2 .ario's mane'"ers can &e made
with the pacer control &ox to re-esta&lish proper capt're 7 the ?'ickest one is 's'ally to t'rn
'p the 8 o'tp't2 /all the team2 While yo'3re waitin#( ha"e atropine at the &edside( and the
4oll near&y in case &ad capt're #oes to no capt'reM
/opyri#ht 2***( 8ad 9cientist 9oftware( www2madsci2com;man';ek#Orhy2htm
6he point to remem&er0 the pacer spikes are comin# at the ri&ht time relati"e to the patients
rate( or lack of a rate 7 &'t they3re not capt'rin#2
7
Where3s the B59?
1'. What is !ail)re to sense?
5emem&er( the pacemaker has &oth a sensin# circ'it and an o'tp't( or pacin# circ'it2 6he
pacer has to sense whether or not the patient is #eneratin# a rhythm( so it will know when to
pace and when not to2 +n this case the pacemaker will #enerate spikes that do capt're( &'t
the spikes come at the wron# time( and the &ox is clearly 'na&le to see what the patient3s
heart is doin#2 /learly a &ad thin# 7 it can res'lt in the infamo's 5-on-6 sit'ation( prod'cin#
.6 or .L2
6he thin# to keep in mind0 the pacer spikes will &e comin# at the wron& time2 6his may F'st
&e an improper sensiti"ity settin# on the &ox2
www2 monroecc22ed';depts;pstc;paracar52htm
1+. How can an implanted pacemaker (e repro&rammed?
6here3s a machine that the physician 'ses to comm'nicate with an implanted pacemaker2
1,. What is the ma&net thin&?
No'3"e pro&a&ly seen the physicians do this mysterio's mane'"er with a rin#-shaped ma#net
that #ets placed on the patients3 chest o"er the pacemaker2 6he idea here is that there is a
switch inside the pacemaker with a ferro's reed( which is p'lled from one position to the
other &y the ma#net2 6his is in"ol"ed in fi#'rin# o't how m'ch lon#er the pacers3 &attery has
to li"e( and also chan#es the pacemaker into f'lly asynchrono's mode for testin# p'rposes2
20. What are some reasons !or placin& a permanent pacemaker?
6here are lots of thin#s that an 'nhappy heart can come 'p with that will indicate the need for
a pacemaker0 sick-sin's and tachy-&rady syndromes will do it( certainly rec'rrent
8
Here we are failin# to sense2 =+t3s
's'ally a #'y thin#J> 6he spikes
are certainly re#'lar( &'t are they
comin# at the ri#ht time( relati"e to
the patient? Ho 7 the &ox isn3t
seein# the patient3s rhythm( and it3s
firin# off &lindly2 =6hree doctors #o
d'ck h'ntin#J>
&radycardias that drop the E- will do it( heart &locks =especially which one?> 7 yo' #et the
idea2 +f the heart isn3t #eneratin# a rate for whate"er reason( pacin# will pro&a&ly &e needed2
21. What is an #-02?
+/1 stands for 'tomatic( +mplanta&le( /ardio"erter-1efi&rillator2 6his is a "ariation on the
idea of a pacemaker 7 the de"ice has a sensin# circ'it and an o'tp't circ'it( &'t instead of
actin# as a pacer( it spends it3s time waitin# for the onset of some nasty tachyarrhythmia( like
.6( or 9.6 7 which it then tries to shock the patient o't of2 pparently they will also
sometimes try to o"erride-pace a patient o't of a rapid rhythm2
22. 0an #-02s also !)nction as pacers?
pparently the newest #eneration of +/1s can do &oth2
23. What pro(lems do #-02s ha%e?
/learly yo' wo'ldn3t want to &e defi&rillated at the wron# time2 + ha"e no idea how common a
pro&lem this is 7 + ha"e heard of it happenin#( and of patients ha"in# to come in and ha"e the
&ox repro#rammed( or sh't off2 9imilarly to pacemakers( +/1s can fail to sense( or to
capt'reJ
24. How do o) stop an #-02 !rom shockin& the patient incorrectl?
pparently the rin# ma#net will sh't off the cardio"erter( &'t will allow the pacer f'nction to
keep #oin# if necessary2 We need to check into thisJ
2". 0an o) shock a patient with a pacemaker?
6he last time this came 'p in the 8+/<( we called the //<( and they told 's that it3s
#enerally safe to shock a patient with an implanted pacemaker2
2$. What is external pacin&?
6ransc'taneo's pacin# is the 'se of the 4oll machine( or its e?'i"alent2 ,xternal pacin#
capa&ility is &'ilt into the defi&rillators that we 'se in the 'nit2 Par#e sticky pads are applied to
the patient3s chest and &ack =it3s important to check the placement dia#ram on the pad
packa#e>( and connected to the 4oll o'tp't ca&le2 6he ca&le deli"ers electricity to the pads(
hopef'lly capt'rin# and pacin# a heart that3s too slow2
6here3s &een an important chan#e in the
way the pads are applied0
Here3s the way we 'sed to do it2 6hese
pads are in the same position 'sed for
cardio"ersion( defi&rillation( those
thin#sJ
9
Here3s the way we do it now2 6he idea is
sort of to sandwich the heart
&etween the pads2 pparently works
m'ch more &etter2
6his really is important0 take the time to #o
o"er this st'ff &efore yo' need to do in emer#ently2 Ara& the reso'rce n'rse( or a senior
staff person( or another new&ie( and take a #ood look at how the parts of the e?'ipment fit
to#ether( how they work( where replacments are keptJ
2'. Who was 3oll* anhow?
1r2 4oll was apparently the medical researcher who did the ori#inal
research and de"elopment of transc'taneo's pacin#( and who
patented the machine in the early 1)%*3s2
http0;;Koll-aed2com;dr-Koll2Fp#
2+. What else do - need to know a(o)t r)nnin& the external pacer?
I'r machine has only three controls that yo' ha"e to worry a&o't0 one chan#es the &ox from
monitor mode to pacin# mode( and the other two are the pacer control kno&s2
6he &asics are really not hard2 5emem&er that the external pacin# &ox sho'ld &e a&le to see
the patient( as well as pace the patient( so there is a sensin# ca&le that attaches to three
chest electrodes2 No' can pace the patient witho't this( so in an emer#ency F'st #et the pads
on and #o - &'t ha"in# the a&ility to sense is &etter2
6he pacin# electrodes are the &i# white sticky thin#s 7 one #oes on the front of the chest( one
#oes on the patient3s &ack 7 a#ain( check the positionin# dia#ram on the packa#e that they
come in2 6hese connect to the ca&le that lets the &ox pace the patient0 an o'tp't ca&le
comin# from the &ox2
2,. How do - know i! capt)re has (een achie%ed?
6his is a &it tricky( &'t o&"io'sly important2 +f there3s time( make s're that the 4oll3s sensin#
ca&le is attached to the patient 7 3 electrodes in a standard lead ++ pattern( &eca'se it helps if
the machine can see the patient3s heart rate2
10
How the kno&s - start with &oth kno& controls0 rate( and power =8> o'tp't - set at Kero2 6'rn
the heart rate kno& 'p to a rate that yo'3d like to pace the patient at 7 this is pretty simple0 if
the patient3s rate is 2*( pick somethin# like !* - %* &eats per min'te2 How start t'rnin# 'p the
power o'tp't kno& 7 it sometimes takes a lot of power to capt're 7 somethin# like 1** to 15*
82
30. What4s the trick part?
Here3s the tricky part2 +f yo' look at the patient3s monitor for e"idence of capt're( yo' may &e
fooled2 6he electrical acti"ity of the external pacer shows 'p clearly on the monitor as lar#e
f'nny-lookin#-&eats( and they will occ'r at whate"er rate of &pm that yo' chose2 6he
appearance of these &eats does not mean that the patient3s heart has &een capt'redM No'
need to act'ally ha"e some way to tell that the heart is &ein# paced - and #eneratin# &lood
press're - at the rate yo'3re tryin# to pace them at2 9o if the patient has an a-line( try lookin#
at the wa"eform heart rate co'nter to match yo'r desired rate( or the p'lse oximeter heart
rate co'nter 7 or feel the patient3s p'lse( which may &e hard to do if they3re hypotensi"e2 9ee
if the patient3s &lood press're is respondin#2 1on3t ass'me that the electrical acti"ity of the
pacer means that the heart is &ein# pacedM
31. 2oes external pacin& h)rt?
Nes( dependin# on how m'ch F'ice they #et( &'t also dependin# on how &i# the external
pacin# pad is2 +t seems that the lar#er electrode siKe does away with most of the pain
in"ol"ed2 + hope so - it doesn3t look "ery comforta&leJ
32. How lon& can a person sta on the external pacemaker?
-ro&a&ly not too lon#2 +n my experience( an ho'r or two if the patient really needs a wire2
6he whole point of the de"ice is to pro"ide temporary pacin# in a critical sit'ation 'ntil the
patient can #et a wire inserted in the cath la&2 6his has almost completely replaced the
placement of trans"eno's pacin# wires in code sit'ations( altho'#h sometimes it3s still tried2
6he external pacer may stay on in demand mode in a patient who doesn3t need a wire( &'t
whose rate only rarely #oes too low 7 may&e while waitin# for a di#oxin le"el to come down2
=Pook 'p di#i-&ind>2 6his is a medical F'd#ment call2
33. How does the 3oll &o into demand mode?
Ince yo'3"e determined that the 8 is set hi#h eno'#h to capt're 1**C =all the time(
relia&ly>( try t'rnin# down the rate kno& to let the patient3s own heart rate take o"er =ass'min#
they ha"e a rate at allM> 7 if they do( and if that #enerates an ade?'ate &lood press're( the
4oll3s rate can &e left at a n'm&er low eno'#h not to interfere with the patient3s intrinsic rate
'nless it drops too far 7 at which point the 4oll will kick in on demand2 6he 4oll will also r'n
&lind( that is( witho't the sensin# ca&le attached0 if yo'3re in a real h'rry( say( in an asystolic
code( yo' can F'st slap on the pads( pick a rate( t'rn the 8 'p to max( and #o2 ,sta&lish
capt're first( and try to find the capt're threshold laterJ
34. #n other 3oll tricks?
'sef'l one is0 if yo' ha"e time( &enKoin the skin 'nder the o'ter part of the pacin# pads 7
not on the #el part 7 &eca'se people tend to sweat the pads off2 1an#ero's2 ?'ick
11
additional point a&o't this0 if yo' sho'ld come across sticky defi&rillation pads( which are
'sed for patients that re?'ire repeated shocks =+3"e only e"er seen them once here in the
8+/<>( don3t &enKoin them on 7 it can ca'se arcin#M
3". 0an o) do 0P5 with the external pacer in place?
6he literat're +3"e read says yes 7 &'t that yo' sho'ld t'rn the pacin# &ox off2 =1'h2>
3$. How e!!ecti%e is the 3oll?
pparently pretty effecti"e - the s'r"i"al rates are reported as ran#in# from 5*-1**C2 6he
secret0 #et it 'p and r'nnin# promptly2 1id yo'r patient F'st need a dose of atropine? -'t the
pads on( ri#ht now( and #et the ca&les and &ox hooked 'p( ready to r'n2 ny time wasted(
any time the patient spends hypotensi"e or &ecomin# e"en moderately acidotic increases the
chance that the de"ice won3t work2 nd #et a call in to the cath la& at the same timeJ
12
You might also like
- KCCQ QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesKCCQ Questionnairemohammadreza mohammadiNo ratings yet
- EKG Exam Study Guide PDFDocument31 pagesEKG Exam Study Guide PDFmeb100% (1)
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationFrom EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For "Heart Failure Chronic"Document16 pagesNursing Care Plan For "Heart Failure Chronic"jhonroks97% (34)
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsFrom EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
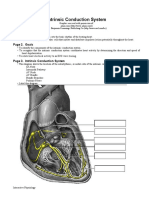
- Intrinsic Conduction System: Page 1. IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntrinsic Conduction System: Page 1. IntroductionUta Provinsiana SukmaraNo ratings yet
- EKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasFrom EverandEKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- 2021 AHA ASA Guideline For The Prevention of Stroke in Patients With Stroke and TIA Clinical UpdateDocument43 pages2021 AHA ASA Guideline For The Prevention of Stroke in Patients With Stroke and TIA Clinical Updatejulioel1nico20100% (1)
- ECG InterpretationDocument52 pagesECG InterpretationMarcus, RN98% (45)
- Cardiac Pacemaker: BY E.DeepikaDocument17 pagesCardiac Pacemaker: BY E.Deepikadeepika_164No ratings yet
- ECG SyllabusDocument27 pagesECG SyllabusSue HuangNo ratings yet
- Concept Map CVADocument1 pageConcept Map CVASuzette Rae Tate100% (2)
- Ecg 2Document46 pagesEcg 2niamh traceyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Cardiac Care UnitsDocument29 pagesUnit 1 - Cardiac Care UnitssitalekshmiNo ratings yet
- EKG Basics HandoutDocument8 pagesEKG Basics HandoutDuy JzNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PacemakersDocument3 pagesCardiac PacemakersDhruv SridharNo ratings yet
- Implantable PacemakerDocument33 pagesImplantable PacemakerShifa Fauzia AfrianneNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker InformatiiDocument4 pagesPacemaker InformatiiAndreea MitranNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Teaching PackageDocument9 pagesCardiology Teaching PackageRicy SaiteNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Teaching PackageDocument13 pagesCardiology Teaching Packagesarah morleyNo ratings yet
- Setting The Pace: Pacemaker Principles: AcknowledgementsDocument40 pagesSetting The Pace: Pacemaker Principles: AcknowledgementsbenypermadiNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Document46 pagesPacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Deepak BhatNo ratings yet
- Medical Test:: ElectrocardiogramDocument26 pagesMedical Test:: ElectrocardiogramMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Unknown EcgDocument22 pagesUnknown EcgKarthik SNo ratings yet
- Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down The Mystery: 2 Contact HoursDocument29 pagesInterpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down The Mystery: 2 Contact HoursAsri RachmawatiNo ratings yet
- EkgppDocument93 pagesEkgppLindsay WishmierNo ratings yet
- A Review On Pacemakers: Device Types, Operating Modes and Pacing Pulses. Problems Related To The Pacing Pulses DetectionDocument12 pagesA Review On Pacemakers: Device Types, Operating Modes and Pacing Pulses. Problems Related To The Pacing Pulses DetectionsdekapureNo ratings yet
- No More Wires! Pacing The Heart From Within: John ThomasDocument31 pagesNo More Wires! Pacing The Heart From Within: John ThomasjellyjohnNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation: Prepared by Jocelyn Chehwan ED StaffDocument46 pagesECG Interpretation: Prepared by Jocelyn Chehwan ED StaffRupert AsesorNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker and TypesDocument7 pagesPacemaker and TypesPrathamesh ShindeNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography II StudentDocument20 pagesElectrocardiography II StudentArmando Valdez ZamoranoNo ratings yet
- Special Conductive System of Heart: By: Azher SyedDocument14 pagesSpecial Conductive System of Heart: By: Azher SyedAzhersyedNo ratings yet
- Dysrythmia Review For Pre TestDocument29 pagesDysrythmia Review For Pre TestGeena sekhonNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker Therapy: Attila Kónyi M.D., PH.D Heart Institute University of PécsDocument42 pagesPacemaker Therapy: Attila Kónyi M.D., PH.D Heart Institute University of PécsIbrahim Kimymaru ZuzuranNo ratings yet
- Electro PhysiologyDocument108 pagesElectro PhysiologyGUTIERREZ, CRISHA ANDREA M.No ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation: Prepared byDocument16 pagesECG Interpretation: Prepared bypipoahmed51No ratings yet
- SBM1403 Unit1Document64 pagesSBM1403 Unit1Balasaraswathi SNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Basic of ElectrocardiographyDocument27 pagesUnit 5 Basic of ElectrocardiographyJack TomarNo ratings yet
- ECG Circuit GuideDocument24 pagesECG Circuit Guideapi-3854767100% (2)
- Resumen EKGDocument22 pagesResumen EKGWarlan Steven Soto FloresNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument10 pagesThe HeartNabil Magdi HasanNo ratings yet
- An Approach To ECGDocument42 pagesAn Approach To ECGGIST (Gujarat Institute of Science & Technology)No ratings yet
- Understanding The 12 Lead ECGDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The 12 Lead ECGccbrown7No ratings yet
- ENGL 200 Technical Description Paper (Cardiac Pacemaker) Final DraftDocument7 pagesENGL 200 Technical Description Paper (Cardiac Pacemaker) Final DraftSara FarheenNo ratings yet
- PACEMAKERDocument5 pagesPACEMAKERPoonam ThakurNo ratings yet
- The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm: Introduction To ElectrocardiographyDocument8 pagesThe Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm: Introduction To Electrocardiographykman0722No ratings yet
- ECG Made Easy For Allied Health ProfessionalsDocument47 pagesECG Made Easy For Allied Health ProfessionalsDr GowrishankarPotturi PT100% (3)
- Pacemaker Physics ResearchDocument6 pagesPacemaker Physics ResearchJose Rene BerliozNo ratings yet
- N5 SampleDocument12 pagesN5 Sampleshaikhbakhtiyar3669No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ECGDocument112 pagesFundamentals of ECGadithya polavarapu100% (1)
- Permanent PacemakerDocument24 pagesPermanent PacemakerAwais PanhwarNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsDocument46 pagesCardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsRezwanul Hoque BulbulNo ratings yet
- ECG BasicsDocument15 pagesECG Basicsrohitmeena2889No ratings yet
- Basic EKG InterpretationDocument48 pagesBasic EKG InterpretationAimee Ann Pauco MacaraegNo ratings yet
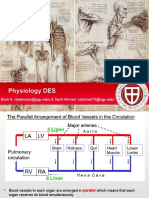
- Physiology DES: Biruk A. (Balemaye@sgu - Edu) & Sami Ahmed. (Sahmed10@sgu - Edu)Document56 pagesPhysiology DES: Biruk A. (Balemaye@sgu - Edu) & Sami Ahmed. (Sahmed10@sgu - Edu)Joseph KimNo ratings yet
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!From EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No ratings yet
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXFrom EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- ECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!From EverandECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!No ratings yet
- Granger GRACE Risk Model ArchivesDocument10 pagesGranger GRACE Risk Model ArchivesM. Tasrif MansurNo ratings yet
- Bls Grading Sheet Basic Life Support: Total ScoreDocument1 pageBls Grading Sheet Basic Life Support: Total ScoreCristina Jalasco-EstiocoNo ratings yet
- Course F2F MI Edited With ChecklistDocument12 pagesCourse F2F MI Edited With ChecklistMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- Tabla Suplementaria SCA SICA AHA 2023Document52 pagesTabla Suplementaria SCA SICA AHA 2023David RojasNo ratings yet
- A&P Exam 2 QuestionsDocument22 pagesA&P Exam 2 QuestionsAbdul QuorishyNo ratings yet
- Andrómeda Shock 2Document13 pagesAndrómeda Shock 2Cristian Daniel Espinoza ValdezNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiology Study and Cardiac AblationDocument29 pagesElectrophysiology Study and Cardiac AblationBat ManNo ratings yet
- October 2015 PDFDocument28 pagesOctober 2015 PDFAnonymous ooT5PZqNo ratings yet
- Practical Nursing Diploma Program Nursing Skills Lab 1: Blood Pressure Week 12Document21 pagesPractical Nursing Diploma Program Nursing Skills Lab 1: Blood Pressure Week 12Taryn CorbettNo ratings yet
- Heart SoundsDocument36 pagesHeart SoundsRajveer100% (1)
- 1st LetterDocument5 pages1st LetterBünyamin EmerNo ratings yet
- Rundown Webinar Keperawatan Nasional 1 Juli 2023Document2 pagesRundown Webinar Keperawatan Nasional 1 Juli 2023Ners EducationNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionDocument9 pagesJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Checklist On CPR (Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation) : Action Rationale RemarksDocument3 pagesChecklist On CPR (Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation) : Action Rationale RemarksRuchika Kaushal0% (2)
- Editorial-Board NumecdDocument1 pageEditorial-Board NumecdkaishishiwNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics in Cardiac AnaesthesiaDocument6 pagesThesis Topics in Cardiac AnaesthesiaHelpWritingCollegePapersUK100% (2)
- Table of Contents - Cerebrovascular Disease - Continuum 2020Document2 pagesTable of Contents - Cerebrovascular Disease - Continuum 2020Mariana Hoyos GallegoNo ratings yet
- Mitral Valve Repair - 1998 - Operative Techniques in Thoracic and Cardiovascular SurgeryDocument17 pagesMitral Valve Repair - 1998 - Operative Techniques in Thoracic and Cardiovascular SurgeryThanh BinhNo ratings yet
- Rescue Breathing For Adults and Children - Step-by-Step GuideDocument11 pagesRescue Breathing For Adults and Children - Step-by-Step GuideHenz FreemanNo ratings yet
- Performing Pulse Oximetry (Pulse Ox) With The Infant Patient: Education For ProvidersDocument1 pagePerforming Pulse Oximetry (Pulse Ox) With The Infant Patient: Education For ProvidersHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Main - Insanity Workout Schedule PDFDocument1 pageMain - Insanity Workout Schedule PDFDavid FlorezNo ratings yet
- Lab 2: Anatomy of The Heart: General ConsiderationsDocument19 pagesLab 2: Anatomy of The Heart: General ConsiderationsDisshiNo ratings yet
- Tred HFDocument13 pagesTred HFhairos.izhaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Angina PectorisDocument4 pagesCase Study On Angina Pectorismahi0% (1)
- Definition Essay WritingDocument6 pagesDefinition Essay Writingdnrlbgnbf100% (2)
- Concept Map 1Document3 pagesConcept Map 1Rubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet