Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Routing: What Is The Difference Between Routing and Forwarding?
Routing: What Is The Difference Between Routing and Forwarding?
Uploaded by
Vô Danh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesRouting determines the path between nodes, while forwarding uses the routing information to transfer packets. The document then discusses routing protocols and describes the distance vector protocol RIP. RIP employs the Bellman-Ford algorithm, supports networks up to 16 hops, and uses UDP port 520 for periodic updates sent every 30 seconds. Problems with RIP include slow convergence due to counting to infinity, which is addressed using split horizon and poison reverse updates. Authentication in RIP version 2 uses a plain text 16-octet password in the first entry of routing updates.
Original Description:
Original Title
Routing.slides
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRouting determines the path between nodes, while forwarding uses the routing information to transfer packets. The document then discusses routing protocols and describes the distance vector protocol RIP. RIP employs the Bellman-Ford algorithm, supports networks up to 16 hops, and uses UDP port 520 for periodic updates sent every 30 seconds. Problems with RIP include slow convergence due to counting to infinity, which is addressed using split horizon and poison reverse updates. Authentication in RIP version 2 uses a plain text 16-octet password in the first entry of routing updates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesRouting: What Is The Difference Between Routing and Forwarding?
Routing: What Is The Difference Between Routing and Forwarding?
Uploaded by
Vô DanhRouting determines the path between nodes, while forwarding uses the routing information to transfer packets. The document then discusses routing protocols and describes the distance vector protocol RIP. RIP employs the Bellman-Ford algorithm, supports networks up to 16 hops, and uses UDP port 520 for periodic updates sent every 30 seconds. Problems with RIP include slow convergence due to counting to infinity, which is addressed using split horizon and poison reverse updates. Authentication in RIP version 2 uses a plain text 16-octet password in the first entry of routing updates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
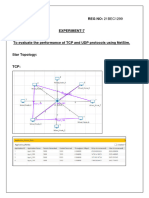
Routing
What is the difference between routing and forwarding?
Routing protocols:
Implemented distributed algorithms (scalability)
Routers should have mutually consistent view of the network.
Can be classified into:
Intradomain versus interdomain routing protocols.
Distance vector versus link state routing protocols.
38
UTD, CS 6390
Ravi Prakash
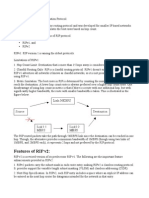
RIP: Distance Vector Protocol
Employs Bellman-Ford algorithm.
Meant for introdomain routing.
Maximum supported network diameter = 16.
Widely deployed: not going to disappear soon.
Latest version: RIP-2.
39
UTD, CS 6390
Ravi Prakash
RIP (contd.)
UDP-based protocol.
RIP port for messaging: 520.
Periodic updates at 30-second intervals.
Each update entry = 20 bytes.
Between 1 - 25 entries per update.
180-second timer to detect link breaks.
40
UTD, CS 6390
Ravi Prakash
Problems with RIP
Count-to-infinity (16): results in slow convergence.
Solution:
Split horizon: do not advertise destination information to node
from which the information is learned.
Poison reverse: advertise infinite cost, instead of omitting the
advertisement, for that destination.
Triggered updates: for fast convergence.
Guard against excessive updates.
Bundle multiple updates using 1-5 second timer.
Split horizon is required, while poison reverse is optional.
41
UTD, CS 6390
Ravi Prakash
Authentication in RIP
Supported in RIP-2.
If present, occupies first RIP entry (20 bytes).
Authentication header contains 16-octet plain text password.
42
UTD, CS 6390
Ravi Prakash
You might also like
- 166 Exp4Document15 pages166 Exp4neha.shroffNo ratings yet
- RIP PresentationDocument43 pagesRIP PresentationNarendra KishoreNo ratings yet
- Lec4 RoutingDocument38 pagesLec4 RoutingTanveer AhmedNo ratings yet
- CCN Lab Exp 21BEC1299Document24 pagesCCN Lab Exp 21BEC1299Dhaanesh S 21BEC1299No ratings yet
- 263 Exp3 CNSDocument15 pages263 Exp3 CNSneha.shroffNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Network Layer ProtocolsDocument34 pagesLecture - Network Layer Protocolsaishamajeed129No ratings yet
- Routing: Unicast and Multicast RoutingDocument32 pagesRouting: Unicast and Multicast RoutingSuranga SampathNo ratings yet
- Ccna Q and AnsDocument9 pagesCcna Q and Ansabisa52No ratings yet
- Routing Protocols (RIP, OSPF, and BGP) : Mi-Jung Choi Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Mjchoi@postech - Ac.krDocument86 pagesRouting Protocols (RIP, OSPF, and BGP) : Mi-Jung Choi Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Mjchoi@postech - Ac.krHafeez MohammedNo ratings yet
- CCNA Cisco Routing Protocols and Concepts Final Exam-PracticeDocument22 pagesCCNA Cisco Routing Protocols and Concepts Final Exam-Practicesabriel69100% (1)
- CCNA2 Final Mar 2010: CCNA Cisco Routing Protocols and Concepts Final Exam PracticeDocument21 pagesCCNA2 Final Mar 2010: CCNA Cisco Routing Protocols and Concepts Final Exam Practicetuananh0788No ratings yet
- Answer: Which of The Following Are True Regarding Passwords On A Cisco Router?Document37 pagesAnswer: Which of The Following Are True Regarding Passwords On A Cisco Router?dijeshkelothNo ratings yet
- Routing ProtocolDocument12 pagesRouting ProtocolKetan GargNo ratings yet
- Ccna 2012-13 AnswersDocument9 pagesCcna 2012-13 AnswersVangelis AthanasiadisNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Cisco CCNP RouteDocument65 pagesWelcome To Cisco CCNP RouteAreefNo ratings yet
- Final Exam CCNA2 - AnswerDocument20 pagesFinal Exam CCNA2 - AnswerJoy Maglantay Dujali100% (1)
- Computer Network: Routing ProtocolsDocument46 pagesComputer Network: Routing ProtocolsEmad Samir FarahatNo ratings yet
- RIP Protocol Using Cisco Packet TracerDocument8 pagesRIP Protocol Using Cisco Packet TracerSwarnali NathNo ratings yet
- RIP Routing FundamentalsDocument3 pagesRIP Routing FundamentalsKarlNo ratings yet
- Rip V1 & V2Document6 pagesRip V1 & V2Sujith VSNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration2: Routing Protocols and Concepts - Final ExamDocument12 pagesCCNA Exploration2: Routing Protocols and Concepts - Final ExamSumi SultanaNo ratings yet
- Semester II. - Chapter 3Document6 pagesSemester II. - Chapter 3KlokanNo ratings yet
- B. Identity Service Engine: AnswerDocument35 pagesB. Identity Service Engine: AnswernoerxNo ratings yet
- Features of RIP v2:: RIP Stands For Routing Information ProtocolDocument2 pagesFeatures of RIP v2:: RIP Stands For Routing Information ProtocolSenan AlkaabyNo ratings yet
- CCNP Ccie 350 401 New 29 Jun 2020Document101 pagesCCNP Ccie 350 401 New 29 Jun 2020Aly Abdelhamed88% (8)
- Lab 12 CCN MUSTAFADocument3 pagesLab 12 CCN MUSTAFAAbdul ShakoorNo ratings yet
- Network LayerDocument27 pagesNetwork Layerrktiwary256034No ratings yet
- HCDA HC 211 Exam Updated Jan2013Document9 pagesHCDA HC 211 Exam Updated Jan2013samu1991tan50% (2)
- Exploration Routing Chapter 2Document43 pagesExploration Routing Chapter 2vildsmanNo ratings yet
- Buffer It Until It Learns A Route To 2.2.0.0 Forward It To 1.1.1.2 Forward It To 1.1.2.2 Forward It To 2.1.1.2 Drop The PacketDocument14 pagesBuffer It Until It Learns A Route To 2.2.0.0 Forward It To 1.1.1.2 Forward It To 1.1.2.2 Forward It To 2.1.1.2 Drop The PacketfazzichNo ratings yet
- Ripng Message FormatDocument2 pagesRipng Message Formatvisakh21No ratings yet
- Subnet Mask That Should Be Assigned To Routes That Are Learned From Neighboring Classless Routers?Document16 pagesSubnet Mask That Should Be Assigned To Routes That Are Learned From Neighboring Classless Routers?Kinga JanasińskaNo ratings yet
- Ccna 3 Chapter 5 (Version 4.0)Document8 pagesCcna 3 Chapter 5 (Version 4.0)_mika_No ratings yet
- CCNA 2 FinalDocument38 pagesCCNA 2 FinalTuấnNo ratings yet
- Routing Information Protocol RIPDocument27 pagesRouting Information Protocol RIPomarkhanfar2No ratings yet
- Lte Bab5lteoptimizationguideline 160229102835Document71 pagesLte Bab5lteoptimizationguideline 160229102835Sunny Girija SapruNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument13 pagesFinallambobNo ratings yet
- Ccna HCL Exam QuestionsDocument25 pagesCcna HCL Exam Questionsshyam80No ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Final Exam Question Ans AnswerDocument100 pagesCCNA 2 Final Exam Question Ans AnswerTú BéoNo ratings yet
- CA Ex S2M05 RIP Version 1Document38 pagesCA Ex S2M05 RIP Version 1http://heiserz.com/No ratings yet
- Static and Dynamic Routing Protocols NotesDocument4 pagesStatic and Dynamic Routing Protocols NotesloadNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Final Exam V4Document13 pagesCCNA 2 Final Exam V4Ale AlvarezNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration2 - Routing Protocols and Concepts - Chapter 3 ExamDocument6 pagesCCNA Exploration2 - Routing Protocols and Concepts - Chapter 3 Examchocolat4No ratings yet
- BGP Multihoming Techniques: Philip Smith Menog 13 Kuwait 24 September 2013Document216 pagesBGP Multihoming Techniques: Philip Smith Menog 13 Kuwait 24 September 2013Supriyo SahaNo ratings yet
- 13 Network LayerDocument15 pages13 Network LayerNehal GuptaNo ratings yet
- SW3 Is Configured As Transparent ModeDocument21 pagesSW3 Is Configured As Transparent ModechkimkimNo ratings yet
- CCNA2 - Final Exam (Version 2) Ccna2 Final Version 4.0 (97,2%)Document10 pagesCCNA2 - Final Exam (Version 2) Ccna2 Final Version 4.0 (97,2%)Tanase CristianNo ratings yet
- Answer:A & EDocument15 pagesAnswer:A & ELvenkatesh VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Ccnaexp 5Document77 pagesCcnaexp 5opsssNo ratings yet
- Final CCNA2 4Document27 pagesFinal CCNA2 4itborgNo ratings yet
- Dynamic RoutingDocument9 pagesDynamic Routingi200634 Areeba SattarNo ratings yet
- What Is Global Configuration Mode Used For?Document10 pagesWhat Is Global Configuration Mode Used For?Abhishek KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 7 ROUTING PROTOCOLS 18 Feb 2021material I 18 Feb 2021 Routing ProtocolsDocument33 pages7 ROUTING PROTOCOLS 18 Feb 2021material I 18 Feb 2021 Routing ProtocolsSharath KumarNo ratings yet
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONFrom EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNo ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet