Professional Documents
Culture Documents
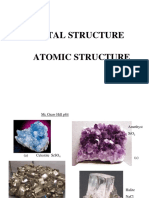
Types of Solid: - Crystalline - Amorphous
Types of Solid: - Crystalline - Amorphous
Uploaded by
Salman KhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Solid: - Crystalline - Amorphous
Types of Solid: - Crystalline - Amorphous
Uploaded by
Salman KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Solid
Crystalline
Amorphous
2
atoms pack in periodic, 3D arrays
Crystalline materials...
-metals
-many ceramics
-some polymers
atoms have no periodic packing
Noncrystalline materials...
-complex structures
-rapid cooling
crystalline SiO2
noncrystalline SiO2
"Amorphous" = Noncrystalline
Adapted from Fig. 3.23(b),
Callister & Rethwisch 8e.
Adapted from Fig. 3.23(a),
Callister & Rethwisch 8e.
Si Oxygen
typical of:
occurs for:
Known as crystalline or morphous, has regular crystal lattices, or
long-range order. These solids are stabilized by the regular
pattern of their atoms. Their characteristic properties include
distinct melting and boiling points, regular geometric shapes,
and flat faces when cleaved or sheared. Some examples include
sodium chloride, ice, metals, and diamonds.
Crystalline materials...
SPACE LATTICE AND UNIT CELLS
Space Lattice/Crystal Lattice -- atoms arranged in a
pattern that repeats itself in three dimensions.
Unit cell -- smallest grouping which can be
translated in three dimensions to recreate the
space lattice.
Lattices in Three Dimensions
Fourteen Lattices
Simple cubic
Atoms per Unit Cell????
9
Adapted from Fig. 3.2,
Callister & Rethwisch 8e.
Atoms touch each other along cube diagonals.
--Note: All atoms are identical; the center atom is shaded
differently only for ease of viewing.
Body Centered Cubic Structure (BCC)
ex: Cr, W, Fe (), Tantalum, Molybdenum
atoms/unit cell:???
Click once on image to start animation
(Courtesy P.M. Anderson)
2 atoms/unit cell: 1 center + 8 corners x 1/8
11
Adapted from Fig. 3.1, Callister & Rethwisch 8e.
Atoms touch each other along face diagonals.
Face Centered Cubic Structure (FCC)
ex: Al, Cu, Pb, Ni
4 atoms/unit cell: 6 face x 1/2 + 8 corners x 1/8
Click once on image to start animation
(Courtesy P.M. Anderson)
4 atoms/unit cell: 6 face x 1/2 + 8 corners x 1/8
13
Coordination # = 12
3D Projection 2D Projection
Adapted from Fig. 3.3(a),
Callister & Rethwisch 8e.
Hexagonal Close-Packed Structure
(HCP)
6 atoms/unit cell
ex: Cd, Mg, Ti, Zn
c
a
A sites
B sites
A sites
Bottom layer
Middle layer
Top layer
Packing Efficiency
P.E =
Volume of one atom* x No. of atoms per cell
Volume of unit cell
*assume hard spheres
You might also like
- 3A Crystal StructureDocument70 pages3A Crystal StructureIvy TovilloNo ratings yet
- Structures of Solids: Engr. Ana Lorraine M. Dalilis, RcheDocument71 pagesStructures of Solids: Engr. Ana Lorraine M. Dalilis, RcheAna Lorraine DalilisNo ratings yet
- Crystal StructureDocument47 pagesCrystal Structurenaz_qd358No ratings yet
- Crystal Structure: Group No:-3 Group MembersDocument23 pagesCrystal Structure: Group No:-3 Group MembersAmlan pandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document75 pagesChapter 3SAIF ULLAHNo ratings yet
- 1-Structure of Solids (Metals)Document41 pages1-Structure of Solids (Metals)karu320No ratings yet
- Keadaan Kristal-2Document47 pagesKeadaan Kristal-2Bhatara Ayi MeataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Materials Science Crystal StructuresDocument51 pagesChapter 3 - Materials Science Crystal Structurestjipotjipi mungundaNo ratings yet
- SSD - L02 - Review On CrystallographyDocument25 pagesSSD - L02 - Review On CrystallographysumonNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors Materials, Crystallographic Terms, Crystal LatticesDocument36 pagesSemiconductors Materials, Crystallographic Terms, Crystal LatticesSalaar KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 2 2 IPE 2203-LecturesDocument44 pagesWeek 2 2 IPE 2203-LecturesMD Al-AminNo ratings yet
- Tema 4: Química Del Estado Sólido: Dr. Jorge CernaDocument27 pagesTema 4: Química Del Estado Sólido: Dr. Jorge CernaSusan FernandezNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Lec2Document59 pagesAtomic Structure Lec2Paras gurungNo ratings yet
- Week2 (1) - Crystalline StructureDocument79 pagesWeek2 (1) - Crystalline StructureLily ERc PeterNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Structure of Solids: Based On Chapter 3 (Callister)Document33 pagesTopic 3: Structure of Solids: Based On Chapter 3 (Callister)Jehu Roblero100% (1)
- 7 Crystalline & Solid StateDocument37 pages7 Crystalline & Solid StateNazmi LatifNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Crystalline SolidsDocument40 pagesThe Structure of Crystalline SolidsGeleta Bekele100% (1)
- SolidDocument38 pagesSolidRalph RebugioNo ratings yet
- Files Chapters ME215 Ch3 RDocument93 pagesFiles Chapters ME215 Ch3 RMohammad Tabrez AlamNo ratings yet
- 3-Crystallinity of Materials Mod ADocument32 pages3-Crystallinity of Materials Mod ATsuki NakamiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To M S M and Crystal Structure-1Document50 pagesIntroduction To M S M and Crystal Structure-1Dhananjay NNo ratings yet
- ch3 p1Document42 pagesch3 p1Sary KilanyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document44 pagesChapter 3malikwaleedsher68No ratings yet
- Lecture3 Material MajuDocument35 pagesLecture3 Material MajuFarid N SNo ratings yet
- Madhav Institute of Technology & Science, Gwalior: Subject:-Engineering Material (EM)Document52 pagesMadhav Institute of Technology & Science, Gwalior: Subject:-Engineering Material (EM)RAGHAV JAIN100% (1)
- 2 - Structure of Crystalline SolidsDocument18 pages2 - Structure of Crystalline Solidslhudielyn abeNo ratings yet
- EE2317-Course-Structures of Crystalline SolidsDocument148 pagesEE2317-Course-Structures of Crystalline SolidsJOSEPH BENEDICT PRIMNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 Metallic StructureDocument34 pagesLec 4 Metallic StructureFaisal NadeemNo ratings yet
- 03 - Crystal Structures of MetalsDocument8 pages03 - Crystal Structures of MetalsJant Erbert GarbosoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - The Structure of Crystalline Solids and Non Crystalline MaterialsDocument81 pagesChapter 3 - The Structure of Crystalline Solids and Non Crystalline MaterialsMaximillian AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Crystalline Properties of SolidsDocument24 pagesCrystalline Properties of SolidsMD. MEHEDI HASANNo ratings yet
- EEM - Lecture 1-3Document95 pagesEEM - Lecture 1-3Shuvo DevNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Crystalline StructureDocument66 pagesChapter 2-Crystalline StructureSimon SisayNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structures: Unit-IDocument69 pagesCrystal Structures: Unit-Irahul_patil85No ratings yet
- The Structure of Crystalline Solids: Chapter 3Document76 pagesThe Structure of Crystalline Solids: Chapter 3ShakeelAhmadNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structure of MetalsDocument31 pagesCrystal Structure of MetalsTanzir Musa100% (2)
- Module 2 The Structure of Crystalline SolidDocument31 pagesModule 2 The Structure of Crystalline SolidMuhammadFaishalFadhlurahmanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Materials: Chap 1Document28 pagesElectrical Properties of Materials: Chap 1Shuvro Sankar SenNo ratings yet
- Lec 3-Crystal Structure of MetalsDocument20 pagesLec 3-Crystal Structure of MetalsAli Hassan100% (1)
- 9-18 Crystal StructuresDocument10 pages9-18 Crystal StructuresChamalNo ratings yet
- Chapter RegsgvDocument4 pagesChapter RegsgvDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Why We Study Solid State PhysicsDocument19 pagesLecture 1 Why We Study Solid State Physicsريمكس REMIXNo ratings yet
- ENS167 Lecture 3Document24 pagesENS167 Lecture 3JANNA MARIE NInA BATENo ratings yet
- Structure of SolidsDocument46 pagesStructure of SolidsManu ChakkingalNo ratings yet
- 02-Pet Eng Design - PTE - 470 - The Structure of Crystalline SolidsDocument15 pages02-Pet Eng Design - PTE - 470 - The Structure of Crystalline SolidsHassan KhalifeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Structures of Metals and CeramicsDocument38 pagesLecture 3 - Structures of Metals and CeramicsDan CostelloNo ratings yet
- Week4 Chapter 5 Packing of Atoms in SolidsDocument33 pagesWeek4 Chapter 5 Packing of Atoms in Solids배현준No ratings yet
- CH 3 Crystalline StructuresDocument71 pagesCH 3 Crystalline StructuresMusab AbdrabbuhNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document91 pagesCH 03Defne SunerNo ratings yet
- Solid State ChemistryDocument7 pagesSolid State ChemistryCatherine PaschalNo ratings yet
- Module 2. Structure of Crystalline SolidsDocument20 pagesModule 2. Structure of Crystalline SolidsPearl Alexandra FabitoNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology: Suwarna Datar - Ap 608Document56 pagesNanotechnology: Suwarna Datar - Ap 608prakush01975225403No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - CrystalDocument33 pagesCHAPTER 6 - CrystalemanjijanNo ratings yet
- EPM - Mid - Lecture - 02 - Chapt - 1 CompressDocument24 pagesEPM - Mid - Lecture - 02 - Chapt - 1 CompressPartho Protim MondolNo ratings yet
- Based On Chapter 3 (Callister) : Topic 3: Structure of SolidsDocument46 pagesBased On Chapter 3 (Callister) : Topic 3: Structure of SolidsLaila IzzaNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structure of Metal-1Document19 pagesCrystal Structure of Metal-1MUHAMMAD NABEEL ARIF100% (1)