Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STPM Trials 2009 Physics Paper 2 (Terengganu)
STPM Trials 2009 Physics Paper 2 (Terengganu)
Uploaded by
HaRry ChgCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ujian BertulisDocument6 pagesUjian BertulisHaryati Fadhlan100% (1)
- STPM Trials 2009 Physics Answer Scheme (Malacca)Document20 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Physics Answer Scheme (Malacca)c3mutNo ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 2 TerengganuDocument11 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 2 Terengganusherry_christyNo ratings yet
- Te027-2 Sem2 2010-2011Document15 pagesTe027-2 Sem2 2010-2011pusatsumberkmtphNo ratings yet
- BMMD 2313 - Final 20202021Document19 pagesBMMD 2313 - Final 20202021fauzaniNo ratings yet
- TF025-2 Sem2 2010-2011Document21 pagesTF025-2 Sem2 2010-2011pusatsumberkmtphNo ratings yet
- J3008 Mekanik Bendalir 2008Document11 pagesJ3008 Mekanik Bendalir 2008Mahfuzah MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Set Kelantan 2018Document8 pagesSet Kelantan 2018RohanaIthninNo ratings yet
- DJJ 2022Document5 pagesDJJ 2022Nathaniel TayNo ratings yet
- 01QDCB30082Document7 pages01QDCB30082Aishah SeiniNo ratings yet
- K2 Fizik F5 2014Document23 pagesK2 Fizik F5 2014Ilya IsmailNo ratings yet
- Laporan Ujian Proba MackintoshDocument10 pagesLaporan Ujian Proba Mackintoshamirulhaziq161006No ratings yet
- Energy and Electric Power: 3.4. Tenaga Dan Kuasa ElektrikDocument12 pagesEnergy and Electric Power: 3.4. Tenaga Dan Kuasa Elektrikflower boomNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Semester I SESSION 2020/2021: Instruction To CandidatesDocument17 pagesFinal Examination Semester I SESSION 2020/2021: Instruction To CandidatesMohd AsriNo ratings yet
- Ta027-2 Sem2 2010-2011Document11 pagesTa027-2 Sem2 2010-2011pusatsumberkmtphNo ratings yet
- Latihan Ting 5 4Document5 pagesLatihan Ting 5 4nfaizah1100% (1)
- 01QDJJ30103Document10 pages01QDJJ30103boss796No ratings yet
- Mekanika Fluida.4Document23 pagesMekanika Fluida.4Marcel OmpiNo ratings yet
- Trial Pahang SPM 2014 Physics K2Document26 pagesTrial Pahang SPM 2014 Physics K2Cikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Skema K2 Set B JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPMDocument8 pagesSkema K2 Set B JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPMCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Ujian 1 Sem1 2013 - 2014Document8 pagesUjian 1 Sem1 2013 - 2014akaiNo ratings yet
- Soalan FizikDocument10 pagesSoalan FizikAnonymous q9bofmNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document16 pagesPaper 2mellaty8127No ratings yet
- ElectricDocument12 pagesElectricLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Ops Gempur 2 FizikDocument7 pagesOps Gempur 2 FizikHamizanWookNo ratings yet
- E1002Document6 pagesE1002Hazim ZimNo ratings yet
- Fizik SPM FIZ Kertas2Set2Document19 pagesFizik SPM FIZ Kertas2Set2api-3841296No ratings yet
- BEEI3423.Actuator & Drive - M3Document27 pagesBEEI3423.Actuator & Drive - M3Zulkarnain ZainudinNo ratings yet
- Ta027-1 Sem2 2010-2011Document13 pagesTa027-1 Sem2 2010-2011pusatsumberkmtphNo ratings yet
- Test 2-Emk21003-2022Document3 pagesTest 2-Emk21003-2022LIEW HUI FANG UNIMAPNo ratings yet
- Bilik Gelap Ammend No.3 PDFDocument1 pageBilik Gelap Ammend No.3 PDFmaliklduNo ratings yet
- Sesi Ii 2022 2023 - Det40073Document7 pagesSesi Ii 2022 2023 - Det40073Amirul AmarNo ratings yet
- Soalan Cadangan Fizik Percubaan K2 2020Document26 pagesSoalan Cadangan Fizik Percubaan K2 2020Joseph LeeNo ratings yet
- Soalan Peperiksaan Akhir (Palt) DJJ20053 Electrical Technology Sesi 1 2021 - 2022Document7 pagesSoalan Peperiksaan Akhir (Palt) DJJ20053 Electrical Technology Sesi 1 2021 - 2022Vetri Thanabalan100% (1)
- JTKM-BMMA 1333 (Sem2-2020) - Question Paper-Set1Document16 pagesJTKM-BMMA 1333 (Sem2-2020) - Question Paper-Set1Fgj JhgNo ratings yet
- Ebb113 2012Document16 pagesEbb113 2012Viknaraj SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Fizik Presentation Set 8 Dan 9Document7 pagesFizik Presentation Set 8 Dan 9shaNo ratings yet
- Modul FizikDocument11 pagesModul FizikAin FarhaniNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2Document31 pagesKertas 2Siti SyurieyatiNo ratings yet
- Per - Spm. 2015Document45 pagesPer - Spm. 2015Hasnah Othman100% (1)
- Akta Dan Peraturan ElektrikDocument10 pagesAkta Dan Peraturan ElektrikHanim Husaif100% (2)
- 2.5 Electricity - ELECT-ENERGY & POWERDocument5 pages2.5 Electricity - ELECT-ENERGY & POWERahsohaNo ratings yet
- Paket 1Document20 pagesPaket 1Tikpo Larasati100% (1)
- Sesi 1 2022 2023 - DJM40103Document9 pagesSesi 1 2022 2023 - DJM40103Amirul AmarNo ratings yet
- Bab 09 - ElektronikDocument40 pagesBab 09 - ElektronikAl Nazuris100% (1)
- Perlis 2010 FIZIK2Document28 pagesPerlis 2010 FIZIK2kamalharmozaNo ratings yet
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Sabah STPM Trial 2010 Maths T Paper 2 (W Ans) (7B9D376F)Document17 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Sabah STPM Trial 2010 Maths T Paper 2 (W Ans) (7B9D376F)HaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- SG Bab 03Document3 pagesSG Bab 03nurulamalina1984No ratings yet
- MRSM 2014Document33 pagesMRSM 2014Cheng WLNo ratings yet
- DCC5163 Jun2019Document13 pagesDCC5163 Jun2019nrhdyaaNo ratings yet
- 2009061801Document7 pages2009061801Shah ShaNo ratings yet
- DCC20053 Mechanics of Civil Engineering StructuresDocument5 pagesDCC20053 Mechanics of Civil Engineering Structuresnurawatiff105No ratings yet
- Final Exam Beke2422.Document20 pagesFinal Exam Beke2422.NOR FATIHAHNo ratings yet
- Papan Suis UtamaDocument19 pagesPapan Suis UtamaMuhammad IskandarNo ratings yet
- Latihan 1Document6 pagesLatihan 1Rosmawati MaarofNo ratings yet
- Latihan BengkelDocument13 pagesLatihan BengkelAishah Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Arus Dan Beza Keupayaan 2021Document44 pages3.1 Arus Dan Beza Keupayaan 2021Muhd Nur Irfan0% (1)
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Sabah STPM Trial 2010 Maths T Paper 2 (W Ans) (7B9D376F)Document17 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Sabah STPM Trial 2010 Maths T Paper 2 (W Ans) (7B9D376F)HaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Physics Answer Scheme (Terengganu) WDocument18 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Physics Answer Scheme (Terengganu) WHaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- Pengajian Am Kertas 2 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 1 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Document11 pagesPengajian Am Kertas 2 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 1 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)HaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Math T Paper 1 (Johor)Document7 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Math T Paper 1 (Johor)HaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- Pengajian Am Kertas 1 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 1 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Document29 pagesPengajian Am Kertas 1 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 1 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)HaRry ChgNo ratings yet
STPM Trials 2009 Physics Paper 2 (Terengganu)
STPM Trials 2009 Physics Paper 2 (Terengganu)
Uploaded by
HaRry ChgCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
STPM Trials 2009 Physics Paper 2 (Terengganu)
STPM Trials 2009 Physics Paper 2 (Terengganu)
Uploaded by
HaRry ChgCopyright:
Available Formats
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
Name : NRIC :
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
JABATAN PELAJARAN TERENGGANUJABATANPELAJARANTERENGGANU JABATANPELAJAR
Instructions to candidates :
This question paper consists of 15 printed pages
Answer all the questions in Section A in the
spaces provided.
Answer any four questions from section B.
For this section, write your answers on the
answer sheets provided. Begin each
answer on a fresh sheet of paper. Answers
should be illustrated by large, clearly
labeled diagrams wherever suitable.
Answers may be written in either Malay or
English.
Arrange your answer in numerical order
and tie the answer sheets to this booklet.
For examiners use
Section Marks
Marks
Obtained
A
1 5
2 5
3 5
4 5
5 5
6 5
7 5
8 5
B
9 15
10 15
11 15
12 15
13 15
14 15
TOTAL 100
TRIAL
2009
JABATAN PELAJARAN
NEGERI TERENGGANU
960/2
PHYSICS
PAPER 2
2 hours
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
2
Physics 960
Constants value
speed of light in vacuum
permeability of vacuum
permittivity of vacuum
magnitude of electron charge
Planck constant
atomic mass unit constant
electron rest mass
proton rest mass
molar gas constant
Avogadro constant
Boltzmann constant
gravitational constant
free fall acceleration
c
o
e
h
u
m
e
m
p
R
L, N
A
k
G
g
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
3.00 x 10
8
m s
-1
4 x 10
-7
H m
-1
8.85 x 10
-12
F m
-1
[1/(36 )] x 10
-9
F m
-1
1.60 x 10
-19
C
6.63 x 10
-34
J s
1.66 x 10
-27
kg
9.11 x 10
-31
kg
1.67 x 10
-27
kg
8.31 J K
-1
mol
-1
6.02 x 10
23
mol
-1
1.38 x 10
-23
J K
-1
6.67 x 10
-11
N m
2
kg
-2
9.81 m s
-2
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
[Turn Over]
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
3
1. A water wheel has eight bucket equally spaced around its circumference as shown in diagram
below.
0
45
1.8 m
The wheel makes six revolution per minute. Calculate
(a) the total change in potential energy of the water in the buckets in one revolution of the wheel.
[2]
(b) the average input power to the wheel
[2]
(c) Suggest why a larger number of small bucket is preferred to a smaller number of large bucket
containing the same total mass of water
[1]
Water
4
6
5
2
1
8
7
3
Water
Full, bucket Empty bucket
Direction of rotation
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
4
2. The figure below illustrates a mass which can be made to vibrate vertically between two springs.
The vibrator itself has constant amplitude. As the frequency is varied, the amplitude of vibration of
the mass is seen to change as shown in Fig 3A
Fig 3A
(a) Name the phenomenon which is illustrated in Fig 3A.
[1]
(b) For the mass vibrating at maximum amplitude, calculate the angular frequency.
[2]
(c) A light piece of card is fixed to the mass with its plane horizontal. On Fig 3A, draw a curve to
show the new variation with frequency of the amplitude of vibration of the mass.
[1]
(d) State one situation in which the phenomenon illustrated in Fig 3A is used to advantage.
[1]
variable frequency
vibrator
mass
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
[Turn Over]
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
5
3 A uniform copper rod with thermal conductivity 380 W m
-1
K
-1
which is perfectly insulated has a
cross-sectional area of 2.50 cm
2
and length 20.0 cm. Heat is conducted by the copper rod. When the
steady state is achieved, the temperatures at the ends of the rod are 130
o
C and 20
o
C.
Calculate
(a) the rate of heat flow in the rod.
[3]
(b) the temperature 15.0 cm from the hot end.
[2]
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
6
4 (a) Electrical conduction in a metal can be explained in terms of motion of free electrons. State the
estimated values at room temperature for mean random velocity of the free electrons.
[1]
(b) A 5.0 A current flows through a wire of length 1.50 m and crass sectional area of 1.2 mm
2
where the potential difference across the wire is 0.24 V.
(i) Calculate the power dissipated from the wire
[2]
(ii) Explain what will happen to the drift velocity of the free electrons if the power produced in
the wire is increased.
[2]
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
[Turn Over]
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
7
V
2
V
1
330 k
33 k
10 k
+15 V
-15 V
V
0
+
5.
(a) State the name of the amplifier circuit which is connected to various input as shown in the
diagram above.
[1]
(b) Calculate the output voltage V
0
if V
1
is 0.50 V and V
2
is 0.20 V.
[3]
(c) What happen to the output voltage if the supply 15 is replaced with V 9 ?.
[1]
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
8
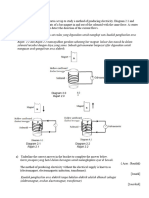
6 (a) Write the lens makers formula. Explain the symbols that you use.
[2]
(b) The diagram below shows a lens that has a curved surfaces with radius of curvature
20.0 cm and 60.0 cm. The refractive index of the lens material is 1.65.
Determine the focal length of the lens when the lens is immersed in water of refractive
index 1.33.
[3]
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
[Turn Over]
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
9
7 Monochromatic light with wavelength 365 nm illuminates a metallic surface with work function 2.30
eV.
(a) Calculate the maximum speed of the photoelectrons emitted.
[3]
(b) Estimate the de Broglie wavelength of the photoelectrons.
[2]
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
10
8
The graph above represents the decay of a sample of a specific radioactive element. Find the half-life
of the element.
Hint :
[5]
t
t
e N rate Count
e N N
=
=
0
0
dt
dN
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
[Turn Over]
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
11
Section B [60 marks]
Answer any four questions in this section
9 (a) Define the terms moment of a force and draw a sketch to illustrate the meaning. [2]
(b) State the condition for a body to be in equilibrium [1]
(c) During the construction of many modern bridges, section are added from both banks until the
two halves meet at the centre. Figure 1 below shows a new section S, of weight N
5
10 0 . 3 ,
after it has been attached to an existing part B of a bridge
The support cable which keeps section S in equilibrium is at an angle of
0
25 to the horizontal.
The existing part B of the bridge provides a horizontal force on S.
(i) Draw a labeled vector diagram and show the three forces on S [2]
(ii) Use your diagram to determine the tension in the cable and the horizontal force which B
exerts on S [2]
(d) In the sport of clay pigeon shooting, a clay disc is launched into the air by a spring, and the
contestant fires a shot at the moving disc. A launching device has been modified to project the
disc vertically upwards. The spring in the launching device has a spring constant of
1
2000
Nm
and the clay disc has mass 80g. In use the spring obeys Hookes law and the extension decreases
from 13 cm to 7.0 cm.
(i) Sketch a graph of force against extension for the spring and shade the area which represent
the loss of energy stored by the spring when launching the clay disc. [2]
(ii) Calculate
(a) the loss of elastic potential energy of the spring [2]
(b) the initial speed of the clay disc, assuming all the energy lost by the spring becomes
kinetic energy of the disc [2]
(c) the height to which the disc will rise, assuming that air resistance is negligible. [2]
S B
Support cable
N
5
10 0 . 3
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
12
10 (a) State three differences between a progressive wave and a stationary wave. [3]
(b) In large auditoriums, the walls are covered with thick curtains. State the effect of thick curtains
on the sound waves and hence explain the advantage of this practice. [2]
(c) Two sound waves have frequencies 890 Hz and 894 Hz respectively. The intensity of the sound
waves at a given point is 6.3 x 10
-9
W m
-2
.
(i) What are the conditions required for beats to be heard from two separate sound
sources? [2]
(ii) What is the frequency of the resultant wave and what is the beat frequency? [2]
(iii) Determine the maximum intensity level of the beats heard at the point concerned.
[The minimum intensity of audible sound is 1.0 x 10
-12
W m
-2
] [2]
(iv) Another sound sources with intensity level 98.0 dB is located at the point. What is the ratio
of the intensity of the first sound to that of the second sound? [2]
(d) A high-speed train is travelling at a speed of 47.4 m s
-1
when the engineer sounds the 418 Hz
warning horn. The speed of the sound is 343 m s
-1
. What is the frequency of the sound as
perceived by a person standing at a crossing when the train is approaching? [2]
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
[Turn Over]
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
13
11 (a) State Hookes Law [2]
(b) Explain the main difference between elastic deformation and plastic deformation [3]
(c) The graph shows a simplified version of the variation of the load applied against
the extension of the material. The original length of the wire is 1.0 m and its
diameter is 1.5 mm.
(i) The material is brittle or ductile ? [1]
(ii) What is the Youngs Modulus of the material ? [3]
(iii) If the wire snaps when the load reaches the value at P, how much energy is
required to snap the wire ? [3]
(iv) Assume that the cross-section of the wire remains constant throughout the
extension. What is the stress in the wire when the load reaches the value at P ?
[3]
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
14
X X X X X
X X X X X
+
-
electron path
12. (a) Explain why a charge Q will move in a circular path in a uniform magnetic field, B. Write an
expression for the force, F exerted on the charged particle. Explain any quantity you have given
in your expression. [4]
(b) An electron is moving in a circular path in a uniform magnetic field. If the radius of the path is
m
2
10 5 . 2
and the magnetic field strength is T
2
10 0 . 2
and the specific charge of electron
(
m
e
) is
1 11
10 76 . 1
Jkg .
(i) Derive an expression for the angular velocity of the electron [2]
(ii) Calculate the orbital period if the electron [2]
(iii) If the kinetic energy of the electron is reduced by half of its initial value, what is the value
of the orbital period? [2]
(c) Figure shows an electron moving with constant velocity enters an electric field which is
perpendicular to a magnetic field. If the magnetic field strength, B is 0.008 T and the electric
field strength, E is
1 4
10 0 . 6
Vm ,
(i) show the direction of the electrostatic force and the magnetic force exerted on the electron.
[2]
(ii) calculate the velocity of the electron [3]
CONFIDENTIAL*
960/2
[Turn Over]
*This question paper is CONFIDENTIAL until the examination is over CONFIDENTIAL*
15
13 (a) State Bohrs second postulate [2]
(b) The energy of the electron in a hydrogen atom is given as
,
6 . 13
2
eV
n
E
n
= n =1, 2, 3,
A hydrogen atom is excited by a photon and makes a transition from energy level n =1 to
energy level n =4.
(i) Explain how the hydrogen atom is excited. [2]
(ii) What is the energy absorbed by the excited atom? [2]
(iii) Calculate the wavelength of the photon. [3]
(c) (i) Explain the difference between the process of production of continuous X-rays with the
process of production of line X-rays from an X-ray tube. [4]
(ii) The accelerating potential difference across an X-ray tube using copper as target is 5.0 kV.
Calculate the minimum wavelength of the X-rays produced. [2]
14 (a) Give definition for each of the following terms
(i) isotope
(ii) nuclear fission
(iii) nuclear fusio [3]
(b) (i) State the quantities that are conserved in the nuclear reaction. [3]
(ii) Copy and complete the equations below :
+ + C He B
13
6
4
2
10
5
..
. He Li
4
2
7
3
2 +
+ + Li n B
7
3
1
0
10
5
.. [3]
(c) (i) Calculate the energy released when Al
28
13
decays to Si
28
13
[2]
(ii) If the - ray emitted has a wavelength of 6.99 x 10
-13
m , calculate the energy of -ray
photon. Hence, deduce the total kinetic energy of the products of decay.
[ Mass of Al
28
13
atom = 27.98191 m
u
,
Mass of Si
28
13
atom = 27.97693 m
u
, where m
u
is the atomic unit.] [4]
END OF THIS PAPER
You might also like
- Ujian BertulisDocument6 pagesUjian BertulisHaryati Fadhlan100% (1)
- STPM Trials 2009 Physics Answer Scheme (Malacca)Document20 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Physics Answer Scheme (Malacca)c3mutNo ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 2 TerengganuDocument11 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 2 Terengganusherry_christyNo ratings yet
- Te027-2 Sem2 2010-2011Document15 pagesTe027-2 Sem2 2010-2011pusatsumberkmtphNo ratings yet
- BMMD 2313 - Final 20202021Document19 pagesBMMD 2313 - Final 20202021fauzaniNo ratings yet
- TF025-2 Sem2 2010-2011Document21 pagesTF025-2 Sem2 2010-2011pusatsumberkmtphNo ratings yet
- J3008 Mekanik Bendalir 2008Document11 pagesJ3008 Mekanik Bendalir 2008Mahfuzah MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Set Kelantan 2018Document8 pagesSet Kelantan 2018RohanaIthninNo ratings yet
- DJJ 2022Document5 pagesDJJ 2022Nathaniel TayNo ratings yet
- 01QDCB30082Document7 pages01QDCB30082Aishah SeiniNo ratings yet
- K2 Fizik F5 2014Document23 pagesK2 Fizik F5 2014Ilya IsmailNo ratings yet
- Laporan Ujian Proba MackintoshDocument10 pagesLaporan Ujian Proba Mackintoshamirulhaziq161006No ratings yet
- Energy and Electric Power: 3.4. Tenaga Dan Kuasa ElektrikDocument12 pagesEnergy and Electric Power: 3.4. Tenaga Dan Kuasa Elektrikflower boomNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Semester I SESSION 2020/2021: Instruction To CandidatesDocument17 pagesFinal Examination Semester I SESSION 2020/2021: Instruction To CandidatesMohd AsriNo ratings yet
- Ta027-2 Sem2 2010-2011Document11 pagesTa027-2 Sem2 2010-2011pusatsumberkmtphNo ratings yet
- Latihan Ting 5 4Document5 pagesLatihan Ting 5 4nfaizah1100% (1)
- 01QDJJ30103Document10 pages01QDJJ30103boss796No ratings yet
- Mekanika Fluida.4Document23 pagesMekanika Fluida.4Marcel OmpiNo ratings yet
- Trial Pahang SPM 2014 Physics K2Document26 pagesTrial Pahang SPM 2014 Physics K2Cikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Skema K2 Set B JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPMDocument8 pagesSkema K2 Set B JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPMCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Ujian 1 Sem1 2013 - 2014Document8 pagesUjian 1 Sem1 2013 - 2014akaiNo ratings yet
- Soalan FizikDocument10 pagesSoalan FizikAnonymous q9bofmNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document16 pagesPaper 2mellaty8127No ratings yet
- ElectricDocument12 pagesElectricLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Ops Gempur 2 FizikDocument7 pagesOps Gempur 2 FizikHamizanWookNo ratings yet
- E1002Document6 pagesE1002Hazim ZimNo ratings yet
- Fizik SPM FIZ Kertas2Set2Document19 pagesFizik SPM FIZ Kertas2Set2api-3841296No ratings yet
- BEEI3423.Actuator & Drive - M3Document27 pagesBEEI3423.Actuator & Drive - M3Zulkarnain ZainudinNo ratings yet
- Ta027-1 Sem2 2010-2011Document13 pagesTa027-1 Sem2 2010-2011pusatsumberkmtphNo ratings yet
- Test 2-Emk21003-2022Document3 pagesTest 2-Emk21003-2022LIEW HUI FANG UNIMAPNo ratings yet
- Bilik Gelap Ammend No.3 PDFDocument1 pageBilik Gelap Ammend No.3 PDFmaliklduNo ratings yet
- Sesi Ii 2022 2023 - Det40073Document7 pagesSesi Ii 2022 2023 - Det40073Amirul AmarNo ratings yet
- Soalan Cadangan Fizik Percubaan K2 2020Document26 pagesSoalan Cadangan Fizik Percubaan K2 2020Joseph LeeNo ratings yet
- Soalan Peperiksaan Akhir (Palt) DJJ20053 Electrical Technology Sesi 1 2021 - 2022Document7 pagesSoalan Peperiksaan Akhir (Palt) DJJ20053 Electrical Technology Sesi 1 2021 - 2022Vetri Thanabalan100% (1)
- JTKM-BMMA 1333 (Sem2-2020) - Question Paper-Set1Document16 pagesJTKM-BMMA 1333 (Sem2-2020) - Question Paper-Set1Fgj JhgNo ratings yet
- Ebb113 2012Document16 pagesEbb113 2012Viknaraj SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Fizik Presentation Set 8 Dan 9Document7 pagesFizik Presentation Set 8 Dan 9shaNo ratings yet
- Modul FizikDocument11 pagesModul FizikAin FarhaniNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2Document31 pagesKertas 2Siti SyurieyatiNo ratings yet
- Per - Spm. 2015Document45 pagesPer - Spm. 2015Hasnah Othman100% (1)
- Akta Dan Peraturan ElektrikDocument10 pagesAkta Dan Peraturan ElektrikHanim Husaif100% (2)
- 2.5 Electricity - ELECT-ENERGY & POWERDocument5 pages2.5 Electricity - ELECT-ENERGY & POWERahsohaNo ratings yet
- Paket 1Document20 pagesPaket 1Tikpo Larasati100% (1)
- Sesi 1 2022 2023 - DJM40103Document9 pagesSesi 1 2022 2023 - DJM40103Amirul AmarNo ratings yet
- Bab 09 - ElektronikDocument40 pagesBab 09 - ElektronikAl Nazuris100% (1)
- Perlis 2010 FIZIK2Document28 pagesPerlis 2010 FIZIK2kamalharmozaNo ratings yet
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Sabah STPM Trial 2010 Maths T Paper 2 (W Ans) (7B9D376F)Document17 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Sabah STPM Trial 2010 Maths T Paper 2 (W Ans) (7B9D376F)HaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- SG Bab 03Document3 pagesSG Bab 03nurulamalina1984No ratings yet
- MRSM 2014Document33 pagesMRSM 2014Cheng WLNo ratings yet
- DCC5163 Jun2019Document13 pagesDCC5163 Jun2019nrhdyaaNo ratings yet
- 2009061801Document7 pages2009061801Shah ShaNo ratings yet
- DCC20053 Mechanics of Civil Engineering StructuresDocument5 pagesDCC20053 Mechanics of Civil Engineering Structuresnurawatiff105No ratings yet
- Final Exam Beke2422.Document20 pagesFinal Exam Beke2422.NOR FATIHAHNo ratings yet
- Papan Suis UtamaDocument19 pagesPapan Suis UtamaMuhammad IskandarNo ratings yet
- Latihan 1Document6 pagesLatihan 1Rosmawati MaarofNo ratings yet
- Latihan BengkelDocument13 pagesLatihan BengkelAishah Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Arus Dan Beza Keupayaan 2021Document44 pages3.1 Arus Dan Beza Keupayaan 2021Muhd Nur Irfan0% (1)
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Sabah STPM Trial 2010 Maths T Paper 2 (W Ans) (7B9D376F)Document17 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Sabah STPM Trial 2010 Maths T Paper 2 (W Ans) (7B9D376F)HaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Physics Answer Scheme (Terengganu) WDocument18 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Physics Answer Scheme (Terengganu) WHaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- Pengajian Am Kertas 2 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 1 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Document11 pagesPengajian Am Kertas 2 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 1 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)HaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Math T Paper 1 (Johor)Document7 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Math T Paper 1 (Johor)HaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- Pengajian Am Kertas 1 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 1 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Document29 pagesPengajian Am Kertas 1 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 1 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)HaRry ChgNo ratings yet