Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abigail A. Garcia, M. SC.: Department of Biological Sciences College of Science University of Santo Tomas
Abigail A. Garcia, M. SC.: Department of Biological Sciences College of Science University of Santo Tomas
Uploaded by
Veronica Gale De Ocampo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views24 pagesThis document summarizes key aspects of photosynthesis. It describes how plants, algae, and some bacteria are able to transform light energy and carbon dioxide into chemical energy by using chloroplasts to drive the light-dependent and light-independent reactions. The light reactions absorb photons and use them to produce ATP and NADPH, which are then used by the Calvin cycle in the chloroplast to fix carbon and produce sugars like glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. Some plants have evolved additional pathways, like C4 and CAM photosynthesis, that allow them to more efficiently fix carbon and conserve water in hot or dry environments.
Original Description:
My ex-professor's powerpoint on photosynthesis.
Original Title
Photosynthesis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes key aspects of photosynthesis. It describes how plants, algae, and some bacteria are able to transform light energy and carbon dioxide into chemical energy by using chloroplasts to drive the light-dependent and light-independent reactions. The light reactions absorb photons and use them to produce ATP and NADPH, which are then used by the Calvin cycle in the chloroplast to fix carbon and produce sugars like glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. Some plants have evolved additional pathways, like C4 and CAM photosynthesis, that allow them to more efficiently fix carbon and conserve water in hot or dry environments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views24 pagesAbigail A. Garcia, M. SC.: Department of Biological Sciences College of Science University of Santo Tomas
Abigail A. Garcia, M. SC.: Department of Biological Sciences College of Science University of Santo Tomas
Uploaded by
Veronica Gale De OcampoThis document summarizes key aspects of photosynthesis. It describes how plants, algae, and some bacteria are able to transform light energy and carbon dioxide into chemical energy by using chloroplasts to drive the light-dependent and light-independent reactions. The light reactions absorb photons and use them to produce ATP and NADPH, which are then used by the Calvin cycle in the chloroplast to fix carbon and produce sugars like glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. Some plants have evolved additional pathways, like C4 and CAM photosynthesis, that allow them to more efficiently fix carbon and conserve water in hot or dry environments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 24
Abigail A. Garcia, M. Sc.
Department of Biological Sciences
College of Science
University of Santo Tomas
Opposite but complimentary processes
Transformation of light energy into chemical energy with CO
2
and water as starting products.
Occurs in plants, bacteria (BGA, green sulfur), algae
and some protozoans
Sunlight contains energy called electromagnetic
energy or radiation
Visible light is only a small part of the
electromagnetic spectrum, the full range of
electromagnetic wavelengths
Electromagnetic energy travels in waves, and the
wavelength is the distance between the crests of
two adjacent waves
Light behaves as discrete packets of energy
called photons
A photon is a fixed quantity of light energy, and the
shorter the wavelength, the greater the energy
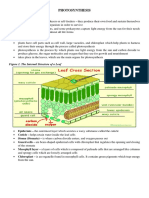
Chloroplasts contain several different
pigments and all absorb light of different
wavelengths
Chlorophyll a absorbs blue violet and red
light and reflects green
Chlorophyll b absorbs blue and orange
and reflects yellow-green
The carotenoids absorb mainly blue-
green light and reflect yellow and orange
The Calvin cycle makes sugar within a
chloroplast
To produce sugar, the necessary ingredients are
atmospheric CO
2
, ATP, and NADPH, which were
generated in the light reactions
Using these three ingredients, an energy-rich, three-
carbon sugar called glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
(G3P) is produced
A plant cell may then use G3P to make glucose and other
organic molecules
ATP and NADPH are oxidized
to form ADP + P and NADP,
respectively
The electrons from these
electron carriers are used to
make the C-H bonds in G3P
For every 3 molecules of CO
2
,
1 molecule of G3P formed.
Some plants have evolved a means of carbon
fixation that saves water during photosynthesis
One group can shut its stomata when the weather
is hot and dry to conserve water but is able to make
sugar by photosynthesis
These are called the C
4
plants because they first fix
carbon dioxide into a four-carbon compound
Another adaptation to hot and dry
environments has evolved in the CAM plants,
such as pineapples and cacti
CAM plants conserve water by opening their
stomata and admitting CO
2
only at night
When CO
2
enters, it is fixed into a four-carbon
compound, like in C
4
plants, and in this way CO
2
is
banked
It is released into the Calvin cycle during the day
You might also like
- Chapter 10:photosynthesisDocument12 pagesChapter 10:photosynthesiskatrinajen ferrerNo ratings yet
- all notesDocument3 pagesall notesbrainngonimangoroNo ratings yet
- BH5post 1Document27 pagesBH5post 1feysalshiiq4No ratings yet
- FotosintesisDocument51 pagesFotosintesisDwi HardianiNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Photosynthesis: - Almost All Plants Are Photosynthetic Autotrophs, As Are Some Bacteria and ProtistsDocument43 pagesThe Basics of Photosynthesis: - Almost All Plants Are Photosynthetic Autotrophs, As Are Some Bacteria and ProtistsYesenia Shashi AnastaNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument55 pagesPhotosynthesischezkanoelleangeliebalolongNo ratings yet
- Els Reviewer 2Document6 pagesEls Reviewer 2Kenjie kunNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesisLancekyle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Energy For LifeDocument41 pagesUtilizing Energy For LifeJOHN PAUL MACALLINGNo ratings yet
- 1 Photosyn General Info 4Document42 pages1 Photosyn General Info 4Ruperto VidalNo ratings yet
- GenBio 1 - 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenBio 1 - 2nd Quarter Reviewerjoshua tejadaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesGrade 9 PhotosynthesisyannsegundinoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis NotesDocument26 pagesPhotosynthesis NotesAdam GlassnerNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Using Light To Make Food: UsuallyDocument12 pagesPhotosynthesis: Using Light To Make Food: UsuallyMARCO ANTONIO CONDOR CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- The Sun: Main Source of Energy For Life On EarthDocument21 pagesThe Sun: Main Source of Energy For Life On Earthsunifeb128075No ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument55 pagesEnergy Transformationelyza gwenNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesPhotosynthesisJESSERYL MARGALLONo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ReadingDocument11 pagesPhotosynthesis ReadingLogan ParkisonNo ratings yet
- BiomassNotes 2019Document155 pagesBiomassNotes 2019Jonathan WrightNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Document35 pagesBy The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)reziegeoNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Document35 pagesBy The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)monica_elysabethNo ratings yet
- What Are The Parts of The Cell?Document31 pagesWhat Are The Parts of The Cell?Karl Wyndyll LambanNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics: Is The Study of How Energy Flows Through Living CellsDocument49 pagesBioenergetics: Is The Study of How Energy Flows Through Living CellsRy CyNo ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer For The Whole Quarter 2Document7 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer For The Whole Quarter 2yxrizipNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respirationmaria genio100% (2)
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationFatima DariaNo ratings yet
- Week - 3 - Lectures 1-1Document74 pagesWeek - 3 - Lectures 1-1Benjamin SamaniNo ratings yet
- Bio2 PhotosynthesisDocument24 pagesBio2 Photosynthesisjvvuvuuv lopezNo ratings yet
- Lecture: 2.3 PHOTOSYNTHESIS: Photosynthesis Converts Light Energy To Chemical Energy of FoodDocument2 pagesLecture: 2.3 PHOTOSYNTHESIS: Photosynthesis Converts Light Energy To Chemical Energy of FoodLorena DizonNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesisMina IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration ReviewerDocument6 pagesCell Respiration ReviewerEllemer Rose CastañaresNo ratings yet
- CS01-Chapter 2Document48 pagesCS01-Chapter 2AJ MoralesNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Power Point NotesDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesis Power Point NotesJohn SchmidtNo ratings yet
- Biosynthetic Pathway Dark ReactionDocument5 pagesBiosynthetic Pathway Dark ReactionspenzercadienteeNo ratings yet
- 27-Week#4-Bio-9-PPT SlidesDocument31 pages27-Week#4-Bio-9-PPT Slidesاحمد جمعهNo ratings yet
- VCE Chapter 6 2018 Study DesignDocument10 pagesVCE Chapter 6 2018 Study DesignParis JoannidesNo ratings yet
- What Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDocument8 pagesWhat Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDiana Jean Alo-adNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument39 pagesPlant Nutritionapi-3059093250% (1)
- BiologyDocument5 pagesBiologyClare Anne Therese EsbietoNo ratings yet
- Outline Electron Transport Chain in PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesOutline Electron Transport Chain in PhotosynthesisspenzercadienteeNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Cellular RespirationDocument27 pagesPhotosynthesis Cellular RespirationSamantha De CastroNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis-WPS Officeimaan buttNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5:genetic Control & Protein Synthesis (Week 10 & 11)Document58 pagesChapter 5:genetic Control & Protein Synthesis (Week 10 & 11)RabbitNo ratings yet
- Energy MetabolismDocument4 pagesEnergy MetabolismKaren ParkNo ratings yet
- 14 Respiration in Plants-NotesDocument4 pages14 Respiration in Plants-NotesAnanth DharanidharanNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesisv 3Document40 pagesPhotosynthesisv 3Sofia CorderoNo ratings yet
- The LightDocument3 pagesThe LightMaya AlashkarNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument26 pagesPhotosynthesisAdithya RajeshNo ratings yet
- Dr. Dono Chapter 13 - How Cells Obtain EnergyDocument41 pagesDr. Dono Chapter 13 - How Cells Obtain EnergyMuhammad Thoriqur Rohman Al-KhotamiNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesispwssewwandiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Reading QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 7 Reading QuestionsDefault AccountNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Light Energy From The Sun Is Converted To Chemical Energy That Is Stored in SugarDocument47 pagesPhotosynthesis: Light Energy From The Sun Is Converted To Chemical Energy That Is Stored in Sugarpsamuel24No ratings yet
- L6 PhotosynthesisDocument28 pagesL6 PhotosynthesisNaomi AceroNo ratings yet
- BIF03 Satellite Tutorial WK 3Document33 pagesBIF03 Satellite Tutorial WK 3Benjamin SamaniNo ratings yet
- Lec4 PhotosynthesisDocument50 pagesLec4 PhotosynthesisPLANARIANo ratings yet
- Autotrophy: Collecting Energy From The Non-Living EnvironmentDocument96 pagesAutotrophy: Collecting Energy From The Non-Living EnvironmentNathan ArthurNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer.Document3 pagesScience Reviewer.harlanecarlsNo ratings yet
- CALVIN CycleDocument13 pagesCALVIN CycleDaphne CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Photosynthesis - COMPLETE PDFDocument14 pages11 - Photosynthesis - COMPLETE PDFToni HeaterNo ratings yet