Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Cystic Fibrosis
What Is Cystic Fibrosis
Uploaded by
steffany8020 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageCystic fibrosis is a genetic disease that causes thick mucus to build up in the lungs and digestive tract, clogging the lungs and leading to life-threatening infections. It affects the lungs, liver, and pancreas and is typically diagnosed via a sweat test before age 2. There is no cure, but treatments have improved and the median survival age is now in the late 30s, compared to the early 20s just two decades ago.
Original Description:
Cystic fibrosis affects everyione in the world
Original Title
What is Cystic Fibrosis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCystic fibrosis is a genetic disease that causes thick mucus to build up in the lungs and digestive tract, clogging the lungs and leading to life-threatening infections. It affects the lungs, liver, and pancreas and is typically diagnosed via a sweat test before age 2. There is no cure, but treatments have improved and the median survival age is now in the late 30s, compared to the early 20s just two decades ago.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageWhat Is Cystic Fibrosis
What Is Cystic Fibrosis
Uploaded by
steffany802Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease that causes thick mucus to build up in the lungs and digestive tract, clogging the lungs and leading to life-threatening infections. It affects the lungs, liver, and pancreas and is typically diagnosed via a sweat test before age 2. There is no cure, but treatments have improved and the median survival age is now in the late 30s, compared to the early 20s just two decades ago.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
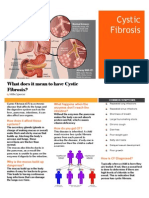
What is Cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic Fibrosis is a chronic genetic
disease that affects the liver, pancreas
and mostly the lungs. It causes thick
mucus to build up and stick to some of
the organs in the body. It clogs the
lungs and leads to life threatening lung
infections. It affects the respiratory,
digestive and reproductive systems.
Cystic Fibrosis affects about 30,000
people in the Unites States and about
70,000 worldwide.
Statistics
1,000 new cases of Cystic Fibrosis are
diagnosed each year.
More the 70% of patients are
diagnosed by age 2.
More that 45% of the cystic fibrosis
patient population is age 18 or older.
In the United States 1 in 4,000
children are born with it.
Approximately 1 in 25 people of
European descent have cystic fibrosis
The predicted median age of survival
for a person with cystic fibrosis is in
the late 30s.
Cystic Fibrosis is most common in
Caucasians but it can affect all races.
Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis
Most people who have Cystic Fibrosis
are diagnosed at birth by newborn
screening or before the age of 2. The
most common test used to diagnose
cystic fibrosis is the sweat test. During
the sweat test a small electrode is
placed on the skin to stimulate the
sweat glands. Then the amount of
chloride is measured. A high level of
chloride means that the person has
Cystic Fibrosis.
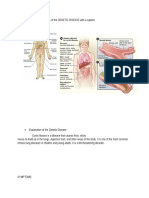
What Causes Cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic Fibrosis is a disease that is
inherited. To have Cystic Fibrosis, a
person must inherit two copies of the
defective CF gene, one copy from each
parent. The carrier, though only has 1
copy of the CF gene mutation. This
means that they do not have the disease
themselves.
Treatment
The treatments used for Cystic Fibrosis
have improved greatly in recent years.
Treatments for Cystic Fibrosis include:
You might also like
- Cystic FibrosisDocument14 pagesCystic FibrosisAlex JassoNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument10 pagesCystic Fibrosisapi-287211503No ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis ResearchDocument7 pagesCystic Fibrosis ResearchElena RamblaNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument4 pagesCystic Fibrosisakram alrdayNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis PPT 4th PeriodDocument13 pagesCystic Fibrosis PPT 4th PeriodGrant Wynn ArnucoNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis: Nicole Price EDU 214 A. A. C. CDocument10 pagesCystic Fibrosis: Nicole Price EDU 214 A. A. C. CnmpriceNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis Fact SheetDocument2 pagesCystic Fibrosis Fact Sheetmilyspencer86No ratings yet
- Nature of DiseaseDocument14 pagesNature of DiseaseLambo Ignacio Queen Quin100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Cystic FibrosisDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Cystic FibrosisMariana DariiNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis CF Health Presentation 1Document15 pagesCystic Fibrosis CF Health Presentation 1api-249865008100% (1)
- Cystic Fibrosis: An Inherited Condition Particularly The Lungs and Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesCystic Fibrosis: An Inherited Condition Particularly The Lungs and Digestive SystemPaul Robins Poso LaredoNo ratings yet
- What Is Cystic FibrosisDocument15 pagesWhat Is Cystic FibrosisSarika YadavNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis Final Handout 12 Hayd RealDocument4 pagesCystic Fibrosis Final Handout 12 Hayd Realapi-272537046No ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument2 pagesCystic Fibrosisნინო ასლამაზაშვილიNo ratings yet
- About Cystic FibrosisDocument1 pageAbout Cystic FibrosisderekNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument8 pagesCystic FibrosisLakshya BansalNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis (CF) : Who Has ItDocument4 pagesCystic Fibrosis (CF) : Who Has ItleenNo ratings yet
- Bio PosterDocument7 pagesBio PosterJean LucenteNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis Research PaperDocument8 pagesCystic Fibrosis Research Paperfkqdnlbkf100% (1)
- Case Study: Cystic Fibrosis: Manalo, Joanne Erica S. BS Respiratory TherapyDocument20 pagesCase Study: Cystic Fibrosis: Manalo, Joanne Erica S. BS Respiratory TherapyJohn Carlo ConsultaNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Cystic FibrosisDocument16 pagesPresentation of Cystic Fibrosisanon-662103100% (3)
- CF Mid Term PaperDocument6 pagesCF Mid Term Paperapi-280357644No ratings yet
- What Is CF: Family History. Because Cystic Fibrosis Is An Inherited Disorder, It Runs inDocument3 pagesWhat Is CF: Family History. Because Cystic Fibrosis Is An Inherited Disorder, It Runs inAbdelrahman NasimNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis Manuscript FinalDocument6 pagesCystic Fibrosis Manuscript FinalgherlethrNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Document جديدDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Word Document جديدakram alrdayNo ratings yet
- Foley Madeleine 11100348 Cystic FibrosisDocument9 pagesFoley Madeleine 11100348 Cystic FibrosisCharles IppolitoNo ratings yet
- CF Case No.2 Revised 55Document107 pagesCF Case No.2 Revised 55Wendell Gian GolezNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis: Anita Thompson Amy Waters Matt Moore Amanda Bowes Jenn WilsonDocument28 pagesCystic Fibrosis: Anita Thompson Amy Waters Matt Moore Amanda Bowes Jenn WilsonAnita ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis: Zoe Drullard and Avril GuillermoDocument18 pagesCystic Fibrosis: Zoe Drullard and Avril Guillermozoe drullardNo ratings yet
- SepsisDocument9 pagesSepsisalakayleh saqerNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis: SymptomsDocument2 pagesCystic Fibrosis: SymptomsMehrul Singh RanavatNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis (CF) : Definition: Cystic Fibrosis Is A Hereditary Disease That Affects The Exocrine System. IDocument1 pageCystic Fibrosis (CF) : Definition: Cystic Fibrosis Is A Hereditary Disease That Affects The Exocrine System. IFintan BrayNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis Research Paper ThesisDocument7 pagesCystic Fibrosis Research Paper Thesisfc34qtwg100% (2)
- Cystic FibrosisDocument19 pagesCystic FibrosisChristian Dene Opada TatoyNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis Essay ThesisDocument4 pagesCystic Fibrosis Essay Thesisaprilgriffinbeaumont100% (2)
- C Stic Fibrosis: AuthorsDocument6 pagesC Stic Fibrosis: AuthorsDrsreeram ValluriNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument76 pagesCystic FibrosisGreeshma ShajiNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis Research Paper OutlineDocument7 pagesCystic Fibrosis Research Paper Outlineznmlubxgf100% (1)
- Cystic Fibrosis Research NotesDocument8 pagesCystic Fibrosis Research NotesNicole KrawitzNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis BrochureDocument2 pagesCystic Fibrosis Brochurezinaida lopezNo ratings yet
- Conditions and DiseasesDocument6 pagesConditions and Diseasesapi-3709951No ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis: DescriptionDocument5 pagesCystic Fibrosis: DescriptionJulliza Joy PandiNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument23 pagesCystic Fibrosisclarytah0% (1)
- Cystic FibrosisDocument9 pagesCystic Fibrosisapi-432406854No ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Child With Respiratory Diseases Nursing Care of The Child With Respiratory DiseasesDocument11 pagesNursing Care of The Child With Respiratory Diseases Nursing Care of The Child With Respiratory DiseasesDody ZainNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis 1Document7 pagesCystic Fibrosis 1api-306098893No ratings yet
- Postmedj00092 0013Document9 pagesPostmedj00092 0013danangpurmdNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument2 pagesCystic FibrosisAMOS MELINo ratings yet
- Overview of Cystic Fibrosis & Its ManagementDocument54 pagesOverview of Cystic Fibrosis & Its Managementvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Public Health Aspects of Urogenital System Diseases: Irwin Aras/ Andi Alfian ZainuddinDocument40 pagesPublic Health Aspects of Urogenital System Diseases: Irwin Aras/ Andi Alfian ZainuddinSadam_fasterNo ratings yet
- Fungal PneumoniaDocument8 pagesFungal PneumoniaJessica AdhykaNo ratings yet
- Liver BiopsyDocument1 pageLiver BiopsyexpayurvedNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Mucoviscidosis (Cystic Fibrosis), Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Mucoviscidosis (Cystic Fibrosis), Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- MauricioDocument1 pageMauricioMauricio ConstanzaNo ratings yet
- Disease EssayDocument7 pagesDisease Essayapi-462798482No ratings yet
- Untitled 11Document1 pageUntitled 11Mostafa MassoudNo ratings yet
- Cysticfibrosisdonebymyfriend 120218095057 Phpapp02Document28 pagesCysticfibrosisdonebymyfriend 120218095057 Phpapp02Elham AlwagaaNo ratings yet
- Inquiry Presentation-1Document11 pagesInquiry Presentation-1api-272568633No ratings yet