Professional Documents
Culture Documents
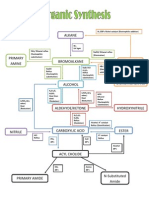
Name of Reagent Conditions Uses Oxidising Agent, Used
Name of Reagent Conditions Uses Oxidising Agent, Used
Uploaded by
Fsdhdf FbxhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of Reagent Conditions Uses Oxidising Agent, Used
Name of Reagent Conditions Uses Oxidising Agent, Used
Uploaded by
Fsdhdf FbxhCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of Reagent Conditions Uses
K
2
Cr
2
O
7
with conc.
H
2
SO
4
Warm gently
Oxidising
agent, used
commonly for
oxidising
secondary
alcohols to
ketones.
Excess conc. H
2
SO
4 heat to 170 C
Dehydrating
agent, used to
dehydrate
alcohols to
alkenes.
Cl
2
(g)
Ultra Violet light
Free radical
reaction, used
to convert
alkanes to
haloalkanes.
Br
2
in CCl
4
Room temperature, in the
dark
Electrophilic
addition,
converts
alkenes to
dihaloalkanes.
H
2
(g)
Nickel catalyst, 300 C and
30 atmospheres pressure
Hydrogenating
agent, used to
convert
benzene to
cylcohexane.
H
2
(g)
Nickel catalyst, 150 C
Reducing
agent, used to
convert alkenes
to alkanes
Tin in hydrochloric acid Reflux
Reducing
agent for
converting
nitrobenzene to
phenylamine.
Acidified KMNO4 Room temperature
Oxidising
agent, converts
alkenes to
diols.
NaOH in ethanol Reflux
Elimination
reaction,
converts
haloalkanes to
alkenes.
Aqueous NaOH Reflux
Nucleophilic
substitution,
converts
haloalkanes to
alcohols.
Mg in dry ether Reflux
Used to make
grignard
reagents with
haloalkanes.
Chlorinating
PCl
5 Room temperature
agent, reacts
with OH group
in alcohols and
carboxyllic
acids
HNO
3
and H
2
SO
4
55 C
Adds NO
2
group onto
benzene ring.
Cl
2
and AlCl
3 Warm gently
Adds Cl group
onto benzene
ring.
CH
3
CH
2
Cl and AlCl
3
Warm gently
Adds CH
3
CH
2
group onto
benzene ring.
HCl and NaNO
2 Below 5 C
Forms
diazonium salts
with
phenylamine
NaI/Acetone RoomTemp. Cleaves Halide
Carbon bond
produce alkene by
ALkyl halide
Hg(OAc)2 +H20 RoomTemp Convert alkene to
2" Alcohol
You might also like
- Functional Group Transformation NotebookDocument78 pagesFunctional Group Transformation NotebookchedhedNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem ReactionsDocument7 pagesOrganic Chem ReactionsTeo Jia Ming NickolasNo ratings yet
- Crux and Reagents of Organic ChemDocument4 pagesCrux and Reagents of Organic ChemBILL RUSSO100% (5)
- Organic Chemistry Reaction TableDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reaction TablePhirun Cheng97% (31)
- Organic Compound Reagent/reactant Condition ClassificationDocument2 pagesOrganic Compound Reagent/reactant Condition ClassificationFaridOraha0% (1)
- Sumary Hydrocarbon AlkeneDocument2 pagesSumary Hydrocarbon AlkeneApple KWNo ratings yet
- List of Reagents of All Chapters and Their Function - askIITiansDocument11 pagesList of Reagents of All Chapters and Their Function - askIITiansall India TamilNo ratings yet
- Mod 4 Revision Guide 10 Synthetic RoutesDocument2 pagesMod 4 Revision Guide 10 Synthetic RoutesdufraiscNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Document53 pagesReactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (1)
- Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King: ELECTRON DENSITY Around The Carbon Atom Rather Than A Complete Transfer ofDocument16 pagesLecture Notes Chem 51B S. King: ELECTRON DENSITY Around The Carbon Atom Rather Than A Complete Transfer ofHuấnĐìnhNguyễnNo ratings yet
- 16 Hydroxyl compound-24-STDDocument38 pages16 Hydroxyl compound-24-STDManh Doan DucNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem Reactions: 1. AlkanesDocument6 pagesOrganic Chem Reactions: 1. AlkanesFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesDocument58 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesNur Aliyah Abdul RazakNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument40 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsMiguelNo ratings yet
- 4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsDocument5 pages4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsFin BrickmanNo ratings yet
- FSPJFSPJSFPJFSPJFSPJDocument6 pagesFSPJFSPJSFPJFSPJFSPJFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons (Hints)Document2 pagesHydrocarbons (Hints)hchawla421No ratings yet
- Organic Chem Reactions: 1. AlkanesDocument6 pagesOrganic Chem Reactions: 1. AlkanesFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Organic SynthesisDocument1 pageOrganic Synthesiszozoxo0% (1)
- Akash & Priyanshu XIIDocument24 pagesAkash & Priyanshu XIIAnindya BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Reagent TableDocument10 pagesReagent Tablebluebeary22No ratings yet
- Hadepe Aldehid Dan KetonDocument31 pagesHadepe Aldehid Dan KetonBagusSatriyaNo ratings yet
- Organic-Chemistry (As Level)Document8 pagesOrganic-Chemistry (As Level)Pirate HunterNo ratings yet
- A2 Organic Reaction SummaryDocument8 pagesA2 Organic Reaction SummaryJessie Wu100% (1)
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument45 pagesAldehydes and Ketonesroku_soraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 Reactions of Carbonyl CompoundsDocument18 pagesLesson 9 Reactions of Carbonyl Compoundsdela2No ratings yet
- 1.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument117 pages1.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsKRISHNARJUNA NNo ratings yet
- AldehydeandketoneDocument15 pagesAldehydeandketoneDj Arts Tarpaulin PrintingNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 HydrocarbonsDocument63 pagesUnit 14 Hydrocarbonsnischalghising16No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions of Alkanes: Mechanism Reaction Reagent Condition Catalysts Product(s)Document9 pagesChemical Reactions of Alkanes: Mechanism Reaction Reagent Condition Catalysts Product(s)Sam LeeNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesDocument62 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesSubhabrata MabhaiNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Ester, Carboxylic Acid PDFDocument17 pagesAlcohol, Ester, Carboxylic Acid PDFJustin LukmanNo ratings yet
- 879ef78f-6dd9-49c6-92c5-ed0880e308dcDocument4 pages879ef78f-6dd9-49c6-92c5-ed0880e308dcSuraj sssNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Aldehydes and KetonesDocument6 pagesWeek 10 Aldehydes and Ketonessam cuadraNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon NotesDocument7 pagesHydrocarbon Notesl8627352No ratings yet
- Done By: Kaijie, Elias, Chenxi, Ashwini, Sahana, Kelly From 0901 and 0914 Compiled From 2007 and 2008 H2 Chemistry Prelim PapersDocument10 pagesDone By: Kaijie, Elias, Chenxi, Ashwini, Sahana, Kelly From 0901 and 0914 Compiled From 2007 and 2008 H2 Chemistry Prelim Papersdiejunqs sNo ratings yet
- St. Joseph's College of Arts & Science (Autonomous)Document20 pagesSt. Joseph's College of Arts & Science (Autonomous)Reyadevi GNo ratings yet
- Alkenes: 1. From Dehydration of AlcoholDocument14 pagesAlkenes: 1. From Dehydration of AlcoholPratik TimalsinaNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument25 pagesHydrocarbonSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Reaction List v002Document5 pagesReaction List v002cecil3414No ratings yet
- Alkenes and AlkynesDocument22 pagesAlkenes and AlkynesAyodele AdeyonuNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes & KetonesDocument104 pagesAldehydes & KetonesCharin Kadian75% (4)
- UNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument50 pagesUNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acidssukaina fatima100% (1)
- Summary of Organic ReactionsDocument3 pagesSummary of Organic ReactionsDhruba FahimNo ratings yet
- Notes MAINDocument22 pagesNotes MAINFarhan TanveerNo ratings yet
- CIE AS Chemistry: 21.1 Organic SynthesisDocument17 pagesCIE AS Chemistry: 21.1 Organic SynthesisiceforgamingNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles CH 20modifiedDocument35 pagesLec 2 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles CH 20modifiedpolinaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Reaction ListDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reaction ListAliSulaimanMohammadNo ratings yet
- Organic ReactionDocument18 pagesOrganic ReactionNishant JainNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Concise Notes - OptDocument11 pagesAldehydes Concise Notes - Optaleena'No ratings yet
- Reaction Notes For Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesReaction Notes For Organic ChemistryTyler Lawrence CoyeNo ratings yet
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument159 pagesPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- Lesson 9 Reactions of Carbonyl CompoundsDocument18 pagesLesson 9 Reactions of Carbonyl Compoundsdela2No ratings yet
- Organic Notes Combined - RemovedDocument510 pagesOrganic Notes Combined - RemovedJanesh SumadNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 9 EditionDocument47 pagesAlcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 9 Edition劉靖騰No ratings yet
- Petrochem 10 - SEM 1 12-13Document40 pagesPetrochem 10 - SEM 1 12-13Saifuddin AzizNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument19 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidPraneel BhattNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids-Anil-hssliveDocument16 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids-Anil-hssliveRanit Mukherjee100% (1)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Ligand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsFrom EverandLigand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsNo ratings yet