Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5.2 Radioactive Decay
5.2 Radioactive Decay
Uploaded by
Faris ShahinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5.2 Radioactive Decay
5.2 Radioactive Decay
Uploaded by
Faris ShahinCopyright:
Available Formats
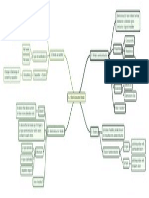
5.
2 Analysing Radioactive
Decay
2. Detectors for radioactive emission
3. Characteristics of
radioactive emission
4. Radioactive Decay
1. Radioactivity
Definition: Spontaneous disintegration of
an unstable nucleus accompanied by the
emission of an energetic particle or
photons
Spontaneous
disintegration
Unstable nucleus
emission of energetic/
photons
also called radioactive
emission
All nuclei with Z>83 or
A>209 are unstable
unstable nuclei (parent nuclide)
tends to decay/disintegrate into
more stable atoms (daughter
nuclide)
ionising effect by radioactive
emission
type of detectors
radiation from unstable
isotopes knocks eletrons off
atoms
Geiger-Muller
tube (GM tube)
Cloud Chamber
Spark Counter
Photographic lm
alpha (!)
gamma (!"
beta (")
Definition: a random and
spontaneous process where
an unstable nucleus
emits radiation to become
a more stable nucleus
Types
spontaneous
random
Alpha decay
Beta decay
gamma decay
ionising power
penetrating power
effect of E
effect of B
charge
velocity
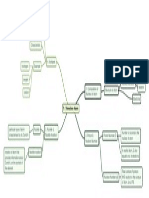
Radioactive decay series
Concept of half-life
Definition: A series of successive
decay processes for a particular
radioisotope until a stable isotope
is achieved
Graph of N againts Z
Half-life: time taken by a radioactive
substance to decay to half of its
original amount
Activity: number of decays of
radioactive material per unit time
Graph of Activity vs. time
Happen by its own & its
rate cannot be controlled
does not affected
chemically & physically
impossible to predict when
atom will decay
You might also like
- PSI Physics - Kinematics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument13 pagesPSI Physics - Kinematics Multiple Choice QuestionsJedah BatisNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 3 NotesDocument52 pagesPhysics Form 3 NotesDISHON100% (5)
- Act. 2 Natural Radioactive SeriesDocument2 pagesAct. 2 Natural Radioactive Seriesxiejie22590No ratings yet
- Radioactive DecayDocument32 pagesRadioactive DecayKHA HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Basic Nuclear Physics 3 - Rad. DisintegrationDocument42 pagesLecture 3 - Basic Nuclear Physics 3 - Rad. DisintegrationDidik Setyawarno 198810132015041004No ratings yet
- Basic Nuclear Physics - 3 Modes of Radioactive Decay and Types of RadiationDocument41 pagesBasic Nuclear Physics - 3 Modes of Radioactive Decay and Types of RadiationphooolNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity - Free Exam AcademyDocument1 pageRadioactivity - Free Exam AcademyMoaz ErakyNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument21 pagesRadioactivityVarun KolathNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity - 2Document21 pagesRadioactivity - 2junpajunar2No ratings yet
- Radioactive NuclearDocument14 pagesRadioactive NuclearrenneNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Decay (Alpha, Beta and Gamma)Document17 pagesNuclear Decay (Alpha, Beta and Gamma)Parahat.TajovNo ratings yet
- RadiationDocument13 pagesRadiationbuttonNo ratings yet
- Gamma RadioactivityDocument20 pagesGamma RadioactivityVivian BorgesNo ratings yet
- 13.3 RadioactivityDocument117 pages13.3 RadioactivityHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Discovery of RadioactivityDocument6 pages8.1 Discovery of RadioactivitysyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Radioactivity: 5.1 Understanding The Nucleus of An AtomDocument18 pagesChapter 5: Radioactivity: 5.1 Understanding The Nucleus of An AtomellacoolNo ratings yet
- Gamma Ray Spectroscopy by Suresh ShahDocument19 pagesGamma Ray Spectroscopy by Suresh ShahSuresh ShahNo ratings yet
- Radioanalytical Techniques: Ali Abbas M.Phil Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument54 pagesRadioanalytical Techniques: Ali Abbas M.Phil Pharmaceutical ChemistryAdia MasooraNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Decay (Also Known As Nuclear Decay, Radioactivity, Radioactive DisintegrationDocument1 pageRadioactive Decay (Also Known As Nuclear Decay, Radioactivity, Radioactive DisintegrationKirstian MartinezNo ratings yet
- Nuclear EquationsDocument21 pagesNuclear EquationsAbigail AmorNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity: Syahir Mansor, PHD Ippt, Usm Syahir - Mansor@Usm - MyDocument42 pagesRadioactivity: Syahir Mansor, PHD Ippt, Usm Syahir - Mansor@Usm - MyLailatul KisstinaNo ratings yet
- Modes of Radioactive Decay & Decay of RadioactivityDocument37 pagesModes of Radioactive Decay & Decay of RadioactivityVanshika GargNo ratings yet
- Physics Final Revision - Radioactivity 2013 PDFDocument11 pagesPhysics Final Revision - Radioactivity 2013 PDFCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Physics Form 5 Chapter 5Document22 pagesPhysics Form 5 Chapter 5Charlene87% (15)
- Radioactive C5 F5 PhysicsDocument22 pagesRadioactive C5 F5 PhysicsMrinaliniNo ratings yet
- 7 1 NotesDocument17 pages7 1 Notesapi-182809945No ratings yet
- Radioactivity - 2023 EditedDocument25 pagesRadioactivity - 2023 EditedLIZ HELENA A/P SUBRAMANIAM MoeNo ratings yet
- 4 Chapter 6 Morden PhysicsDocument33 pages4 Chapter 6 Morden PhysicsNABIKAMBA PHILIPNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Chem LecDocument5 pagesModule 3 - Chem LecErianne ReyesNo ratings yet
- Radiation Physics: PHY370 Physics Instrumentation and ApplicationDocument47 pagesRadiation Physics: PHY370 Physics Instrumentation and ApplicationaisyahNo ratings yet
- GRE FactsDocument25 pagesGRE FactsMohamed ElashriNo ratings yet
- GCSE 1b6 RadioactivityDocument48 pagesGCSE 1b6 RadioactivityChahinese FahsiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Stability and RadioactivityDocument35 pagesNuclear Stability and RadioactivityAmirHakimRusliNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC PHYSICS Double - FinalDocument8 pagesATOMIC PHYSICS Double - FinalaquamogolwaneNo ratings yet
- Phy O' Level Ch-22 ND 23 RadioactivityDocument12 pagesPhy O' Level Ch-22 ND 23 RadioactivityJahirul Jahir0% (1)
- Stanes SchoolDocument19 pagesStanes SchoolShibiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Phy 2Document31 pagesNuclear Phy 2Namitha RajeevNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Nuclear ChemistryDocument58 pagesLecture On Nuclear Chemistrysadia SultanaNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity Week 2Document9 pagesRadioactivity Week 2Muqaddas FatimaNo ratings yet
- Report For Experiment On Gamma Spectroscopy of Bismuth-207 - Nida Riaz - Alfred Mishi - vf1Document28 pagesReport For Experiment On Gamma Spectroscopy of Bismuth-207 - Nida Riaz - Alfred Mishi - vf1Alfred MishiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: Name: Aiman Zikri B. Zullkeppli Amin Class: 5sta IC NO: 960304-08-6543Document6 pagesNuclear Energy: Name: Aiman Zikri B. Zullkeppli Amin Class: 5sta IC NO: 960304-08-6543Faiz HapoNo ratings yet
- RADIOACTIVITYDocument26 pagesRADIOACTIVITYHarIsh SangwanNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 2 - CH 28-29-30 Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsDocument31 pagesAP Physics 2 - CH 28-29-30 Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsLê Văn Hiệu Khoa KH Tự NhiênNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1412 Ch. 18 -20 _ QuizletDocument25 pagesCHEM 1412 Ch. 18 -20 _ QuizletShiloh RiverNo ratings yet
- Chm524 4 RadiochemistryDocument67 pagesChm524 4 Radiochemistryasyraf azlan99No ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument18 pagesRadioactivityAkaNayep ApNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Testing.Document99 pagesRadiographic Testing.The Engineers EDGE, Coimbatore0% (1)
- Lesson 4 Nuclear TransformationDocument6 pagesLesson 4 Nuclear TransformationJoshua LimosneroNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ReactionDocument2 pagesNuclear ReactionMB CastilloNo ratings yet
- S4 Phy (Modern Physics)Document19 pagesS4 Phy (Modern Physics)jalgatkuothgangNo ratings yet
- navneetDocument58 pagesnavneetdrsubhashrtNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry: Unit 2.5Document48 pagesNuclear Chemistry: Unit 2.5Richelle CharleneNo ratings yet
- Rtfi Notes 1Document27 pagesRtfi Notes 1Ajith PayyanurNo ratings yet
- Exam Tips INTI Physics6Document10 pagesExam Tips INTI Physics6Marjorie OlgaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Radioactive RadiationsDocument37 pagesProperties of Radioactive RadiationsWaqar BashirNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 RadioactivityDocument64 pagesLecture 2 RadioactivityKakon AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- Ai CP 01Document6 pagesAi CP 01Random gmailNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Decay (Also Known As Nuclear Decay, Radioactivity or Nuclear Radiation) Is TheDocument2 pagesRadioactive Decay (Also Known As Nuclear Decay, Radioactivity or Nuclear Radiation) Is Thedwarika2006No ratings yet
- Physics (Radioactivity)Document21 pagesPhysics (Radioactivity)Hery HadzrenNo ratings yet
- Alpha ParticleDocument3 pagesAlpha ParticleFarhad shawNo ratings yet
- 13 Radiochemical Methods...Document23 pages13 Radiochemical Methods...Mtw WondNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandAn Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: Techniques and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- What Did Mathematics Do To Physics?Document34 pagesWhat Did Mathematics Do To Physics?Faris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Applications of Spin CoatingDocument10 pagesApplications of Spin CoatingFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Jalalul-Din Rumi - Selected Poems of RumiDocument46 pagesJalalul-Din Rumi - Selected Poems of RumiFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Generation of ElectricityDocument1 page3.5 Generation of ElectricityFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Experiment: 4.3 Understanding TransistorDocument1 pageExperiment: 4.3 Understanding TransistorFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- 4.2 DiodeDocument1 page4.2 DiodeFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Nucleus of AtomDocument1 page5.1 Nucleus of AtomFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Thermodynamics and Statistical MechanicsDocument502 pagesLecture Notes On Thermodynamics and Statistical MechanicsM Naufal Aqil FarhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SensorDocument13 pagesIntroduction To SensorFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Selected Poems - Rumi (17 Pages)Document17 pagesSelected Poems - Rumi (17 Pages)Faris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Thesis GuidelinesDocument6 pagesThesis GuidelinesFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Physics Olympiad Error and Data Analysis NoteDocument7 pagesPhysics Olympiad Error and Data Analysis NoteScience Olympiad Blog100% (1)
- Classical Electromagnetism - FitzpatrickDocument227 pagesClassical Electromagnetism - Fitzpatrickgamekingd07No ratings yet
- Modern Physics TutorialDocument131 pagesModern Physics TutorialFaris Shahin50% (4)
- Daqia Al KalamDocument9 pagesDaqia Al KalamFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Ketinggian Bidang Terjemahan Sebagai Satu Manifestasi Bangsa Berilmu - Ratna Roshida Ab. Razak & Aiza Maslan at BaharudinDocument12 pagesKetinggian Bidang Terjemahan Sebagai Satu Manifestasi Bangsa Berilmu - Ratna Roshida Ab. Razak & Aiza Maslan at BaharudinFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- 1D SensorsDocument23 pages1D SensorsFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Kalam's Necessary Engagement With Modern Science - Nidhal GouessomDocument12 pagesKalam's Necessary Engagement With Modern Science - Nidhal GouessomFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Saidku42129 ch09Document24 pagesSaidku42129 ch09rami wahshehNo ratings yet
- Concept of Drag: Viscous Drag and 1D MotionDocument23 pagesConcept of Drag: Viscous Drag and 1D MotionJustas BalčiūnasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document38 pagesChapter 19IntanNurDaniaNo ratings yet
- Electr Magnetic For Eng 5Document50 pagesElectr Magnetic For Eng 5Abdi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics WSDocument19 pagesKinematics WSMadhav JainNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes For Secondary Education of UgandaDocument11 pagesPhysics Notes For Secondary Education of UgandaMukiibi DuncanNo ratings yet
- Friction Notes - Iit-Jee - Bitsat - Neet - AiimsDocument32 pagesFriction Notes - Iit-Jee - Bitsat - Neet - Aiims145Ducks50% (10)
- Force: Chapter Out LineDocument17 pagesForce: Chapter Out LinePUSHKAR KUMARNo ratings yet
- Physics 71 EquationsDocument3 pagesPhysics 71 EquationsElah PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Kinematics - NEETDocument25 pagesKinematics - NEETAlok SinghNo ratings yet
- QuestionsExamPrep PDFDocument2 pagesQuestionsExamPrep PDFBowen XuNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 17 - Safety N Work Proc in SaleDocument27 pagesChapter - 17 - Safety N Work Proc in SaleMohd Isa HarunNo ratings yet
- Planar Kinetics of A Rigid Body Force and AccelerationDocument10 pagesPlanar Kinetics of A Rigid Body Force and AccelerationManjunath DNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Notes1Document26 pagesChapter7 Notes1WesrineNo ratings yet
- Physics Sec QuarterDocument4 pagesPhysics Sec QuarterLaurence MatthewNo ratings yet
- Motion in One Dimension: Topic 2, P. 31-40Document65 pagesMotion in One Dimension: Topic 2, P. 31-40khaled daherNo ratings yet
- Kinetic - Potential Energy (Grade 9) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingDocument2 pagesKinetic - Potential Energy (Grade 9) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingMOHDFADZLY84No ratings yet
- Solved Problems in Mechanics 2016Document28 pagesSolved Problems in Mechanics 2016Debbie TonogNo ratings yet
- EebodydiagramDocument41 pagesEebodydiagramTechhhniniNo ratings yet
- BAT Y11 Session 8 - Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Sheet1Document2 pagesBAT Y11 Session 8 - Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Sheet1superpooh-1No ratings yet
- MBM38202934 5Document2 pagesMBM38202934 5Luis OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Displacement and Force in Two Dimensions-5Document4 pagesDisplacement and Force in Two Dimensions-5varaprasadNo ratings yet
- Radio PharmacologyDocument32 pagesRadio PharmacologyKaise GuerreroNo ratings yet
- 4-Laws of Motion - 05Document66 pages4-Laws of Motion - 05Ali100% (1)
- 1 Kinematics in Two Dimensions STUDENTSDocument46 pages1 Kinematics in Two Dimensions STUDENTSJai VillaNo ratings yet
- Problem: SolutionDocument6 pagesProblem: SolutionOverHorizon shameNo ratings yet
- Notes of Science Class 9 MOTIONDocument6 pagesNotes of Science Class 9 MOTIONRama NandakumarNo ratings yet