Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsMathematics GR 12
Mathematics GR 12
Uploaded by
reacharunkThe document discusses solving cubic equations of the form ax3 + bx2 + cx + d = 0. It provides an example of solving the cubic equation 6x3 - 5x2 - 17x + 6 = 0. The steps shown are: (1) find one factor using the factor theorem, (2) factorize by inspection, (3) factorize fully, and (4) solve the fully factorized equation by setting each factor equal to 0. The example is fully factorized as (x - 2)(2x + 3)(3x - 1) = 0, resulting in solutions of x = 2, x = 1/3, or x = -3/2. It notes that if full
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Algebraic Expressions ExerciseDocument18 pagesAlgebraic Expressions ExerciseLi Ann ChungNo ratings yet
- Factoring Flow Sheet PDFDocument7 pagesFactoring Flow Sheet PDFReginald LopezNo ratings yet
- Completing The SquareDocument5 pagesCompleting The Squaremohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Math Primer ExcercisesDocument10 pagesMath Primer Excercisessilly_rabbitzNo ratings yet
- 5 17 44 418Document17 pages5 17 44 418kesharNo ratings yet
- 6.7 Solve by Factoring PDFDocument6 pages6.7 Solve by Factoring PDFIrish Serdeña - SigueNo ratings yet
- Quadratics: KAZIBA StephenDocument11 pagesQuadratics: KAZIBA Stephenkaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- Math 121 Test 1 Review 1Document3 pagesMath 121 Test 1 Review 1Sapna StanleyNo ratings yet
- Mathematical OperationsDocument7 pagesMathematical OperationsDarren LeslieNo ratings yet
- MC Ty Quadeqns 2009 1Document9 pagesMC Ty Quadeqns 2009 1PrayasAgrawalNo ratings yet
- 7 Quadratic Expressions: 7.1 Expansion (Multiplication)Document11 pages7 Quadratic Expressions: 7.1 Expansion (Multiplication)tamleduc1810dnNo ratings yet
- Integration by Partial FractionsDocument6 pagesIntegration by Partial FractionsStashNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Fractions SheetDocument9 pagesAlgebraic Fractions Sheetjwilkins1041No ratings yet
- IGCSE Factorisation Simultanuous EquationsDocument14 pagesIGCSE Factorisation Simultanuous Equationsagentdog175No ratings yet
- CH 4Document55 pagesCH 4Lawrence Dumalag100% (1)
- Remainder TheoremDocument26 pagesRemainder TheoremLyka Diane GagalangNo ratings yet
- MTH 100 Review Key 01Document24 pagesMTH 100 Review Key 01AB876No ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document6 pagesLesson 2Shan Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- General-Mathematics Q1 Module-3aDocument13 pagesGeneral-Mathematics Q1 Module-3aMalen GallegosNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 5 - Quadratic EquationsDocument111 pagesSelina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 5 - Quadratic Equationsdinesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring MethodDocument8 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations by Factoring MethodMicaelahNo ratings yet
- Examen Matemáticas Radicales y Ecuaciones 4º EsoDocument6 pagesExamen Matemáticas Radicales y Ecuaciones 4º EsoJosé Francisco Navarro MartínNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations MethodsDocument29 pagesQuadratic Equations MethodsPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- Factoring MethodsDocument8 pagesFactoring MethodsErdoan MustafovNo ratings yet
- FawaffwDocument11 pagesFawaffwJanaki KaushaniNo ratings yet
- Quadratic SDocument20 pagesQuadratic SAnubastNo ratings yet
- Ex 5 3 FSC Part1 Ver3 1Document9 pagesEx 5 3 FSC Part1 Ver3 1Awais BhattiNo ratings yet
- 2010 HMMT Algebra Practice SolutionsDocument3 pages2010 HMMT Algebra Practice SolutionsAlex YuNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Mathematics: Midterm Exam AnswerDocument3 pagesPre-Calculus Mathematics: Midterm Exam AnswerFernandoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1. Factor - CommonDocument5 pagesActivity 1. Factor - CommonJohair BalindongNo ratings yet
- Algebra 3Document37 pagesAlgebra 3Michael Damian100% (1)
- Factorisation: Methods of FactorizationDocument33 pagesFactorisation: Methods of Factorizationkanchan kalraNo ratings yet
- Gif - PrmoDocument6 pagesGif - PrmoapocalypticNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument18 pagesQuadratic EquationsErwani KamaruddinNo ratings yet
- Equations and InequationsDocument15 pagesEquations and InequationsMehwish FatimaNo ratings yet
- 0310 Final Exam ReviewDocument4 pages0310 Final Exam ReviewhoustontxabNo ratings yet
- Ex 5 3 FSC Part1Document6 pagesEx 5 3 FSC Part1Omer Muneer QaziNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 9 - Quadratic Equation ReviewerDocument3 pagesMathematics 9 - Quadratic Equation ReviewerJames Russel MariNo ratings yet
- Compendium of Notes Final 1 1Document37 pagesCompendium of Notes Final 1 1Macapinlac AaronNo ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument5 pagesAdditional MathematicsAdam NaqibNo ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument5 pagesAdditional MathematicsAdam NaqibNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Ii: Quadratic EquationsDocument29 pagesMathematics Ii: Quadratic Equationsbernadeth villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation 1Document29 pagesQuadratic Equation 1Athena Jane NapolisNo ratings yet
- 18 Quadratic EquationsDocument28 pages18 Quadratic Equationsapi-259236539No ratings yet
- MAT111 by Prof IloriDocument168 pagesMAT111 by Prof IloriFáróminíyì Mathefaro SimeonNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgCj5-qElIag41gyZJNw-uZj0qHj L2DmwAbHVk0JwASR7FygAHX5QJxdeU5VnJPcX7j ICbsv1HqTvPsB7xspRrg3MaPmrTKz7Bz4SkJpr8 Cwgjd2nCzXhZuATba7r3dWR3P-9DCo7322oDocument5 pagesACFrOgCj5-qElIag41gyZJNw-uZj0qHj L2DmwAbHVk0JwASR7FygAHX5QJxdeU5VnJPcX7j ICbsv1HqTvPsB7xspRrg3MaPmrTKz7Bz4SkJpr8 Cwgjd2nCzXhZuATba7r3dWR3P-9DCo7322oBhargs VenkatNo ratings yet
- CONTASSSDocument42 pagesCONTASSSluiz_andrade_KNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming Exercises Exercise 1. Given A Problem: Prove That Is An Extreme Optimal Solution of This ProblemDocument7 pagesLinear Programming Exercises Exercise 1. Given A Problem: Prove That Is An Extreme Optimal Solution of This ProblemHang PhamNo ratings yet
- Answers: Alg 2 Equations & Inequalities Review Name - DateDocument4 pagesAnswers: Alg 2 Equations & Inequalities Review Name - DatebwlomasNo ratings yet
- Persamaan Kuadratik: MTE1014 Ipg Kampus Darulaman Pn. HJH Saruvari Bt. Badru Duja KhanDocument29 pagesPersamaan Kuadratik: MTE1014 Ipg Kampus Darulaman Pn. HJH Saruvari Bt. Badru Duja KhanElavarasi SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Ch.8 - More About Equations - Method of EliminationDocument6 pagesCh.8 - More About Equations - Method of EliminationWayne TsoiNo ratings yet
- 0a.review of Pre-Requisite Skills - Ja21 (Answers)Document5 pages0a.review of Pre-Requisite Skills - Ja21 (Answers)tylerchoykwNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations by FactoringDocument11 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations by FactoringSour PlumNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorization and Completing The SquareDocument3 pages3.5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorization and Completing The SquareAanya RalhanNo ratings yet
- Selina Solution Concise Maths Class 10 Chapter 5Document39 pagesSelina Solution Concise Maths Class 10 Chapter 5radha raman UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Polynomials Class 9 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2 With Solutions AnswersDocument12 pagesPolynomials Class 9 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2 With Solutions AnswersElina RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document21 pagesLecture 4Colin LongNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 pagesProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1459)Document1 pageEn (1459)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- General Terms and Conditions of The Pzu NNW (Personal Accident Insurance Pzu Edukacja InsuranceDocument19 pagesGeneral Terms and Conditions of The Pzu NNW (Personal Accident Insurance Pzu Edukacja InsurancereacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1464)Document1 pageEn (1464)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1458)Document1 pageEn (1458)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1451)Document1 pageEn (1451)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1386)Document1 pageEn (1386)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- Mate The: (Fig. - VrouldDocument1 pageMate The: (Fig. - VrouldreacharunkNo ratings yet
- And Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atDocument1 pageAnd Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1383)Document1 pageEn (1383)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1382)Document1 pageEn (1382)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- The The Jamb The Name Much The: Tlio CL - AssesDocument1 pageThe The Jamb The Name Much The: Tlio CL - AssesreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1374)Document1 pageEn (1374)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1376)Document1 pageEn (1376)reacharunkNo ratings yet
Mathematics GR 12
Mathematics GR 12
Uploaded by
reacharunk0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThe document discusses solving cubic equations of the form ax3 + bx2 + cx + d = 0. It provides an example of solving the cubic equation 6x3 - 5x2 - 17x + 6 = 0. The steps shown are: (1) find one factor using the factor theorem, (2) factorize by inspection, (3) factorize fully, and (4) solve the fully factorized equation by setting each factor equal to 0. The example is fully factorized as (x - 2)(2x + 3)(3x - 1) = 0, resulting in solutions of x = 2, x = 1/3, or x = -3/2. It notes that if full
Original Description:
pkortuiyiuyi
Original Title
228403049-Mathematics-Gr-12(210)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses solving cubic equations of the form ax3 + bx2 + cx + d = 0. It provides an example of solving the cubic equation 6x3 - 5x2 - 17x + 6 = 0. The steps shown are: (1) find one factor using the factor theorem, (2) factorize by inspection, (3) factorize fully, and (4) solve the fully factorized equation by setting each factor equal to 0. The example is fully factorized as (x - 2)(2x + 3)(3x - 1) = 0, resulting in solutions of x = 2, x = 1/3, or x = -3/2. It notes that if full
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageMathematics GR 12
Mathematics GR 12
Uploaded by
reacharunkThe document discusses solving cubic equations of the form ax3 + bx2 + cx + d = 0. It provides an example of solving the cubic equation 6x3 - 5x2 - 17x + 6 = 0. The steps shown are: (1) find one factor using the factor theorem, (2) factorize by inspection, (3) factorize fully, and (4) solve the fully factorized equation by setting each factor equal to 0. The example is fully factorized as (x - 2)(2x + 3)(3x - 1) = 0, resulting in solutions of x = 2, x = 1/3, or x = -3/2. It notes that if full
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
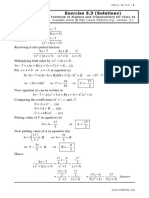
5.
5 Solving cubic equations EMCGX
Now that we know how to factorise cubic polynomials, it is also easy to solve cubic
equations of the form ax
3
+ bx
2
+ cx + d = 0.
Worked example 13: Solving cubic equations
QUESTION
Solve: 6x
3
5x
2
17x + 6 = 0
SOLUTION
Step 1: Find one factor using the factor theorem
Let f(x) = 6x
3
5x
2
17x + 6
Try f (1) = 6(1)
3
5(1)
2
17 (1) + 6 = 6 5 17 + 6 = 10
Therefore (x 1) is not a factor.
Try f (2) = 6(2)
3
5(2)
2
17 (2) + 6 = 48 20 34 + 6 = 0
Therefore (x 2) is a factor.
Step 2: Factorise by inspection
6x
3
5x
2
17x + 6 = (x 2)
6x
2
+ 7x 3
Step 3: Factorise fully
6x
3
5x
2
17x + 6 = (x 2) (2x + 3) (3x 1)
Step 4: Solve the equation
6x
3
5x
2
17x + 6 = 0
(x 2) (2x + 3) (3x 1) = 0
x = 2 or x =
1
3
or x =
3
2
Sometimes it is not possible to factorise a quadratic expression using inspection, in
which case we use the quadratic formula to fully factorise and solve the cubic equation.
x =
b
b
2
4ac
2a
199 Chapter 5. Polynomials
You might also like
- Algebraic Expressions ExerciseDocument18 pagesAlgebraic Expressions ExerciseLi Ann ChungNo ratings yet
- Factoring Flow Sheet PDFDocument7 pagesFactoring Flow Sheet PDFReginald LopezNo ratings yet
- Completing The SquareDocument5 pagesCompleting The Squaremohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Math Primer ExcercisesDocument10 pagesMath Primer Excercisessilly_rabbitzNo ratings yet
- 5 17 44 418Document17 pages5 17 44 418kesharNo ratings yet
- 6.7 Solve by Factoring PDFDocument6 pages6.7 Solve by Factoring PDFIrish Serdeña - SigueNo ratings yet
- Quadratics: KAZIBA StephenDocument11 pagesQuadratics: KAZIBA Stephenkaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- Math 121 Test 1 Review 1Document3 pagesMath 121 Test 1 Review 1Sapna StanleyNo ratings yet
- Mathematical OperationsDocument7 pagesMathematical OperationsDarren LeslieNo ratings yet
- MC Ty Quadeqns 2009 1Document9 pagesMC Ty Quadeqns 2009 1PrayasAgrawalNo ratings yet
- 7 Quadratic Expressions: 7.1 Expansion (Multiplication)Document11 pages7 Quadratic Expressions: 7.1 Expansion (Multiplication)tamleduc1810dnNo ratings yet
- Integration by Partial FractionsDocument6 pagesIntegration by Partial FractionsStashNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Fractions SheetDocument9 pagesAlgebraic Fractions Sheetjwilkins1041No ratings yet
- IGCSE Factorisation Simultanuous EquationsDocument14 pagesIGCSE Factorisation Simultanuous Equationsagentdog175No ratings yet
- CH 4Document55 pagesCH 4Lawrence Dumalag100% (1)
- Remainder TheoremDocument26 pagesRemainder TheoremLyka Diane GagalangNo ratings yet
- MTH 100 Review Key 01Document24 pagesMTH 100 Review Key 01AB876No ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document6 pagesLesson 2Shan Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- General-Mathematics Q1 Module-3aDocument13 pagesGeneral-Mathematics Q1 Module-3aMalen GallegosNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 5 - Quadratic EquationsDocument111 pagesSelina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 5 - Quadratic Equationsdinesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring MethodDocument8 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations by Factoring MethodMicaelahNo ratings yet
- Examen Matemáticas Radicales y Ecuaciones 4º EsoDocument6 pagesExamen Matemáticas Radicales y Ecuaciones 4º EsoJosé Francisco Navarro MartínNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations MethodsDocument29 pagesQuadratic Equations MethodsPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- Factoring MethodsDocument8 pagesFactoring MethodsErdoan MustafovNo ratings yet
- FawaffwDocument11 pagesFawaffwJanaki KaushaniNo ratings yet
- Quadratic SDocument20 pagesQuadratic SAnubastNo ratings yet
- Ex 5 3 FSC Part1 Ver3 1Document9 pagesEx 5 3 FSC Part1 Ver3 1Awais BhattiNo ratings yet
- 2010 HMMT Algebra Practice SolutionsDocument3 pages2010 HMMT Algebra Practice SolutionsAlex YuNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Mathematics: Midterm Exam AnswerDocument3 pagesPre-Calculus Mathematics: Midterm Exam AnswerFernandoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1. Factor - CommonDocument5 pagesActivity 1. Factor - CommonJohair BalindongNo ratings yet
- Algebra 3Document37 pagesAlgebra 3Michael Damian100% (1)
- Factorisation: Methods of FactorizationDocument33 pagesFactorisation: Methods of Factorizationkanchan kalraNo ratings yet
- Gif - PrmoDocument6 pagesGif - PrmoapocalypticNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument18 pagesQuadratic EquationsErwani KamaruddinNo ratings yet
- Equations and InequationsDocument15 pagesEquations and InequationsMehwish FatimaNo ratings yet
- 0310 Final Exam ReviewDocument4 pages0310 Final Exam ReviewhoustontxabNo ratings yet
- Ex 5 3 FSC Part1Document6 pagesEx 5 3 FSC Part1Omer Muneer QaziNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 9 - Quadratic Equation ReviewerDocument3 pagesMathematics 9 - Quadratic Equation ReviewerJames Russel MariNo ratings yet
- Compendium of Notes Final 1 1Document37 pagesCompendium of Notes Final 1 1Macapinlac AaronNo ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument5 pagesAdditional MathematicsAdam NaqibNo ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument5 pagesAdditional MathematicsAdam NaqibNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Ii: Quadratic EquationsDocument29 pagesMathematics Ii: Quadratic Equationsbernadeth villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation 1Document29 pagesQuadratic Equation 1Athena Jane NapolisNo ratings yet
- 18 Quadratic EquationsDocument28 pages18 Quadratic Equationsapi-259236539No ratings yet
- MAT111 by Prof IloriDocument168 pagesMAT111 by Prof IloriFáróminíyì Mathefaro SimeonNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgCj5-qElIag41gyZJNw-uZj0qHj L2DmwAbHVk0JwASR7FygAHX5QJxdeU5VnJPcX7j ICbsv1HqTvPsB7xspRrg3MaPmrTKz7Bz4SkJpr8 Cwgjd2nCzXhZuATba7r3dWR3P-9DCo7322oDocument5 pagesACFrOgCj5-qElIag41gyZJNw-uZj0qHj L2DmwAbHVk0JwASR7FygAHX5QJxdeU5VnJPcX7j ICbsv1HqTvPsB7xspRrg3MaPmrTKz7Bz4SkJpr8 Cwgjd2nCzXhZuATba7r3dWR3P-9DCo7322oBhargs VenkatNo ratings yet
- CONTASSSDocument42 pagesCONTASSSluiz_andrade_KNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming Exercises Exercise 1. Given A Problem: Prove That Is An Extreme Optimal Solution of This ProblemDocument7 pagesLinear Programming Exercises Exercise 1. Given A Problem: Prove That Is An Extreme Optimal Solution of This ProblemHang PhamNo ratings yet
- Answers: Alg 2 Equations & Inequalities Review Name - DateDocument4 pagesAnswers: Alg 2 Equations & Inequalities Review Name - DatebwlomasNo ratings yet
- Persamaan Kuadratik: MTE1014 Ipg Kampus Darulaman Pn. HJH Saruvari Bt. Badru Duja KhanDocument29 pagesPersamaan Kuadratik: MTE1014 Ipg Kampus Darulaman Pn. HJH Saruvari Bt. Badru Duja KhanElavarasi SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Ch.8 - More About Equations - Method of EliminationDocument6 pagesCh.8 - More About Equations - Method of EliminationWayne TsoiNo ratings yet
- 0a.review of Pre-Requisite Skills - Ja21 (Answers)Document5 pages0a.review of Pre-Requisite Skills - Ja21 (Answers)tylerchoykwNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations by FactoringDocument11 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations by FactoringSour PlumNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorization and Completing The SquareDocument3 pages3.5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorization and Completing The SquareAanya RalhanNo ratings yet
- Selina Solution Concise Maths Class 10 Chapter 5Document39 pagesSelina Solution Concise Maths Class 10 Chapter 5radha raman UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Polynomials Class 9 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2 With Solutions AnswersDocument12 pagesPolynomials Class 9 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2 With Solutions AnswersElina RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document21 pagesLecture 4Colin LongNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 pagesProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1459)Document1 pageEn (1459)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- General Terms and Conditions of The Pzu NNW (Personal Accident Insurance Pzu Edukacja InsuranceDocument19 pagesGeneral Terms and Conditions of The Pzu NNW (Personal Accident Insurance Pzu Edukacja InsurancereacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1464)Document1 pageEn (1464)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1458)Document1 pageEn (1458)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1451)Document1 pageEn (1451)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1386)Document1 pageEn (1386)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- Mate The: (Fig. - VrouldDocument1 pageMate The: (Fig. - VrouldreacharunkNo ratings yet
- And Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atDocument1 pageAnd Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1383)Document1 pageEn (1383)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1382)Document1 pageEn (1382)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- The The Jamb The Name Much The: Tlio CL - AssesDocument1 pageThe The Jamb The Name Much The: Tlio CL - AssesreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1374)Document1 pageEn (1374)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1376)Document1 pageEn (1376)reacharunkNo ratings yet