Professional Documents
Culture Documents
325 Chapter 8. Euclidean Geometry
325 Chapter 8. Euclidean Geometry
Uploaded by
reacharunkCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- 8 Circular MeasuresDocument12 pages8 Circular MeasuresNor Hanina100% (6)
- C2 Trigonometry - QuestionsDocument17 pagesC2 Trigonometry - QuestionsRichard AdioNo ratings yet
- 05 - MensurationDocument28 pages05 - Mensurationthinkiit88% (8)
- Maharashtra-Mathematics Geometry Sample Paper-1-SOLUTION-Class 10 Question PaperDocument9 pagesMaharashtra-Mathematics Geometry Sample Paper-1-SOLUTION-Class 10 Question PaperFirdosh KhanNo ratings yet
- SPM Circular Measure F4Document4 pagesSPM Circular Measure F4Chrystal BrownNo ratings yet
- Answers (October 2009) : Example 1Document5 pagesAnswers (October 2009) : Example 1robanloiNo ratings yet
- Class X Maths (S) 23-24 Pre-Board SolDocument26 pagesClass X Maths (S) 23-24 Pre-Board Sol12345krish0guptaNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument74 pagesCircleteguhedy100% (1)
- Circle Quiz 3Document10 pagesCircle Quiz 3Orange TcNo ratings yet
- Geometric Trig - SLDocument15 pagesGeometric Trig - SLNatNo ratings yet
- Heron's Formular Surface Areas and Volumes & TrianglesDocument121 pagesHeron's Formular Surface Areas and Volumes & Trianglesthinkiit100% (3)
- 2012 Class 10 All India Set-1 Section-CDocument13 pages2012 Class 10 All India Set-1 Section-Choney1002No ratings yet
- Trig Test Marking Scheme 1Document8 pagesTrig Test Marking Scheme 1api-318829239No ratings yet
- Module 8A - Circular MeasureDocument11 pagesModule 8A - Circular MeasureHayati Aini Ahmad100% (2)
- Class 7 Mensuration - Perimeter, Area, Volume: All Questions Are 1 MarksDocument13 pagesClass 7 Mensuration - Perimeter, Area, Volume: All Questions Are 1 Markswb csNo ratings yet
- (Worksheet) Arc & Area of SectorsDocument21 pages(Worksheet) Arc & Area of SectorsAmir Faisal83% (6)
- Geometry & Mensuration 3Document35 pagesGeometry & Mensuration 3Neetu Jain100% (2)
- Chapter 12 Areas Related To CirclesDocument31 pagesChapter 12 Areas Related To CirclesFanisus RNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Final Exam Paper MarkingDocument10 pagesForm 3 Final Exam Paper Markinghoi ching wongNo ratings yet
- CBSE X 2009 Mathematics: Section CDocument11 pagesCBSE X 2009 Mathematics: Section Capi-19808758No ratings yet
- Circular Measure: 1.1 Converting Measurements in Radians To Degrees and Vice Versa SDocument12 pagesCircular Measure: 1.1 Converting Measurements in Radians To Degrees and Vice Versa SrodprinceNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 PDFDocument30 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 PDFswapna allaNo ratings yet
- Trapezoids and Kites WorksheetDocument24 pagesTrapezoids and Kites WorksheetAlfel Ringo AgustinNo ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Jan2021 Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10Document21 pagesNcert Exemplar Jan2021 Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10Shivam EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- STD 8 - Maths - Chapter 17 - NotesDocument6 pagesSTD 8 - Maths - Chapter 17 - NotesMamata MannaNo ratings yet
- Blue Print: Sa-Ii (Ix) : Mathematics.: MensurationDocument19 pagesBlue Print: Sa-Ii (Ix) : Mathematics.: Mensurationapi-243565143No ratings yet
- Maths F2 QSDocument4 pagesMaths F2 QSjulian.kibet07No ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Math Chapter 11 Ex 11 2Document16 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Math Chapter 11 Ex 11 2Divyanshu JhaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Maths 230730 075651Document261 pagesCBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Maths 230730 075651shekhar sharmaNo ratings yet
- Msbshse Class 10 Geometry Mathematics Question Paper With Solutions 2018Document12 pagesMsbshse Class 10 Geometry Mathematics Question Paper With Solutions 2018JunnuNo ratings yet
- Weebly - 3d TrigDocument4 pagesWeebly - 3d Trigapi-200177496No ratings yet
- Math GR 10 Lesson 6Document8 pagesMath GR 10 Lesson 6LoH 3bkNo ratings yet
- Maths CirclesDocument28 pagesMaths CirclesAdhi AdhiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit 7 TrigonometryDocument14 pagesAssignment Unit 7 TrigonometryCheriol LeungNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure - HL MathDocument13 pagesCircular Measure - HL MathPrakash PhilipNo ratings yet
- Poly Test 2Document9 pagesPoly Test 2waiwaimoe123No ratings yet
- Mathemathic SubjektifDocument10 pagesMathemathic Subjektifjoyce juok zhi shangNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths Term 2 Important QuestionsDocument13 pagesClass 10 Maths Term 2 Important QuestionsBhargavi JujjavarapuNo ratings yet
- Ar (Circles)Document16 pagesAr (Circles)Akshit MalhotraNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 MathsDocument43 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 9 Mathsfunson123No ratings yet
- Activity 3 - The Sector of A CircleDocument3 pagesActivity 3 - The Sector of A Circlebj0623573No ratings yet
- BMTSC Exam Reference Problems GeometryDocument13 pagesBMTSC Exam Reference Problems GeometryAloma Fonseca100% (1)
- 12 Area of A Circle PDFDocument10 pages12 Area of A Circle PDFDasoNo ratings yet
- Polygon Interior/Exterior Angles: Geometry 5.1Document23 pagesPolygon Interior/Exterior Angles: Geometry 5.1Baskaran SeetharamanNo ratings yet
- 9th GeometryDocument28 pages9th Geometrywww.r2dk2No ratings yet
- Solution of Triangle: KLN LKN KLN LKNDocument2 pagesSolution of Triangle: KLN LKN KLN LKNakuesukaNo ratings yet
- Polytech Congruence and Modulo CongruenceDocument6 pagesPolytech Congruence and Modulo CongruencechicknaliaNo ratings yet
- Some Geonmetry College ArchitecuteDocument7 pagesSome Geonmetry College ArchitecutepranavdeepakvNo ratings yet
- Here You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostDocument12 pagesHere You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostMohd Shahbaz100% (1)
- HMMT February 2019: GeometryDocument6 pagesHMMT February 2019: GeometryPaul TaniwanNo ratings yet
- Circle 14 NovemberDocument71 pagesCircle 14 NovemberTanya JainNo ratings yet
- CAT Quant Questions PDFDocument65 pagesCAT Quant Questions PDFSuryansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 pagesProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkNo ratings yet
- General Terms and Conditions of The Pzu NNW (Personal Accident Insurance Pzu Edukacja InsuranceDocument19 pagesGeneral Terms and Conditions of The Pzu NNW (Personal Accident Insurance Pzu Edukacja InsurancereacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1451)Document1 pageEn (1451)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1459)Document1 pageEn (1459)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1464)Document1 pageEn (1464)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- And Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atDocument1 pageAnd Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1458)Document1 pageEn (1458)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1386)Document1 pageEn (1386)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- Mate The: (Fig. - VrouldDocument1 pageMate The: (Fig. - VrouldreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1383)Document1 pageEn (1383)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1382)Document1 pageEn (1382)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1376)Document1 pageEn (1376)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1374)Document1 pageEn (1374)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- The The Jamb The Name Much The: Tlio CL - AssesDocument1 pageThe The Jamb The Name Much The: Tlio CL - AssesreacharunkNo ratings yet
325 Chapter 8. Euclidean Geometry
325 Chapter 8. Euclidean Geometry
Uploaded by
reacharunkOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
325 Chapter 8. Euclidean Geometry
325 Chapter 8. Euclidean Geometry
Uploaded by
reacharunkCopyright:
Available Formats
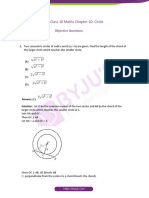
SOLUTION
Step 1: Use the ratio to determine the length of AB
AB : BD = 3 : 4
AB
BD
=
3
4
AB
12
=
3
4
AB = 12
3
4
= 9 cm
Step 2: Calculate the length of AO
We use the properties of a rhombus and the theorem of Pythagoras to nd AO.
BD = 12 cm
BO = 6 cm (diagonals bisect each other)
In ABO, A
OB = 90
(diagonals intersect at )
AO
2
= AB
2
BO
2
(Pythagoras)
= 9
2
6
2
AO =
45
= 6,71 cm
Step 3: Determine the area of rhombus ABCD
Area ABCD =
1
2
AC BD
=
1
2
(2
45)(12)
= 80,50 cm
2
Exercise 8 3: Proportionality of polygons
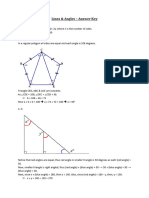
1. MNOP is a rectangle with MN : NO = 5 : 3 and QN = 10 cm.
P
M N
O
Q
10 cm
a) Calculate MN (correct to 2 decimal places).
b) Calculate the area of OPQ (correct to 2 decimal places).
325 Chapter 8. Euclidean geometry
You might also like
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- 8 Circular MeasuresDocument12 pages8 Circular MeasuresNor Hanina100% (6)
- C2 Trigonometry - QuestionsDocument17 pagesC2 Trigonometry - QuestionsRichard AdioNo ratings yet
- 05 - MensurationDocument28 pages05 - Mensurationthinkiit88% (8)
- Maharashtra-Mathematics Geometry Sample Paper-1-SOLUTION-Class 10 Question PaperDocument9 pagesMaharashtra-Mathematics Geometry Sample Paper-1-SOLUTION-Class 10 Question PaperFirdosh KhanNo ratings yet
- SPM Circular Measure F4Document4 pagesSPM Circular Measure F4Chrystal BrownNo ratings yet
- Answers (October 2009) : Example 1Document5 pagesAnswers (October 2009) : Example 1robanloiNo ratings yet
- Class X Maths (S) 23-24 Pre-Board SolDocument26 pagesClass X Maths (S) 23-24 Pre-Board Sol12345krish0guptaNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument74 pagesCircleteguhedy100% (1)
- Circle Quiz 3Document10 pagesCircle Quiz 3Orange TcNo ratings yet
- Geometric Trig - SLDocument15 pagesGeometric Trig - SLNatNo ratings yet
- Heron's Formular Surface Areas and Volumes & TrianglesDocument121 pagesHeron's Formular Surface Areas and Volumes & Trianglesthinkiit100% (3)
- 2012 Class 10 All India Set-1 Section-CDocument13 pages2012 Class 10 All India Set-1 Section-Choney1002No ratings yet
- Trig Test Marking Scheme 1Document8 pagesTrig Test Marking Scheme 1api-318829239No ratings yet
- Module 8A - Circular MeasureDocument11 pagesModule 8A - Circular MeasureHayati Aini Ahmad100% (2)
- Class 7 Mensuration - Perimeter, Area, Volume: All Questions Are 1 MarksDocument13 pagesClass 7 Mensuration - Perimeter, Area, Volume: All Questions Are 1 Markswb csNo ratings yet
- (Worksheet) Arc & Area of SectorsDocument21 pages(Worksheet) Arc & Area of SectorsAmir Faisal83% (6)
- Geometry & Mensuration 3Document35 pagesGeometry & Mensuration 3Neetu Jain100% (2)
- Chapter 12 Areas Related To CirclesDocument31 pagesChapter 12 Areas Related To CirclesFanisus RNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Final Exam Paper MarkingDocument10 pagesForm 3 Final Exam Paper Markinghoi ching wongNo ratings yet
- CBSE X 2009 Mathematics: Section CDocument11 pagesCBSE X 2009 Mathematics: Section Capi-19808758No ratings yet
- Circular Measure: 1.1 Converting Measurements in Radians To Degrees and Vice Versa SDocument12 pagesCircular Measure: 1.1 Converting Measurements in Radians To Degrees and Vice Versa SrodprinceNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 PDFDocument30 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 PDFswapna allaNo ratings yet
- Trapezoids and Kites WorksheetDocument24 pagesTrapezoids and Kites WorksheetAlfel Ringo AgustinNo ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Jan2021 Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10Document21 pagesNcert Exemplar Jan2021 Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10Shivam EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- STD 8 - Maths - Chapter 17 - NotesDocument6 pagesSTD 8 - Maths - Chapter 17 - NotesMamata MannaNo ratings yet
- Blue Print: Sa-Ii (Ix) : Mathematics.: MensurationDocument19 pagesBlue Print: Sa-Ii (Ix) : Mathematics.: Mensurationapi-243565143No ratings yet
- Maths F2 QSDocument4 pagesMaths F2 QSjulian.kibet07No ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Math Chapter 11 Ex 11 2Document16 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Math Chapter 11 Ex 11 2Divyanshu JhaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Maths 230730 075651Document261 pagesCBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Maths 230730 075651shekhar sharmaNo ratings yet
- Msbshse Class 10 Geometry Mathematics Question Paper With Solutions 2018Document12 pagesMsbshse Class 10 Geometry Mathematics Question Paper With Solutions 2018JunnuNo ratings yet
- Weebly - 3d TrigDocument4 pagesWeebly - 3d Trigapi-200177496No ratings yet
- Math GR 10 Lesson 6Document8 pagesMath GR 10 Lesson 6LoH 3bkNo ratings yet
- Maths CirclesDocument28 pagesMaths CirclesAdhi AdhiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit 7 TrigonometryDocument14 pagesAssignment Unit 7 TrigonometryCheriol LeungNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure - HL MathDocument13 pagesCircular Measure - HL MathPrakash PhilipNo ratings yet
- Poly Test 2Document9 pagesPoly Test 2waiwaimoe123No ratings yet
- Mathemathic SubjektifDocument10 pagesMathemathic Subjektifjoyce juok zhi shangNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths Term 2 Important QuestionsDocument13 pagesClass 10 Maths Term 2 Important QuestionsBhargavi JujjavarapuNo ratings yet
- Ar (Circles)Document16 pagesAr (Circles)Akshit MalhotraNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 MathsDocument43 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 9 Mathsfunson123No ratings yet
- Activity 3 - The Sector of A CircleDocument3 pagesActivity 3 - The Sector of A Circlebj0623573No ratings yet
- BMTSC Exam Reference Problems GeometryDocument13 pagesBMTSC Exam Reference Problems GeometryAloma Fonseca100% (1)
- 12 Area of A Circle PDFDocument10 pages12 Area of A Circle PDFDasoNo ratings yet
- Polygon Interior/Exterior Angles: Geometry 5.1Document23 pagesPolygon Interior/Exterior Angles: Geometry 5.1Baskaran SeetharamanNo ratings yet
- 9th GeometryDocument28 pages9th Geometrywww.r2dk2No ratings yet
- Solution of Triangle: KLN LKN KLN LKNDocument2 pagesSolution of Triangle: KLN LKN KLN LKNakuesukaNo ratings yet
- Polytech Congruence and Modulo CongruenceDocument6 pagesPolytech Congruence and Modulo CongruencechicknaliaNo ratings yet
- Some Geonmetry College ArchitecuteDocument7 pagesSome Geonmetry College ArchitecutepranavdeepakvNo ratings yet
- Here You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostDocument12 pagesHere You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostMohd Shahbaz100% (1)
- HMMT February 2019: GeometryDocument6 pagesHMMT February 2019: GeometryPaul TaniwanNo ratings yet
- Circle 14 NovemberDocument71 pagesCircle 14 NovemberTanya JainNo ratings yet
- CAT Quant Questions PDFDocument65 pagesCAT Quant Questions PDFSuryansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 pagesProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkNo ratings yet
- General Terms and Conditions of The Pzu NNW (Personal Accident Insurance Pzu Edukacja InsuranceDocument19 pagesGeneral Terms and Conditions of The Pzu NNW (Personal Accident Insurance Pzu Edukacja InsurancereacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1451)Document1 pageEn (1451)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1459)Document1 pageEn (1459)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1464)Document1 pageEn (1464)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- And Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atDocument1 pageAnd Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1458)Document1 pageEn (1458)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1386)Document1 pageEn (1386)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- Mate The: (Fig. - VrouldDocument1 pageMate The: (Fig. - VrouldreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1383)Document1 pageEn (1383)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1382)Document1 pageEn (1382)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1376)Document1 pageEn (1376)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1374)Document1 pageEn (1374)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- The The Jamb The Name Much The: Tlio CL - AssesDocument1 pageThe The Jamb The Name Much The: Tlio CL - AssesreacharunkNo ratings yet