Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6 Radioactive Substances
Chapter 6 Radioactive Substances
Uploaded by
Enniey RoxellCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Folio Radioactivity Ting 5Document16 pagesFolio Radioactivity Ting 5akunaruto92100% (3)
- Radiopharmaceutics Presentation1Document52 pagesRadiopharmaceutics Presentation1alibinaminNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy Form 4Document14 pagesNuclear Energy Form 4Akmar MataliNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Inanam: PhysicsDocument46 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Inanam: PhysicsMuhammad Safril Abdul HalimNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Nucleus of An AtomDocument25 pagesUnderstanding The Nucleus of An Atomnfaizah1100% (2)
- 7 1 NotesDocument17 pages7 1 Notesapi-182809945No ratings yet
- Radioanalytical Techniques: Ali Abbas M.Phil Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument54 pagesRadioanalytical Techniques: Ali Abbas M.Phil Pharmaceutical ChemistryAdia MasooraNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy.: 6.1 Radioactive SubstancesDocument7 pagesNuclear Energy.: 6.1 Radioactive SubstancesElly EllynaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Tech English - PDFDocument20 pagesNuclear Tech English - PDFShivang BhardwajNo ratings yet
- IGCSE UNIT - 5 ATOMIC PHYSICS NotesDocument12 pagesIGCSE UNIT - 5 ATOMIC PHYSICS Notesvishrudh lakshminarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Nuclear Energy: 6.1 Radioactive SubstancesDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Nuclear Energy: 6.1 Radioactive SubstancesNg Lay HoonNo ratings yet
- Physics: The Study of MatterDocument15 pagesPhysics: The Study of MatterTaha RashidNo ratings yet
- Measurement of RadioactivesDocument20 pagesMeasurement of RadioactivesAnonymous Nl973ID1d8No ratings yet
- Radio PharmaceuticsDocument52 pagesRadio PharmaceuticsDrGaurav TiwariNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: Name: Aiman Zikri B. Zullkeppli Amin Class: 5sta IC NO: 960304-08-6543Document6 pagesNuclear Energy: Name: Aiman Zikri B. Zullkeppli Amin Class: 5sta IC NO: 960304-08-6543Faiz HapoNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity ExplainedDocument1 pageRadioactivity ExplainedqwertyNo ratings yet
- Class - Nine: Physics: Radioactivity Handout-2 Ionizing ChamberDocument5 pagesClass - Nine: Physics: Radioactivity Handout-2 Ionizing ChamberBEASTBOY GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Radiation 22Document56 pagesRadiation 22amad4445555No ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument7 pagesRadioactivitySalmanNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity 5 LessonsDocument6 pagesRadioactivity 5 LessonsHLSSummerInstituteNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Atomic Physics Notes PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 5 Atomic Physics Notes PDFpreeti.2405100% (2)
- Nuclear Physics - 2Document121 pagesNuclear Physics - 2Rose MusariraNo ratings yet
- Properties of Radioactive RadiationsDocument37 pagesProperties of Radioactive RadiationsWaqar BashirNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument41 pagesAtomic PhysicsFaiq IrfanNo ratings yet
- Phy ChemDocument248 pagesPhy ChemBitter SugarNo ratings yet
- RADIOGRAPHY STUDY MATERIAL LatestDocument52 pagesRADIOGRAPHY STUDY MATERIAL LatestManish SinghNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy 1 2003Document19 pagesNuclear Energy 1 2003Aisyah Dan AnuaruddinNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument22 pagesRadioactivitymerezemenike272No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - RadioactivityDocument28 pagesChapter 12 - RadioactivityAljoša GraovacNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Introduction To Nuclear RadioactivityDocument45 pages7.1 Introduction To Nuclear RadioactivityReyzhel Mae MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 - Nuclear Chemistry - Notes - KEYDocument2 pagesUnit 13 - Nuclear Chemistry - Notes - KEYSumathi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity or Radioactive Decay:: Topic 5 - Atomic PhysicsDocument5 pagesRadioactivity or Radioactive Decay:: Topic 5 - Atomic PhysicsAbdullah MACNo ratings yet
- Analysing Radioactive Decay: Lesson 2Document16 pagesAnalysing Radioactive Decay: Lesson 2TS ShongNo ratings yet
- The ABC's of RadioactivityDocument17 pagesThe ABC's of RadioactivityAnggita DwiNo ratings yet
- Physics Final Revision - Radioactivity 2013 PDFDocument11 pagesPhysics Final Revision - Radioactivity 2013 PDFCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Stanes SchoolDocument19 pagesStanes SchoolShibiNo ratings yet
- Natural Radioactivity and StatisticsDocument9 pagesNatural Radioactivity and StatisticsgiornoxxNo ratings yet
- Geiger Muller CounterDocument27 pagesGeiger Muller CounterUsmanMustafa88% (16)
- Radioactive Physics - Research PaperDocument18 pagesRadioactive Physics - Research PaperJovicaSutevNo ratings yet
- Inverse Square LawDocument70 pagesInverse Square LawEngr Rab Nawaz ButtNo ratings yet
- Rad Prod Lesson 2Document6 pagesRad Prod Lesson 2LARA ADAYNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Nuclear PhysicsDocument8 pagesUnit 6 Nuclear PhysicsJonathan LeeNo ratings yet
- Physics (Radioactivity)Document21 pagesPhysics (Radioactivity)Hery HadzrenNo ratings yet
- Detection & Measurement of RadioactivityDocument7 pagesDetection & Measurement of RadioactivityChetan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity NotesDocument16 pagesRadioactivity NotesNooruddin SheikNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry and EnergyDocument18 pagesNuclear Chemistry and EnergyJm EscobarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Nuclear Energy: What Is RadioactiveDocument2 pagesChapter 6 - Nuclear Energy: What Is RadioactiveRadhiah RashidNo ratings yet
- Basic Radiation PhysicsDocument31 pagesBasic Radiation PhysicseetuaNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity & Radionuclide ProductionDocument92 pagesRadioactivity & Radionuclide Productionvex2rex100% (2)
- Thesis RadioactivityDocument13 pagesThesis RadioactivitysaanvicodingNo ratings yet
- C A S - S - S C P R O "N C ": Submitted To:-Submitted By: - M S - A GDocument21 pagesC A S - S - S C P R O "N C ": Submitted To:-Submitted By: - M S - A GAyush GangwaniNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument2 pagesSummarySyaza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument20 pagesAtomic PhysicsjyothsnadevibandojuNo ratings yet
- CP6 Radiocativity NotesDocument9 pagesCP6 Radiocativity NotesshaikhmoazanNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 - Radioactivity, Beta, and Gamma RaysDocument18 pagesLab 12 - Radioactivity, Beta, and Gamma RayssaleemNo ratings yet
- Folio Fizik RadioactivityDocument16 pagesFolio Fizik RadioactivityMohammad AmirulNo ratings yet
- Everything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandEverything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
Chapter 6 Radioactive Substances
Chapter 6 Radioactive Substances
Uploaded by
Enniey RoxellOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6 Radioactive Substances
Chapter 6 Radioactive Substances
Uploaded by
Enniey RoxellCopyright:
Available Formats
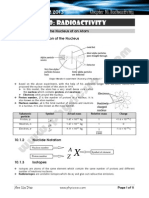
6.
1 Radioactive Substances
Bahan Radioaktif
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
ITeach Science Form 4
ITeach Science Form 4
The Human Nervous System
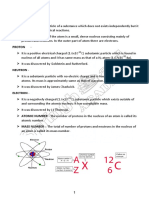
Unstable isotopes of radioactive element which will undergo radioactive
decay are called radioisotopes.
Radioactive Substances
Radioactive substance are material which contain radioisotope.
Example of Radioactive substance
Radioactive substance Isotopes Symbol
Carbon - 14 Carbon - 14
C
14
6
Iodine - 131 Iodine - 131
I
131
53
Cobalt - 60 Cobalt - 60
C
60
27
Uranium - 238 Uranium - 238
U
238
92
Uranium - 235 Uranium - 235
U
238
92
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Bahan Radioaktif
Radioisotop ialah isotop unsur radioaktif yang tidak stabil yang akan
mengalami pereputan.
Bahan Radioaktif
Bahan radioaktif adalah bahan yang mengandungi nukleus yang tidak
stabil.
Contoh bahan radioaktif
Bahan Radioaktif Isotop Simbol
Karbon - 14 Karbon - 14
C
14
6
Iodin - 131 Iodin - 131
I
131
53
Kobalt - 60 Kobalt - 60
C
60
27
Uranium - 238 Uranium - 238
U
238
92
Uranium - 235 Uranium - 235
U
238
92
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
ITeach Science Form 4
The Human Nervous System
Characteristics Of Radioactive Substance
Unstable nuclei tend to decay spontaneously to become more stable.
As they decay, they emit dangerous and invisible radioactive
radiations and lots of energy.
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
alpha,
gamma rays, g
beta,
Unstable radioactive
material
A
Z
X
A
Z
Y
Not influenced by any
physical factors
(temperature,
pressure, time)
Happen spontaneous
Emit at irregular
intervals and not at
the same rate
Random emission
Y can be same or different element of X
A > 209
Z > 83
More
stable
material
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Bahan Radioaktif
Ciri-ciri Bahan Rdioaktif
Nukleus tidak stabil yang akan mereput secara spontan untuk menjadi
lebih stabil.
Apabila bahan radioaktif mereput, ia akan membebaskan banyak tenaga
bersama dengan sinaran radioaktif yang merbahaya.
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
alfa,
Sinar gama, g
beta,
Bahan radioaktif yang
tidak stabil
A
Z
X
A
Z
Y
Tidak dipengaruhi
sebarang faktor fizikal
(suhu, tekanan,masa)
Berlaku secara spontan
Pemancaran zarah-
zarah berlaku pada
kadar yang berbeza.
Pemancaran secara rawak
Y boleh menjadi unsur yang sama atau berbeza
daripada X
A > 209
Z > 83 Bahan yang
lebih stabil
ITeach Science Form 4
The Human Nervous System
Radioactive decay is the process where unstable nucleus undergoes
spontaneous breaks down to become more stable nucleus by emitting
radioactive radiation and release lots of energy.
Radioactive decay happens randomly and spontaneously without being
influence by external factors such as pressure, temperature, chemical changes
or external forces.
Unstable
nucleus
of an
radioisotope
atom
Gamma radiation
Radioactive
decay
New nucleus that is
smaller and move stable
Radioactive Decay
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Bahan Radioaktif
Pereputan radioaktif ialah proses penguraian nukleus yang tidak stabil suatu
bahan radioaktif untuk membentuk nukleus yang lebih stabil melalui
pemancaran zarah-zarah daripada nukleus itu.
Pereputan radioaktif berlaku secara rawak dan spontan tanpa dipengaruhi
oleh faktor-faktor fizikal seperti tekanan, suhu, perubahan kimia atau daya.
Nukleus tidak
stabil bagi
suatu atom
radioisotop
Sinaran gamma
Pereputan
radioaktif
Nukleus baru yang lebih
stabil dan lebih kecil
Pereputan Radioaktif
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
ITeach Science Form 4
The Human Nervous System
Types Of Radioactive Radiation
Alpha()
radiation
Beta()
radiation
Gamma(g)
radiation
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
ITeach Sains Tingkatn 4
Bahan Radioaktif
Tiga Jenis Sinaran Radioaktif
Sinaran Alfa() Sinaran Beta() Sinaran Gama(g)
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
ITeach Science Form 4
The Human Nervous System
Characteristics
Type of radioactive radiation
Alpha() Radiation Beta() Radiation Gamma(g) Radiation
Made up of Helium nucleus Electron Electromagnetic wave
Mass Heaviest of the three Very light No mass
Electric change Positive Negative Neutral
Speed
Slowest compare to
and
Fast
Very fast (equal to
speed of light)
Ionising power High Weak Very weak
Penetrating
power
Lowest. Can be
blocked by a sheet of
paper.
Moderate. Can be
blocked by a thin
sheet of aluminium.
Highest. Can only be
blocked by a block of
lead or thick
concrete.
Effect of electric
field
Deflected to negative
plate of electrical field
Deflected to positive
plate of electrical field
Not deflected
Effect of
magnetic field
Deflected Deflected Not deflected
The Characteristics Of Radioactive Radiation
Can be produced by radioactive substance
Can be detected by Geiger-Muller counter
Similar characteristics of
the 3 radioactive radiation
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Bahan Radioaktif
Ciri-ciri
Jenis Sinaran Radioaktif
Sinar Alfa() Sinar Beta() Sinar Gama(g)
Jenis
Nukleus helium Elektron
Gelombang
elektromagnet
Jisim Paling berat Paling ringan Tiada jisim
Cas Positif Negatif Neutral
Kelajuan Paling perlahan
Laju
Sangat laju (halaju
sama seperti cahaya)
Kuasa pengionan Tinggi Sederhana Rendah
Kuasa
Penembusan
Rendah (boleh
dihalang dengan
sehelai kertas)
Sederhana (boleh
dihalang dengan
kepingan aluminium
setebal 5 mm)
Tinggi (boleh
dihalang dengan
plumbum setebal 25
mm)
Kesan medan
elektrik
Terpesong menjauhi
plat negatif
Terpesong menjauhi
plat positif
Tidak terpesong
Kesan medan
magnet
Terpesong Terpesong Tidak terpesong
Ciri-ciri Sinaran Radioaktif
Boleh dihasilkan oleh bahan radioaktif
Boleh dikesan dengan tiub Geiger-Muller
Ciri-ciri yang sama antara
ketiga-tiga sinaran
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
ITeach Science Form 4
The Human Nervous System
Penetrating Power Of Alpha, Beta and Gamma
2 4 5
Lead (10cm)
aluminium
(7mm)
Paper
beta
alpha
gamma
Source of
radioactive
radiation
Alpha particle () Beta particle () Gamma particle (g)
Alpha ()
Moves at slow speed
Beta ()
Move at higher speed
than alpha
Gamma (g)
Moves at very high
speed and frequency
Conclusion
Penetrating
power
Alpha () - lowest
Beta ()
Gamma (g) - Highest
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
Geiger-Muller
tube
Geiger-Muller
counter
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Bahan Radioaktif
Kuasa Penembusan Sinaran Alfa, Beta Dan Gamma
2 4 5
Plumbum (10cm)
aluminium
(7mm)
Kertas
beta
alfa
gamma
Sumber
sinaran
radioaktif
Zarah Alfa () Zarah Beta () Zarah Gama (g)
Alfa ()
Bergerak dengan
halaju perlahan
Beta ()
Bergerak dengan halaju
yang lebih daripada
sinar Alfa
Gama (g)
Bergerak dengan sangat
laju (sama dengan
halaju cahaya)
Kesimpulan
Kuasa
Penembusan
Alfa () Paling rendah
Beta ()
Gamma (g) Paling tinggi
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
Tiub Geiger-Muller
ITeach Science Form 4
The Human Nervous System
-
+
Beta radiation () (negative charge)
Alpha radiation () (positive charge)
Gamma radiation (g) (no charge)
Electrical field
Sources of
radioactive
radiation
Deflection Of Radioactive Radiation
In Electric Field
Aplha () particles are deflected toward negative plate of the electrical
field as they are positively changed.
Beta () particles are deflected toward positive plate of the electrical
field as they are negatively charged.
Gamma (g) radiations are electromagnetic waves which are neutral.
Thus, gamma radiations are not affected by electrical field.
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Bahan Radioaktif
-
+
Sinaran Beta () (cas negatif)
Sinaran Alfa () (cas positif)
Sinaran Gama (g) (Tiada cas)
Medan Elektrik
Sumber sinaran
radioaktif
Kesan Medan Elektrik
Sinar Alfa () bercas positif. Sinar ini akan dipesongkan menjauhi plat
positif medan elektrik.
Sinar Beta () bercas negatif. Sinar ini akan dipesongkan menjauhi plat
negatif medan elektrik.
Sinar Gama (g) adalah gelombang elektromagnet yang neutral. Oleh
itu, sinar ini tidak akan dipengaruhi oleh medan elektrik.
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
ITeach Science Form 4
The Human Nervous System
The Uses Of Radioactive
Substance In Industry
Radioactive
source
detector
Conveyor belt
Gamma rays
To detect the content level in container or
packages of food to ensure that the
container or package is full.
A
B
s
2
s
1
medicine
Sodium-24
Add to the fluid in pipe to detect leakages in
underground pipes.
detector
Geiger-Muller
counter
Leakage
Underground pipe
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
Continue
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Kegunaan Bahan Radioaktif
Kegunaan Bahan Radioaktif Dalam Industri
Sumber
radioaktif
pengesan
Tali pengangkut
Sinaran Gama
Untuk mengesan paras atau kandungan
bahan dalam sesuatu bekas atau peket
makanan bagi memastikan bekas atau
peket itu penuh dengan bahan.
A
B
s
2
s
1
Ubat
Natrium-24
Untuk mengesan kebocoran dalam paip
bawah tanah.
pengesan
Tiub Geiger-
Muller
Kebocoran
Paip bawah tanah
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
Bersambung
ITeach Science Form 4
The Human Nervous System
The Uses Of Radioactive
Substance In Agriculture
Phosphorus-32 and nitrogen-145
Add to fertilizer to track the absorption rate of fertilisers in plants.
Rate meter
G.tube
A leaf is tested for radioactive
everyday for a week by using
Geiger-Muller tube.
Water with solution
containe radioactive
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
Continue
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Kegunaan Bahan Radioaktif
Kegunaan Bahan Radioaktif Dalam
Pertanian
Fosforus-32 dan nitrogen-145
Dimasukkan ke dalam baja untuk mengkaji kadar penyerapan baja oleh akar
tumbuhan.
Meter
Tiub Geiger-Muller
Tumbuhan diuji dengan bahan
radioaktif dengan
menggunakan tiub Geiger-
Muller
Air dengan larutan yang
mengandungi bahan
radioaktif
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
Bersambung
ITeach Science Form 4
The Human Nervous System
The Uses Of Radioactive
Substance In Medical Treatment
Iodine-131
As tracers to check the uptake of iodine
131 by thyroid gland or detect blockage
in kidney of patient.
Cobalt-60
Use in radiotherapy to weaken or
destroy cancer cells.
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
Continue
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Kegunaan Bahan Radioaktif
Kegunaan Bahan Rdioaktif Dalam
Perubatan
Iodin-131
Untuk memeriksa pengambilan iodin
oleh kelenjar tiroid dan mengesan
ketulan darah dalam buah pinggang
pesakit.
Kobalt-60
Digunakan dalam radioterapi untuk
membunuh sel-sel kanser.
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
Bersambung
ITeach Science Form 4
The Human Nervous System
Gamma rays
To kill microorganisms such as bacteria
fungi in food which can cause food to
decay.
Gamma rays
To decay the ripening of stored fruits and
prevent shooting of potatoes while being
stored.
The Uses Of Radioactive
Substance In Food Preservation
Example : strawberries, cherries and
grapes.
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
ITeach Sains Tingkatn 4
Kegunaan Bahan Radioaktif
Sinaran Gama
Membunuh mikroorganisma seperti
bakteria, kulat dan serangga dalam
makanan. Proses ini dipanggil penyinaran
makanan
Sinaran Gama
Mereputkan buah yang telah masak dan
menghalang pucuk kentang daripada
bertumbuh semasa disimpan.
Kegunaan Bahan Rdioaktif Dalam Pengawetan
Makanan
Contoh : strawberi, ceri dan anggur.
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
ITeach Science Form 4
The Human Nervous System
Carbon-14
To estimate the age of ancient remain by carbon dating
The Uses Of Radioactive
Substance In Archaeology
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Kegunaan Bahan Radioaktif
Karbon-14
Menganggarkan usia bahan tinggalan purba dengan mengukur kuantiti karbon
yang masih tinggal dalam bahan itu.
Kegunaan Bahan Radioaktif Dalam Arkeologi
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
6.2 Production Of Nuclear Energy And Its Uses
Penghasilan Tenaga Nuklear Dan Kegunaannya
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
ITeach Science Form 4
ITeach Science Form 4
nuclear fission
The Production Of Nuclear Energy
Production Of Nuclear Energy And It Uses
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
nuclear fusion
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Pembelahan Nukleus
Penghasilan Tenaga Nuklear
Penghasilan Tenaga Nuklear Dan Kegunaannya
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
Pelakuran Nukleus
ITeach Science Form 4
Nuclear fission happens when an unstable nucleus is being bombarded by a high-
speed neutrons.
Example Uranium-235
Nuclear Fission
Production Of Nuclear Energy And It Uses
Explanation
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
Causing it to split into two more stable nuclei and produce more neutrons and
energy.
barium nucleus
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Pembelahan nukleus berlaku apabila nukleus yang tidak stabil dihentam oleh
neuton yang berkelajuan tinggi.
Contoh Uranium-235
Pembelahan Nukleus
Penghasilan Tenaga Nuklear Dan Kegunaannya
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
Ini menyebabkan nukleus itu terpecah menjadi dua nukleus unsur lain yang lebih
stabil. Banyak tenaga dihasilkan dan tiga neutron berhalaju tinggi dihasilkan.
Nukleus Barium
Nukleus uranium
Nukleus kripton
Sinar radioaktif dan
tenaga nuklear
Sinar radioaktif dan
tenaga nuklear
Penerangan
Nuclear fusion produces more nuclear energy compared to nuclear fission,
however the rate of nuclear fusion process still cannot be controlled.
Chain reaction of nuclear fission is controlled by graphite and boron in nuclear
station. The enormous amount of nuclear energy produced is converted into more
useful energy such as generating electricity.
ITeach Science Form 4
Nuclear fusion happens when two light nuclei fuse (combine) to form a heavier nucleus
while releasing nuclear energy.
Example : isotopes hydrogen-2 and hydrogen-3 fuse together to form helium
nucleus.
Nuclear Fusion
+
n
n
n
+
+ n
n n +
n
n
n
+
+
Large amount of
Energy released
Helium nucleus
is formed
Combine
Hydrogen-2
Hydrogen-3
Neutron
Production Of Nuclear Energy And It Uses
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
A very high temperature and pressure are required for nuclear fusion to occur.
Pelakuran nukleus menghasilkan lebih banyak tenaga berbanding pembelahan
nukleus, tetapi kadar proses pelakuran nukleus tidak boleh dikawal.
Tindak balas rantai bagi pelakuran nukleus dikawal oleh karbon dan boron dalam
stesen nukleur. Penghasilan tenaga nuklear yang banyak ditukar kepada tenaga
lain seperti tenaga elektrik.
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Pelakuran nukleus ialah proses penyatuan atau penggabungan dua nukleus yang
ringan untuk membentuk nukleus yang lebih berat dan lebih stabil dengan
membebaskan tenaga.
Contoh : Isotop hidrogen-2 and hidrogen-3 bercantum untuk membentuk nukleus
helium.
Pelakuran Nukleus
+
n
n
n
+
+ n
n n +
n
n
n
+
+
Membebaskan banyak
tenaga
Nukleus helium
terbentuk
Bergabung
Hidrogen-2
Hidrogen-3
Neutron
Penghasilan Tenaga Nuklear Dan Kegunaannya
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
Pelakuran nukleus memerlukan suhu dan tekanan yang tinggi untuk berlaku.
Nuclear fission in
the reactor
produces
enormous energy
Heats up water in
the pressurised
reactor
Steam
Electricity
Rotates the
dynamo in the
generator
Rotates the
turbines
Consumer
heat
energy
produce
send
to generate
To power vessel such as
battleship and submarines.
To operate satellites
To generate electricity
Nuclear energy is an alternative source of energy which can replace the
depleting fossil fuels such as petroleum, natural gas and coal.
ITeach Science Form 4
Production Of Nuclear Energy And It Uses
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
The Uses Of Nuclear Energy
Uses Of Nuclear Energy
However, Uranium-235 is non-renewable resource too.
Pembelahan nukleus
menghasilkan tenaga
yang banyak
Haba mendidihkan
air di dalam
janakuasa stim
Stim
Elektrik
Memutarkan
dinamo dalam
janakuasa elektrik
Memutarkan
turbin
Pengguna
haba
tenaga
hasilkan
dihantar
ke hasilkan
Membekalkan tenaga kepada
kapal.
Membekalkan tenaga kepada
satelit
Penjanaan elektrik
Tenaga nuklear ialah tenaga alternatif yang dapat menggantikan bahan api fosil
seperti petroleum, gas semulajadi dan arang batu.
Tetapi, Uranium-235 adalah sumber yang tidak boleh diperbaharui.
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Penghasilan Tenaga Nuklear Dan Kegunaannya
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
Kegunaan Tenaga Nuklear
Kegunaan Tenaga Nuklear
Uranium rods are the radioactive substances to produce nuclear energy
from nuclear fission chain reactions.
Graphite rods are used to control the rate of the chain reactions.
Heat produced by nuclear fission heats up the water. The hot water flows to
the steam generator to produce steam at high temperature and pressure.
This steam rotates the turbine which then rotates the dynamo in the
generator to produce electricity.
Thick concrete wall is used to protect the environment from being exposed
to radioactive radiations.
ITeach Science Form 4
Production Of Nuclear Energy And It Uses
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
The Process Of Generating Electricity From Nuclear Energy
water out
water in
generator
paip
paip
Containment
structure
uranium
rods
reactor
Turbine
steam
generator
Water
Water under
high
pressure
Steam
Rod uranium ialah bahan radioaktif yang digunakan untuk menghasilkan
tenaga nuklear daripada tindak balas pembelahan nukleus.
Rod karbon digunakan untuk mengawal kadar tindak balas.
Haba yang terhasil daripada pembelahan nukleus mendidihkan air. Air
panas mengalir ke janakuasa stim untuk menghasilkan stim pada suhu dan
tekanan yang tinggi.
Stim memutarkan turbin yang mana akan memutarkan dinamo pada
janakuasa untuk menghasilkan elektrik.
Dinding konkrit yang tebal digunakan untuk melindungi persekitaran
daripada terdedah kepada sinaran radioaktif.
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Penghasilan Tenaga Nuklear Dan Kegunaannya
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
Proses Penjanaan Elektrik Daripada Tenaga Nuklear
Air keluar
Air masuk
Janakuasa
paip
paip
Rod kawalan
Rod uranium
reaktor
Turbin
Janakuasa
stim
Air
Air pada
suhu tinggi
Stim
ITeach Science Form 4
Production Of Nuclear Energy And It Uses
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
Advantage of using nuclear energy
Disadvantage of using nuclear
energy
No air pollution because no
poisonous or toxic gases is
released
Low cost of generating electricity
because small amount of
radioactive substance is only
required to generate a large
amount of energy.
High cost of building nuclear
reactors.
High cost of maintaining nuclear
reactor.
Have to deal with radioactive
substances and wastes carefully
as it emits dangerous radiations
that cause damage to living
organisms and environment.
The Effect Of Nuclear
Energy Production
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Penghasilan Tenaga Nuklear Dan Kegunaannya
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
Kebaikan Menggunakan Tenaga
Nuklear
Keburukan Menggunakan Tenaga
Nuklear
Tiada pencemaran udara kerana
tiada pembebasan gas beracun
atau gas toksik.
Kos yang rendah untuk menjana
elektrik kerana hanya sedikit
bahan radioaktif yang diperlukan
untuk menjana tenaga elektrik
yang banyak.
Kos tinggi untuk membina stesen
janakuasa nuklear.
Kos yang tinggi untuk
menyelenggara stesen
janakuasa nuklear.
Perlu menggendalikan bahan
radioaktif dan sisa bahan
radioaktif dengan cermat dan
betul kerana bahan radioaktif
membebaskan sinaran yang
merbahaya yang boleh
mengancam kehidupan manusia
dan alam sekitar.
Kesan Penghasilan
Tenaga Nuklear
6.3 The Need For Proper Handling Of Radioactive
Substance
Pengendalian Bahan Radioaktif Dengan Cara Yang
Betul
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
ITeach Science Form 4
ITeach Science Form 4
The Need For Proper Handling Of Radioactive Substance
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
The Effect Of Radioactive Radiations Living Things
Exposure Effects and symptoms
Short term
(small doses)
Radiation sickness such as
Nausea
Loss of appetite
Vomiting
Short term
(large doses)
Radiation sickness such as
Internal bleeding
Infertility
Premature aging
Skin and lung disease
Long term
Cause mutation and kill body cell which lead to
Leukaemia
Giving birth to deformed babies
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Pengendalian Bahan Radioaktif Dengan Cara Yang Betul
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
Kesan Sinaran Radioaktif Kepada Benda Hidup
Pendedahan Kesan Dan Gejala
Jangka masa
pendek
(Dos rendah)
Gejala penyakit seperti:
Loya
Hilang selera makan
Muntah
Jangka masa
pendek
(Dos tinggi)
Gejala penyakit seperti:
Pendarahan dalaman
Mandul
Sakit kulit dan paru-paru
Jangka masa
panjang
Menyebabkan mutasi dan memusnahkan sel-sel badan
yang mengakibatkan:
Leukaemia
Melahirkan bayi cacat
ITeach Science Form 4
The Need For Proper Handling Of Radioactive Substance
Topic 6 Nuclear Energy
Correct Way Of Handling Radioactive Substances And
Radioactive Waste
A. Work in designated areas, behind
protective shield such as a
concrete wall
B. Wear proper protective attire
C. Use robotic hand in airtight
chambers to handle radioactive
materials
D. Use tongs or forceps to move
radioactive materials
Radioactive
material
Wear lead
cloth
Radioactive
material
Lead glass
Radioactive
material
Continue
Lead glass
ITeach Sains Tingkatan 4
Pengendalian Bahan Radioaktif Dengan Cara Yang Betul
Topik 6 Tenaga Nuklear
Cara Yang Betul Mengendalikan Bahan Radioaktif Dan Sisa
Bahan Radioaktif
A. Plumbum tebal perlu diletakkan di
antara sumber bahan radioaktif
dengan pekerja
B. Memakai pakaian perlindungan
khas dan lencana filem.
C. Menggunakan tangan robot di
tempat kedap udara ketika
mengendalikan bahan radioaktif
berbahaya
D. Menggunakan penyepit ketika
mengendalikan bahan radioaktif
lemah
Bahan
radioaktif
Pakai pakaian diperbuat
daripada plumbum
Bahan
radioaktif
Dinding
plumbum
Bahan
radioaktif
Bersambung
Dinding plumbum
The End
i - Teach
You might also like
- Folio Radioactivity Ting 5Document16 pagesFolio Radioactivity Ting 5akunaruto92100% (3)
- Radiopharmaceutics Presentation1Document52 pagesRadiopharmaceutics Presentation1alibinaminNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy Form 4Document14 pagesNuclear Energy Form 4Akmar MataliNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Inanam: PhysicsDocument46 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Inanam: PhysicsMuhammad Safril Abdul HalimNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Nucleus of An AtomDocument25 pagesUnderstanding The Nucleus of An Atomnfaizah1100% (2)
- 7 1 NotesDocument17 pages7 1 Notesapi-182809945No ratings yet
- Radioanalytical Techniques: Ali Abbas M.Phil Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument54 pagesRadioanalytical Techniques: Ali Abbas M.Phil Pharmaceutical ChemistryAdia MasooraNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy.: 6.1 Radioactive SubstancesDocument7 pagesNuclear Energy.: 6.1 Radioactive SubstancesElly EllynaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Tech English - PDFDocument20 pagesNuclear Tech English - PDFShivang BhardwajNo ratings yet
- IGCSE UNIT - 5 ATOMIC PHYSICS NotesDocument12 pagesIGCSE UNIT - 5 ATOMIC PHYSICS Notesvishrudh lakshminarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Nuclear Energy: 6.1 Radioactive SubstancesDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Nuclear Energy: 6.1 Radioactive SubstancesNg Lay HoonNo ratings yet
- Physics: The Study of MatterDocument15 pagesPhysics: The Study of MatterTaha RashidNo ratings yet
- Measurement of RadioactivesDocument20 pagesMeasurement of RadioactivesAnonymous Nl973ID1d8No ratings yet
- Radio PharmaceuticsDocument52 pagesRadio PharmaceuticsDrGaurav TiwariNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: Name: Aiman Zikri B. Zullkeppli Amin Class: 5sta IC NO: 960304-08-6543Document6 pagesNuclear Energy: Name: Aiman Zikri B. Zullkeppli Amin Class: 5sta IC NO: 960304-08-6543Faiz HapoNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity ExplainedDocument1 pageRadioactivity ExplainedqwertyNo ratings yet
- Class - Nine: Physics: Radioactivity Handout-2 Ionizing ChamberDocument5 pagesClass - Nine: Physics: Radioactivity Handout-2 Ionizing ChamberBEASTBOY GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Radiation 22Document56 pagesRadiation 22amad4445555No ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument7 pagesRadioactivitySalmanNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity 5 LessonsDocument6 pagesRadioactivity 5 LessonsHLSSummerInstituteNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Atomic Physics Notes PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 5 Atomic Physics Notes PDFpreeti.2405100% (2)
- Nuclear Physics - 2Document121 pagesNuclear Physics - 2Rose MusariraNo ratings yet
- Properties of Radioactive RadiationsDocument37 pagesProperties of Radioactive RadiationsWaqar BashirNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument41 pagesAtomic PhysicsFaiq IrfanNo ratings yet
- Phy ChemDocument248 pagesPhy ChemBitter SugarNo ratings yet
- RADIOGRAPHY STUDY MATERIAL LatestDocument52 pagesRADIOGRAPHY STUDY MATERIAL LatestManish SinghNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy 1 2003Document19 pagesNuclear Energy 1 2003Aisyah Dan AnuaruddinNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument22 pagesRadioactivitymerezemenike272No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - RadioactivityDocument28 pagesChapter 12 - RadioactivityAljoša GraovacNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Introduction To Nuclear RadioactivityDocument45 pages7.1 Introduction To Nuclear RadioactivityReyzhel Mae MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 - Nuclear Chemistry - Notes - KEYDocument2 pagesUnit 13 - Nuclear Chemistry - Notes - KEYSumathi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity or Radioactive Decay:: Topic 5 - Atomic PhysicsDocument5 pagesRadioactivity or Radioactive Decay:: Topic 5 - Atomic PhysicsAbdullah MACNo ratings yet
- Analysing Radioactive Decay: Lesson 2Document16 pagesAnalysing Radioactive Decay: Lesson 2TS ShongNo ratings yet
- The ABC's of RadioactivityDocument17 pagesThe ABC's of RadioactivityAnggita DwiNo ratings yet
- Physics Final Revision - Radioactivity 2013 PDFDocument11 pagesPhysics Final Revision - Radioactivity 2013 PDFCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Stanes SchoolDocument19 pagesStanes SchoolShibiNo ratings yet
- Natural Radioactivity and StatisticsDocument9 pagesNatural Radioactivity and StatisticsgiornoxxNo ratings yet
- Geiger Muller CounterDocument27 pagesGeiger Muller CounterUsmanMustafa88% (16)
- Radioactive Physics - Research PaperDocument18 pagesRadioactive Physics - Research PaperJovicaSutevNo ratings yet
- Inverse Square LawDocument70 pagesInverse Square LawEngr Rab Nawaz ButtNo ratings yet
- Rad Prod Lesson 2Document6 pagesRad Prod Lesson 2LARA ADAYNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Nuclear PhysicsDocument8 pagesUnit 6 Nuclear PhysicsJonathan LeeNo ratings yet
- Physics (Radioactivity)Document21 pagesPhysics (Radioactivity)Hery HadzrenNo ratings yet
- Detection & Measurement of RadioactivityDocument7 pagesDetection & Measurement of RadioactivityChetan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity NotesDocument16 pagesRadioactivity NotesNooruddin SheikNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry and EnergyDocument18 pagesNuclear Chemistry and EnergyJm EscobarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Nuclear Energy: What Is RadioactiveDocument2 pagesChapter 6 - Nuclear Energy: What Is RadioactiveRadhiah RashidNo ratings yet
- Basic Radiation PhysicsDocument31 pagesBasic Radiation PhysicseetuaNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity & Radionuclide ProductionDocument92 pagesRadioactivity & Radionuclide Productionvex2rex100% (2)
- Thesis RadioactivityDocument13 pagesThesis RadioactivitysaanvicodingNo ratings yet
- C A S - S - S C P R O "N C ": Submitted To:-Submitted By: - M S - A GDocument21 pagesC A S - S - S C P R O "N C ": Submitted To:-Submitted By: - M S - A GAyush GangwaniNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument2 pagesSummarySyaza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument20 pagesAtomic PhysicsjyothsnadevibandojuNo ratings yet
- CP6 Radiocativity NotesDocument9 pagesCP6 Radiocativity NotesshaikhmoazanNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 - Radioactivity, Beta, and Gamma RaysDocument18 pagesLab 12 - Radioactivity, Beta, and Gamma RayssaleemNo ratings yet
- Folio Fizik RadioactivityDocument16 pagesFolio Fizik RadioactivityMohammad AmirulNo ratings yet
- Everything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandEverything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet