Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hooke's Law: The Following Topics Will Be Discussed in This Presentation
Hooke's Law: The Following Topics Will Be Discussed in This Presentation
Uploaded by
Saurabh Jain0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesThis document discusses Hooke's law and the elastic and plastic behavior of materials when subjected to forces. It explains that Hooke's law states that the extension of a material is directly proportional to the tensile force applied within the material's elastic limit. It then describes an experiment where a spring is extended by increasing forces and the extensions are plotted on a force vs. extension graph. The graph shows a straight line relationship at low forces, indicating elastic behavior, but bends at higher forces as the extension no longer increases proportionally, showing the start of plastic behavior.
Original Description:
http://mechanical-engineering.in/forum/files/
Original Title
Hookes Law
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses Hooke's law and the elastic and plastic behavior of materials when subjected to forces. It explains that Hooke's law states that the extension of a material is directly proportional to the tensile force applied within the material's elastic limit. It then describes an experiment where a spring is extended by increasing forces and the extensions are plotted on a force vs. extension graph. The graph shows a straight line relationship at low forces, indicating elastic behavior, but bends at higher forces as the extension no longer increases proportionally, showing the start of plastic behavior.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesHooke's Law: The Following Topics Will Be Discussed in This Presentation
Hooke's Law: The Following Topics Will Be Discussed in This Presentation
Uploaded by
Saurabh JainThis document discusses Hooke's law and the elastic and plastic behavior of materials when subjected to forces. It explains that Hooke's law states that the extension of a material is directly proportional to the tensile force applied within the material's elastic limit. It then describes an experiment where a spring is extended by increasing forces and the extensions are plotted on a force vs. extension graph. The graph shows a straight line relationship at low forces, indicating elastic behavior, but bends at higher forces as the extension no longer increases proportionally, showing the start of plastic behavior.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
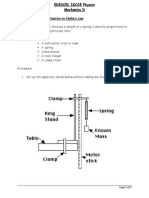
Hookes Law
The following topics will be discussed in this presentation:
1. Hookes law
2. Elastic behaviour of materials by stretching a spring and
producing a graph of force versus extension
3. Plastic behaviour of materials
Hookes Law
a
b
c
d
e
f
Hookes law: Extension produced in
a material is proportional to the
tensile force, within the elastic limit.
In this test a spring is extended by an
applied force. The extension
produced is recorded and plotted
against force.
At the start of the test the extension
is zero as no force is applied to the
spring.
Extension
F
o
r
c
e
Hookes Law
1
a
b
c
d
e
f
a
2
b
The spring is extended by an applied force. Force 1 produces an extension
which is plotted on Force versus Extension graph i.e. point a.
Extension
F
o
r
c
e
Extension
F
o
r
c
e
b
a
As the applied force is increased to Force 2, the extension increases too.
This is shown by point b on the graph.
Hookes Law
3
a
b
c
d
e
f
a
4
d
As the force is increased, the extension of the spring increases to mark c.
Extension
F
o
r
c
e
Extension
F
o
r
c
e
b
a
b
c
c
d
On further increasing the force, the spring extends to mark d. The graph
is a straight line showing elastic behaviour of spring.
Hookes Law
a
b
c
d
e
f
a
4
e
Extension
F
o
r
c
e
Extension
F
o
r
c
e
b
a
b
c
c
d
d
If the force is removed at any
point up to the elastic limit,
the spring reverts back to its
original shape and size
5
e
f
A further increase in force will cause a
larger extension of the spring and its
extension is no longer proportional to the
force, hence the shape of the graph
changes.
Hookes Law
e
Extension
F
o
r
c
e
b
a
c
d
5
e
f
If the force is removed now the
spring does not revert back to its
original shape and size. This
change is called the permanent
set.
Permanent set
You might also like
- Physics Report HOOKE'S LAWDocument6 pagesPhysics Report HOOKE'S LAWHulwan Mukhlis82% (44)
- Hooke's Law Lab Report 1 SunealDocument5 pagesHooke's Law Lab Report 1 SunealMonari Perera67% (3)
- Mechanical Aptitude & Spatial Relations Practice QuestionsFrom EverandMechanical Aptitude & Spatial Relations Practice QuestionsNo ratings yet
- hookes_lawDocument6 pageshookes_lawMainakh DasNo ratings yet
- Ideal Spring Lab ActivityDocument4 pagesIdeal Spring Lab ActivitySCIENCE Benjie AvecillaNo ratings yet
- 2.7 Hooke's LawDocument11 pages2.7 Hooke's Laweugenewaweru5527No ratings yet
- Hookes Law DemonstrationDocument7 pagesHookes Law DemonstrationKasunDilshanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 (Stretching and Compressing)Document3 pagesAssignment 4 (Stretching and Compressing)Priyanka DubeyNo ratings yet
- As Level Chapter 6 NotesDocument30 pagesAs Level Chapter 6 NotesVivehaNo ratings yet
- Deformation Grade 9 and 10Document19 pagesDeformation Grade 9 and 10Shams ZubairNo ratings yet
- Peka 2+ Hooke's LawDocument2 pagesPeka 2+ Hooke's Lawnik mohamad solehinNo ratings yet
- Lab 13Document3 pagesLab 135377773No ratings yet
- Physics Form 4Document20 pagesPhysics Form 4faizi_ammarNo ratings yet
- DEFORMATIONDocument5 pagesDEFORMATIONpalmerdalton014No ratings yet
- Verification of Hookes LawDocument3 pagesVerification of Hookes Lawtessa mariaNo ratings yet
- Sunshine SSM Senior Secondary SchoolDocument11 pagesSunshine SSM Senior Secondary Schoolmohammed ashfaqueNo ratings yet
- 3.06 Stretching ForcesDocument22 pages3.06 Stretching ForcesMohab MqattashNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law and ForcesDocument15 pagesHooke's Law and ForcesMHNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics Projectmohammed ashfaqueNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Forces and Matter NotesDocument8 pagesChap 5 Forces and Matter NotesMoomal AnsariNo ratings yet
- 2.12 Understanding ElasticityDocument10 pages2.12 Understanding ElasticityBid HassanNo ratings yet
- Hooke's LawDocument19 pagesHooke's Lawraj33singh75No ratings yet
- LEP1301 - 01 Hooke's LawDocument5 pagesLEP1301 - 01 Hooke's LawDanilo SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Elastic DeformationDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Elastic DeformationEshaal Maryam0% (1)
- Elastic DeformationDocument9 pagesElastic DeformationAbdi Bora YüzbaşıNo ratings yet
- Hookes Law LabDocument5 pagesHookes Law LabVenroy ReidNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law Experimental Design and AnalysisDocument9 pagesHooke's Law Experimental Design and Analysisapi-486301766No ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Faculty of Applied Sciences Department of Physical Sciences Py142: Engineering Physics - IDocument19 pagesExperiment 2: Faculty of Applied Sciences Department of Physical Sciences Py142: Engineering Physics - IDev HalvawalaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Faculty of Applied Sciences Department of Physical Sciences Py142: Engineering Physics - IDocument19 pagesExperiment 2: Faculty of Applied Sciences Department of Physical Sciences Py142: Engineering Physics - IDev HalvawalaNo ratings yet
- Hooke’s Law and Deformation (Mar 11, 2021)Document30 pagesHooke’s Law and Deformation (Mar 11, 2021)candace.gentlesNo ratings yet
- Eksperimen Hooke's LawDocument28 pagesEksperimen Hooke's LawMJ ChowNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law, Adding Forces and Resolving Forces - 2440060742 - Jeffrey LiandiDocument14 pagesHooke's Law, Adding Forces and Resolving Forces - 2440060742 - Jeffrey LiandiJeffrey LiandiNo ratings yet
- Hooke Law LabDocument2 pagesHooke Law LabYusranNo ratings yet
- 2.12 Und Erstandin G Elastici TyDocument31 pages2.12 Und Erstandin G Elastici TyNor Hasniyyah Ab HalimNo ratings yet
- Physics IGCSE Summary PDFDocument43 pagesPhysics IGCSE Summary PDFAdeRayenNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Deformation NotesDocument3 pagesTopic 3 Deformation NotesgoldphishNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3EminaTopalovićNo ratings yet
- Report 5Document6 pagesReport 5Paul Adrian JavénNo ratings yet
- Hooke's LawDocument4 pagesHooke's LawKurarisuNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE Forces Hookes Law OnlyDocument22 pagesCIE IGCSE Forces Hookes Law Onlyh aNo ratings yet
- Forces - Hookes Law: Cie Igcse PhysicsDocument22 pagesForces - Hookes Law: Cie Igcse Physicsmechanical_lecturerNo ratings yet
- Form 2 17 Hookes LawDocument16 pagesForm 2 17 Hookes LawMAGDALENE MWANGANGINo ratings yet
- Forces - Hookes Law: Cie Igcse PhysicsDocument20 pagesForces - Hookes Law: Cie Igcse PhysicsViola AditaNo ratings yet
- Weight and StretchingDocument4 pagesWeight and Stretchingnyabuti300No ratings yet
- Mec IDocument15 pagesMec Iali ahmedNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 11 ProDocument20 pagesPhysics Grade 11 ProSupritha SrNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Class 11 (Final)Document12 pagesPhysics Project Class 11 (Final)chemistry project90% (10)
- Paper Hukum HookeDocument7 pagesPaper Hukum HookeFakhrurrozi AmranNo ratings yet
- XI Physics Project Hookes LawDocument9 pagesXI Physics Project Hookes LawharshdeeppardheNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law ExperimentDocument4 pagesHooke's Law ExperimentMarini Tampubolon100% (1)
- HPhys Unit 04 UBFPM Packet 2012Document16 pagesHPhys Unit 04 UBFPM Packet 2012Kelly O'SheaNo ratings yet
- Physics Mefie New New PrintoutDocument15 pagesPhysics Mefie New New Printoutarleen.mefie.mjNo ratings yet
- Spring 1Document4 pagesSpring 1fazal_nctNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Presentation: Environmental/Safety Impacts of Selected IndustriesDocument24 pagesPhysics Lab Presentation: Environmental/Safety Impacts of Selected Industrieshanif274No ratings yet
- Cape Physics Unit 1st EditionDocument70 pagesCape Physics Unit 1st EditionJunior Dollas100% (10)
- Assessed Coursework Cover Sheet InstructionsDocument7 pagesAssessed Coursework Cover Sheet InstructionsNiyant SapaNo ratings yet
- For PhysicsDocument12 pagesFor Physicsd7171707No ratings yet