Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Draw The Structure of The Following Compounds:: 2) 2-Methylpentane Not 4-Methylpentane
Draw The Structure of The Following Compounds:: 2) 2-Methylpentane Not 4-Methylpentane
Uploaded by
anjilinbraganza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesThis document provides instructions for naming alkanes and alkenes according to IUPAC nomenclature rules. For alkanes, the parent chain is the longest continuous carbon chain, and substituents are designated by name and location. For alkenes, the parent chain contains the double bond, the suffix is changed to -ene, and the double bond location is indicated. Examples are given to demonstrate the nomenclature systems.
Original Description:
Organic Chemistry
Original Title
1-3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides instructions for naming alkanes and alkenes according to IUPAC nomenclature rules. For alkanes, the parent chain is the longest continuous carbon chain, and substituents are designated by name and location. For alkenes, the parent chain contains the double bond, the suffix is changed to -ene, and the double bond location is indicated. Examples are given to demonstrate the nomenclature systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesDraw The Structure of The Following Compounds:: 2) 2-Methylpentane Not 4-Methylpentane
Draw The Structure of The Following Compounds:: 2) 2-Methylpentane Not 4-Methylpentane
Uploaded by
anjilinbraganzaThis document provides instructions for naming alkanes and alkenes according to IUPAC nomenclature rules. For alkanes, the parent chain is the longest continuous carbon chain, and substituents are designated by name and location. For alkenes, the parent chain contains the double bond, the suffix is changed to -ene, and the double bond location is indicated. Examples are given to demonstrate the nomenclature systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
1
2) 2-METHYLPENTANE NOT 4-METHYLPENTANE
3) 3,5-DIMETHYLPENTANE NOT 4,6-DIMETHYLOCTANE
4) 2,2,4,5-TETRAMETHYLHEXANE NOT 2,3,5,5-TETRAMETHYLHEXANE
5) 4-ETHYL-4-METHYLOCTANE NOT 5-METHYL-5-METHYLOCTANE
6) 3-ETHYL-4-ISOPROPYL-5,7,9-TRIMETHYLDECANE
Draw the Structure of the following compounds:
A. 4-ETHYL-2-METHYLHEXANE
a) PARENT: HEXANE
2
B. 2,2-DIMETHYLPENTANE
A) 2,5-DIMETHYL-3-ETHYLOCTANE
NOMENCLATURE (SYSTEM for NAMING) FOR
ALKANES
- For those alkanes w/c have branching determine the longest continuous chain of C atoms
and the longest C chain.
EX:
The compound shown has a longest continuous chain of 7 C atoms and therefore, its parent
name is heptane.
In order to designate the position of the substituent (CH3), the longest chain is
numbered as shown. The substituent is called methyl. The name being derived from the methane
for the alkane CH4, where the ane ending is changed to yl. The name of the compound is 2-
METHYLHEPTANE, the no. 2 designating the C atom on w/c the methyl group is attached. Always
number the longest chain of C atoms in such a way that the substituents have the smallest
numbers. The compound shown was numbered to give the methyl group position the smallest
number. If the numbering has been right to left, the name would be 6- METHYLHEPTANE and is
incorrect because the position of attachment for the methyl group is not the lowest no. possible.
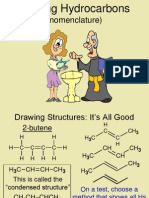
ALKENES/ OLEFINS: CnH2n
- w/ double bonds
C. Common System: named as derivatives of ethylene
3
Examples Common Name
1) CH2=CH2 ETHYLENE
2)
3) ETHYLETHYLENE
4) CH3CH=CHCH3 SYM-DIMETHYLETHYLENE
5) UNSYM-DIMETHYLETHYLENE
6) CH3CH2CH=CH2CH3 SYM-ETHYLMETHYLETHYLENE
alphabetical
7) UNSYM-ETHYLMETHYLETHYLENE
SYM- both are bonded to each C of same hybridization.
UNSYM- different hybridization.
D. IUPAC
- select the longest HC chain containing the = bond
- name as an alkane
- change ane to ene
- indicate position of double bond (=)
You might also like
- Basic Organic Nomenclature Packet Chemistry Level II: Name: - PeriodDocument12 pagesBasic Organic Nomenclature Packet Chemistry Level II: Name: - PeriodNyein Nu WinnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument142 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryHafiz Hamidi100% (1)
- The Language of Organic Chemistry: Answers To Worked ExamplesDocument22 pagesThe Language of Organic Chemistry: Answers To Worked ExamplesDana Capbun100% (1)
- Stereo ChemistryDocument27 pagesStereo ChemistryAtul KambleNo ratings yet
- Organic Nomenclature - The Basics: CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CHDocument4 pagesOrganic Nomenclature - The Basics: CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CHRobert Wayne JrNo ratings yet
- Aliphatic HyrocarbonsDocument30 pagesAliphatic HyrocarbonsNaemar Jr,No ratings yet
- Alkyl GroupsDocument10 pagesAlkyl GroupsMyrrh Oliver CasinabeNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 HydrocarbonDocument41 pagesUnit 2 Hydrocarbonzila maskamNo ratings yet
- Lecture Alkane - Part 1 SKMRDocument27 pagesLecture Alkane - Part 1 SKMRehva lyfeNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and Alkynes - Y11Document9 pagesAlkenes and Alkynes - Y11Iftitahur Rohmah -No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 AlkanesDocument50 pagesChapter 2 AlkanesAndreea ElenaNo ratings yet
- Iupac Nomenclature OrganicDocument14 pagesIupac Nomenclature Organicaj619624No ratings yet
- Naming Organic CompoundsDocument15 pagesNaming Organic CompoundsEdward Estrella GuceNo ratings yet
- Chem12 Answer Key 1.1Document6 pagesChem12 Answer Key 1.1SophiaNo ratings yet
- IIMYP HydrocarbonsDocument14 pagesIIMYP HydrocarbonsVaida MatulevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- Naming Organic CompoundsDocument28 pagesNaming Organic Compoundspjblessreyes5No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Module (Part 1)Document6 pagesOrganic Chemistry Module (Part 1)Rita ZhouNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument16 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compoundspromit guha0% (1)
- Chm457: Fundamental of Organic Chemistry: Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument97 pagesChm457: Fundamental of Organic Chemistry: Alkanes and CycloalkanesAIMAN IMAN SHAIFUDDINNo ratings yet
- Chem1 Lec10 HydrocarbonsDocument73 pagesChem1 Lec10 HydrocarbonsSkud GuillermoNo ratings yet
- ALKENESDocument54 pagesALKENESdarleen joy dimaanoNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesDocument13 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic ChemistryYashwanth SrinivasaNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature: IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic ChemistryDocument46 pagesNomenclature: IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistrynhur22No ratings yet
- Module 4 OrgchemDocument7 pagesModule 4 OrgchemJHUNNTY LOZANONo ratings yet
- Naming Branched AlkanesDocument2 pagesNaming Branched Alkanesmischafrljak2005No ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proofs: Tetrahedron LettersDocument17 pagesJournal Pre-Proofs: Tetrahedron LettersGiovanni R. PereiraNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry - WikipediaDocument26 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry - WikipediaYa seen khanNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document9 pagesDocument 1Nishi tomarNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 AlkenesDocument17 pagesTopic 8 Alkenesmark regino TuyayNo ratings yet
- Alkenes: Organic ChemistryDocument21 pagesAlkenes: Organic ChemistryMelissa Marie CustodioNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Rules For NomenclatureDocument7 pagesIUPAC Rules For NomenclatureGroupB4No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry AlkanesDocument81 pagesOrganic Chemistry AlkanesrichienickyNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry - WikipediaDocument63 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry - WikipediaAnonymous BB82lXF0m2No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes AlkynesDocument5 pagesLecture Notes AlkynesBrian SamendeNo ratings yet
- Drill 1 WorksheetDocument15 pagesDrill 1 WorksheetKEZIAH DAWN DABATIANNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry BasicDocument104 pagesOrganic Chemistry Basicanikesh JainNo ratings yet
- AlkanesDocument19 pagesAlkanesRob McKenzieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 AlkanesDocument61 pagesChapter 2 AlkanesKonoli NuingNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument17 pagesNomenclature of Organic Compoundsubonge822No ratings yet
- Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument5 pagesAlkanes and CycloalkanesAlineNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature 1Document35 pagesNomenclature 1Anchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesDocument17 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesSUBHENDU5174124No ratings yet
- Perform The Molecular, Structural, and Condensed Formula: of PentaneDocument16 pagesPerform The Molecular, Structural, and Condensed Formula: of PentaneJerard BalalaNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Naming ExampleDocument2 pagesIUPAC Naming ExampleShimanta EasinNo ratings yet
- 2023 Chemistry CPTDocument9 pages2023 Chemistry CPTAllister LoboNo ratings yet
- CHE 112 - Lecture 2Document103 pagesCHE 112 - Lecture 2Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- OC01 - AlkanesDocument6 pagesOC01 - AlkanesAlizay ImranNo ratings yet
- SCH 106 Lecture V, 2024Document28 pagesSCH 106 Lecture V, 2024okumuenock000No ratings yet
- McMurry9e PPT CH03Document48 pagesMcMurry9e PPT CH03김가영No ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesDocument11 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesPablo KamgneNo ratings yet
- Isomerism PP 4Document12 pagesIsomerism PP 4Aderemi LyndabaeNo ratings yet
- 5 - AlkenesDocument12 pages5 - AlkenesSean Gabriel LacambraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document77 pagesChemistry 2Victor MutugiNo ratings yet
- Naming Organic CompoundsDocument22 pagesNaming Organic CompoundsNovira ChandisaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon NomenclatureDocument20 pagesHydrocarbon Nomenclatureapi-246744309No ratings yet
- AlkanesDocument16 pagesAlkanesNoor 3laaNo ratings yet
- Programmed Instruction For Alkanes PDFDocument7 pagesProgrammed Instruction For Alkanes PDFJohn Gabriel SamonteNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Biological and Clinical Mass Spectrometry: An IntroductionFrom EverandQuantitative Biological and Clinical Mass Spectrometry: An IntroductionNo ratings yet
- Molecular Devices: An Introduction to Technomimetics and its Biological ApplicationsFrom EverandMolecular Devices: An Introduction to Technomimetics and its Biological ApplicationsNo ratings yet