Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vibration Is A Mechanical Phenomenon Whereby: Oscillations Equilibrium Point Periodic Random
Vibration Is A Mechanical Phenomenon Whereby: Oscillations Equilibrium Point Periodic Random
Uploaded by
Marcus Washington0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageVibration refers to oscillations around an equilibrium point that can be either periodic or random. While some vibrations are desirable for certain devices to function properly, most vibrations are undesirable as they waste energy and create unwanted noise. Vibrations are typically caused by imbalances or imperfections in rotating or moving parts and result in inefficiencies. Reducing vibration and noise often requires careful engineering to minimize unwanted oscillations in mechanical systems.
Original Description:
Vibrations Starter
Original Title
Vibrations Intro From Wiki
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVibration refers to oscillations around an equilibrium point that can be either periodic or random. While some vibrations are desirable for certain devices to function properly, most vibrations are undesirable as they waste energy and create unwanted noise. Vibrations are typically caused by imbalances or imperfections in rotating or moving parts and result in inefficiencies. Reducing vibration and noise often requires careful engineering to minimize unwanted oscillations in mechanical systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageVibration Is A Mechanical Phenomenon Whereby: Oscillations Equilibrium Point Periodic Random
Vibration Is A Mechanical Phenomenon Whereby: Oscillations Equilibrium Point Periodic Random
Uploaded by
Marcus WashingtonVibration refers to oscillations around an equilibrium point that can be either periodic or random. While some vibrations are desirable for certain devices to function properly, most vibrations are undesirable as they waste energy and create unwanted noise. Vibrations are typically caused by imbalances or imperfections in rotating or moving parts and result in inefficiencies. Reducing vibration and noise often requires careful engineering to minimize unwanted oscillations in mechanical systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
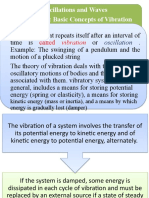
Vibration is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur
about an equilibrium point. The oscillations may be periodicsuch as the
motion of a pendulum or random such as the movement of a tire on a
gravel road.
Vibration is occasionally "desirable". For example, the motion of a tuning
fork, the reed in a woodwind instrument or harmonica, or mobile
phones or the cone of a loudspeaker is desirable vibration, necessary for
the correct functioning of the various devices.
More often, vibration is undesirable, wasting energy and creating
unwanted sound noise. For example, the vibrational motions
of engines, electric motors, or any mechanical device in operation are
typically unwanted. Such vibrations can be caused by imbalances in the
rotating parts, uneven friction, the meshing of gear teeth, etc. Careful
designs usually minimize unwanted vibrations.
The study of sound and vibration are closely related. Sound, or
"pressure waves", are generated by vibrating structures (e.g.vocal
cords); these pressure waves can also induce the vibration of structures
(e.g. ear drum). Hence, when trying to reduce noise it is often a problem
in trying to reduce vibration.
You might also like
- Frequency and MusicDocument58 pagesFrequency and MusicAdelina TurcuNo ratings yet
- Noise and Fluctuations: An IntroductionFrom EverandNoise and Fluctuations: An IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Vibration Is A Mechanical Phenomenon Whereby: Oscillations Equilibrium Point Periodic RandomDocument1 pageVibration Is A Mechanical Phenomenon Whereby: Oscillations Equilibrium Point Periodic RandomFatur RachmanNo ratings yet
- Vibration Vibration Is A Mechanical Phenomenon Whereby Oscillations Occur About An EquilibriumDocument1 pageVibration Vibration Is A Mechanical Phenomenon Whereby Oscillations Occur About An EquilibriumDanielNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion Applications in Engineering FieldDocument1 pageSimple Harmonic Motion Applications in Engineering Fieldmrpoyo100% (1)
- Jabay, Benmark D. Stem302-Volts Mechanics in Vibration and FluidDocument2 pagesJabay, Benmark D. Stem302-Volts Mechanics in Vibration and FluidBenmark JabayNo ratings yet
- Types of Vibration: PeriodicDocument3 pagesTypes of Vibration: PeriodicBilal Ahmed RogiNo ratings yet
- Resonances in Analogue PlaybackDocument5 pagesResonances in Analogue PlaybackJosé CarlosNo ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics: Part of A Series of Articles AboutDocument4 pagesClassical Mechanics: Part of A Series of Articles AboutrishitNo ratings yet
- Non Electrical QuantitiesDocument2 pagesNon Electrical QuantitiesJames DorfNo ratings yet
- How Speakers Work by NafeesDocument11 pagesHow Speakers Work by NafeesnafeesNo ratings yet
- Assignments VibrationDocument1 pageAssignments VibrationAdzmin AshrafNo ratings yet
- How Speakers WorkDocument6 pagesHow Speakers WorkmicolawanNo ratings yet
- Design Lab - Vibration of PlatesDocument5 pagesDesign Lab - Vibration of PlatesKiran JadhavNo ratings yet
- Resonance: ExamplesDocument4 pagesResonance: ExamplesGrace DatuNo ratings yet
- Overview of Sound WavesDocument4 pagesOverview of Sound WavesEthanNo ratings yet
- Akansha Resonance Project FInalDocument18 pagesAkansha Resonance Project FInalPramod PandeyNo ratings yet
- To Remember: Slide 1 oDocument9 pagesTo Remember: Slide 1 oDeni -No ratings yet
- ResonanceDocument1 pageResonanceKevonSingh1No ratings yet
- Oscillations (Rishita's Physics Project)Document14 pagesOscillations (Rishita's Physics Project)nrishita21No ratings yet
- Resonance: K Hinds 2012Document1 pageResonance: K Hinds 2012Akshay Starzz LalNo ratings yet
- Resonance by SHADABDocument14 pagesResonance by SHADABShadab Sipar Pranon100% (2)
- Vibration Chapter01 Intro1Document13 pagesVibration Chapter01 Intro1Mada KurniawanNo ratings yet
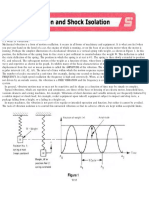
- Vibration and Shock IsolationDocument3 pagesVibration and Shock IsolationSaravanan.KNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms Sound TheoryDocument28 pagesDefinition of Terms Sound TheoryAnonymous 5kOS4tNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument59 pagesChapter OneAbenezer MarkNo ratings yet
- Static and Dynamic Analysis of TATRA ChasisDocument2 pagesStatic and Dynamic Analysis of TATRA Chasisபிரபாகரன் ஆறுமுகம்No ratings yet
- Noise of Induction MachinesDocument6 pagesNoise of Induction Machinesdino_bosnjakovicNo ratings yet
- Chapter One-WaveDocument36 pagesChapter One-WaveMerawi TilahunNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Glossary of Vibration Terminologies (PDF)Document6 pagesThe Ultimate Glossary of Vibration Terminologies (PDF)Christan LNo ratings yet
- How Musical Instruments WorkDocument20 pagesHow Musical Instruments Workvadithya1515No ratings yet
- My Lecture in Vibration EngineeringDocument29 pagesMy Lecture in Vibration EngineeringrollramsNo ratings yet
- Acoustic For Music TheoryDocument6 pagesAcoustic For Music TheoryAriputhiran NarayananNo ratings yet
- Sound Study GuideDocument11 pagesSound Study GuidedasxaxNo ratings yet
- Vibration: 1. Common Vibration Hazards and ControlsDocument6 pagesVibration: 1. Common Vibration Hazards and ControlsPranshu GaurNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Phonetics - Kel 10Document9 pagesAcoustic Phonetics - Kel 10Salwa Diva az zahraNo ratings yet
- CATs Vibration AnalysisDocument7 pagesCATs Vibration AnalysisJose Rattia100% (1)
- 1.0 FUNDAMENTALS of VIBRATION 1.1 What Is Vibration? Mechanical VibrationDocument56 pages1.0 FUNDAMENTALS of VIBRATION 1.1 What Is Vibration? Mechanical VibrationLuis Balducci100% (1)
- What Is Sound?Document3 pagesWhat Is Sound?Jaybert DumaranNo ratings yet
- Brüell&Kjaer - Human Vibration br056Document32 pagesBrüell&Kjaer - Human Vibration br056N. BaumgratzNo ratings yet
- Physics Tutorial - Natural FrequencyDocument5 pagesPhysics Tutorial - Natural FrequencyvalorecoragemNo ratings yet
- UltrasoundDocument22 pagesUltrasoundDavid FlynnNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy Genration Throu GH Sound: Indresh Kunwar Gaurav Shakya ShivjeDocument55 pagesElectrical Energy Genration Throu GH Sound: Indresh Kunwar Gaurav Shakya ShivjermotNo ratings yet
- Physics Tutorial - ResonanceDocument4 pagesPhysics Tutorial - ResonancevalorecoragemNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic: 1. Piezoelectric Generator 2. Magnetostrictive GeneratorDocument6 pagesUltrasonic: 1. Piezoelectric Generator 2. Magnetostrictive GeneratorvjtiitNo ratings yet
- Vakev Physics Term 2 L5 Els&sodDocument21 pagesVakev Physics Term 2 L5 Els&sodvigiraneza0No ratings yet
- Physics-SOUND (IGCSE)Document14 pagesPhysics-SOUND (IGCSE)LamarNo ratings yet
- What Is A Sound WaveDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Sound WavedeepasanmughamNo ratings yet
- Free Vibration: Presented by Tuan Mohd Hafeez Bin Tuan IbrahimDocument56 pagesFree Vibration: Presented by Tuan Mohd Hafeez Bin Tuan IbrahimhamryNo ratings yet
- Physics of Sound: Traveling WavesDocument3 pagesPhysics of Sound: Traveling WavesReksa Indika SuryaNo ratings yet
- ResonanceDocument15 pagesResonanceJames Cabaldo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing - NDTDocument25 pagesUltrasonic Testing - NDTsekarsanthanamNo ratings yet
- How Speakers WorkDocument4 pagesHow Speakers WorkGovind RajputNo ratings yet
- A1) IntroDocument53 pagesA1) IntrochocsoftwareNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves MYP4Document9 pagesSound Waves MYP4ehan.ilrnestersNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VibrationsDocument1 pageMechanical VibrationsTolulope Akinbola OgunbosoyeNo ratings yet
- How The Telephone WorksDocument2 pagesHow The Telephone Workssurya_dharma00100% (1)
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet