Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final Presentation
Final Presentation
Uploaded by
api-2534123540 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views23 pagesOriginal Title
final presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views23 pagesFinal Presentation
Final Presentation
Uploaded by
api-253412354Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 23
Jason Budge
How can ICT be used to engage children and enrich teaching
and learning in primary Literacy ?
Children respond
to screens
Project
Rationale
Why ?
Digital Natives
Already in schools 2012-13 SIP
Teachers underuse ICT
Time given for training
Engagement
Staff concerns about ICT skills
Narrowed focus: IWBs can engage and motivate children when used effectively by
teachers. If teachers skills in using IWB and other ICT improve this will lead to an
enriched learning environment.
Explore teaching and
Learning with ICT
Identified by SLT 2011
Anecdotal and through
staff appraisals
Via SIP
Monitoring
Reflection and practice
Observation / research
Experience
Observation / Experience
* Through the project I lead using a wide range of technology and how they can enrich learning. Such as video, cameras,
microphones and mp3 players. But for this presentation I want to focus on the IWB as it is such a central and powerful tool.
.
Understand expectations
of leadership
Leadership
Development
Why ?
How to lead from the middle
More efficient in Coord role
Work as team
Improve relationships
Create a team
Develop CPD skills
Simply put, I wanted to develop my middle leadership qualities to give me the skills,
knowledge and experience to maximize my role as coordinator. Also, to find out how
to make improvements in general, while leading these successfully from the middle.
Experience a different
form of leadership
Initial Assessments
Conferencing with staff.
Staff explaining lack of knowledge/confidence.
Listening to feedback at staff meetings
Staff as a whole explaining group concerns
Talking to SLT
Knowledge of SLT expectations and needs
Staff Questionnaires based on NC.
Specific needs and quantitative data regarding
present skills and needs of staff (97% in need).
Staff
Initial Assessments
Staff
Following these initial assessments, and
the various data provided, I was able to:
Gain specific understanding of staff
needs, concerns and skill gaps to
address these in the initial planning of
the project.
Work with the SLT to agree upon a
final structure for the project and
develop an initial content and training
schedule.
Initial Assessments
Conferencing
Exploring how ICT helps them learn
Model lessons and feedback
Comparing the same learning using ICT and no ICT
Observation
Observing engagement using tick sheets
Looking at my cohorts initial writing levels.
To use as a quantitative base for how effective the
project might be over the year
Children
Initial Assessments
Children
Following this, and the various data
provided, I was able to:
Gain a qualitative understanding how
children view the IWB and other ICT;
and its potential impact on their
engagement and motivation
Develop initial content and training to
address childrens needs and focus
Find out how much IWB presently
used
Feedback to staff and SLT
Beginning the Project
Could now plan the first stage of
the project. With the aims and
outcomes linked to the initial
assessments.
This had various positive
impacts on the staff, children
and my own development.
Reflection and Adaptation
The model of the
course in itself had
plenty of points for
reflection and adapting
the planning to
improve the project.
It happened
throughout the length
of the project.
All participants given opportunities for reflection
and to feed back for future planning
The process of reflection and
adaptation happened in many different
ways during the project and, as a
result, enabled definite improvements
to the project over time.
These include:
Reflection and Adaptation
Approaches
Training sessions trying out ideas.
Working in teams.
Staff meetings
Gap tasks
Observations
Taking lessons
Asking others to train each other
(blog)
Governors walk.
Data and Monitoring
As already seen both kinds of
data were useful in informing
the inception and planning of
the project.
This use of data, collected
through monitoring and
feedback, was important
throughout the project and its
development.
As well as its final evaluation.
Data and Monitoring
Qualitative data:
Interviews
Discussions and group activities
Questionnaires
Observations
Content analysis
Data and Monitoring
Quantitative data:
Tick sheets
Evaluation forms
Phonics assessment results
Pupil Tracker
Diagnostic Report
Staff Outcomes
Quantitative
Qualitative
Outcomes
There was greater engagement
(including parents via blog)
Teachers felt more skilled and
confident.
IWB used more often and effectively
Childrens Literacy impacted
positively.
Creation of ICT roles and team
Outcomes
Data showed the project to be
successful.
But this doesnt tell half the story
It was only through the process
of reflection, development of my
leadership skills and monitoring
that led to this success.
Leading from the
Middle
Successes:
Holding people to account
Able to hold challenging conversations
To plan ahead and see something
through
Working with different teams
Inspiring people
Leading from the
Middle
Challenges:
Finding ways to remove blocks
Use of qualitative data
Feeding back appropriately
Making myself clear
Working with people with different
learning styles
Making Improvements
If I could go back again I can
think of many improvements I
would and should have made.
Original question more focused
More time for monitoring
A more robust action research
trial to generate quantitative data
To build in more time for support
Next Steps
Sustaining and embedding
practice derived from the
project
This was considered in a whole
school staff meeting as part of
the projects evaluation.
This was to give all staff a role in
leading the project going
forward.
My Next Steps
Using ML skills to enhance CPD
To continue to develop key ML
skills.
To continue with research into
this area of teaching and
learning.
But more robust and targeted.
You might also like
- Kodály in The Fifth Grade ClassroomDocument377 pagesKodály in The Fifth Grade ClassroomLaydsonBraga100% (6)
- Cixous - Portrait of DoraDocument21 pagesCixous - Portrait of DoraYoyoli PerezNo ratings yet
- Dóczi - 2019 - An Overview of Conceptual Models and Theories of Lexical Representation in The Mental LexiconDocument20 pagesDóczi - 2019 - An Overview of Conceptual Models and Theories of Lexical Representation in The Mental LexiconAnthony RancourtNo ratings yet
- Education Planning For QualityDocument44 pagesEducation Planning For QualityMabuza Dumisa97% (29)
- Introduction To Psychology - The Full Noba CollectionDocument2,264 pagesIntroduction To Psychology - The Full Noba CollectionCornelPop100% (1)
- Cspel 5 NarrativeDocument5 pagesCspel 5 Narrativeapi-377039370No ratings yet
- HRD ChecklistDocument9 pagesHRD ChecklistAnoop Parameswaran100% (1)
- Edlp 6090 Leadership ProjectDocument8 pagesEdlp 6090 Leadership Projectapi-510869532No ratings yet
- Ead 523 Benchmark Reflection of Professional Development SessionDocument7 pagesEad 523 Benchmark Reflection of Professional Development Sessionapi-309737337100% (2)
- Psychology Journal of Humanistic: Abraham Maslow The Failure of Self-Actualization Theory: A Critique of Carl Rogers andDocument19 pagesPsychology Journal of Humanistic: Abraham Maslow The Failure of Self-Actualization Theory: A Critique of Carl Rogers andBenaoNo ratings yet
- Why Consulting - Anatomy of The Perfect Interview Answer PDFDocument54 pagesWhy Consulting - Anatomy of The Perfect Interview Answer PDFcdcdiverNo ratings yet
- PPD Alin C100048725Document14 pagesPPD Alin C100048725tatualynaNo ratings yet
- PMP PresentationDocument25 pagesPMP PresentationMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- Digital Learning & Teaching Coaching Roadmap - : ECI519 SP2015Document20 pagesDigital Learning & Teaching Coaching Roadmap - : ECI519 SP2015api-284638910No ratings yet
- Project 2Document4 pagesProject 2api-231544274No ratings yet
- Formative Assessment: SurinameDocument67 pagesFormative Assessment: SurinameTeachers Without Borders100% (1)
- Final PD Project RoidtDocument12 pagesFinal PD Project Roidtapi-418802585No ratings yet
- New Word - Evidence of Professional Competency in Instructional PracticeDocument8 pagesNew Word - Evidence of Professional Competency in Instructional Practiceapi-334122321No ratings yet
- Portfolio-Professional Statement and GoalsDocument10 pagesPortfolio-Professional Statement and Goalsapi-235551194No ratings yet
- Project Work Course OutcomesDocument5 pagesProject Work Course Outcomesbcqxqha3100% (2)
- Learning and Development First ModuleDocument27 pagesLearning and Development First ModulepadmanabhdixitNo ratings yet
- Guide For Ratees Sy 2022 2023 2Document6 pagesGuide For Ratees Sy 2022 2023 2VANISSA CENIZANo ratings yet
- t5 Benchmark - Reflection of Professional Development SessionDocument6 pagest5 Benchmark - Reflection of Professional Development Sessionapi-619576791No ratings yet
- Reflection of Professional Development SessionDocument11 pagesReflection of Professional Development Sessionapi-547243899No ratings yet
- Grad Online Workshop SyllabusDocument6 pagesGrad Online Workshop Syllabusapi-266873840No ratings yet
- Training & Development BaristaDocument49 pagesTraining & Development BaristaManish SharmaNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument5 pagesBasicsapi-285165512No ratings yet
- Teaching Class Employee Performance and Development PlanDocument19 pagesTeaching Class Employee Performance and Development Planapi-298158473No ratings yet
- NBA Closing The LoopDocument30 pagesNBA Closing The LoopEr Umesh ThoriyaNo ratings yet
- Smart Goals Jparker 2014 Year 3Document6 pagesSmart Goals Jparker 2014 Year 3api-231469652No ratings yet
- Reflection of Professional Development SessionDocument6 pagesReflection of Professional Development Sessionapi-475628631No ratings yet
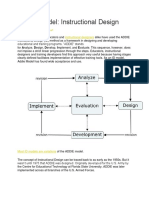
- Addie ModelDocument11 pagesAddie ModelPanis RyanNo ratings yet
- Dennis Tan Caballed Beed Iv: Instructional DesignersDocument6 pagesDennis Tan Caballed Beed Iv: Instructional DesignersDennis Tan CaballesNo ratings yet
- Course: BA Business Studies Module: Personal and Professional DevelopmentDocument7 pagesCourse: BA Business Studies Module: Personal and Professional DevelopmentKamrul Islam SakibNo ratings yet
- Five Models of Professional DevelopmentDocument8 pagesFive Models of Professional DevelopmentIain Cook-Bonney100% (1)
- ADDIE Model: Instructional DesignDocument10 pagesADDIE Model: Instructional DesignJames ReyesNo ratings yet
- Training and DevelopmentDocument39 pagesTraining and DevelopmentSalman ShaxShax HeissNo ratings yet
- Instructional Design Model The ADDIE ModelDocument8 pagesInstructional Design Model The ADDIE ModelUyungndutNo ratings yet
- Gray R BlogsDocument28 pagesGray R Blogsapi-259261296No ratings yet
- Comp Reflection Short 1Document10 pagesComp Reflection Short 1api-295784162No ratings yet
- Model Addie 5Document7 pagesModel Addie 5Egan-Ash ArijenanNo ratings yet
- Notes For Training DesignDocument10 pagesNotes For Training Designkalyani_iyer63504No ratings yet
- ADDIE Instructional Design Certificate ProgramDocument12 pagesADDIE Instructional Design Certificate ProgramJoeManikNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment of Final PracticumDocument3 pagesSelf Assessment of Final Practicumapi-317126601No ratings yet
- Staff DevelopmentDocument40 pagesStaff DevelopmentJegenthambal Arumugam100% (1)
- ADDIE ModelDocument12 pagesADDIE ModelMel Bautista DomingoNo ratings yet
- Ab Lowery KarmenDocument5 pagesAb Lowery Karmenapi-632517517No ratings yet
- Addie ModelDocument6 pagesAddie ModelIrene Balane AranillaNo ratings yet
- Q&a Written ExamDocument14 pagesQ&a Written ExamAirric Cario BalladaresNo ratings yet
- BB 3 D 160308591 A 7 FFCFBDocument6 pagesBB 3 D 160308591 A 7 FFCFBapi-578727511No ratings yet
- The ADDIE ModelDocument14 pagesThe ADDIE ModelPaul De Las Alas100% (1)
- Addie Model of Instructional DesignDocument8 pagesAddie Model of Instructional Designfariez79No ratings yet
- Thesis On Effectiveness of Training and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesThesis On Effectiveness of Training and Developmentalanacartwrightnorman100% (2)
- FinalcoursereflectionDocument5 pagesFinalcoursereflectionapi-351749683No ratings yet
- Benchmark Reflection of Professional Development SessionDocument5 pagesBenchmark Reflection of Professional Development Sessionapi-475628377No ratings yet
- Technical Assistant ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesTechnical Assistant ResponsibilitiesManuel CruzNo ratings yet
- L&D NotesDocument13 pagesL&D NotesSanpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Thesis On School Improvement PlanDocument8 pagesThesis On School Improvement Plankatemillerportland100% (2)
- Design of A Training Program CorrectDocument13 pagesDesign of A Training Program CorrectJusy Bingura100% (1)
- Best Practices Guide For Instructional DesignDocument8 pagesBest Practices Guide For Instructional Designearlk02No ratings yet
- ADDIE WorksheetDocument6 pagesADDIE WorksheetVasudha97No ratings yet
- Self Reflection and Professional Growth PlanningDocument24 pagesSelf Reflection and Professional Growth PlanningJenny Rose AndresNo ratings yet
- Benchmark-Reflection of Professional Development SessionDocument7 pagesBenchmark-Reflection of Professional Development Sessionapi-520679261No ratings yet
- Final TrainingDocument56 pagesFinal Trainingabhiyadav48No ratings yet
- A Report On T&D by IbrahimDocument17 pagesA Report On T&D by IbrahimMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication OverviewDocument4 pagesPurposive Communication OverviewLineClar RealNo ratings yet
- Educational Provisions For Learners With Disabilities in IndiaDocument22 pagesEducational Provisions For Learners With Disabilities in IndiaKishori RaoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Valuation - Hedonic PricingDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Valuation - Hedonic PricingCarlos Ferreira100% (1)
- Intermediate Workbook Unit 1Document8 pagesIntermediate Workbook Unit 1Anonymous RySeVnleLNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Collaborative Activity To The Academic Performance of Grade 11 Students in D2Nhs. Problem and Its BackgroundDocument14 pagesThe Effects of Collaborative Activity To The Academic Performance of Grade 11 Students in D2Nhs. Problem and Its Backgroundshiela marie simabahanNo ratings yet
- David Wilcock Wanderer AwakeningDocument10 pagesDavid Wilcock Wanderer AwakeningNuno CarreiraNo ratings yet
- Consultoria en MarketingDocument74 pagesConsultoria en MarketingSergio EstradaNo ratings yet
- Patrick's Negative PlatonismusDocument11 pagesPatrick's Negative PlatonismusBlaNo ratings yet
- Student HandbookDocument36 pagesStudent Handbookhouda houdaNo ratings yet
- Reviewing and EditingDocument7 pagesReviewing and Editingmokhtari raniaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Templateapi-318605228No ratings yet
- СОР Англ.яз 5кл англ PDFDocument32 pagesСОР Англ.яз 5кл англ PDFnadezhdaNo ratings yet
- Unexpected Income Program - Center For Spiritual Living, FresnoDocument2 pagesUnexpected Income Program - Center For Spiritual Living, FresnoCSLFresnoNo ratings yet
- Ot Goals NuevoDocument157 pagesOt Goals NuevoElbania PerezNo ratings yet
- DLL - 1st WK - Electrical Installaiton and MaintenanceDocument28 pagesDLL - 1st WK - Electrical Installaiton and Maintenancemjc100% (1)
- Carl Rogers Humanistic Learning PrinciplesDocument2 pagesCarl Rogers Humanistic Learning PrinciplesSAZALI BIN MOHAMED MOKHTARUDINNo ratings yet
- The Functions and Elements of CultureDocument12 pagesThe Functions and Elements of CultureLeondreNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For BleedingDocument1 pageNCP Risk For BleedingJen Garzo75% (4)
- Cbe K 12tesda Final1Document13 pagesCbe K 12tesda Final1Rj Saneubac GuhabacNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Social Studies 9.Document7 pagesMicrosoft Word - Social Studies 9.Brooke ZaikNo ratings yet
- Office of The School PrincipalDocument26 pagesOffice of The School PrincipalCecilia Guevarra DumlaoNo ratings yet
- How Would You Describe Yourself? (4 Perfect Example Answers)Document4 pagesHow Would You Describe Yourself? (4 Perfect Example Answers)Tino SalabsabNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Sustainable Low-Cost Housing in Ethiopia - An Innovation Diffusion PerspectiveDocument7 pagesIntroduction of Sustainable Low-Cost Housing in Ethiopia - An Innovation Diffusion PerspectiveninashiroNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing SampleDocument8 pagesAcademic Writing Sampletatiana zarmatiNo ratings yet