Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power Mosfets: - Two Types
Power Mosfets: - Two Types
Uploaded by
Diane Bonilla LacenaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Contingency Plan: I. Brief Project DescriptionDocument12 pagesContingency Plan: I. Brief Project DescriptionDiane Bonilla Lacena100% (1)
- Power MosfetDocument15 pagesPower Mosfetnandhakumarme100% (1)
- Description of Existing Solid Waste Management Plan - Aart Id NumberDocument1 pageDescription of Existing Solid Waste Management Plan - Aart Id NumberDiane Bonilla Lacena50% (2)
- Power Mosfets: Two Types Depletion TypeDocument14 pagesPower Mosfets: Two Types Depletion TypeGokul ShanmuganNo ratings yet
- Power Mosfets: - Two TypesDocument13 pagesPower Mosfets: - Two TypesHOD EEE TRPNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument62 pagesPower Semiconductor DevicesMD. SADEKUL ISLAM RIMON 1502084No ratings yet
- PN-junction Diodes and Its ApplicationsDocument37 pagesPN-junction Diodes and Its ApplicationsRahul sandireddyNo ratings yet
- Electical and Electronics Engineering: Unit-I Power Semi Condctor Devices Iii-I B.Tech EeeDocument56 pagesElectical and Electronics Engineering: Unit-I Power Semi Condctor Devices Iii-I B.Tech EeehimajatataNo ratings yet
- Two Terminal Electronic DevicesDocument28 pagesTwo Terminal Electronic DevicesFahad GhanyNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BEEE102L TH VL2022230105984 Reference Material I 19-01-2023 003 MOSFETDocument22 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BEEE102L TH VL2022230105984 Reference Material I 19-01-2023 003 MOSFETvishwadeepNo ratings yet
- DC GenerationDocument18 pagesDC GenerationAlfred OkacheNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument22 pagesPower ElectronicsBharatNo ratings yet
- EE 21-Lecture 2 - Diode Construction & CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesEE 21-Lecture 2 - Diode Construction & CharacteristicsAids Sumalde100% (1)
- Module 1 MidtermsDocument57 pagesModule 1 MidtermsKin Luther De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- BooksDocument30 pagesBooksHabib IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Passive Components: Resistors Capacitors Inductors Diodes Interface ComponentsDocument186 pagesPassive Components: Resistors Capacitors Inductors Diodes Interface ComponentsyokeshNo ratings yet
- PE1 - Lect 1-PN Junction Diode PrinciplesDocument32 pagesPE1 - Lect 1-PN Junction Diode PrinciplesAbdel-aziz SamiNo ratings yet
- Buck-Boost Converter - EET504 PDFDocument13 pagesBuck-Boost Converter - EET504 PDFsiti izyan100% (1)
- Lecture10 - MOSFETDocument18 pagesLecture10 - MOSFETahmedgamal7856320No ratings yet
- Generation of HV Ac and DC VoltageDocument57 pagesGeneration of HV Ac and DC VoltageSharif UllahNo ratings yet
- Avalanche Transit Time DevicesDocument40 pagesAvalanche Transit Time DevicespapanyameNo ratings yet
- Overview of High-Speed Logic Families (08 Hours) : Doece, SvnitDocument109 pagesOverview of High-Speed Logic Families (08 Hours) : Doece, SvnitJay KadelNo ratings yet
- IECD Capsule NotesDocument59 pagesIECD Capsule NotesANANTHU PRADEEPNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor Diodes and CircuitsDocument20 pagesPower Semiconductor Diodes and CircuitsHassan FrazNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuits Perspective: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEDocument23 pagesDiode Circuits Perspective: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEDEEPIKA PAVUNDOSS 20BEC0285No ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Lecture - 2Document180 pagesPower Electronics: Lecture - 2Arun prasathNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Study MaterialDocument63 pagesUnit-5 Study MaterialSrivatsan SPNo ratings yet
- 3rd Semester Lab 201Document36 pages3rd Semester Lab 201Noor HussainNo ratings yet
- 2 Power Semiconductor Diodes & BJTDocument63 pages2 Power Semiconductor Diodes & BJTSayan DasNo ratings yet
- UNIT I and II NewDocument171 pagesUNIT I and II Newdinesh.vNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lecture 4: The MOSFET and The IGBTDocument16 pagesPower Electronics Lecture 4: The MOSFET and The IGBTSolayman Salindato MasoNo ratings yet
- Multiplexer: Multiplex - Many Into OneDocument40 pagesMultiplexer: Multiplex - Many Into OneSamee UllahNo ratings yet
- Buck ConverterDocument13 pagesBuck ConverterDinesh MahtoNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument61 pages1 Introductionfiraol temesgenNo ratings yet
- EMT 369 Wk1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument25 pagesEMT 369 Wk1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsgurdianskyNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Circuits NewDocument40 pagesBasic Electrical Circuits NewSafnas KariapperNo ratings yet
- Analog Fault DerivationDocument89 pagesAnalog Fault DerivationSachidananda SwarNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab 2019Document37 pagesElectronics Lab 2019Noor HussainNo ratings yet
- MOS Field-Effect Transistor (Mosfet)Document40 pagesMOS Field-Effect Transistor (Mosfet)Trần Minh NhậtNo ratings yet
- Series-Resonant Inverter: ECE 442 Power Electronics 1Document34 pagesSeries-Resonant Inverter: ECE 442 Power Electronics 116117 GOURAB SAHANo ratings yet
- KE47503 High Voltage Chapter 6 - Generation of High Volatges and Currents (Autosaved)Document41 pagesKE47503 High Voltage Chapter 6 - Generation of High Volatges and Currents (Autosaved)Ceticia KellyNo ratings yet
- DiodeApplications 1spDocument32 pagesDiodeApplications 1spHakkı AKYÜZNo ratings yet
- Yashwant HDocument37 pagesYashwant HRohitUikeyNo ratings yet
- Basics of Power ElectronicsDocument34 pagesBasics of Power ElectronicsSharween KaurNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lecture 2Document43 pagesUnit 1 Lecture 2Shamil GadaNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits: 0.1 Series RLC Circuit Series RLC Circuit - PhasorsDocument6 pagesAC Circuits: 0.1 Series RLC Circuit Series RLC Circuit - PhasorsMahmudul HasanNo ratings yet
- 3 Power MosfetDocument23 pages3 Power MosfetSayan DasNo ratings yet
- BJT Mosfet IgbtDocument48 pagesBJT Mosfet IgbtJeanmark NeilNo ratings yet
- Enhancement MOSFET: Biasing Techniques of MosfetDocument10 pagesEnhancement MOSFET: Biasing Techniques of MosfetNaveen ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 01Document21 pagesUnit 01mathanstar77No ratings yet
- Diode and Its ApplicationsDocument39 pagesDiode and Its ApplicationsUsama Sidhu100% (1)
- PE1 - Lect 2-Diode LoadsDocument19 pagesPE1 - Lect 2-Diode LoadsAbdel-aziz SamiNo ratings yet
- EI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersDocument16 pagesEI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersASPCN 2017No ratings yet
- Module 1-Chapter 1 Diode Clipping and ClampingDocument41 pagesModule 1-Chapter 1 Diode Clipping and ClampingummeNo ratings yet
- Application of Power Diode in Power ElectronicsDocument18 pagesApplication of Power Diode in Power ElectronicsSahale Shera Lutse 18BEE0376No ratings yet
- Turn On Methods of SCRDocument5 pagesTurn On Methods of SCRxae778899No ratings yet
- Rectifier and SMPSDocument85 pagesRectifier and SMPSVignesh MeyyappanNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 2010-2011Document68 pagesPower Electronics 2010-2011Adnan Younus100% (1)
- Diodes and Applications FinalDocument117 pagesDiodes and Applications FinalCris Diane G. Datingginoo100% (1)
- WinantaSitanggang.G.20.21.Electricity Circ - nsesP.2019.PPT - Active and Passive ElementDocument6 pagesWinantaSitanggang.G.20.21.Electricity Circ - nsesP.2019.PPT - Active and Passive ElementTiomeldaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- AA EIS Manila Waterfront City 2Document344 pagesAA EIS Manila Waterfront City 2Diane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- 8990 Pampanga Public Scoping 1Document2 pages8990 Pampanga Public Scoping 1Diane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- Climate Out LookDocument49 pagesClimate Out LookDiane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- Turn It Up Chords by Planetshakers: A B C#M B/D# E A E A E A E ADocument3 pagesTurn It Up Chords by Planetshakers: A B C#M B/D# E A E A E A E ADiane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- Hwaste Form 0001Document2 pagesHwaste Form 0001Diane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- EprmpAir ModuleDocument30 pagesEprmpAir ModuleDiane Bonilla Lacena100% (1)
- 13 PSO Project Status DeckDocument1 page13 PSO Project Status DeckDiane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- Waste Management Flow ChartDocument2 pagesWaste Management Flow ChartDiane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
Power Mosfets: - Two Types
Power Mosfets: - Two Types
Uploaded by
Diane Bonilla LacenaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Power Mosfets: - Two Types
Power Mosfets: - Two Types
Uploaded by
Diane Bonilla LacenaCopyright:
Available Formats
ECD 442 Power Electronics 1
Power MOSFETs
Two Types
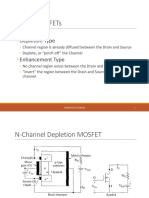
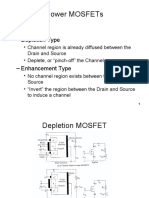
Depletion Type
Channel region is already diffused between the
Drain and Source
Deplete, or pinch-off the Channel
Enhancement Type
No channel region exists between the Drain and
Source
Invert the region between the Drain and Source
to induce a channel
ECD 442 Power Electronics 2
Depletion MOSFET
ECD 442 Power Electronics 3
N-Channel Depletion MOSFET
Normally Reverse-Bias the Gate-Source Junction
ECD 442 Power Electronics 4
Enhancement MOSFET
ECD 442 Power Electronics 5
N-Channel Enhancement MOSFET
The Gate-Source Junction will be Forward-Biased
The bias voltage must be greater than a threshold voltage
A Channel region is induced between the Drain and Source
ECD 442 Power Electronics 6
Drain Characteristics
ECD 442 Power Electronics 7
Steady-State Characteristics
ECD 442 Power Electronics 8
Switching Characteristics
ECD 442 Power Electronics 9
Equivalent Circuit
ECD 442 Power Electronics 10
Switching Model
ECD 442 Power Electronics 11
Switching Waveforms and Times
ECD 442 Power Electronics 12
Turn-on Delay, t
d(on)
= time to charge the input
capacitance to V
T
Rise time, t
r
= Charging time to charge the input
capacitance to the full gate voltage, V
GSP
in order to drive
the transistor into the linear region of operation
ECD 442 Power Electronics 13
Turn-off delay time, t
d(off)
= time for the input capacitance to
discharge from overdrive voltage V
1
to pinch-off.
V
GS
must decrease significantly for V
DS
to rise.
Fall time, t
f
= time for the input capacitance to discharge
from pinch-off to the threshold voltage.
You might also like
- Contingency Plan: I. Brief Project DescriptionDocument12 pagesContingency Plan: I. Brief Project DescriptionDiane Bonilla Lacena100% (1)
- Power MosfetDocument15 pagesPower Mosfetnandhakumarme100% (1)
- Description of Existing Solid Waste Management Plan - Aart Id NumberDocument1 pageDescription of Existing Solid Waste Management Plan - Aart Id NumberDiane Bonilla Lacena50% (2)
- Power Mosfets: Two Types Depletion TypeDocument14 pagesPower Mosfets: Two Types Depletion TypeGokul ShanmuganNo ratings yet
- Power Mosfets: - Two TypesDocument13 pagesPower Mosfets: - Two TypesHOD EEE TRPNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument62 pagesPower Semiconductor DevicesMD. SADEKUL ISLAM RIMON 1502084No ratings yet
- PN-junction Diodes and Its ApplicationsDocument37 pagesPN-junction Diodes and Its ApplicationsRahul sandireddyNo ratings yet
- Electical and Electronics Engineering: Unit-I Power Semi Condctor Devices Iii-I B.Tech EeeDocument56 pagesElectical and Electronics Engineering: Unit-I Power Semi Condctor Devices Iii-I B.Tech EeehimajatataNo ratings yet
- Two Terminal Electronic DevicesDocument28 pagesTwo Terminal Electronic DevicesFahad GhanyNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BEEE102L TH VL2022230105984 Reference Material I 19-01-2023 003 MOSFETDocument22 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BEEE102L TH VL2022230105984 Reference Material I 19-01-2023 003 MOSFETvishwadeepNo ratings yet
- DC GenerationDocument18 pagesDC GenerationAlfred OkacheNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument22 pagesPower ElectronicsBharatNo ratings yet
- EE 21-Lecture 2 - Diode Construction & CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesEE 21-Lecture 2 - Diode Construction & CharacteristicsAids Sumalde100% (1)
- Module 1 MidtermsDocument57 pagesModule 1 MidtermsKin Luther De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- BooksDocument30 pagesBooksHabib IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Passive Components: Resistors Capacitors Inductors Diodes Interface ComponentsDocument186 pagesPassive Components: Resistors Capacitors Inductors Diodes Interface ComponentsyokeshNo ratings yet
- PE1 - Lect 1-PN Junction Diode PrinciplesDocument32 pagesPE1 - Lect 1-PN Junction Diode PrinciplesAbdel-aziz SamiNo ratings yet
- Buck-Boost Converter - EET504 PDFDocument13 pagesBuck-Boost Converter - EET504 PDFsiti izyan100% (1)
- Lecture10 - MOSFETDocument18 pagesLecture10 - MOSFETahmedgamal7856320No ratings yet
- Generation of HV Ac and DC VoltageDocument57 pagesGeneration of HV Ac and DC VoltageSharif UllahNo ratings yet
- Avalanche Transit Time DevicesDocument40 pagesAvalanche Transit Time DevicespapanyameNo ratings yet
- Overview of High-Speed Logic Families (08 Hours) : Doece, SvnitDocument109 pagesOverview of High-Speed Logic Families (08 Hours) : Doece, SvnitJay KadelNo ratings yet
- IECD Capsule NotesDocument59 pagesIECD Capsule NotesANANTHU PRADEEPNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor Diodes and CircuitsDocument20 pagesPower Semiconductor Diodes and CircuitsHassan FrazNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuits Perspective: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEDocument23 pagesDiode Circuits Perspective: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEDEEPIKA PAVUNDOSS 20BEC0285No ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Lecture - 2Document180 pagesPower Electronics: Lecture - 2Arun prasathNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Study MaterialDocument63 pagesUnit-5 Study MaterialSrivatsan SPNo ratings yet
- 3rd Semester Lab 201Document36 pages3rd Semester Lab 201Noor HussainNo ratings yet
- 2 Power Semiconductor Diodes & BJTDocument63 pages2 Power Semiconductor Diodes & BJTSayan DasNo ratings yet
- UNIT I and II NewDocument171 pagesUNIT I and II Newdinesh.vNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lecture 4: The MOSFET and The IGBTDocument16 pagesPower Electronics Lecture 4: The MOSFET and The IGBTSolayman Salindato MasoNo ratings yet
- Multiplexer: Multiplex - Many Into OneDocument40 pagesMultiplexer: Multiplex - Many Into OneSamee UllahNo ratings yet
- Buck ConverterDocument13 pagesBuck ConverterDinesh MahtoNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument61 pages1 Introductionfiraol temesgenNo ratings yet
- EMT 369 Wk1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument25 pagesEMT 369 Wk1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsgurdianskyNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Circuits NewDocument40 pagesBasic Electrical Circuits NewSafnas KariapperNo ratings yet
- Analog Fault DerivationDocument89 pagesAnalog Fault DerivationSachidananda SwarNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab 2019Document37 pagesElectronics Lab 2019Noor HussainNo ratings yet
- MOS Field-Effect Transistor (Mosfet)Document40 pagesMOS Field-Effect Transistor (Mosfet)Trần Minh NhậtNo ratings yet
- Series-Resonant Inverter: ECE 442 Power Electronics 1Document34 pagesSeries-Resonant Inverter: ECE 442 Power Electronics 116117 GOURAB SAHANo ratings yet
- KE47503 High Voltage Chapter 6 - Generation of High Volatges and Currents (Autosaved)Document41 pagesKE47503 High Voltage Chapter 6 - Generation of High Volatges and Currents (Autosaved)Ceticia KellyNo ratings yet
- DiodeApplications 1spDocument32 pagesDiodeApplications 1spHakkı AKYÜZNo ratings yet
- Yashwant HDocument37 pagesYashwant HRohitUikeyNo ratings yet
- Basics of Power ElectronicsDocument34 pagesBasics of Power ElectronicsSharween KaurNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lecture 2Document43 pagesUnit 1 Lecture 2Shamil GadaNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits: 0.1 Series RLC Circuit Series RLC Circuit - PhasorsDocument6 pagesAC Circuits: 0.1 Series RLC Circuit Series RLC Circuit - PhasorsMahmudul HasanNo ratings yet
- 3 Power MosfetDocument23 pages3 Power MosfetSayan DasNo ratings yet
- BJT Mosfet IgbtDocument48 pagesBJT Mosfet IgbtJeanmark NeilNo ratings yet
- Enhancement MOSFET: Biasing Techniques of MosfetDocument10 pagesEnhancement MOSFET: Biasing Techniques of MosfetNaveen ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 01Document21 pagesUnit 01mathanstar77No ratings yet
- Diode and Its ApplicationsDocument39 pagesDiode and Its ApplicationsUsama Sidhu100% (1)
- PE1 - Lect 2-Diode LoadsDocument19 pagesPE1 - Lect 2-Diode LoadsAbdel-aziz SamiNo ratings yet
- EI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersDocument16 pagesEI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersASPCN 2017No ratings yet
- Module 1-Chapter 1 Diode Clipping and ClampingDocument41 pagesModule 1-Chapter 1 Diode Clipping and ClampingummeNo ratings yet
- Application of Power Diode in Power ElectronicsDocument18 pagesApplication of Power Diode in Power ElectronicsSahale Shera Lutse 18BEE0376No ratings yet
- Turn On Methods of SCRDocument5 pagesTurn On Methods of SCRxae778899No ratings yet
- Rectifier and SMPSDocument85 pagesRectifier and SMPSVignesh MeyyappanNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 2010-2011Document68 pagesPower Electronics 2010-2011Adnan Younus100% (1)
- Diodes and Applications FinalDocument117 pagesDiodes and Applications FinalCris Diane G. Datingginoo100% (1)
- WinantaSitanggang.G.20.21.Electricity Circ - nsesP.2019.PPT - Active and Passive ElementDocument6 pagesWinantaSitanggang.G.20.21.Electricity Circ - nsesP.2019.PPT - Active and Passive ElementTiomeldaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- AA EIS Manila Waterfront City 2Document344 pagesAA EIS Manila Waterfront City 2Diane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- 8990 Pampanga Public Scoping 1Document2 pages8990 Pampanga Public Scoping 1Diane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- Climate Out LookDocument49 pagesClimate Out LookDiane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- Turn It Up Chords by Planetshakers: A B C#M B/D# E A E A E A E ADocument3 pagesTurn It Up Chords by Planetshakers: A B C#M B/D# E A E A E A E ADiane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- Hwaste Form 0001Document2 pagesHwaste Form 0001Diane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- EprmpAir ModuleDocument30 pagesEprmpAir ModuleDiane Bonilla Lacena100% (1)
- 13 PSO Project Status DeckDocument1 page13 PSO Project Status DeckDiane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- Waste Management Flow ChartDocument2 pagesWaste Management Flow ChartDiane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet