Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Web API Poster
Web API Poster
Uploaded by
Nestor Felipe Viscarra Ramirez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 views1 pageapi poster
Original Title
ASP.net Web API Poster
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentapi poster
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 views1 pageWeb API Poster
Web API Poster
Uploaded by
Nestor Felipe Viscarra Ramirezapi poster
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
2012 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
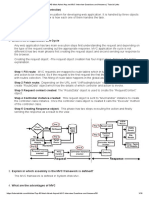
ASP.NET WEB API: HTTP MESSAGE LIFECYLE
ASP.NET Hosting
HTTP Message Handlers
Controller
Model Binding
Controller Action
Per-route
Message Handlers
HttpControllerHandler
Self-Hosting
HttpSelfHostServer
HTTP message handlers are the first stage in
the processing pipeline. They process HTTP
request messages on the way in, and HTTP
response messages on the way out.
To create a custom message handler, derive
from the DelegatingHandler class. You can
add multiple message handlers.
Message handlers can be global or assigned
to a specific route. A per-route message
handler is invoked only when the request
matches that route. Per-route message
handlers are configured in the routing table.
You can host Web API within an ASP.NET application, or
inside your own process (self-hosting). After the initial
entry point, the HTTP messages go through the same
pipeline. The HTTP request message is first converted to
an HttpRequestMessage object, which provides strongly
typed access to the HTTP message.
The controller is where you define the main
logic for handling an HTTP request. Your
controller derives from the ApiController class
or implements the IHttpController interface.
Model binding uses the request to
create values for the parameters of the
action. These values are passed to the
action when the action is invoked.
Result Conversion
HttpServer
HttpRequestMessage
HttpRequestMessage
HttpResponseMessage
DelegatingHandler
Authorization
Filters
Exception
Filters
Action Filters
URI
Headers
Entity-body
Request message
HttpRoutingDispatcher
HttpControllerDispatcher
Model Binding Result Conversion
HttpResponseMessage
Route.Handler
DelegatingHandler
HttpMessageHandler
Route.Handler
is null?
Create API
controller
Invoke Action
Select controller
action
Action parameters Action return value
This message handler can invoke
HttpControllerDispatcher and return to the
main path, or provide a custom end point.
A message handler can create
the response directly, skipping
the rest of the pipeline.
A message handler can create
the response directly, skipping
the rest of the pipeline.
Error response
Unhandled exceptions are
routed to exception filters.
If the request is not authorized, an
authorization filter can create an error
response and skip the rest of the pipeline.
Action filters are invoked
twice, before and after the
controller action.
A media-type formatter
reads the message body
(if any).
The default model binders
read from the URI path
and query string.
A custom parameter
binding can read any part
of the HTTP request.
Exception!
FormatterParameterBinding ModelBinderParameterBinding HttpParameterBinding
Media Type Formatter
Complex Type
IModelBinder
Simple Type Any Type
IValueProvider
HttpResponseMessage void Other types
The return value from the
action is converted to an
HttpResponseMessage.
If return type is
HttpResponseMessage,
pass through.
If return type is
void, create
response with
status 204 (No
Content).
For all other return
types, a media-type
formatter serializes
the value and writes
it to the message
body.
Media Type Formatter
IContentNegotiator
A
B
E
C D
C D
ASP.NET Web API is a framework that makes it easy
to build HTTP services that reach a broad range of
clients, including browsers and mobile devices. It is
an ideal platform for building RESTful applications on
the .NET Framework.
This poster shows how an HTTP request flows
through the Web API pipeline, and how the HTTP
response flows back. The diagram also shows
extensibility points, where you can add custom code
or even replace the default behavior entirely. You can
find documentation and tutorials for ASP.NET Web
API at http://www.asp.net/web-api.
Key
Built-in Class
Extensibility Point
Note
Request
Response
ApiController
InvokeActionAsync Task<HttpResponseMessage>
IHttpActionInvoker
Invoke Controller Action
Invoke controller action, using HttpActionContext
for bindings and model state.
E
HttpControllerDispatcher
SelectController HttpControllerDescriptor
IHttpControllerSelector
HttpControllerDispatcher
Create IHttpController
IHttpControllerActivator
IAssembliesResolver
GetControllerTypes ICollection<Type>
IHttpControllerTypeResolver
GetAssemblies ICollection<Assembly>
Create Controller
Create an API controller based on the request.
1. Select controller type
2. Activate controller
A
ApiController
SelectAction HttpActionDescriptor
IHttpActionSelector
Select Controller Action
Select an action based on the request.
B
OnActionExecuting OnActionExecuted
No
Yes
Email: MSPoster@microsoft.com
You might also like
- ASP.NET For Beginners: The Simple Guide to Learning ASP.NET Web Programming Fast!From EverandASP.NET For Beginners: The Simple Guide to Learning ASP.NET Web Programming Fast!No ratings yet
- Aspnet Web API PosterDocument1 pageAspnet Web API PosterKiran Kumar PNo ratings yet
- ASPDocument3 pagesASPOana CiuleiNo ratings yet
- Web API 1Document29 pagesWeb API 1Amareswara RaoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between MvcController and APIControllerDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MvcController and APIControllersureshbabupuli_24No ratings yet
- HTTP Handlers and HTTP ModulesDocument22 pagesHTTP Handlers and HTTP Modulesnitin_singh_24No ratings yet
- Web API Poster GrayscaleDocument1 pageWeb API Poster GrayscaleDeathTrapperNo ratings yet
- Different Return Types of A Controller Action MethodDocument11 pagesDifferent Return Types of A Controller Action MethodBasil JacobNo ratings yet
- ServletsDocument42 pagesServletsnaresh madduNo ratings yet
- Day1 PresentationDocument24 pagesDay1 PresentationNour Terra-linkNo ratings yet
- Spring-Framework - Optimize - Chapter 7. IntegrationDocument110 pagesSpring-Framework - Optimize - Chapter 7. IntegrationCiprian Nicu RosuNo ratings yet
- A) HTML Server Controls: System - Web.Ui - Webcontrols NamespaceDocument26 pagesA) HTML Server Controls: System - Web.Ui - Webcontrols NamespaceTsegaye HailuNo ratings yet
- Top 50 Asp Interview QuestionsDocument10 pagesTop 50 Asp Interview QuestionsJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Angular HTTPDocument10 pagesAngular HTTPbnavnredyNo ratings yet
- SCWCDDocument18 pagesSCWCDbookworm094No ratings yet
- Module 3 Overview Module Learning Outcomes: Create Web API ProjectDocument9 pagesModule 3 Overview Module Learning Outcomes: Create Web API ProjectRedan Pablo DitNo ratings yet
- Ws PatternDocument8 pagesWs PatternNitin GuptaNo ratings yet
- ASPNET Pipeline SreedharKogantiDocument21 pagesASPNET Pipeline SreedharKogantiap1482No ratings yet
- Spring50 Interview QuestionsDocument16 pagesSpring50 Interview QuestionsReddy KumarNo ratings yet
- Sun Certified Web Component Developer Study GuideDocument60 pagesSun Certified Web Component Developer Study Guideprakumis100% (2)
- ASPDocument138 pagesASPKulandaivel Al KanagasabaiNo ratings yet
- Java Advanced Java Servlets ARQB TRCQB v1.0Document43 pagesJava Advanced Java Servlets ARQB TRCQB v1.0Bharath Kumar100% (1)
- Unit1-1.3servlet LifecycleDocument5 pagesUnit1-1.3servlet LifecycleShweta JoshiNo ratings yet
- BasicServlet 1Document104 pagesBasicServlet 1bhargav_prasadNo ratings yet
- Java Tutorial: Sudip MaityDocument8 pagesJava Tutorial: Sudip Maityamiable_sudipNo ratings yet
- Top 40 Most Asked ASP - Net MVC Interview Questions and Answers - Tutorial LinksDocument18 pagesTop 40 Most Asked ASP - Net MVC Interview Questions and Answers - Tutorial LinksVenkat MalepatiNo ratings yet
- Set 2Document5 pagesSet 2Kannan KannempillyNo ratings yet
- Validation Controls in ASPDocument12 pagesValidation Controls in ASPAnivesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- SoapuiDocument112 pagesSoapuiAdriano BarbirNo ratings yet
- Spring and SpringMVC SlidesDocument25 pagesSpring and SpringMVC Slidesggzxc12345678910No ratings yet
- Java Servlets: M. L. LiuDocument31 pagesJava Servlets: M. L. LiuOm Bala100% (1)
- Servlet 2Document44 pagesServlet 2naresh madduNo ratings yet
- Node - Js Modules and HTML Form HandlingDocument20 pagesNode - Js Modules and HTML Form HandlingB. POORNIMANo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Web Application: Hardware and Software Components For Web ApplicationsDocument14 pagesAn Introduction To Web Application: Hardware and Software Components For Web ApplicationsBobby BrownNo ratings yet
- Servlets: Complete Reference To Java - HerbertschildtDocument35 pagesServlets: Complete Reference To Java - HerbertschildtSudhanshu PrasadNo ratings yet
- Ervlets: Abhishek Mane February 8 2013Document54 pagesErvlets: Abhishek Mane February 8 2013Chetan ShindeNo ratings yet
- Servlet Technology Is Used To Create A Web Application (Resides at Server Side and Generates A Dynamic Web Page)Document41 pagesServlet Technology Is Used To Create A Web Application (Resides at Server Side and Generates A Dynamic Web Page)Omkar KumtaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Bean Factory and Application Context ?Document7 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Bean Factory and Application Context ?RavikumarmaddiNo ratings yet
- Mule 4 Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesMule 4 Interview QuestionsAshok Kumar RamsankarNo ratings yet
- How To Make Your Web API Responses Consistent and UsefulDocument7 pagesHow To Make Your Web API Responses Consistent and UsefulAlekNo ratings yet
- MVC EssentialsDocument52 pagesMVC EssentialsVassil VassilevNo ratings yet
- MVC 4Document79 pagesMVC 4paparos486No ratings yet
- HTTP Handlers in ASPDocument6 pagesHTTP Handlers in ASPpatidar.shekharNo ratings yet
- CoreDocument13 pagesCoreashish ojhaNo ratings yet
- Page Life Cycle FinalDocument2 pagesPage Life Cycle FinalsandysirNo ratings yet
- Java ServletsUnitVDocument13 pagesJava ServletsUnitVsamreenNo ratings yet
- Servlet Interview Questions: (All APP Labs)Document9 pagesServlet Interview Questions: (All APP Labs)api-3748960No ratings yet
- Routing, Controllers, Acti Ons, Views, Areas : Softuni TeamDocument53 pagesRouting, Controllers, Acti Ons, Views, Areas : Softuni TeamGrig MărcușNo ratings yet
- Web APIDocument56 pagesWeb APIR.A. AruneashNo ratings yet
- Single Sign On:allows You To Get Access To All Other Applications OnceDocument6 pagesSingle Sign On:allows You To Get Access To All Other Applications OncejavaNo ratings yet
- Mad Unit 4 NotesDocument9 pagesMad Unit 4 Notesmaniking9346No ratings yet
- Laravel LifecycleDocument2 pagesLaravel LifecycleKalash ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Spring Boot Intermediate Microservices: Resilient Microservices with Spring Boot 2 and Spring CloudFrom EverandSpring Boot Intermediate Microservices: Resilient Microservices with Spring Boot 2 and Spring CloudNo ratings yet
- API Gateway, Cognito and Node.js LambdasFrom EverandAPI Gateway, Cognito and Node.js LambdasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Web Programming with HTML, CSS, Bootstrap, JavaScript, React.JS, PHP, and MySQL Fourth EditionFrom EverandWeb Programming with HTML, CSS, Bootstrap, JavaScript, React.JS, PHP, and MySQL Fourth EditionNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microsoft Content Management Server DevelopmentFrom EverandAdvanced Microsoft Content Management Server DevelopmentRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (1)