Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Expt3 - Methodology - Linear Expansion
Expt3 - Methodology - Linear Expansion
Uploaded by
Ann KimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Expt3 - Methodology - Linear Expansion
Expt3 - Methodology - Linear Expansion
Uploaded by
Ann KimCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSITY OF SANTO TOMAS
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION AND COMPUTING SCIENCES
PHYSICS 104L, PHYSICS LABORATORY
Coefficient of Linear Expansion (Manual)
Materials: Linear expansion apparatus, steel, copper and brass tubes, steam generator, and rubber
tubing
Methodology:
1] Measure the length of the rod using a meter stick and record it as the initial length, L
0
, in the Data
Table.
2] Determine the room temperature and record it as the initial temperature, T
0
.
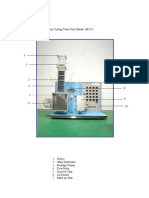
3] Connect the apparatus as shown below in Figure 1a.
Figure 1a. Linear Expansion Experiment using a Steam Figure 1b. Linear Expansion Apparatus by LD Didactic GmbH (n.d.).
Generator by LD Didactic GmbH (n.d.).
4] Adjust the tube while tightening the screw so that the scale pointer indicates a zero reading.
5] Fill the steam generator with water
3
4
its capacity. Cover it tightly, then connect it to the tube outlet
near the scale with rubber tubing. Connect another rubber tubing to the other outlet with its other end
connected to an empty container.
6] Connect the steam generator to 220 V source. Wait until water boils and steam is passed into the tube.
7] The expansion of the rod will be indicated by the scale reading. Record it as the change in length, !L,
of the tube, at the final temperature. Record the steam temperature as the final temperature, T
f
, of
the tube.
8] Compute for the coefficient of linear expansion of the rod using the formula: !=
!L
L
0
(T
f
-T
0
)
9] Repeat procedures 1 to 8 with the other rods.
Table 1. Coefficient of Linear Expansion of some common solids by C.H. Colwell (2014).
References:
LD Didactic GmbH. (n.d.). Longitudinal Expansion Apparatus Instruction Sheet. Retrieved from:
http://www.ld-didactic.de/documents/en-US/GA/GA/3/381/381341e.pdf
Colwell, C.H. (2014). PhysicsLAB. Retrieved from
http://dev.physicslab.org/PracticeProblems/Worksheets/APB/Heat/thermalexpansion.aspx
You might also like
- Report Fluid Friction TestDocument12 pagesReport Fluid Friction TestAbdul Fatah Najmi60% (5)
- Lab 3 Pitot TubeDocument16 pagesLab 3 Pitot TubeTeCkMun100% (1)
- Act 2Document6 pagesAct 2JHON LHOYD CORPUZNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Coefficient of Linear Expansion For Copper, Brass & AluminumDocument8 pagesLab 4 Coefficient of Linear Expansion For Copper, Brass & Aluminumsachin3030100% (2)
- Lab 7Document18 pagesLab 7coopere23100% (1)
- Expt Guide A2 - Efflux TimeDocument3 pagesExpt Guide A2 - Efflux Timeariana religiosoNo ratings yet
- University of Santo Tomas: Faculty of Arts & LettersDocument5 pagesUniversity of Santo Tomas: Faculty of Arts & LettersAnn KimNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literatures ReviewerDocument46 pagesPhilippine Literatures ReviewerAnn Kim75% (4)
- Tehcnical Paper: Calculating Freezing Times in Blast and Plate Freezers by Dr. Andy PearsonDocument36 pagesTehcnical Paper: Calculating Freezing Times in Blast and Plate Freezers by Dr. Andy PearsonBerry_1986_Berry100% (1)
- Expt 3 - Methodology - Linear Expansion PDFDocument1 pageExpt 3 - Methodology - Linear Expansion PDFClyde Ravi R. BiteraNo ratings yet
- E301: Linear ExpansionDocument5 pagesE301: Linear ExpansionPJ Bundalian100% (1)
- Experiment 2Document4 pagesExperiment 2cawke cabdi raxiimNo ratings yet
- U3 Thermal Expansion in Solids and LiquidsDocument5 pagesU3 Thermal Expansion in Solids and LiquidsMUHAMMAD AMEERUL AIFFIX BIN GHAZALINo ratings yet
- Manual PVTDocument17 pagesManual PVTDanyela LuengasNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Coefficient of Linear ExpansionDocument4 pagesMeasuring The Coefficient of Linear ExpansionNorbert StarotchiNo ratings yet
- Models - Heat.turbulent Heat ExchangerDocument18 pagesModels - Heat.turbulent Heat ExchangerMaximiliano FaríaNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of Linear Expansion: 1) IntroductionDocument10 pagesCoefficient of Linear Expansion: 1) IntroductionCynthia PeterNo ratings yet
- Linear Thermal ExpansionDocument13 pagesLinear Thermal ExpansionDhanvini BasavaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Fluid FrictionDocument7 pagesLab Report Fluid FrictionMohd Haikal ShukorNo ratings yet
- Determining The Volumetric Expansion Coefficient of LiquidsDocument7 pagesDetermining The Volumetric Expansion Coefficient of LiquidsUgur ASİT100% (2)
- SteelDocument6 pagesSteelayesha amjadNo ratings yet
- 13 Thermal ExpansionDocument4 pages13 Thermal ExpansionSumit GhoshNo ratings yet
- 2006 Part IPaper 1Document9 pages2006 Part IPaper 1Oliver IyerNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 - FreeDocument15 pagesExperiment 8 - Freeluis_uni_fimNo ratings yet
- Thermal ConductivityDocument19 pagesThermal ConductivityNGOYA COURTNEYNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Coefficient of Double Pipe Heat ExchangerDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer Coefficient of Double Pipe Heat ExchangerSushil KumarNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 1 ThermoDocument7 pagesEXPERIMENT 1 ThermoDogus HurdoganogluNo ratings yet
- Liew 2012 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 395 012066Document9 pagesLiew 2012 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 395 012066Yusuf EfendiNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Coefficient of Linear Expansion For Copper, Steel, and AluminumDocument4 pagesMeasuring The Coefficient of Linear Expansion For Copper, Steel, and AluminumSaifNo ratings yet
- Linear CoefficientDocument6 pagesLinear Coefficientayesha amjadNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 001793109290054V Main PDFDocument13 pages1 s2.0 001793109290054V Main PDF李品賢No ratings yet
- New Developments in Differential EbulliometryDocument13 pagesNew Developments in Differential EbulliometryTheolenNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of Linear ExpansionDocument3 pagesCoefficient of Linear ExpansionJameil Decatoria Magomnang Jr.No ratings yet
- Thermal - Expansion and ConductivityDocument7 pagesThermal - Expansion and ConductivityrasprasadNo ratings yet
- G. Benedek, P. Nieto and J.P. Toennies - The Geyser Effect in The Expansion of Solid Helium Into VacuumDocument13 pagesG. Benedek, P. Nieto and J.P. Toennies - The Geyser Effect in The Expansion of Solid Helium Into VacuumJuaxmawNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer ManualDocument30 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer ManualSushil ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Fahad Sauod Opt.Document23 pagesFahad Sauod Opt.Haitham AliNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Report 1 20Document18 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab Report 1 20manthan100% (1)
- Exp 01Document24 pagesExp 01Sadia HasanNo ratings yet
- Lab 4-Friction Losses and Minor LossesDocument7 pagesLab 4-Friction Losses and Minor LossesJJ Sean CruzNo ratings yet
- Calibration of ThermometersDocument24 pagesCalibration of ThermometerspsgonzalesNo ratings yet
- Civl 151 LAB2Document5 pagesCivl 151 LAB2Ong George SammyNo ratings yet
- Determination of Coefficient of Linear Expansion of A Metal RodDocument3 pagesDetermination of Coefficient of Linear Expansion of A Metal RodKhadeejaNo ratings yet
- CFD Analysis of Feedwater Flow in The HPLWR Pressure Vessel: Helena - Foulonk@iket - Fzk.deDocument4 pagesCFD Analysis of Feedwater Flow in The HPLWR Pressure Vessel: Helena - Foulonk@iket - Fzk.deSlim KanounNo ratings yet
- Mapúa University Department of Physics: Experiment No. 105Document5 pagesMapúa University Department of Physics: Experiment No. 105qweqweNo ratings yet
- MC Kee - Thermosiphon Reboileres A ReviewDocument7 pagesMC Kee - Thermosiphon Reboileres A Reviewbltzkrig100% (1)
- Inear Coefficient of Thermal Expansion Lab: Reading AssignmentDocument8 pagesInear Coefficient of Thermal Expansion Lab: Reading AssignmentchiranjiviraiNo ratings yet
- 305-261/262 Measurement Laboratory Experiment IV Time ConstantDocument4 pages305-261/262 Measurement Laboratory Experiment IV Time ConstantMohammad KhNo ratings yet
- Natural ConvectionDocument6 pagesNatural ConvectionSarvajot SinghNo ratings yet
- Informe Del Laboratorio de Fisica LLDocument9 pagesInforme Del Laboratorio de Fisica LLDaniela Maquera MamaniNo ratings yet
- Fallsem2016-17 4628 RM001 Mee303 ElaDocument57 pagesFallsem2016-17 4628 RM001 Mee303 ElamansurNo ratings yet
- Fluid Phase Equilibria, 87 (1993) 133-152Document20 pagesFluid Phase Equilibria, 87 (1993) 133-152Gaurav KunduNo ratings yet
- I. Determination of E/k Through Electrolysis Process: Background TheoryDocument4 pagesI. Determination of E/k Through Electrolysis Process: Background TheoryJavier MéndezNo ratings yet
- Exp301 Linear ExpansionDocument4 pagesExp301 Linear ExpansionJhenz Santos Bayadas0% (1)
- Cooling Tower (From Apparatus To Calculation Only) )Document13 pagesCooling Tower (From Apparatus To Calculation Only) )AlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Linear ExpansionDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 1: Linear ExpansionTreksha DCNo ratings yet
- Direq/CorDocument64 pagesDireq/CorMohamed Ben MansourNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument2 pagesResearch Proposalmike kandoloNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant in Capillary Tube PDFDocument6 pagesRefrigerant in Capillary Tube PDFMayank Kumar100% (2)
- Simulation and Study of Shell and Tube Type Heat EDocument9 pagesSimulation and Study of Shell and Tube Type Heat EILEENVIRUSNo ratings yet
- Dphe PDFDocument4 pagesDphe PDFMutiaraNo ratings yet
- Dphe PDFDocument4 pagesDphe PDFMutiaraNo ratings yet
- Case Study-Time SeriesDocument1 pageCase Study-Time SeriesAnn KimNo ratings yet
- Real Enterprise ArchitectureDocument157 pagesReal Enterprise ArchitectureAnn Kim100% (3)
- RC Chapter 1: Study Online atDocument2 pagesRC Chapter 1: Study Online atAnn KimNo ratings yet
- VoiceoverDocument2 pagesVoiceoverAnn KimNo ratings yet
- History of Socio AnthropologyDocument3 pagesHistory of Socio AnthropologyAnn KimNo ratings yet
- Towards A Christian Morality Part IIDocument5 pagesTowards A Christian Morality Part IIAnn KimNo ratings yet
- General Ledger: Date Particulars F Debit Date Particulars F Credit Date Particulars FDocument10 pagesGeneral Ledger: Date Particulars F Debit Date Particulars F Credit Date Particulars FAnn KimNo ratings yet
- Class of AccountsDocument5 pagesClass of AccountssalynnaNo ratings yet
- See The Sights of San FranciscoDocument2 pagesSee The Sights of San FranciscoAnn KimNo ratings yet
- ATM Specification, ToC, BodyDocument8 pagesATM Specification, ToC, BodyAnn KimNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literature PrelimsDocument28 pagesPhilippine Literature PrelimsAnn Kim100% (4)
- Calculator TechniquesDocument31 pagesCalculator TechniquesAnn Kim100% (2)
- Definition of LITERATUREDocument2 pagesDefinition of LITERATUREAnn KimNo ratings yet
- 2 Stars Tier: WaterDocument11 pages2 Stars Tier: WaterAnn KimNo ratings yet
- Game Rules:: Athena Pyrrhus AchillesDocument2 pagesGame Rules:: Athena Pyrrhus AchillesAnn KimNo ratings yet
- Xray FilmsDocument13 pagesXray FilmspriyankaagarwallNo ratings yet
- ECSS E ST 35C (15november2008) PDFDocument99 pagesECSS E ST 35C (15november2008) PDFAndreeNo ratings yet
- BEARINGS by HarishDocument42 pagesBEARINGS by HarishHarishNo ratings yet
- Estimating Drift Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Structural WallsDocument31 pagesEstimating Drift Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Structural WallsPastor PachecoNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Design of Moulds Molding PartsDocument8 pagesUnit-V Design of Moulds Molding Partsyuvaraj4509No ratings yet
- Externally Post-Tensioned Carbon FRP Bar System For de Ection ControlDocument12 pagesExternally Post-Tensioned Carbon FRP Bar System For de Ection ControlGedysonLimaNo ratings yet
- Visible Light PresentationDocument17 pagesVisible Light PresentationMichelle Leigh100% (1)
- Grade 6 DLL Science 6 q3 Week 1Document5 pagesGrade 6 DLL Science 6 q3 Week 1MICHELE PEREZNo ratings yet
- CDC - Meehanite - Tuyauterie Acid SulfuriqueDocument3 pagesCDC - Meehanite - Tuyauterie Acid SulfuriqueAyoub LaouinateNo ratings yet
- DRM-Double Ring Magnetron en NetDocument4 pagesDRM-Double Ring Magnetron en NetkrivenkoNo ratings yet
- Redox PhotobleachingDocument5 pagesRedox PhotobleachingKapil BambardekarNo ratings yet
- Equipment CatalogDocument6 pagesEquipment CatalogHannah Patricia TanNo ratings yet
- Baseplate 4 Bolts For PoleDocument5 pagesBaseplate 4 Bolts For PoleAlma M. LaraNo ratings yet
- Inhalt: Marine Catalogue 2005/06Document36 pagesInhalt: Marine Catalogue 2005/06Philip van AstNo ratings yet
- NMR - WATER Exploration, Presentation - Water - ProjectDocument35 pagesNMR - WATER Exploration, Presentation - Water - Projectmichel louis friedmanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Specific Gravity of Hydraulic CementDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 1 Specific Gravity of Hydraulic CementManuel John Contridas PallonesNo ratings yet
- Kishan Intership ReportDocument20 pagesKishan Intership ReportBhavesh PariharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Chemical KineticsDocument7 pagesChapter 4 - Chemical KineticsMADHAVNo ratings yet
- Teknologi Nanopartikel Untuk Penghantaran ObatDocument56 pagesTeknologi Nanopartikel Untuk Penghantaran ObatYunita KurniaNo ratings yet
- WB4303EDocument1 pageWB4303EcwiksjNo ratings yet
- PSC Unit (2) - NoRestrictionDocument3 pagesPSC Unit (2) - NoRestrictionAbinayaHemaRajNo ratings yet
- Brosjyre ChemineerDocument14 pagesBrosjyre ChemineerRaul DiazNo ratings yet
- Remaining Fatigue Life of Corroded SteelDocument10 pagesRemaining Fatigue Life of Corroded SteelRaees MazharNo ratings yet
- Stone Three Portable Pulp Sensor (Bubble Sizer) Product BrochureDocument1 pageStone Three Portable Pulp Sensor (Bubble Sizer) Product BrochureRafaelNo ratings yet
- Plastic Omnium Tank Shell PDFDocument12 pagesPlastic Omnium Tank Shell PDFkamelNo ratings yet
- Guide For The Preparation and Bend Testing of Welder and Welding Procedure Qualification Test SpecimensDocument2 pagesGuide For The Preparation and Bend Testing of Welder and Welding Procedure Qualification Test Specimensmadhu_raz6834No ratings yet
- Materi Perpindahan Kalor - BAB 3Document32 pagesMateri Perpindahan Kalor - BAB 3winandaNo ratings yet
- Millikan Oil Drop ExperimentDocument6 pagesMillikan Oil Drop ExperimentruleevanNo ratings yet
- IAGP 2018 - Adrian-Moreno-Michel-Sivila - Dynamic Material Balance in GC NFR With We - vs4-1Document21 pagesIAGP 2018 - Adrian-Moreno-Michel-Sivila - Dynamic Material Balance in GC NFR With We - vs4-1Marcelo MichelNo ratings yet