Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Trapezium Rule
The Trapezium Rule
Uploaded by
wolfretonmathsCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CPM Calculus Chapter 1-FULLDocument26 pagesCPM Calculus Chapter 1-FULLSquiggleTheCat83% (6)
- Using Parametric Equations - Solutions PDFDocument4 pagesUsing Parametric Equations - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Using Parametric Equations Exercise PDFDocument1 pageUsing Parametric Equations Exercise PDFwolfretonmaths0% (2)
- Using Graphs - Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesUsing Graphs - Solutions PDFwolfretonmaths100% (1)
- Connected Particles Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesConnected Particles Exercise PDFwolfretonmaths100% (1)
- Using Graphs Exercise PDFDocument4 pagesUsing Graphs Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Connected Particles - Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesConnected Particles - Solutions PDFwolfretonmaths67% (3)
- Using GraphsDocument9 pagesUsing GraphswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Numerical IntegrationDocument42 pagesChapter 5 Numerical Integrationmuhd munzirNo ratings yet
- TrigDocument38 pagesTrigM.T. K.No ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument41 pagesPlane and Spherical TrigonometryHowie BanestNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument43 pagesPlane and Spherical TrigonometryLeonard Diego Bareng IINo ratings yet
- 2011 GCE A Level Solution H2 Math Paper 2Document12 pages2011 GCE A Level Solution H2 Math Paper 2lacewingNo ratings yet
- Numerical IntegrationDocument9 pagesNumerical Integrationyhzsgy26m6No ratings yet
- Chapter6 (MBI) ElDocument51 pagesChapter6 (MBI) Eljokowi123No ratings yet
- Please Use The Following Google Form Link To Answer The Following QuestionsDocument4 pagesPlease Use The Following Google Form Link To Answer The Following QuestionsPrakash AnandNo ratings yet
- Calculus ET1 AntonDocument4 pagesCalculus ET1 Antonaceit911No ratings yet
- 6.6 Pose Graph SLAMDocument11 pages6.6 Pose Graph SLAMeverNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods ECE Dept.: Uphsd - CalambaDocument41 pagesNumerical Methods ECE Dept.: Uphsd - CalambaShantal MarieNo ratings yet
- Week08&09 - Numerical Integration & Differentiation PDFDocument39 pagesWeek08&09 - Numerical Integration & Differentiation PDFnoorhafiz07No ratings yet
- ME5110 Grid GenerationDocument10 pagesME5110 Grid GenerationlakiizNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Trajectory Compression: 2022 Fall EECS205002 Linear Algebra Due: 2022/12/14Document4 pagesAssignment 3: Trajectory Compression: 2022 Fall EECS205002 Linear Algebra Due: 2022/12/14Samuel DharmaNo ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics With MATLAB Applications: Corrections ToDocument10 pagesClassical Mechanics With MATLAB Applications: Corrections ToSuhailUmarNo ratings yet
- Section 10-5 Parametric EquationsDocument11 pagesSection 10-5 Parametric EquationsBhupesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ballbeam EE380 Fall09 PDFDocument13 pagesBallbeam EE380 Fall09 PDFShahid KINo ratings yet
- 5.5 Trapezoid RuleDocument9 pages5.5 Trapezoid RuleCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Five-Dimensional Warped Geometry With A Bulk Scalar Field: DPNU-01-24 Hep-Th/0109040Document8 pagesFive-Dimensional Warped Geometry With A Bulk Scalar Field: DPNU-01-24 Hep-Th/0109040wendel_physicsNo ratings yet
- Ece2306 Surveying IIIDocument65 pagesEce2306 Surveying IIIInfinity Architectural design technologistNo ratings yet
- Numerical Computing Lab 3Document8 pagesNumerical Computing Lab 3Aamna ImranNo ratings yet
- End Term PaperDocument2 pagesEnd Term PaperRingtone darbaarNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 - Numerical Integration (II)Document20 pagesLecture10 - Numerical Integration (II)Na2ryNo ratings yet
- 141 8.6 Lecture Notes PDFDocument4 pages141 8.6 Lecture Notes PDFMuqaddas SarwarNo ratings yet
- P1 Engineering Computation: David MurrayDocument46 pagesP1 Engineering Computation: David MurrayStelios KondosNo ratings yet
- Proof of The Cofactor Expansion Theorem 1Document13 pagesProof of The Cofactor Expansion Theorem 1pasomagaNo ratings yet
- Multi Scalar Multiplication For Recursive SNARKs and MoreDocument16 pagesMulti Scalar Multiplication For Recursive SNARKs and Moreeth everNo ratings yet
- Matrix Algorithms (Part 1)Document28 pagesMatrix Algorithms (Part 1)Debangan DeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Roots of EquationDocument20 pagesChapter 2 Roots of EquationDawit MengisteabNo ratings yet
- Efficient Clipping of Arbitrary PolygonsDocument8 pagesEfficient Clipping of Arbitrary Polygons梁耀灿No ratings yet
- Improper Integrals Involving Rational and Exponential Functions PDFDocument10 pagesImproper Integrals Involving Rational and Exponential Functions PDFhammoudeh13No ratings yet
- Fractal Dimension As Measure of Control TimeDocument8 pagesFractal Dimension As Measure of Control Timecsernak2No ratings yet
- Mechines of Mechinism Chapter 2Document13 pagesMechines of Mechinism Chapter 2abdulmajeedNo ratings yet
- Interduction: Trapezoidal RuleDocument5 pagesInterduction: Trapezoidal RuleanandNo ratings yet
- Planar Robot KinematicsDocument7 pagesPlanar Robot Kinematicsasalifew belachewNo ratings yet
- Nahp1 2020 PDFDocument4 pagesNahp1 2020 PDFVangheli TVNo ratings yet
- FX X X X Orx X X X FX X X: Test 1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesFX X X X Orx X X X FX X X: Test 1 SolutionsexamkillerNo ratings yet
- A ApproximationsDocument8 pagesA ApproximationschatuusumitavaNo ratings yet
- Linear Functions: SummaryDocument9 pagesLinear Functions: SummaryDusan KadovicNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 (Week 5)Document3 pagesTutorial 4 (Week 5)kbxw9s7x6jNo ratings yet
- m20 Rev4 - Dugopolski - PDFDocument2 pagesm20 Rev4 - Dugopolski - PDFSkyezine Via Kit FoxNo ratings yet
- M2V104 FS 01eDocument23 pagesM2V104 FS 01eLewis BryanNo ratings yet
- Further Trigonometric EquationsDocument3 pagesFurther Trigonometric EquationswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Celm 3Document40 pagesCelm 3Xinrex NicolasNo ratings yet
- Trapezoidal Rule With Non-Uniform Spacing - IBDP Mathematics - Applications and Interpretation SL FE2021 - KognityDocument8 pagesTrapezoidal Rule With Non-Uniform Spacing - IBDP Mathematics - Applications and Interpretation SL FE2021 - KognityMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- SEM 3 BC0043 1 Computer Oriented Numerical MethodsDocument20 pagesSEM 3 BC0043 1 Computer Oriented Numerical MethodsRajat NandyNo ratings yet
- Geostatistics Project 2 (PETE 630)Document28 pagesGeostatistics Project 2 (PETE 630)dptsen100% (1)
- Using Parametric EquationsDocument5 pagesUsing Parametric EquationswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- I NtegratDocument18 pagesI NtegratArsene MawejaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Number Theory 163: K K K 1 K 1 1 0 0 1 2 KDocument7 pagesApplications of Number Theory 163: K K K 1 K 1 1 0 0 1 2 Ktukicool8892No ratings yet
- A ApproximationsDocument8 pagesA Approximationsafsas fasfasfasNo ratings yet
- MWN 780 Assignment1 Block 1Document5 pagesMWN 780 Assignment1 Block 1DenielNo ratings yet
- SmithMinton Calculus ET 5e C03 S06Document29 pagesSmithMinton Calculus ET 5e C03 S06Mario AguilarNo ratings yet
- Cal1 Chapter 3Document80 pagesCal1 Chapter 3Vân Anh Nguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Using Vectors Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesUsing Vectors Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Forces & Equilibrium Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesForces & Equilibrium Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion - Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesProjectile Motion - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesProjectile Motion Exercise PDFwolfretonmaths100% (3)
- Constant Acceleration Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesConstant Acceleration Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Friction Exercise PDFDocument1 pageFriction Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Using Partial Fractions in Integration Exercise PDFDocument1 pageUsing Partial Fractions in Integration Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum Exercise PDFDocument1 pageConservation of Momentum Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion - Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Conservation of MomentumDocument2 pagesConservation of MomentumwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- The Binomial ExpansionDocument6 pagesThe Binomial ExpansionwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum CPDocument1 pageConservation of Momentum CPwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion CPDocument1 pageProjectile Motion CPwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument10 pagesProjectile MotionwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Vectors in Two & Three Dimensions Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesVectors in Two & Three Dimensions Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
The Trapezium Rule
The Trapezium Rule
Uploaded by
wolfretonmathsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Trapezium Rule
The Trapezium Rule
Uploaded by
wolfretonmathsCopyright:
Available Formats
AQA Core 2 Calculus
1 of 2 15/01/13 MEI
Section 3: The trapezium rule
Notes and Examples
These notes contain subsections on:
- The trapezium rule
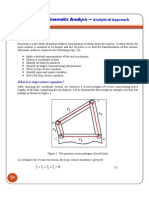
The trapezium rule
Not all functions can be integrated. For functions which cannot be integrated,
you can find an approximate value for a definite integral by using a numerical
method such as the trapezium rule. In this method, the area under the graph
can be approximated by dividing it into a number of trapezia.
If the trapezia have width h, and the y-coordinates are y
1
, y
2
, , y
n,
then the
total area A is:
( )
0 1 2 1
2 ...
2
n n
h
A y y y y y
~ + + + + + (
where
( ) b a
h
n
= .
Example 1
(i) Use the trapezium rule with: (a) 3 strips and (b) 6 strips, to find the
approximate value of
3
0
1 d +
}
x x .
(ii) Given that the exact value of this integral is
14
3
, find the relative error in each
case, and explain why the trapezium rule is an under-estimate of the true
value.
O h a b
y
0
y
1
y
2
y
3
y
n
AQA C2 Calculus 3 Notes and Examples
2 of 2 15/01/13 MEI
Solution
(i) (a) With 3 strips of width h = 1:
( )
1
2
1 2 2 2 3 4.646264... A
(
~ + + + =
(b) With 6 strips of width h = 0.5:
( )
1
4
1 2 2 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4.661488... A
(
~ + + + + + + =
(ii) (a) relative error =
14
3
14
3
4.646264
= 0.00437
(b) relative error =
14
3
14
3
4.661488
= 0.00111
From the graph of the function, it is clear that the trapezia lie underneath the curve, so
the trapezium rule gives an under-estimate.
You can see more examples like this one using the Flash resource The
trapezium rule.
You can also use the Geogebra resource The trapezium rule to see the
result of applying the trapezium rule with different numbers of strips.
-1
-1 0 1 2 3
x 0 1 2 3
y 1
2 3
2
x 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
y 1
1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5
2
You might also like
- CPM Calculus Chapter 1-FULLDocument26 pagesCPM Calculus Chapter 1-FULLSquiggleTheCat83% (6)
- Using Parametric Equations - Solutions PDFDocument4 pagesUsing Parametric Equations - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Using Parametric Equations Exercise PDFDocument1 pageUsing Parametric Equations Exercise PDFwolfretonmaths0% (2)
- Using Graphs - Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesUsing Graphs - Solutions PDFwolfretonmaths100% (1)
- Connected Particles Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesConnected Particles Exercise PDFwolfretonmaths100% (1)
- Using Graphs Exercise PDFDocument4 pagesUsing Graphs Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Connected Particles - Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesConnected Particles - Solutions PDFwolfretonmaths67% (3)
- Using GraphsDocument9 pagesUsing GraphswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Numerical IntegrationDocument42 pagesChapter 5 Numerical Integrationmuhd munzirNo ratings yet
- TrigDocument38 pagesTrigM.T. K.No ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument41 pagesPlane and Spherical TrigonometryHowie BanestNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument43 pagesPlane and Spherical TrigonometryLeonard Diego Bareng IINo ratings yet
- 2011 GCE A Level Solution H2 Math Paper 2Document12 pages2011 GCE A Level Solution H2 Math Paper 2lacewingNo ratings yet
- Numerical IntegrationDocument9 pagesNumerical Integrationyhzsgy26m6No ratings yet
- Chapter6 (MBI) ElDocument51 pagesChapter6 (MBI) Eljokowi123No ratings yet
- Please Use The Following Google Form Link To Answer The Following QuestionsDocument4 pagesPlease Use The Following Google Form Link To Answer The Following QuestionsPrakash AnandNo ratings yet
- Calculus ET1 AntonDocument4 pagesCalculus ET1 Antonaceit911No ratings yet
- 6.6 Pose Graph SLAMDocument11 pages6.6 Pose Graph SLAMeverNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods ECE Dept.: Uphsd - CalambaDocument41 pagesNumerical Methods ECE Dept.: Uphsd - CalambaShantal MarieNo ratings yet
- Week08&09 - Numerical Integration & Differentiation PDFDocument39 pagesWeek08&09 - Numerical Integration & Differentiation PDFnoorhafiz07No ratings yet
- ME5110 Grid GenerationDocument10 pagesME5110 Grid GenerationlakiizNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Trajectory Compression: 2022 Fall EECS205002 Linear Algebra Due: 2022/12/14Document4 pagesAssignment 3: Trajectory Compression: 2022 Fall EECS205002 Linear Algebra Due: 2022/12/14Samuel DharmaNo ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics With MATLAB Applications: Corrections ToDocument10 pagesClassical Mechanics With MATLAB Applications: Corrections ToSuhailUmarNo ratings yet
- Section 10-5 Parametric EquationsDocument11 pagesSection 10-5 Parametric EquationsBhupesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ballbeam EE380 Fall09 PDFDocument13 pagesBallbeam EE380 Fall09 PDFShahid KINo ratings yet
- 5.5 Trapezoid RuleDocument9 pages5.5 Trapezoid RuleCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Five-Dimensional Warped Geometry With A Bulk Scalar Field: DPNU-01-24 Hep-Th/0109040Document8 pagesFive-Dimensional Warped Geometry With A Bulk Scalar Field: DPNU-01-24 Hep-Th/0109040wendel_physicsNo ratings yet
- Ece2306 Surveying IIIDocument65 pagesEce2306 Surveying IIIInfinity Architectural design technologistNo ratings yet
- Numerical Computing Lab 3Document8 pagesNumerical Computing Lab 3Aamna ImranNo ratings yet
- End Term PaperDocument2 pagesEnd Term PaperRingtone darbaarNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 - Numerical Integration (II)Document20 pagesLecture10 - Numerical Integration (II)Na2ryNo ratings yet
- 141 8.6 Lecture Notes PDFDocument4 pages141 8.6 Lecture Notes PDFMuqaddas SarwarNo ratings yet
- P1 Engineering Computation: David MurrayDocument46 pagesP1 Engineering Computation: David MurrayStelios KondosNo ratings yet
- Proof of The Cofactor Expansion Theorem 1Document13 pagesProof of The Cofactor Expansion Theorem 1pasomagaNo ratings yet
- Multi Scalar Multiplication For Recursive SNARKs and MoreDocument16 pagesMulti Scalar Multiplication For Recursive SNARKs and Moreeth everNo ratings yet
- Matrix Algorithms (Part 1)Document28 pagesMatrix Algorithms (Part 1)Debangan DeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Roots of EquationDocument20 pagesChapter 2 Roots of EquationDawit MengisteabNo ratings yet
- Efficient Clipping of Arbitrary PolygonsDocument8 pagesEfficient Clipping of Arbitrary Polygons梁耀灿No ratings yet
- Improper Integrals Involving Rational and Exponential Functions PDFDocument10 pagesImproper Integrals Involving Rational and Exponential Functions PDFhammoudeh13No ratings yet
- Fractal Dimension As Measure of Control TimeDocument8 pagesFractal Dimension As Measure of Control Timecsernak2No ratings yet
- Mechines of Mechinism Chapter 2Document13 pagesMechines of Mechinism Chapter 2abdulmajeedNo ratings yet
- Interduction: Trapezoidal RuleDocument5 pagesInterduction: Trapezoidal RuleanandNo ratings yet
- Planar Robot KinematicsDocument7 pagesPlanar Robot Kinematicsasalifew belachewNo ratings yet
- Nahp1 2020 PDFDocument4 pagesNahp1 2020 PDFVangheli TVNo ratings yet
- FX X X X Orx X X X FX X X: Test 1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesFX X X X Orx X X X FX X X: Test 1 SolutionsexamkillerNo ratings yet
- A ApproximationsDocument8 pagesA ApproximationschatuusumitavaNo ratings yet
- Linear Functions: SummaryDocument9 pagesLinear Functions: SummaryDusan KadovicNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 (Week 5)Document3 pagesTutorial 4 (Week 5)kbxw9s7x6jNo ratings yet
- m20 Rev4 - Dugopolski - PDFDocument2 pagesm20 Rev4 - Dugopolski - PDFSkyezine Via Kit FoxNo ratings yet
- M2V104 FS 01eDocument23 pagesM2V104 FS 01eLewis BryanNo ratings yet
- Further Trigonometric EquationsDocument3 pagesFurther Trigonometric EquationswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Celm 3Document40 pagesCelm 3Xinrex NicolasNo ratings yet
- Trapezoidal Rule With Non-Uniform Spacing - IBDP Mathematics - Applications and Interpretation SL FE2021 - KognityDocument8 pagesTrapezoidal Rule With Non-Uniform Spacing - IBDP Mathematics - Applications and Interpretation SL FE2021 - KognityMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- SEM 3 BC0043 1 Computer Oriented Numerical MethodsDocument20 pagesSEM 3 BC0043 1 Computer Oriented Numerical MethodsRajat NandyNo ratings yet
- Geostatistics Project 2 (PETE 630)Document28 pagesGeostatistics Project 2 (PETE 630)dptsen100% (1)
- Using Parametric EquationsDocument5 pagesUsing Parametric EquationswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- I NtegratDocument18 pagesI NtegratArsene MawejaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Number Theory 163: K K K 1 K 1 1 0 0 1 2 KDocument7 pagesApplications of Number Theory 163: K K K 1 K 1 1 0 0 1 2 Ktukicool8892No ratings yet
- A ApproximationsDocument8 pagesA Approximationsafsas fasfasfasNo ratings yet
- MWN 780 Assignment1 Block 1Document5 pagesMWN 780 Assignment1 Block 1DenielNo ratings yet
- SmithMinton Calculus ET 5e C03 S06Document29 pagesSmithMinton Calculus ET 5e C03 S06Mario AguilarNo ratings yet
- Cal1 Chapter 3Document80 pagesCal1 Chapter 3Vân Anh Nguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Using Vectors Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesUsing Vectors Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Forces & Equilibrium Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesForces & Equilibrium Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion - Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesProjectile Motion - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesProjectile Motion Exercise PDFwolfretonmaths100% (3)
- Constant Acceleration Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesConstant Acceleration Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Friction Exercise PDFDocument1 pageFriction Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Using Partial Fractions in Integration Exercise PDFDocument1 pageUsing Partial Fractions in Integration Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum Exercise PDFDocument1 pageConservation of Momentum Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion - Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Conservation of MomentumDocument2 pagesConservation of MomentumwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- The Binomial ExpansionDocument6 pagesThe Binomial ExpansionwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum CPDocument1 pageConservation of Momentum CPwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion CPDocument1 pageProjectile Motion CPwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument10 pagesProjectile MotionwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Vectors in Two & Three Dimensions Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesVectors in Two & Three Dimensions Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet