Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ASUD Philippines Planned City Extension - Cagayan de Oro City
ASUD Philippines Planned City Extension - Cagayan de Oro City
Uploaded by
UNHabitatPhilippinesCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Department of Education: Annex C: School Career Guidance Implementation ReportDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Annex C: School Career Guidance Implementation ReportJoy PanesNo ratings yet
- Engine Room Resource ManagementDocument29 pagesEngine Room Resource Managementcarlo panganiban100% (2)
- EpidemiologyDocument58 pagesEpidemiologyrebecca100% (4)
- Bussiness Phone CallsDocument2 pagesBussiness Phone CallsYeison HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Devex 2018 Introduction To Reservoir SimulationDocument52 pagesDevex 2018 Introduction To Reservoir SimulationKonul AlizadehNo ratings yet
- 9 Class Holiday HomeworkDocument5 pages9 Class Holiday HomeworksavageitgirlNo ratings yet
- Industry 4.0. German Standardization RoadmapDocument77 pagesIndustry 4.0. German Standardization Roadmapmihai.banicaNo ratings yet
- Fractions in Excel - Easy Excel Tutorial PDFDocument4 pagesFractions in Excel - Easy Excel Tutorial PDFJamalodeen MohammadNo ratings yet
- Comparative Essay PromptDocument4 pagesComparative Essay Promptapi-293165455No ratings yet
- Director IT Vendor Management in Philadelphia PA Resume Mark DiTomasoDocument3 pagesDirector IT Vendor Management in Philadelphia PA Resume Mark DiTomasoMark DiTomasoNo ratings yet
- PYRAMIDOLOGYDocument92 pagesPYRAMIDOLOGYverdiblue100% (2)
- HieuTQ Asm2 529 PDFDocument16 pagesHieuTQ Asm2 529 PDFQuân ShellNo ratings yet
- KAIZEN: A Lean Manufacturing TechniqueDocument5 pagesKAIZEN: A Lean Manufacturing TechniqueVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- 3673-Article Text-13648-1-10-20230806Document15 pages3673-Article Text-13648-1-10-20230806alrie muhammadNo ratings yet
- Q L F StructuredProgrammingManual Fundamentals SH 080782 JDocument122 pagesQ L F StructuredProgrammingManual Fundamentals SH 080782 JMohamad SafhireNo ratings yet
- 1 (Ciphers)Document23 pages1 (Ciphers)Anand RajNo ratings yet
- Relationships: Ielts Success 4.0Document94 pagesRelationships: Ielts Success 4.0maihuong1181No ratings yet
- Automation and CIMSDocument27 pagesAutomation and CIMSgavin_d265No ratings yet
- Gel in SituDocument10 pagesGel in SituNur IslamiaNo ratings yet
- Cirque Du Soleil-FinalDocument16 pagesCirque Du Soleil-FinalArun Hariharan50% (2)
- RefacDocument5 pagesRefacknight1729No ratings yet
- A Study On E-WalletDocument4 pagesA Study On E-WalletEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Principals' Report 2022 As On 13 NovDocument90 pagesPrincipals' Report 2022 As On 13 NovMohammad SarimNo ratings yet
- CSC 3 Degree: Michigan Department of State PoliceDocument40 pagesCSC 3 Degree: Michigan Department of State PoliceFergus BurnsNo ratings yet
- Autism-Mind, Emotion, and The Spectrum of Autism - Dr. Dan SiegelDocument2 pagesAutism-Mind, Emotion, and The Spectrum of Autism - Dr. Dan Siegelcinfer75No ratings yet
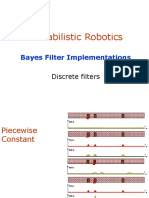
- Probabilistic Robotics: Bayes Filter ImplementationsDocument11 pagesProbabilistic Robotics: Bayes Filter ImplementationsRogers SureNo ratings yet
- b28113433 PDFDocument202 pagesb28113433 PDFJuthika GogoiNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of Classical Association Vol. 14Document278 pagesProceedings of Classical Association Vol. 14pharetimaNo ratings yet
- Paket 6 To Bumn 2024 Tbi - ReadingDocument19 pagesPaket 6 To Bumn 2024 Tbi - ReadingSabrina Jihan NabilaNo ratings yet
ASUD Philippines Planned City Extension - Cagayan de Oro City
ASUD Philippines Planned City Extension - Cagayan de Oro City
Uploaded by
UNHabitatPhilippinesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ASUD Philippines Planned City Extension - Cagayan de Oro City
ASUD Philippines Planned City Extension - Cagayan de Oro City
Uploaded by
UNHabitatPhilippinesCopyright:
Available Formats
September 2014
Urbanizaton Scenario
Cagayan de Oro City is a highly urbanized city in Northern Mindanao. Much of its
urban development has been along the east-west corridor of the Iligan-Cagayan de
Oro-Butuan Natonal Highway.
Over tme, barangays (districts) straddling this highway have evolved into vibrant
commercial and residental areas. Rapid demographic and economic growth in the
last 15 years was accompanied by changes in the citys land use, where forests and
agricultural areas made way for residental and commercial projects.
The landscape of the city was transformed into a highly urbanized area sprawling
from the central business district. Residental subdivisions were built on hills
overlooking the city, and commercial districts thrived along the natonal highway and
main streets. The emerging setlement patern in Cagayan de Oro City is urban sprawl
from poblacion barangays to the next ring of barangays that are no longer in the city
center but are stll connected to it.
If expansion is lef unchecked and unplanned, the city is likely to experience a
lopsided distributon of setlements favoring only a few districts and driven by the
real estate market with gated communites that will hamper urban connectvity and
efcient agglomeratons.
This kind of urban development is clearly unsustainable, necessitatng a guided
and planned city extension (PCE) development.
P
H
I
L
I
P
P
I
N
E
S
P
L
A
N
N
E
D
C
I
T
Y
E
X
T
E
N
S
I
O
N
C
A
G
A
Y
A
N
D
E
O
R
O
Challenges In City Planning & Management
Lack of a comprehensive plan for city
extension
Development is currently driven by the
private sector and poorly regulated
Limited road network and capacity,
resultng in trafc congeston in the
built-up areas
Lack of mass transport to and from the
extension site
Limited technical expertse of local
planners on city extension planning
Land development cost of the extension
site is high due to the sites uneven,
rolling terrain
CAGAYAN DE ORO CITY
Sustainable urbanizaton: planning for urban
growth, resilience, and economic development
planned city extension
Achieving Sustainable
Urban Development (ASUD)
Cagayan de Oro
City Profle
land area: 578.5 square kilometers
population: 602,088 (2010)
annual population growth rate:
2.54%
number of households: 127,672
density (citywide): 1,040 persons
per square kilometer
density continuous urban zone:
2,799 persons per square kilometer
street density: 10.84 kilometers per
square kilometer
intersection density: 92.34 per
square kilometer
number of barangays (districts):
80
economy: Manufacturing,
commercial, services, tourism
internal revenue allocation
share: PHP 796.8 million
(USD 18.3 million)
local sourced revenues:
PHP 1.04 billion (USD 23 million)
total revenue (2012):
Php 1.84 billion (USD 41.82 million)
internal revenue allocation
dependency rate: 48%
ecosystem type: Ridge to reef with
river system (Cagayan River)
city/regional role: Trading center,
government center, conventon area,
educaton area, tourism
special citation: Ranked in 2013
as second most compettve city
in the Philippines by the Natonal
Compettveness Council Philippines
If expansion is lef unchecked and unplanned, the city is
likely to experience a lopsided distributon of setlements
favoring only a few districts...
Absence of a masterplan for a
drainage system
Limited local policies for beter urban
design, especially on regulatng street
sizes and open space
Tendency of land banking
programmes to be reactve, short-
sighted, and parochial
Unmaximized potental of the
old airport site (105 hectares) for
economic and other productve uses
Outdatedness of the Comprehensive
Land Use Plan (last update was in
2000) and the zoning ordinance.
UN-Habitat Philippines
City Extension Profle
Site: District of Lumbia, located at
the midpoint of the north-south
axis of Cagayan de Oro City, about
10 kilometers from the city center.
One of its advantages over other
barangays is its elevaton of 180
meters above sea level, making it
safer than the rest from fooding or
storm surge.
Location: Lumbia, where the
Cagayan de Oro airport was formerly
located, not only links the uptown to
the built-up downtown Cagayan de Oro,
it is considered the gateway to other
provinces such as Bukidnon, providing
an inter-provincial transport hub for
the trade and commerce of agricultural
goods.
Terrain: Flat in the old airport
premises, then gently sloping and
rolling to the west. Calaanan Creek lies
at the center of the site, connectng
Benefts of Planned City Extensions
Improves local
revenue generaton
and local economic
development
Improves efciency
of services and
avoids unregulated sprawling
development
Introduces a good entry point for
long-term climate change planning
and disaster preparedness, especially
in developing human setlements
Beter regulates land development
and optmizes land value by
convertng the site
from a military
use to a mixed-use
development
Increases city wealth
and identty and
provides sustained growth for local
economic development
The plan can serve as a negotatng
tool for natonal government and an
investment promotons tool for the
alternatve use of the old airport
Addresses congeston in the city
center
Addresses housing needs of those
afected by Typhoon Sendong, a tropical
cyclone that totally destroyed 5,800
houses in the city in December 2011
Enhances safety and security
north to Barangay Pagatpat, while
Tagpangi Creek provides a natural
boundary on the west. Natural drainage
follows a northwest directon.
Land Area: 547 hectares
(5.47 square kilometers)
Current Land Use: Residental and
agricultural
Current Zoning: Residental
Cagayan de Oro Cagayan de Oro City Center City Extension Site
Strategic Response: Planned City Extensions
UN-Habitats Achieving Sustainable
Urban Development (ASUD)
programme seeks to address urban
development issues afectng todays
cites. It integrates three pillars
governance and legislaton, fnance and
economy, and planning and design
in developing PCEs. PCEs represent
an alternatve to unplanned urban
expansion characterized by sprawling,
segregated, and poorly connected
developments. The PCE for Cagayan
de Oro City pursues and promotes
the following:
adequate space for streets and
mobility
expansion of mixed housing
disincentvizaton of exclusionary
(gated) developments
sustainable density
engagement of city stakeholders
in planning
a shared vision for the development
of the extension site by all
stakeholders
synergy and connectvity of the site with
the existng city
policy advocacy for the protecton of
public space and land management
improved social integraton
land use reclassifcaton, especially for
the old airport area
strong integraton of eco-tourism
development programmes
climate change adaptaton and disaster
risk reducton.
The city extension area can absorb
of the growth over the next 30
years with adequate density of a
floor area ratio of 1.5
25
%
September 2014
I
C
O
N
S
:
W
W
W
.
F
L
A
T
I
C
O
N
.
C
O
M
.
P
H
O
T
O
S
:
G
O
O
G
L
E
E
A
R
T
H
Situatonal Analysis
Facilitated the establishment of the local
project management structure
Completed city data profling and
mapping
Completed the citys climate change and
vulnerability and adaptaton assessment
report
Facilitated partnerships with
government line agencies
Assessed the policy and legal
environment
Assessed municipal fnances and
fnancial capacity
Facilitated knowledge sharing with
other pilot cites
Conducted technical coaching and
mentoring, including planning
workshops on city extensions
Managed boundary mapping and land
owner inventory listng within the city
extension site (ongoing)
Prepared the conceptual plan with the
city technical working group.
Actvites &
Milestones
Conceptual Plan Map
UN-Habitat Philippines
What We Have Accomplished
Introduced ASUD concepts
and approaches which the
city embraced to guide their
development plans henceforth
Enhanced the capacites of
technical working groups for
urban planning, urban economy,
and municipal fnance and legal
support through sustained
technical mentoring and
coaching
Completed climate change
vulnerability and adaptaton
assessment
Formulated the city extension
conceptual plan with the city
team, which was then presented
to the city mayor and local
partners
Assessed the fnancial capacity
of the city
Scaled up advocacies for
mixed land uses, especially
among land owners, who then
considered the PCE in their
individual private development
plans
Extended the urban planning
horizon to 30 years from the
current 5- to 10-year paradigm
among city planners
Enhance
profle infor-
maton of the
site: inventory
of landowners,
boundary and
facilites mapping
Stakeholder consultatons and
consensus building
Next Steps: Moving the PCE Forward
Enhancement of
the city extension
conceptual plan
Partnership with
universites and
professional associatons for spa-
tal planning and data gathering
Completon of the legal and local
legislatve framework assessment
to provide specifc
recommendatons
on how to enforce
and regulate the
development of
the site
Financial modeling to identfy
investment optons and pro-
grammes
I
C
O
N
S
:
W
W
W
.
F
L
A
T
I
C
O
N
.
C
O
M
UN-Habitat Philippines UN-Habitat Regional Office
for Asia and the Pacific
ACROS Fukuoka Building, 8th Floor
1-1-1 Tenjin, Chuo-ku, Fukuoka 810-0001
Japan
Tel: (81-92) 724 - 7121 / 23
Fax: (81-92) 724 - 7124
habitat.fukuoka@unhabitat.org
htp://www.fukuoka.unhabitat.org
31st Floor, Yuchengco Tower, RCBC Plaza
6819 Ayala Avenue, Makat City 1229
Philippines
Tel: (63-2) 901 - 04 - 32
htp://unhabitat.org.ph
UN-Habitat Global Website
htp://unhabitat.org
Cagayan de Oro City Planning
and Development Office
3rd Floor, South Wing Administratve
Building, City Hall Compound,
Capistrano Street, Cagayan de Oro City
Philippines
Tel: (63-39) 857 - 31 - 48
htp://www.cagayandeoro.gov.ph
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Department of Education: Annex C: School Career Guidance Implementation ReportDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Annex C: School Career Guidance Implementation ReportJoy PanesNo ratings yet
- Engine Room Resource ManagementDocument29 pagesEngine Room Resource Managementcarlo panganiban100% (2)
- EpidemiologyDocument58 pagesEpidemiologyrebecca100% (4)
- Bussiness Phone CallsDocument2 pagesBussiness Phone CallsYeison HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Devex 2018 Introduction To Reservoir SimulationDocument52 pagesDevex 2018 Introduction To Reservoir SimulationKonul AlizadehNo ratings yet
- 9 Class Holiday HomeworkDocument5 pages9 Class Holiday HomeworksavageitgirlNo ratings yet
- Industry 4.0. German Standardization RoadmapDocument77 pagesIndustry 4.0. German Standardization Roadmapmihai.banicaNo ratings yet
- Fractions in Excel - Easy Excel Tutorial PDFDocument4 pagesFractions in Excel - Easy Excel Tutorial PDFJamalodeen MohammadNo ratings yet
- Comparative Essay PromptDocument4 pagesComparative Essay Promptapi-293165455No ratings yet
- Director IT Vendor Management in Philadelphia PA Resume Mark DiTomasoDocument3 pagesDirector IT Vendor Management in Philadelphia PA Resume Mark DiTomasoMark DiTomasoNo ratings yet
- PYRAMIDOLOGYDocument92 pagesPYRAMIDOLOGYverdiblue100% (2)
- HieuTQ Asm2 529 PDFDocument16 pagesHieuTQ Asm2 529 PDFQuân ShellNo ratings yet
- KAIZEN: A Lean Manufacturing TechniqueDocument5 pagesKAIZEN: A Lean Manufacturing TechniqueVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- 3673-Article Text-13648-1-10-20230806Document15 pages3673-Article Text-13648-1-10-20230806alrie muhammadNo ratings yet
- Q L F StructuredProgrammingManual Fundamentals SH 080782 JDocument122 pagesQ L F StructuredProgrammingManual Fundamentals SH 080782 JMohamad SafhireNo ratings yet
- 1 (Ciphers)Document23 pages1 (Ciphers)Anand RajNo ratings yet
- Relationships: Ielts Success 4.0Document94 pagesRelationships: Ielts Success 4.0maihuong1181No ratings yet
- Automation and CIMSDocument27 pagesAutomation and CIMSgavin_d265No ratings yet
- Gel in SituDocument10 pagesGel in SituNur IslamiaNo ratings yet
- Cirque Du Soleil-FinalDocument16 pagesCirque Du Soleil-FinalArun Hariharan50% (2)
- RefacDocument5 pagesRefacknight1729No ratings yet
- A Study On E-WalletDocument4 pagesA Study On E-WalletEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Principals' Report 2022 As On 13 NovDocument90 pagesPrincipals' Report 2022 As On 13 NovMohammad SarimNo ratings yet
- CSC 3 Degree: Michigan Department of State PoliceDocument40 pagesCSC 3 Degree: Michigan Department of State PoliceFergus BurnsNo ratings yet
- Autism-Mind, Emotion, and The Spectrum of Autism - Dr. Dan SiegelDocument2 pagesAutism-Mind, Emotion, and The Spectrum of Autism - Dr. Dan Siegelcinfer75No ratings yet
- Probabilistic Robotics: Bayes Filter ImplementationsDocument11 pagesProbabilistic Robotics: Bayes Filter ImplementationsRogers SureNo ratings yet
- b28113433 PDFDocument202 pagesb28113433 PDFJuthika GogoiNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of Classical Association Vol. 14Document278 pagesProceedings of Classical Association Vol. 14pharetimaNo ratings yet
- Paket 6 To Bumn 2024 Tbi - ReadingDocument19 pagesPaket 6 To Bumn 2024 Tbi - ReadingSabrina Jihan NabilaNo ratings yet