Professional Documents
Culture Documents
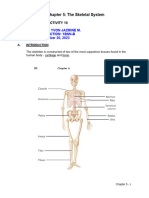
Invertebrate - : Caco Caf So Ca Po Ca
Invertebrate - : Caco Caf So Ca Po Ca
Uploaded by
yashsodhaniCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Topic 6 Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesTopic 6 Skeletal SystemMary Ann Morillo TenederoNo ratings yet
- Skeleton: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesSkeleton: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediacut amaliaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Biology Ss1Document33 pages2nd Term Biology Ss1dasiakennethNo ratings yet
- Bone and CartilageDocument61 pagesBone and CartilageMohamed AtefNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument23 pagesUntitled PresentationSamia MustafaNo ratings yet
- Form 4 17 Support Movement and ProtectionDocument62 pagesForm 4 17 Support Movement and ProtectionRichard NestorNo ratings yet
- Locomotion SystemDocument151 pagesLocomotion Systemaynurwepayewa40No ratings yet
- SKELETAL SYSTEM ReviewerDocument7 pagesSKELETAL SYSTEM ReviewerKrize Colene dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument157 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System OverviewDocument2 pagesAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System OverviewChula Anak Bina IPGKRNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System OverviewDocument2 pagesAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System OverviewChula Anak Bina IPGKRNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Supporting SystemDocument15 pagesTissue and Supporting SystemjolaolumolusinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument157 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsOliver Talip100% (1)
- Tissue 2Document34 pagesTissue 2nneduchiemerieNo ratings yet
- Movement and Locomotion Question Bank For Class 9Document7 pagesMovement and Locomotion Question Bank For Class 9piyushmandal4567No ratings yet
- SkeletalsystemDocument43 pagesSkeletalsystemSamantha EllaineNo ratings yet
- UPV Bio 1 NotesDocument24 pagesUPV Bio 1 NotesJustin CatalanNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Lecture: Functions of The IntegumentsDocument8 pagesGeneral Zoology Lecture: Functions of The IntegumentsKirkNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMDocument12 pagesAnaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMKenzoNo ratings yet
- 20201012-20201019-1149-Skeletal SystemDocument61 pages20201012-20201019-1149-Skeletal Systemdrin zekaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Lab Exercise - Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesWeek 5 Lab Exercise - Skeletal SystemchristinelorrainegatchalianNo ratings yet
- Module Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesModule Skeletal SystemEMEM QUENNo ratings yet
- Act08 The Skeletal System DiscussionDocument8 pagesAct08 The Skeletal System DiscussionSofia A.No ratings yet
- Lecture On Classification of BonesDocument21 pagesLecture On Classification of BonesUzochukwu UmesiamaNo ratings yet
- Unit Three: General Anatomy of The of Skeletal System (Osteology)Document78 pagesUnit Three: General Anatomy of The of Skeletal System (Osteology)Gifti DemisseNo ratings yet
- Relationship To Other Organ SystemsDocument11 pagesRelationship To Other Organ SystemsVern NuquiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument52 pagesSkeletal SystemHarish musictryNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesSkeletal SystemArra BeatrizNo ratings yet
- Skeleton Ikan IIDocument15 pagesSkeleton Ikan IIYvonee XaviersNo ratings yet
- Locomotiom & The Human Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesLocomotiom & The Human Skeletal SystemNathanael MfumbaikaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument19 pagesThe Skeletal SystemMatthew YoungNo ratings yet
- Ch07 Ext OutlineDocument14 pagesCh07 Ext OutlineGabe LeviNo ratings yet
- Human Skeletal System AnatomyDocument2 pagesHuman Skeletal System Anatomyag8211729No ratings yet
- Animal Tissue l4Document27 pagesAnimal Tissue l4Rudrapalash ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Classification of Bones.Document20 pagesClassification of Bones.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument23 pagesSkeletal SystemrosabelalebsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System OverviewDocument2 pagesAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System Overviewrapunzel777No ratings yet
- Unit VII Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesUnit VII Lecture NotesSteve SullivanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1Document69 pagesAnatomy 1ravinder malwalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Introduction To Bones and The SkullDocument22 pagesUnit 4 Introduction To Bones and The SkullrynNo ratings yet
- (Reading 3) The Skeletal SystemDocument18 pages(Reading 3) The Skeletal SystemTrúc Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Group2 - BSHM 1 BDocument43 pagesGroup2 - BSHM 1 BSAPILAN DENMARNo ratings yet
- $R4UVS5TDocument32 pages$R4UVS5Tnechtech6No ratings yet
- Skeletal System Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesSkeletal System Lesson PlanNicketa AndersonNo ratings yet
- THE Musculoskeletal SystemDocument36 pagesTHE Musculoskeletal SystemDidier chanelNo ratings yet
- Ebook Biology ShazwaniDocument20 pagesEbook Biology ShazwaniNurul shazwaniNo ratings yet
- Work Book Activity 10 Ana LabDocument37 pagesWork Book Activity 10 Ana LabJazmine Yvonne100% (1)
- 2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and AnimalsDocument2 pages2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and AnimalsBalpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- 2ND Grading Laboratory SheetsDocument16 pages2ND Grading Laboratory SheetsAllecia Leona Arceta SoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Lesson Plan 2Document12 pagesSkeletal System Lesson Plan 2Trudy- Ann CaineNo ratings yet
- DUSTIN NUESTRO Skeletal System Lab. WorksheetDocument10 pagesDUSTIN NUESTRO Skeletal System Lab. WorksheetDustin NuestroNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 SkeletalDocument9 pagesLaboratory 3 SkeletalKyla InoferioNo ratings yet
- Espartero Chapter3, Individual TaskDocument7 pagesEspartero Chapter3, Individual TaskDanelleNo ratings yet
- Movement and Locomotion-23-24Document3 pagesMovement and Locomotion-23-24Chintan ShahNo ratings yet
- Secret MineralizeDocument2 pagesSecret MineralizeMaricris CosmeNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment 1Document4 pagesBiology Assignment 1Zoe UnambaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-4 Anatomy and Human Physiology NotesDocument90 pagesUnit 2-4 Anatomy and Human Physiology NotesAbi .JNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument88 pagesThe Skeletal SystemjpotiNo ratings yet
- Surface Tension: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument1 pageSurface Tension: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediayashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Public Notice: CBSE/JEE/201 7-18Document2 pagesPublic Notice: CBSE/JEE/201 7-18yashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- N Identical Balls Lie Equally Spaced in A Semicircle On A Frictionless Horizontal TableDocument1 pageN Identical Balls Lie Equally Spaced in A Semicircle On A Frictionless Horizontal TableyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Fragmentation in Various Organisms: Yeasts Mushrooms Fungi Kingdom HyphaeDocument1 pageFragmentation in Various Organisms: Yeasts Mushrooms Fungi Kingdom HyphaeyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Forms: AccelerationDocument1 pageForms: AccelerationyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Newtonian Mechanics: Single ParticleDocument1 pageNewtonian Mechanics: Single ParticleyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Fragmentation (Reproduction) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument1 pageFragmentation (Reproduction) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediayashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Projection Uniform Circular Motion OriginDocument1 pageProjection Uniform Circular Motion OriginyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Ideal Rocket EquationDocument1 pageIdeal Rocket EquationyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Variable-Mass System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument1 pageVariable-Mass System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediayashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Mass Ablation/ejection: AblatedDocument1 pageMass Ablation/ejection: AblatedyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Derivation: Mass AccretionDocument1 pageDerivation: Mass AccretionyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Scotch YokeDocument1 pageScotch YokeyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesDoppler Effect: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediayashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument8 pagesFluidsyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Mass of A Simple Pendulum: Small-Angle ApproximationDocument2 pagesMass of A Simple Pendulum: Small-Angle ApproximationyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Examples: Mass On A SpringDocument1 pageExamples: Mass On A SpringyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Kinetic EnergyDocument1 pageKinetic EnergyyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Angular Frequency Calculus Velocity Acceleration: IsochronousDocument1 pageAngular Frequency Calculus Velocity Acceleration: IsochronousyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Oscillator Equilibrium Force Elastic Hooke's LawDocument1 pageSimple Harmonic Oscillator Equilibrium Force Elastic Hooke's LawyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Simple Harmonic Motion: Ordinary Differential Equation Newton's Second Law Hooke's Law Mass SpringDocument1 pageDynamics of Simple Harmonic Motion: Ordinary Differential Equation Newton's Second Law Hooke's Law Mass SpringyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Accelerates MomentumDocument1 pageAccelerates MomentumyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
Invertebrate - : Caco Caf So Ca Po Ca
Invertebrate - : Caco Caf So Ca Po Ca
Uploaded by
yashsodhaniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Invertebrate - : Caco Caf So Ca Po Ca
Invertebrate - : Caco Caf So Ca Po Ca
Uploaded by
yashsodhaniCopyright:
Available Formats
Invertebrate
Protozoa No skeleton.
Porifera Calcarius spicules + silicious spicules + spongin fibre.
Spicules in porifera represent endoskeleton.
Coelentrata Calcareous corals.
Helminth No skeleton, cuticle present.
Annaelida No skeleton, cuticle present.
In earthworm and ascaris is hydrostatic skeleton is found that is fluid is filled in coelom and
form turgid skeleton.
Arthropoda Chitinus exoskeleton.
Chitin is modified cuticle.
Mollusca Calcarius shell.
Echinodermata Calcareous plates are present.
In vertebrates exoskeleton may be epidermal or dermal.
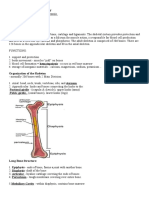
Vertebrates : In vertebrates dermal skeleton is formed by bones. Bone is the connective tissue
with intercellular spaces filled with ossein matrix composed of calcium salts 2/3
3 2 3 4 2 4
, , CaCO CaF SO Ca Po Ca
and calcium oxalate) and organic matter 1/3. In the ossein
osteocyte cells are found and outer surface of bone is covered by periosteum. The inner most
region is full of bone marrow having various types of cells. In mammals the bone is full of
haversian canals. The bones are of three types :
(a) Cartilage bones : The bones which are formed by the ossification of preexisting cartilage
are called cartilage bones or replacing bones.
(b) Membrane or dermal bones : The bones which are formed by independent ossification in
connective tissue are called dermal, membrane or investing bones.
(c) Sesmoid bone : Ossification takes place on Ligament and Tendons.
(1) Functions of endoskeleton : Chief function of vertebrate endoskeleton can be
enumerated as follows
(a) To provide physical support to body by forming a firm and rigid internal framework.
(b) To give definite body shape and form.
(c) To protect by surrounding delicate internal organs like brain, heart, lungs etc.
(d) To permit growth of huge body size (whale, elephant, extinct dinosaurs), since it is living and
growing.
(e) To provide surface for attachment of muscles.
(f) To serve as levers on which muscles can act.
(g) To manufacture blood corpuscles in bone marrow.
(h) To help in breathing (tracheal rings, ribs).
You might also like
- Topic 6 Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesTopic 6 Skeletal SystemMary Ann Morillo TenederoNo ratings yet
- Skeleton: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesSkeleton: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediacut amaliaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Biology Ss1Document33 pages2nd Term Biology Ss1dasiakennethNo ratings yet
- Bone and CartilageDocument61 pagesBone and CartilageMohamed AtefNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument23 pagesUntitled PresentationSamia MustafaNo ratings yet
- Form 4 17 Support Movement and ProtectionDocument62 pagesForm 4 17 Support Movement and ProtectionRichard NestorNo ratings yet
- Locomotion SystemDocument151 pagesLocomotion Systemaynurwepayewa40No ratings yet
- SKELETAL SYSTEM ReviewerDocument7 pagesSKELETAL SYSTEM ReviewerKrize Colene dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument157 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System OverviewDocument2 pagesAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System OverviewChula Anak Bina IPGKRNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System OverviewDocument2 pagesAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System OverviewChula Anak Bina IPGKRNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Supporting SystemDocument15 pagesTissue and Supporting SystemjolaolumolusinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument157 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsOliver Talip100% (1)
- Tissue 2Document34 pagesTissue 2nneduchiemerieNo ratings yet
- Movement and Locomotion Question Bank For Class 9Document7 pagesMovement and Locomotion Question Bank For Class 9piyushmandal4567No ratings yet
- SkeletalsystemDocument43 pagesSkeletalsystemSamantha EllaineNo ratings yet
- UPV Bio 1 NotesDocument24 pagesUPV Bio 1 NotesJustin CatalanNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Lecture: Functions of The IntegumentsDocument8 pagesGeneral Zoology Lecture: Functions of The IntegumentsKirkNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMDocument12 pagesAnaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMKenzoNo ratings yet
- 20201012-20201019-1149-Skeletal SystemDocument61 pages20201012-20201019-1149-Skeletal Systemdrin zekaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Lab Exercise - Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesWeek 5 Lab Exercise - Skeletal SystemchristinelorrainegatchalianNo ratings yet
- Module Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesModule Skeletal SystemEMEM QUENNo ratings yet
- Act08 The Skeletal System DiscussionDocument8 pagesAct08 The Skeletal System DiscussionSofia A.No ratings yet
- Lecture On Classification of BonesDocument21 pagesLecture On Classification of BonesUzochukwu UmesiamaNo ratings yet
- Unit Three: General Anatomy of The of Skeletal System (Osteology)Document78 pagesUnit Three: General Anatomy of The of Skeletal System (Osteology)Gifti DemisseNo ratings yet
- Relationship To Other Organ SystemsDocument11 pagesRelationship To Other Organ SystemsVern NuquiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument52 pagesSkeletal SystemHarish musictryNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesSkeletal SystemArra BeatrizNo ratings yet
- Skeleton Ikan IIDocument15 pagesSkeleton Ikan IIYvonee XaviersNo ratings yet
- Locomotiom & The Human Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesLocomotiom & The Human Skeletal SystemNathanael MfumbaikaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument19 pagesThe Skeletal SystemMatthew YoungNo ratings yet
- Ch07 Ext OutlineDocument14 pagesCh07 Ext OutlineGabe LeviNo ratings yet
- Human Skeletal System AnatomyDocument2 pagesHuman Skeletal System Anatomyag8211729No ratings yet
- Animal Tissue l4Document27 pagesAnimal Tissue l4Rudrapalash ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Classification of Bones.Document20 pagesClassification of Bones.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument23 pagesSkeletal SystemrosabelalebsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System OverviewDocument2 pagesAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System Overviewrapunzel777No ratings yet
- Unit VII Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesUnit VII Lecture NotesSteve SullivanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1Document69 pagesAnatomy 1ravinder malwalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Introduction To Bones and The SkullDocument22 pagesUnit 4 Introduction To Bones and The SkullrynNo ratings yet
- (Reading 3) The Skeletal SystemDocument18 pages(Reading 3) The Skeletal SystemTrúc Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Group2 - BSHM 1 BDocument43 pagesGroup2 - BSHM 1 BSAPILAN DENMARNo ratings yet
- $R4UVS5TDocument32 pages$R4UVS5Tnechtech6No ratings yet
- Skeletal System Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesSkeletal System Lesson PlanNicketa AndersonNo ratings yet
- THE Musculoskeletal SystemDocument36 pagesTHE Musculoskeletal SystemDidier chanelNo ratings yet
- Ebook Biology ShazwaniDocument20 pagesEbook Biology ShazwaniNurul shazwaniNo ratings yet
- Work Book Activity 10 Ana LabDocument37 pagesWork Book Activity 10 Ana LabJazmine Yvonne100% (1)
- 2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and AnimalsDocument2 pages2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and AnimalsBalpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- 2ND Grading Laboratory SheetsDocument16 pages2ND Grading Laboratory SheetsAllecia Leona Arceta SoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Lesson Plan 2Document12 pagesSkeletal System Lesson Plan 2Trudy- Ann CaineNo ratings yet
- DUSTIN NUESTRO Skeletal System Lab. WorksheetDocument10 pagesDUSTIN NUESTRO Skeletal System Lab. WorksheetDustin NuestroNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 SkeletalDocument9 pagesLaboratory 3 SkeletalKyla InoferioNo ratings yet
- Espartero Chapter3, Individual TaskDocument7 pagesEspartero Chapter3, Individual TaskDanelleNo ratings yet
- Movement and Locomotion-23-24Document3 pagesMovement and Locomotion-23-24Chintan ShahNo ratings yet
- Secret MineralizeDocument2 pagesSecret MineralizeMaricris CosmeNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment 1Document4 pagesBiology Assignment 1Zoe UnambaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-4 Anatomy and Human Physiology NotesDocument90 pagesUnit 2-4 Anatomy and Human Physiology NotesAbi .JNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument88 pagesThe Skeletal SystemjpotiNo ratings yet
- Surface Tension: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument1 pageSurface Tension: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediayashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Public Notice: CBSE/JEE/201 7-18Document2 pagesPublic Notice: CBSE/JEE/201 7-18yashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- N Identical Balls Lie Equally Spaced in A Semicircle On A Frictionless Horizontal TableDocument1 pageN Identical Balls Lie Equally Spaced in A Semicircle On A Frictionless Horizontal TableyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Fragmentation in Various Organisms: Yeasts Mushrooms Fungi Kingdom HyphaeDocument1 pageFragmentation in Various Organisms: Yeasts Mushrooms Fungi Kingdom HyphaeyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Forms: AccelerationDocument1 pageForms: AccelerationyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Newtonian Mechanics: Single ParticleDocument1 pageNewtonian Mechanics: Single ParticleyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Fragmentation (Reproduction) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument1 pageFragmentation (Reproduction) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediayashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Projection Uniform Circular Motion OriginDocument1 pageProjection Uniform Circular Motion OriginyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Ideal Rocket EquationDocument1 pageIdeal Rocket EquationyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Variable-Mass System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument1 pageVariable-Mass System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediayashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Mass Ablation/ejection: AblatedDocument1 pageMass Ablation/ejection: AblatedyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Derivation: Mass AccretionDocument1 pageDerivation: Mass AccretionyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Scotch YokeDocument1 pageScotch YokeyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesDoppler Effect: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediayashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument8 pagesFluidsyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Mass of A Simple Pendulum: Small-Angle ApproximationDocument2 pagesMass of A Simple Pendulum: Small-Angle ApproximationyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Examples: Mass On A SpringDocument1 pageExamples: Mass On A SpringyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Kinetic EnergyDocument1 pageKinetic EnergyyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Angular Frequency Calculus Velocity Acceleration: IsochronousDocument1 pageAngular Frequency Calculus Velocity Acceleration: IsochronousyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Oscillator Equilibrium Force Elastic Hooke's LawDocument1 pageSimple Harmonic Oscillator Equilibrium Force Elastic Hooke's LawyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Simple Harmonic Motion: Ordinary Differential Equation Newton's Second Law Hooke's Law Mass SpringDocument1 pageDynamics of Simple Harmonic Motion: Ordinary Differential Equation Newton's Second Law Hooke's Law Mass SpringyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Accelerates MomentumDocument1 pageAccelerates MomentumyashsodhaniNo ratings yet