Professional Documents
Culture Documents
E - Content
E - Content
Uploaded by
Margaret JosephOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
E - Content
E - Content
Uploaded by
Margaret JosephCopyright:
Available Formats
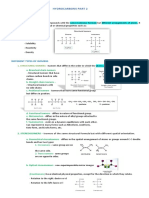
Examples
Example
Butane
Ethanol
Examples
Cis-but-2-ene
Butan-2-ol
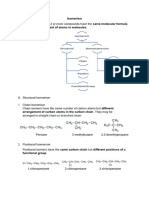
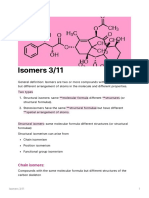
ISOMERISM
It is the phenomenon whereby certain
compounds,with same molecular formula
existing in different forms owing to their
different organizations of atoms
Structural isomerism
Isomers have different
structueres
Stereoisomerism
Isomers have same
structure, but atoms are
oriented differently in
space
Geometric
isomerism
Optical
isomerism
E-CONTENT DEVELOPMENT OF
ISOMERISM
1. HOME
http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/isomersm/lesson-1
http://www.physics.about.com
http://www.physics.umn.edu
http://physics info/isomerism
http://www.physics4kids.com
2. OBJECTIVES
To develop e-content on the topic Isomerism
To form the concept of Isomerism
To form the idea of Structural isomerism, Stereo isomerism, Geometric isomerism and
optical isomerism
E- CONTENT ANALYSIS
TERMS: Isomerism, structural Isomerism, Stereo isomerism, Geometrical isomerism and Optical
isomerism
FACTS:
Carbon have a capacity to make large number of compounds
Valency of carbon is four
Carbon have ability to form single bond, double bond and triple bond
SUMMARY
A coordination compound or complex ion is a molecule that contains a central metal
ion to which are attached one or more legends. In many complexes there is more than
one way in which the ligands may be attached to or arranged around the metal
center. Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but possess
different arrangements of atoms. Two isomers are non-superimposable, which means
that one cannot mentally have the two compounds occur the same space with each
atom in one isomer perfectly coinciding with the same atom in the other isomer.
The scheme and definitions provided below are commonly used to classify coordination
chemistry isomers. A compound can exhibit multiple types of isomerism.
You might also like
- IsomerismDocument2 pagesIsomerismdaramolamekaiahNo ratings yet
- STEREOCHEMISTRY - With DiscussionDocument20 pagesSTEREOCHEMISTRY - With DiscussionWeljoy LabbaoNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument3 pagesIsomerismhaqfazal2007No ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument16 pagesIsomerismcvjaykumarreddy100% (2)
- Biology Basics Workshop by Slidesgo-2Document18 pagesBiology Basics Workshop by Slidesgo-26n7bxmgfxfNo ratings yet
- IsomersDocument3 pagesIsomersjaiNo ratings yet
- Pre Lab 1Document2 pagesPre Lab 1jlgestaNo ratings yet
- Isomerism: Isomer Flowchart, byDocument6 pagesIsomerism: Isomer Flowchart, bySam KOkeloNo ratings yet
- Isomerism Part 1Document3 pagesIsomerism Part 1amitNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument4 pagesIsomerismBisha MonNo ratings yet
- Isomerism: TypesDocument9 pagesIsomerism: TypesAmirah AbdullatifNo ratings yet
- Isomerism: TypesDocument9 pagesIsomerism: TypesKabali KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of IsomerismDocument20 pagesTypes of IsomerismXyrielle GarciaNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 - IsomerismDocument14 pagesHandout 1 - Isomerismboriwat thaengthonglang100% (1)
- Gen Chem Module Q2Week 7 8Document23 pagesGen Chem Module Q2Week 7 8Dan MacabingilNo ratings yet
- Isomerism & Its Types: Name: - Zafar Ali CMS ID: - 33722 Department: - BIOTECH (1 Semester) InstructorDocument6 pagesIsomerism & Its Types: Name: - Zafar Ali CMS ID: - 33722 Department: - BIOTECH (1 Semester) InstructorZafarNo ratings yet
- Structural IsomerismDocument3 pagesStructural IsomerismMohd DaudNo ratings yet
- StereochemistryDocument4 pagesStereochemistrykamalia89No ratings yet
- Types of Structural IsomersDocument1 pageTypes of Structural IsomersAarhon AblongNo ratings yet
- Stereo Isomerism and Its Types PDFDocument3 pagesStereo Isomerism and Its Types PDFMohd DaudNo ratings yet
- Stereo Isomerism and Its Types PDFDocument3 pagesStereo Isomerism and Its Types PDFTahreem FatimaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Carbon Compounds - Structure and FormulaeDocument53 pagesChemistry of Carbon Compounds - Structure and FormulaeTashane officialNo ratings yet
- Isomerism 1Document11 pagesIsomerism 1Sultana RashidaNo ratings yet
- Llogers - General Chemistry m1-m6Document18 pagesLlogers - General Chemistry m1-m6api-639087356No ratings yet
- What Is Structural Isomerism?Document29 pagesWhat Is Structural Isomerism?stefanjack4uNo ratings yet
- Types of IsomerismDocument14 pagesTypes of IsomerismAbdullah MunawarNo ratings yet
- Geometric IsomerismDocument88 pagesGeometric IsomerismRENYRICK MANALOTO0% (1)
- Chapter 3 IsomerismDocument9 pagesChapter 3 IsomerismOchem90No ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument22 pagesIsomerismShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument30 pagesIsomerismTristan PereyNo ratings yet
- Isomers: Constitutional Isomers Stereoisomers Conformational IsomersDocument6 pagesIsomers: Constitutional Isomers Stereoisomers Conformational IsomersJules BrunoNo ratings yet
- IsomerDocument1 pageIsomerranarohan15102005No ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1672493608699 7014946632941408990 PDFDocument40 pagesOrca Share Media1672493608699 7014946632941408990 PDFpk 77No ratings yet
- Stereo ChemistryDocument45 pagesStereo Chemistrysanjanaganguly2005No ratings yet
- 4 IsomerDocument15 pages4 IsomerNessma SoltanNo ratings yet
- Isomers HandoutDocument5 pagesIsomers HandoutMohamed MeeranNo ratings yet
- Isomerism in BiomoleculesDocument14 pagesIsomerism in BiomoleculesNaji Mohamed Alfatih100% (6)
- 1.17-1.19structural Isomerism and StereoisomerismDocument11 pages1.17-1.19structural Isomerism and StereoisomerismLyana TaylorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Stereochemistry: Isomers, Which Are Not Readily InterconvertableDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Stereochemistry: Isomers, Which Are Not Readily InterconvertableShiva Krishna KamjulaNo ratings yet
- F5 KSSM 2.4 Part 1Document28 pagesF5 KSSM 2.4 Part 1Anna ParkNo ratings yet
- NSSCAS Chemistry Theme 4 Topic 4.5 - 4.6 - 4.7 - Updated 05 November 2020Document71 pagesNSSCAS Chemistry Theme 4 Topic 4.5 - 4.6 - 4.7 - Updated 05 November 2020sikereteromanus9No ratings yet
- Part-1 Stereochemistry of Organic CompoundsDocument28 pagesPart-1 Stereochemistry of Organic CompoundsIct Pfa ClubNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Part 2: IsomerismDocument3 pagesHydrocarbons Part 2: IsomerismFaller, Fiona Luie C.No ratings yet
- Palayan City National High School General Chemistry I Senior High School 2 Quarter Week 6 Lesson 1 Structural IsomerismDocument3 pagesPalayan City National High School General Chemistry I Senior High School 2 Quarter Week 6 Lesson 1 Structural IsomerismMark Christian BrlNo ratings yet
- Somerism: Efine With Examples Tructural SomerismDocument6 pagesSomerism: Efine With Examples Tructural SomerismXavier BrownNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Stereo-3Document14 pagesUNIT-4 Stereo-3KARTIKAY LADDHANo ratings yet
- 3° SciencieDocument1 page3° SciencieCesar EscareñoNo ratings yet
- Org ChemDocument2 pagesOrg ChemSabbyAlonzoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry by Elishama HubiDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistry by Elishama HubiCSF DIGITAL CONSULTANCYNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument11 pagesIsomerismapplejelly021No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Molecules and CompoundsDocument19 pagesChapter 5 Molecules and CompoundsChristian JamesNo ratings yet
- Isomers 311 PDFDocument5 pagesIsomers 311 PDFIsaa gabNo ratings yet
- Classification, Nomenclature and Isomerism PDFDocument34 pagesClassification, Nomenclature and Isomerism PDFSantosh Potdar100% (4)
- Isomerism PDFDocument28 pagesIsomerism PDFBilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- IsomersDocument64 pagesIsomerszakariaNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry of Organic CompoundsDocument22 pagesStereochemistry of Organic CompoundsArya Chowdhury100% (1)
- Geometric IsomerismDocument18 pagesGeometric IsomerismRoezenn GonzagaNo ratings yet