Professional Documents
Culture Documents
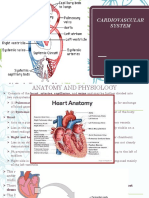
Echocardiography: Not To Be Confused With
Echocardiography: Not To Be Confused With
Uploaded by
greathari1998Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Types of Biomedical InstrumentsDocument12 pagesTypes of Biomedical Instrumentsgzb0120% (2)
- Echocardiograph Y: Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHDocument17 pagesEchocardiograph Y: Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between An ECG and Echo Tests Done For Heart Ailments? An Is Used To MeasureDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between An ECG and Echo Tests Done For Heart Ailments? An Is Used To MeasureSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument36 pagesCardiovascularShield Mae BalanlayNo ratings yet
- Instrumental Diagnostic Methods of Heart DiseasesDocument15 pagesInstrumental Diagnostic Methods of Heart DiseasesA A D H INo ratings yet
- Heart Procedures GlossaryDocument2 pagesHeart Procedures Glossary姜華No ratings yet
- Echocardiogram MayoDocument4 pagesEchocardiogram MayoMarta KitaNo ratings yet
- What Is An Echocardiogram? - InformedHealth - Org - NCBI BookshelfDocument1 pageWhat Is An Echocardiogram? - InformedHealth - Org - NCBI BookshelfemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Best Cardiologist in Pune - Cardiologist in Pune - DR Ajit MehtaDocument10 pagesBest Cardiologist in Pune - Cardiologist in Pune - DR Ajit MehtaAjit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography PDFDocument4 pagesEchocardiography PDFDualaut AndiNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Heart Disease-Echo TestDocument4 pagesDiagnosing Heart Disease-Echo TestjanaNo ratings yet
- Instrumental MethodDocument24 pagesInstrumental Methodzerish0208No ratings yet
- AngiographyDocument1 pageAngiographyMaftei NicusorNo ratings yet
- X Rays, Ecg Routine Blood SugarDocument2 pagesX Rays, Ecg Routine Blood SugarNitin AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Cardiac ImagingDocument9 pagesNon-Invasive Cardiac Imagingoddone_outNo ratings yet
- Different DiagnosticDocument26 pagesDifferent DiagnosticDanica Alyssa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument12 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeElsy MayjoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test For Heart DiseasesDocument16 pagesDiagnostic Test For Heart DiseasesJaimee Jonah ChristieNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument3 pagesCHFmariaestercampos22No ratings yet
- Echocardiogram (Heart Ultrasound) : Name:Fatema Ilyas Organization:Tabba Heart Institute ROLL NO:16-02 Batch:ViiDocument28 pagesEchocardiogram (Heart Ultrasound) : Name:Fatema Ilyas Organization:Tabba Heart Institute ROLL NO:16-02 Batch:ViiFatema IlyasNo ratings yet
- Tress Test: The Gale Encyclopedia of MedicineDocument7 pagesTress Test: The Gale Encyclopedia of MedicineSalsabilla KimikoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1murli dharNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Diseasesanimesh pandaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On EchocardiogramDocument17 pagesPresentation On EchocardiogramSoniya NakkaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Heart DiseaseDocument3 pagesDiagnosing Heart DiseaseJaz SantosNo ratings yet
- Investigations in Cardiology M1 Lecture 08082017Document40 pagesInvestigations in Cardiology M1 Lecture 08082017frankozed1No ratings yet
- Cardiac TestsDocument6 pagesCardiac TestsRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography (Cardiac Echography, Heart Sonography)Document2 pagesEchocardiography (Cardiac Echography, Heart Sonography)Broc Il SerbatoioNo ratings yet
- Murmur: CausesDocument21 pagesMurmur: CausesJessica AdhykaNo ratings yet
- Complete Heart BlockDocument13 pagesComplete Heart BlockSubhranil MaityNo ratings yet
- AngiographyDocument3 pagesAngiographySai SridharNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome PDFDocument12 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome PDFElsy MayjoNo ratings yet
- Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument10 pagesAltered Tissue PerfusionLaurence ZernaNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Laboratory TestsDocument2 pagesCardiology Laboratory TestsBeatrice SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Regie Delariarte, Trexie Dipa - Khrystle Dote, Clarice Estores BN3A October 3, 2017Document4 pagesRegie Delariarte, Trexie Dipa - Khrystle Dote, Clarice Estores BN3A October 3, 2017random sharkNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders Diagnostic Tests and ProceduresDocument16 pagesCardiovascular Disorders Diagnostic Tests and ProceduresMonette Abalos MendovaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrestDocument8 pagesCardiac ArrestMICHELLE JOY GAYOSONo ratings yet
- What Is An UltrasoundDocument9 pagesWhat Is An UltrasoundKaren RégulesNo ratings yet
- All ProcedureDocument247 pagesAll ProcedureRakesh ChoudhryNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography (ECG)Document11 pagesElectrocardiography (ECG)Hassan AnwarNo ratings yet
- Medical Ultrasound - WikipediaDocument30 pagesMedical Ultrasound - WikipedianibNo ratings yet
- Grp. 5 Coronary Artery Disease WrittenDocument9 pagesGrp. 5 Coronary Artery Disease WrittenCha AlegriaNo ratings yet
- 10introduction To EchocardiographyDocument21 pages10introduction To EchocardiographyMaria EdelNo ratings yet
- A Research: Perpetual Help College of Manila V.Conception ST., Sampaloc, Manila Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument8 pagesA Research: Perpetual Help College of Manila V.Conception ST., Sampaloc, Manila Bachelor of Science in NursingRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Heart AttackDocument31 pagesHeart AttackARUN PAULNo ratings yet
- Echocardiogram: Echocardiogram, Also Known As Echocardiography, or Heart Ultrasound Is ADocument23 pagesEchocardiogram: Echocardiogram, Also Known As Echocardiography, or Heart Ultrasound Is AKarl RobleNo ratings yet
- What Is An ECG?: Heart DiseaseDocument4 pagesWhat Is An ECG?: Heart DiseaseAjay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument7 pagesCase Study For Acute Coronary SyndromeGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Lai Pei Xin Kib2001 U2103121/1Document19 pagesLai Pei Xin Kib2001 U2103121/1Pei XinNo ratings yet
- Non Invasive Diagnostic Instruments: By. Kailash - Pandey Aditya - MayekarDocument32 pagesNon Invasive Diagnostic Instruments: By. Kailash - Pandey Aditya - MayekarkrupalithakkerNo ratings yet
- ECG Chapter ThreeDocument11 pagesECG Chapter Threeد. سعد قاسم الاجهزة الطبيةNo ratings yet
- Stroke PhilhealthDocument5 pagesStroke PhilhealthErwin BrionesNo ratings yet
- Basic Cardiac Ds C-1 RadiologyDocument30 pagesBasic Cardiac Ds C-1 RadiologygetemeselewNo ratings yet
- Introduction Definition: Types of PacemakersDocument8 pagesIntroduction Definition: Types of PacemakersPrasann RoyNo ratings yet
- TIADocument22 pagesTIAArabylle Maranca AbuelNo ratings yet
- ICu EquipmentDocument3 pagesICu Equipmentkremlin23455No ratings yet
- Haemodynamic mo-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesHaemodynamic mo-WPS Officermconvidhya sri2015No ratings yet
- Electro Cardiogram: NCM 112:skills LaboratoryDocument7 pagesElectro Cardiogram: NCM 112:skills LaboratoryFaye Domini FederisNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Methods in Cardiac DisordersDocument29 pagesDiagnostic Methods in Cardiac Disordersmanzoor bhatNo ratings yet
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!From EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No ratings yet
Echocardiography: Not To Be Confused With
Echocardiography: Not To Be Confused With
Uploaded by
greathari1998Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Echocardiography: Not To Be Confused With
Echocardiography: Not To Be Confused With
Uploaded by
greathari1998Copyright:
Available Formats
Not to be confused with Electrocardiography (ECG).
Echocardiography
Intervention
An abnormal Echocardiogram. Image shows a
mid-muscular ventricular septal defect. The trace in
the lower left shows the cardiac cycleand the red
mark the time in the cardiac cycle that the image
was captured. Colors are used to represent the
velocity and direction of blood flow.
ICD-9-CM 88.72
MeSH D004452
OPS-301 code: 3-052
MedlinePlus 003869
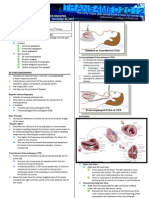
Sonographer doing pediatric echocardiography
Echocardiogram in the parasternal long-axis view, showing a measurement of the heart's left
ventricle
Echocardiogram, often referred to as a cardiac echo or simply an echo, is
asonogram of the heart. (It is not abbreviated as ECG, which in medicine usually
refers to an electrocardiogram.) Echocardiography uses standard two-
dimensional, three-dimensional, and Doppler ultrasound to create images of the
heart.
Echocardiography has become routinely used in the diagnosis, management,
and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of
the most widely used diagnostic tests in cardiology. It can provide a wealth of
helpful information, including the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber
size quantification), pumping capacity, and the location and extent of any tissue
damage. An Echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart
function such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and
diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes).
Echocardiography can help detect cardiomyopathies, such as hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, and many others. The use of Stress
Echocardiography may also help determine whether any chest pain or
associated symptoms are related to heart disease. The biggest advantage to
echocardiography is that it is noninvasive (doesn't involve breaking the skin or
entering body cavities) and has no known risks or side effects.
Not only can an echocardiogram create ultrasound images of heart structures,
but it can also produce accurate assessment of the blood flowing through the
heart, using pulsed or continuous wave Doppler ultrasound. This allows
assessment of both normal and abnormal blood flow through the heart. Color
Doppler as well as spectral Doppler is used to visualize any abnormal
communications between the left and right side of the heart, any leaking of blood
through the valves (valvular regurgitation), and to estimate how well the valves
open (or do not open in the case of valvular stenosis).
Echocardiography was also the first ultrasound subspecialty to use intravenous
contrast. (See Contrast Echocardiography)
Echocardiography is performed by cardiac sonographers, cardiac physiologists
(UK) or doctors trained in echocardiography
You might also like
- Types of Biomedical InstrumentsDocument12 pagesTypes of Biomedical Instrumentsgzb0120% (2)
- Echocardiograph Y: Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHDocument17 pagesEchocardiograph Y: Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between An ECG and Echo Tests Done For Heart Ailments? An Is Used To MeasureDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between An ECG and Echo Tests Done For Heart Ailments? An Is Used To MeasureSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument36 pagesCardiovascularShield Mae BalanlayNo ratings yet
- Instrumental Diagnostic Methods of Heart DiseasesDocument15 pagesInstrumental Diagnostic Methods of Heart DiseasesA A D H INo ratings yet
- Heart Procedures GlossaryDocument2 pagesHeart Procedures Glossary姜華No ratings yet
- Echocardiogram MayoDocument4 pagesEchocardiogram MayoMarta KitaNo ratings yet
- What Is An Echocardiogram? - InformedHealth - Org - NCBI BookshelfDocument1 pageWhat Is An Echocardiogram? - InformedHealth - Org - NCBI BookshelfemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Best Cardiologist in Pune - Cardiologist in Pune - DR Ajit MehtaDocument10 pagesBest Cardiologist in Pune - Cardiologist in Pune - DR Ajit MehtaAjit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography PDFDocument4 pagesEchocardiography PDFDualaut AndiNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Heart Disease-Echo TestDocument4 pagesDiagnosing Heart Disease-Echo TestjanaNo ratings yet
- Instrumental MethodDocument24 pagesInstrumental Methodzerish0208No ratings yet
- AngiographyDocument1 pageAngiographyMaftei NicusorNo ratings yet
- X Rays, Ecg Routine Blood SugarDocument2 pagesX Rays, Ecg Routine Blood SugarNitin AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Cardiac ImagingDocument9 pagesNon-Invasive Cardiac Imagingoddone_outNo ratings yet
- Different DiagnosticDocument26 pagesDifferent DiagnosticDanica Alyssa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument12 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeElsy MayjoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test For Heart DiseasesDocument16 pagesDiagnostic Test For Heart DiseasesJaimee Jonah ChristieNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument3 pagesCHFmariaestercampos22No ratings yet
- Echocardiogram (Heart Ultrasound) : Name:Fatema Ilyas Organization:Tabba Heart Institute ROLL NO:16-02 Batch:ViiDocument28 pagesEchocardiogram (Heart Ultrasound) : Name:Fatema Ilyas Organization:Tabba Heart Institute ROLL NO:16-02 Batch:ViiFatema IlyasNo ratings yet
- Tress Test: The Gale Encyclopedia of MedicineDocument7 pagesTress Test: The Gale Encyclopedia of MedicineSalsabilla KimikoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1murli dharNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Diseasesanimesh pandaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On EchocardiogramDocument17 pagesPresentation On EchocardiogramSoniya NakkaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Heart DiseaseDocument3 pagesDiagnosing Heart DiseaseJaz SantosNo ratings yet
- Investigations in Cardiology M1 Lecture 08082017Document40 pagesInvestigations in Cardiology M1 Lecture 08082017frankozed1No ratings yet
- Cardiac TestsDocument6 pagesCardiac TestsRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography (Cardiac Echography, Heart Sonography)Document2 pagesEchocardiography (Cardiac Echography, Heart Sonography)Broc Il SerbatoioNo ratings yet
- Murmur: CausesDocument21 pagesMurmur: CausesJessica AdhykaNo ratings yet
- Complete Heart BlockDocument13 pagesComplete Heart BlockSubhranil MaityNo ratings yet
- AngiographyDocument3 pagesAngiographySai SridharNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome PDFDocument12 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome PDFElsy MayjoNo ratings yet
- Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument10 pagesAltered Tissue PerfusionLaurence ZernaNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Laboratory TestsDocument2 pagesCardiology Laboratory TestsBeatrice SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Regie Delariarte, Trexie Dipa - Khrystle Dote, Clarice Estores BN3A October 3, 2017Document4 pagesRegie Delariarte, Trexie Dipa - Khrystle Dote, Clarice Estores BN3A October 3, 2017random sharkNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders Diagnostic Tests and ProceduresDocument16 pagesCardiovascular Disorders Diagnostic Tests and ProceduresMonette Abalos MendovaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrestDocument8 pagesCardiac ArrestMICHELLE JOY GAYOSONo ratings yet
- What Is An UltrasoundDocument9 pagesWhat Is An UltrasoundKaren RégulesNo ratings yet
- All ProcedureDocument247 pagesAll ProcedureRakesh ChoudhryNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography (ECG)Document11 pagesElectrocardiography (ECG)Hassan AnwarNo ratings yet
- Medical Ultrasound - WikipediaDocument30 pagesMedical Ultrasound - WikipedianibNo ratings yet
- Grp. 5 Coronary Artery Disease WrittenDocument9 pagesGrp. 5 Coronary Artery Disease WrittenCha AlegriaNo ratings yet
- 10introduction To EchocardiographyDocument21 pages10introduction To EchocardiographyMaria EdelNo ratings yet
- A Research: Perpetual Help College of Manila V.Conception ST., Sampaloc, Manila Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument8 pagesA Research: Perpetual Help College of Manila V.Conception ST., Sampaloc, Manila Bachelor of Science in NursingRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Heart AttackDocument31 pagesHeart AttackARUN PAULNo ratings yet
- Echocardiogram: Echocardiogram, Also Known As Echocardiography, or Heart Ultrasound Is ADocument23 pagesEchocardiogram: Echocardiogram, Also Known As Echocardiography, or Heart Ultrasound Is AKarl RobleNo ratings yet
- What Is An ECG?: Heart DiseaseDocument4 pagesWhat Is An ECG?: Heart DiseaseAjay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument7 pagesCase Study For Acute Coronary SyndromeGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Lai Pei Xin Kib2001 U2103121/1Document19 pagesLai Pei Xin Kib2001 U2103121/1Pei XinNo ratings yet
- Non Invasive Diagnostic Instruments: By. Kailash - Pandey Aditya - MayekarDocument32 pagesNon Invasive Diagnostic Instruments: By. Kailash - Pandey Aditya - MayekarkrupalithakkerNo ratings yet
- ECG Chapter ThreeDocument11 pagesECG Chapter Threeد. سعد قاسم الاجهزة الطبيةNo ratings yet
- Stroke PhilhealthDocument5 pagesStroke PhilhealthErwin BrionesNo ratings yet
- Basic Cardiac Ds C-1 RadiologyDocument30 pagesBasic Cardiac Ds C-1 RadiologygetemeselewNo ratings yet
- Introduction Definition: Types of PacemakersDocument8 pagesIntroduction Definition: Types of PacemakersPrasann RoyNo ratings yet
- TIADocument22 pagesTIAArabylle Maranca AbuelNo ratings yet
- ICu EquipmentDocument3 pagesICu Equipmentkremlin23455No ratings yet
- Haemodynamic mo-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesHaemodynamic mo-WPS Officermconvidhya sri2015No ratings yet
- Electro Cardiogram: NCM 112:skills LaboratoryDocument7 pagesElectro Cardiogram: NCM 112:skills LaboratoryFaye Domini FederisNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Methods in Cardiac DisordersDocument29 pagesDiagnostic Methods in Cardiac Disordersmanzoor bhatNo ratings yet
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!From EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No ratings yet