Professional Documents
Culture Documents
For The Signal F (T) Shown in Fig.1 Sketch F (-T)
For The Signal F (T) Shown in Fig.1 Sketch F (-T)
Uploaded by
Tarak A Positive100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
15 views3 pagesThis document contains questions about representing and manipulating signals. It asks the reader to sketch signals that are time-shifted, time-scaled, or time-inverted versions of given signals. It also asks the reader to express combinations of unit step functions and signals made up of rectangular pulses in terms of basic signals. Finally, it provides signal diagrams and asks the reader to sketch combinations of the signals using different operations like time-shifting, time-scaling, and inversion.
Original Description:
trabs
Original Title
Tutorial 0
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains questions about representing and manipulating signals. It asks the reader to sketch signals that are time-shifted, time-scaled, or time-inverted versions of given signals. It also asks the reader to express combinations of unit step functions and signals made up of rectangular pulses in terms of basic signals. Finally, it provides signal diagrams and asks the reader to sketch combinations of the signals using different operations like time-shifting, time-scaling, and inversion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
15 views3 pagesFor The Signal F (T) Shown in Fig.1 Sketch F (-T)
For The Signal F (T) Shown in Fig.1 Sketch F (-T)
Uploaded by
Tarak A PositiveThis document contains questions about representing and manipulating signals. It asks the reader to sketch signals that are time-shifted, time-scaled, or time-inverted versions of given signals. It also asks the reader to express combinations of unit step functions and signals made up of rectangular pulses in terms of basic signals. Finally, it provides signal diagrams and asks the reader to sketch combinations of the signals using different operations like time-shifting, time-scaling, and inversion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
1
EE-612 Digital Signal Processing
Tutorial-0
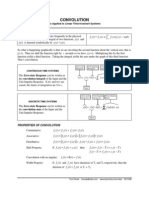
Representation of Signals
1. For the signal f(t) shown in Fig.1 sketch f(-t).
2. In the Fig.2 the signal f
1
(t) = f(-t). Express the signals f
2
(t), f
3
(t),f
4
(t) and f
5
(t) in terms of
signals f(t), f
1
(t) and the time shifted, time scaled, or time inverted versions.
f(t)
t
-7 -5 -3 -1
e
t/2
Fig.1
t
f(t)
-1
1
t
f
1
(t)
1
1
t
f
2
(t)
1
1
2
t
f
3
(t)
-1
1
1
f
4
(t)
-1/2 1/2
f
5
(t)
2
1.5
t
t
1
Fig.2
2
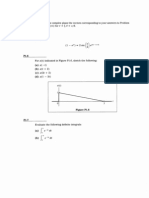
3. For the signal f(t) depicted in Fig.3, sketch f(-t), f(t+6),f(3t),f(t/2).
4. For the signal f(t) shown in Fig.4, sketch f(t-4), f(t/1.5),f(-t),f(2t-4),f(2-t).
5. Sketch the signals: (a) u(t-5)-u(t-7) (b) u(t-5)+u(t-7) (c) t
2
[u(t-1)-u(t-2)]
(d) (t-4)[u(t-2)-u(t-4)].
6. Express each of the signals shown in Fig.6 by a single expression valid for all t.
f(t)
t
6 12 15 24
0.5
-1
0
Fig.3
f(t)
t
2
-4
4
2
0
Fig.4
t
f
1
t)
-1
2
4
f
2
t)
t
4
2
4
-4
t
2
Fig.6
3
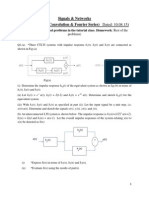
7. Let x(t) and y(t) be given in Fig. 7 (a) and 7 (b) respectively. Sketch the following
signals.
(a) x(t) y(t-1) (b) x(t-1) y(-t) (c) x(t+1) y(t-2) (d) x(t)y(-1-t) (e) x(t) y(2-t)
(f) x(2t) y((1/2)t+1) (g) x(4-t) y(t)
8. Fig. 8 shows the staircase like signal x(t) that may be viewed as the superposition of four
rectangular pulses. Express x(t) in terms of g(t).
x(t)
t
0
1 2 3
-1
-1
1
y(t)
t
0
1
2
-1
-1
1
-2
Fig.7
x(t)
t
0
1 2 3
4
1
2
3
4
t
1 -1
g(t)
1
Fig.8
You might also like
- RespuestasDocument18 pagesRespuestasAndres HerediaNo ratings yet
- hw2 SolDocument8 pageshw2 SolfilmonNo ratings yet
- Solution Part1Document30 pagesSolution Part1Valeri Suarez100% (2)
- Haykin5 PDFDocument33 pagesHaykin5 PDFdhananjayan89100% (1)
- Tutorial Signal ProcessingDocument3 pagesTutorial Signal ProcessingeerkmeenaNo ratings yet
- Class 7Document24 pagesClass 7karthikNo ratings yet
- EEC4 4A SS Problem Ch1Document14 pagesEEC4 4A SS Problem Ch1minhhuy2004.nguyenNo ratings yet
- S S Tuto2Document1 pageS S Tuto2Sunny LeoneNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems Analysis Using Transform Methods and MatlabDocument17 pagesSignals and Systems Analysis Using Transform Methods and MatlabDiego RubénNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial1 PDFVisakan ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3 Summary: Useful Signal ModelsDocument3 pagesLecture-3 Summary: Useful Signal ModelsThajid Ibna Rouf UdayNo ratings yet
- Exercises For Signals and Systems (Part One)Document3 pagesExercises For Signals and Systems (Part One)Vincent YuchiNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems EEEB233 Tutorial 1 (Due Date: 19.06.2015 5.30pm)Document2 pagesSignals and Systems EEEB233 Tutorial 1 (Due Date: 19.06.2015 5.30pm)zawirNo ratings yet
- Ch-1: Elementary of Signal and System: P1.1. A Continuous-Time Signal F (T) Shown in Figure P1.1. SketchDocument7 pagesCh-1: Elementary of Signal and System: P1.1. A Continuous-Time Signal F (T) Shown in Figure P1.1. SketchLong CaoNo ratings yet
- Ch-1: Elementary of Signal and System: P1.1. A Continuous-Time Signal F (T) Shown in Figure P1.1. SketchDocument7 pagesCh-1: Elementary of Signal and System: P1.1. A Continuous-Time Signal F (T) Shown in Figure P1.1. SketchNguyễn Tấn HưngNo ratings yet
- Convolution TableDocument2 pagesConvolution TablebbutschNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Introduction To Signals and SystemsDocument5 pagesTutorial 1 - Introduction To Signals and SystemsMirza DanishNo ratings yet
- Exercises For Signals and Systems (Part Three)Document6 pagesExercises For Signals and Systems (Part Three)Vincent YuchiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document16 pagesAssignment 1secidih495No ratings yet
- EE 102 Cabric Final Spring08 o Id15Document10 pagesEE 102 Cabric Final Spring08 o Id15Anonymous TbHpFLKNo ratings yet
- EE Homework - Partially CompletedDocument8 pagesEE Homework - Partially CompletedRickNo ratings yet
- Video Lectures - Assignment Questions - Lecture 2 Signals and Systems - Part I PDF FormatDocument7 pagesVideo Lectures - Assignment Questions - Lecture 2 Signals and Systems - Part I PDF Formatrodie0122No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Signals: Problem 1.1Document40 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Signals: Problem 1.1awl123No ratings yet
- ENGG2310A (Fall 2018) : Problem 1-1Document11 pagesENGG2310A (Fall 2018) : Problem 1-1Tsz Wing YipNo ratings yet
- Linear Systems Homework 1Document2 pagesLinear Systems Homework 1Anas ElgaudNo ratings yet
- Homework No. 2 EE-410 Communication SystemsDocument3 pagesHomework No. 2 EE-410 Communication SystemsM Usman RiazNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Communication Signals and Systems - MODIFIED PDFDocument69 pagesCharacterization of Communication Signals and Systems - MODIFIED PDFgaussnadal50% (2)
- Roldan Tocmo Activity No.1Document7 pagesRoldan Tocmo Activity No.1Roldan TocmoNo ratings yet
- Ultimo 24 Supch17 PDFDocument7 pagesUltimo 24 Supch17 PDFmri_leonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1yamen.nasser7No ratings yet
- Signals and Networks Assignment 2Document6 pagesSignals and Networks Assignment 2Avikalp SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- SLS Assignment 1Document3 pagesSLS Assignment 1Abdullah MohasienNo ratings yet
- Importnt Notes On SystemsDocument12 pagesImportnt Notes On SystemsNitishNo ratings yet
- Stochastic Calculus For Finance II - Some Solutions To Chapter VIDocument12 pagesStochastic Calculus For Finance II - Some Solutions To Chapter VIAditya MittalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-1Document31 pagesChapter 1-1lu huangNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Operational Properties IIDocument8 pages7.4 Operational Properties IIFatimah Nik MazlanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3Mahes WarNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems - Homework 6 - Spring 2024Document3 pagesSignals and Systems - Homework 6 - Spring 2024moha amroNo ratings yet
- MITRES 6 007S11 hw04 SolDocument16 pagesMITRES 6 007S11 hw04 SolEla BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Table of Fourier TransformsDocument1 pageTable of Fourier TransformsgbmsirNo ratings yet
- (Signals) (Information) (Data) (Systems) (Inputs) (Outputs)Document14 pages(Signals) (Information) (Data) (Systems) (Inputs) (Outputs)王和盛100% (1)
- Notes 3Document3 pagesNotes 3Asad AsadiNo ratings yet
- European Normal Black ScholesDocument14 pagesEuropean Normal Black ScholesrahiminatorNo ratings yet
- Evolutional Equations of Parabolic Type, Hiroki Tanabe, 1961Document4 pagesEvolutional Equations of Parabolic Type, Hiroki Tanabe, 1961Fis MatNo ratings yet
- FourierDocument2 pagesFourierMarco Marchito SabatiniNo ratings yet
- Ee602 Fourier SeriesDocument110 pagesEe602 Fourier SeriesSyaa MalyqaNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Signal and SystemsDocument82 pagesCharacterization of Signal and SystemsbiruckNo ratings yet
- ELEG 3124 Assignment # 1Document16 pagesELEG 3124 Assignment # 1Nguyễn Văn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Transformation de LaplaceDocument20 pagesTransformation de LaplaceA.BenhariNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series NOTESDocument67 pagesFourier Series NOTESAzue RamliNo ratings yet
- Mid SemDocument2 pagesMid Semsourish.ambatiNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformsDocument2 pagesLaplace TransformsRandson CunhaNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems Question BankDocument3 pagesSignals and Systems Question BankEdward HarveyNo ratings yet
- Single Channel Phase-Aware Signal Processing in Speech Communication: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandSingle Channel Phase-Aware Signal Processing in Speech Communication: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Commensurabilities among Lattices in PU (1,n). (AM-132), Volume 132From EverandCommensurabilities among Lattices in PU (1,n). (AM-132), Volume 132No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Parametric Study of The Required Seating Length For Bridge Deck During EarthquakeDocument14 pagesParametric Study of The Required Seating Length For Bridge Deck During EarthquakeTarak A PositiveNo ratings yet
- Irctcs E Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Document2 pagesIrctcs E Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Tarak A PositiveNo ratings yet
- Manpower Management: Ravi Rai Mittal GO-004387L Prabhat Kumar GO - 004394F Chahat Sharma GO-004391NDocument16 pagesManpower Management: Ravi Rai Mittal GO-004387L Prabhat Kumar GO - 004394F Chahat Sharma GO-004391NTarak A PositiveNo ratings yet
- List of Figures Figure No Title Page NoDocument2 pagesList of Figures Figure No Title Page NoTarak A PositiveNo ratings yet
- Extreme Seismic Event Analysis of A Cable Stayed Bridge: Name1Surname1, Name2 Surname2 and Name3 Surname3Document1 pageExtreme Seismic Event Analysis of A Cable Stayed Bridge: Name1Surname1, Name2 Surname2 and Name3 Surname3Tarak A PositiveNo ratings yet
- Modal Pushover-Based Scaling of Records For Nonlinear RHA of One-Story Unsymmetric-Plan BuildingsDocument10 pagesModal Pushover-Based Scaling of Records For Nonlinear RHA of One-Story Unsymmetric-Plan BuildingsTarak A PositiveNo ratings yet
- ArchiveDocument1,448 pagesArchiveredsky991No ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur: Application Form For Admissions To Post Graduate 2015-2016Document3 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Kanpur: Application Form For Admissions To Post Graduate 2015-2016Tarak A PositiveNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Uttarakhand, INDIA 247667Document1 pageIndian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Uttarakhand, INDIA 247667Tarak A PositiveNo ratings yet
- Intro Bridge ProjectDocument33 pagesIntro Bridge ProjectTarak A PositiveNo ratings yet