Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Foundations of Circuit Analysis: Passive Sign Convention: Depiero Ee 201
Foundations of Circuit Analysis: Passive Sign Convention: Depiero Ee 201
Uploaded by
bwNorY0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views5 pagesThis document discusses the passive sign convention used in circuit analysis. The passive sign convention ensures conservation of energy by defining that passive circuit elements like resistors can only absorb power, with current flowing into the positive terminal. The sign convention is helpful for assigning voltage and current polarities. It determines whether power is absorbed or delivered by defining active elements to deliver power, with current flowing out of the positive terminal. For passive elements, the sign convention defines current flowing into the positive terminal results in power being absorbed.
Original Description:
EE 201 Cal Ply Passive Sign Convention
Original Title
B) Passv_Sign v6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the passive sign convention used in circuit analysis. The passive sign convention ensures conservation of energy by defining that passive circuit elements like resistors can only absorb power, with current flowing into the positive terminal. The sign convention is helpful for assigning voltage and current polarities. It determines whether power is absorbed or delivered by defining active elements to deliver power, with current flowing out of the positive terminal. For passive elements, the sign convention defines current flowing into the positive terminal results in power being absorbed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views5 pagesFoundations of Circuit Analysis: Passive Sign Convention: Depiero Ee 201
Foundations of Circuit Analysis: Passive Sign Convention: Depiero Ee 201
Uploaded by
bwNorYThis document discusses the passive sign convention used in circuit analysis. The passive sign convention ensures conservation of energy by defining that passive circuit elements like resistors can only absorb power, with current flowing into the positive terminal. The sign convention is helpful for assigning voltage and current polarities. It determines whether power is absorbed or delivered by defining active elements to deliver power, with current flowing out of the positive terminal. For passive elements, the sign convention defines current flowing into the positive terminal results in power being absorbed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Foundations of Circuit Analysis:
Passive Sign Convention
DePiero
EE 201
Learning Objectives
Apply the passive sign convention and
compute power dissipated by circuit
elements.
Passive Sign Convention Ensures
Conservation of Energy
Energy is Conserved When:
Total energy generated in a circuit equals
the total energy dissipated.
Ignoring issue of energy storage for now
Sign convention also helpful when
assigning voltage polarities in analysis
problems.
Sign Convention Determines
Power Absorption/Delivery
In these cases, V>0 and
I>0.
Passive devices (resistors)
can only absorb power. I
enters (+)
Active sources typically
deliver power. I leaves (+)
Active sources can also
absorb power. I enters (+)
P>0.
Absorbed
P<0.
Delivered
P>0.
Absorbed
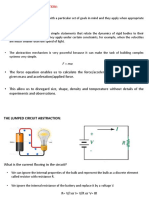
Using Passive Sign Convention
Works for an arbitrary direction for I flow
1) Label active elements (if unspecified).
Suggestion: Assume power is delivered.
For a voltage source, define I flowing out the (+) terminal.
For a current source, define +V terminal where I flows out.
If power is actually absorbed, then a V or I quantity will
evaluate to a negative value.
2) Label passive elements (resistors).
Power always absorbed. I flows in (+) terminal.
3) As needed, compute power absorbed.
If positive I flows into (+) terminal -> Power absorbed.
V>0 and I>0 in the above definitions!
You might also like
- Commercial-Style CP Dipole FMDocument5 pagesCommercial-Style CP Dipole FMStephen Dunifer100% (2)
- PH302 Exp 5 - Dipole AntennaDocument10 pagesPH302 Exp 5 - Dipole AntennaTerence CheonNo ratings yet
- EHB211 - Lec - 1-2-s22Document116 pagesEHB211 - Lec - 1-2-s22İsmet YıldırımNo ratings yet
- 3 Power, Passive Sign Convention, Resistor and Ohm's LawDocument19 pages3 Power, Passive Sign Convention, Resistor and Ohm's LawNainum FAREEDNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Analysis: Lecturer Dr. Ahmed Maamoon Al-KababjiDocument26 pagesElectrical Circuits Analysis: Lecturer Dr. Ahmed Maamoon Al-KababjiObaida AlmoulaNo ratings yet
- ME214 Lec2Document8 pagesME214 Lec2woboc79249No ratings yet
- Engr260-Lec1-Basics (Ink)Document34 pagesEngr260-Lec1-Basics (Ink)Nick RentschNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Analysis: Adnan YousafDocument26 pagesElectric Circuit Analysis: Adnan Yousafsufyan ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Current and Voltage LawsDocument21 pagesCurrent and Voltage LawssajjadNo ratings yet
- NT Unit Part 1Document62 pagesNT Unit Part 1ece placementNo ratings yet
- Cheat-Sheet Ebook 6thDocument11 pagesCheat-Sheet Ebook 6thNguyễn Bá HoàngNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1Document56 pagesLecture - 1mehariashfare2012No ratings yet
- Introduction To Circuits: Saiful Hasan Iot EngineerDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Circuits: Saiful Hasan Iot EngineerMusa AmanNo ratings yet
- The Power of AbstractionDocument22 pagesThe Power of Abstractionlisa annNo ratings yet
- Circuits, Ohm's Law, DC Circuit Analysis: EEE 3 Lecture 02Document25 pagesCircuits, Ohm's Law, DC Circuit Analysis: EEE 3 Lecture 02IanneSahagunNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3Document60 pagesLecture - 3mehariashfare2012No ratings yet
- CH1 Basic ConceptsDocument13 pagesCH1 Basic Conceptsjimmychium510srNo ratings yet
- Power in AC Circuits: EEE 3 Lecture 8Document23 pagesPower in AC Circuits: EEE 3 Lecture 8No OneNo ratings yet
- Slideset 1Document83 pagesSlideset 1Kishor KunalNo ratings yet
- ENGR12 Circuit Theory: Basic ConceptsDocument35 pagesENGR12 Circuit Theory: Basic ConceptsJohn Nate RiveraNo ratings yet
- Ee Unit 1Document170 pagesEe Unit 1samirsamir3244No ratings yet
- Electronics For IT Ch3 20212 P1Document54 pagesElectronics For IT Ch3 20212 P1Trịnh QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - MechDocument40 pagesLecture 1 - MechHassan El SayedNo ratings yet
- Lecture12 - 12284 - Lecture12 - 12284 - Fundamentaof DC Circuit 1Document40 pagesLecture12 - 12284 - Lecture12 - 12284 - Fundamentaof DC Circuit 1akshayasahoo402No ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical Engineering - 1st and 2nd ClassDocument21 pagesBasics of Electrical Engineering - 1st and 2nd ClassThe Lover BoyNo ratings yet
- Lec02 DC Circuits Mod YapDocument36 pagesLec02 DC Circuits Mod YapAndrea OnglaoNo ratings yet
- 5ECA0 Class 3: Equivalent Circuits (CH 5)Document81 pages5ECA0 Class 3: Equivalent Circuits (CH 5)Lars ReijndersNo ratings yet
- BME373 Electronics 2 CW 1Document53 pagesBME373 Electronics 2 CW 1azuma moses chijiokeNo ratings yet
- Circuits, Ohm's Law, DC Circuit Analysis: EEE 3 Lecture 02Document27 pagesCircuits, Ohm's Law, DC Circuit Analysis: EEE 3 Lecture 02No OneNo ratings yet
- 2 Resistor and Ohm's LawDocument17 pages2 Resistor and Ohm's LawNainum FAREEDNo ratings yet
- Basic Components and Electric CircuitsDocument30 pagesBasic Components and Electric CircuitsآشيشNo ratings yet
- 5ECA0 Lecture 2 v4Document114 pages5ECA0 Lecture 2 v4Jacob KwonNo ratings yet
- Al-Mansour University College Computer Technical Engineering First ClassDocument17 pagesAl-Mansour University College Computer Technical Engineering First ClassranjdarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 MechDocument41 pagesLecture 1 MechAinaa El-sayed MatwalyNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionDeepa ShreeNo ratings yet
- EEN 112 - Unit 2Document69 pagesEEN 112 - Unit 2abcccNo ratings yet
- Skeu2033 Circuit Theory IIIDocument20 pagesSkeu2033 Circuit Theory IIIAsdiyanna Johari0% (1)
- Circuit TheoremsDocument40 pagesCircuit TheoremsMostafa AymanNo ratings yet
- Matdid441904 PDFDocument180 pagesMatdid441904 PDFMohsen SaidiNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory: DR Paul S SpencerDocument13 pagesCircuit Theory: DR Paul S SpencerMathew ClewlowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Fundamental of Electric CircuitsDocument44 pagesChapter 1 - Fundamental of Electric CircuitsNur HazwanieNo ratings yet
- University of Hormuud: Circuit Analysis IDocument49 pagesUniversity of Hormuud: Circuit Analysis ISalmaanCadeXaajiNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit TheoryDocument19 pagesElectric Circuit TheoryAhmet AslanNo ratings yet
- 18Ees101J-Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering: Unit 1Document57 pages18Ees101J-Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering: Unit 1Mohammed JavidhNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3 Circuit ElementsDocument20 pagesLecture-3 Circuit Elementsabdul samiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document36 pagesChapter 1MUHAMMAD LUKMAN ARSHADNo ratings yet
- You Should Not Find This 2Document26 pagesYou Should Not Find This 2No OneNo ratings yet
- Topic 1. Basic Concepts & Laws PDFDocument93 pagesTopic 1. Basic Concepts & Laws PDFkeinhuat79No ratings yet
- Unit IDocument65 pagesUnit IShubhanshu VatsNo ratings yet
- Electrotechniques 143 NotesDocument12 pagesElectrotechniques 143 Notesrubygib1No ratings yet
- Ece249 Unit1Document182 pagesEce249 Unit1Sabick ANo ratings yet
- ME 214 Mechatronics: Associate Professor Kutay İçöz AGÜDocument62 pagesME 214 Mechatronics: Associate Professor Kutay İçöz AGÜAhmet Salih SEÇGÜNNo ratings yet
- Guc 47 62 42769 2024-03-12T11 18 13Document18 pagesGuc 47 62 42769 2024-03-12T11 18 13dodo sesaNo ratings yet
- Super Position and Maximum Power Transfer TheoremDocument70 pagesSuper Position and Maximum Power Transfer TheoremKasani Tirumala tejaNo ratings yet
- 03 Voltage and Current LawsDocument25 pages03 Voltage and Current Lawssaadbutt43215No ratings yet
- LN4 Geng2340Document111 pagesLN4 Geng2340Seth VineetNo ratings yet
- EEE141 - Topic 1Document49 pagesEEE141 - Topic 1mdnissan620No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - EEDocument43 pagesChapter 1 - EEFaiz Nazeri ZawawiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 EceDocument122 pagesUnit 1 EcedeepthidesettyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Circuit TheoremsDocument43 pagesLecture 5 - Circuit TheoremsYip Tuck WaiNo ratings yet
- Ece131: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Unit 1: DC CircuitsDocument108 pagesEce131: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Unit 1: DC CircuitsVimal KunwarNo ratings yet
- Engr / Brae 213: Bioengineering Fundamentals: Spring 2015 James Eason (Jceason@calpoly - Edu)Document25 pagesEngr / Brae 213: Bioengineering Fundamentals: Spring 2015 James Eason (Jceason@calpoly - Edu)bwNorYNo ratings yet
- Handout 6 Fixed PT Rotation ExamplesDocument3 pagesHandout 6 Fixed PT Rotation ExamplesbwNorYNo ratings yet
- Founda'Ons of Circuit Analysis: KVL and KCL: Depiero Ee 201Document6 pagesFounda'Ons of Circuit Analysis: KVL and KCL: Depiero Ee 201bwNorYNo ratings yet
- Ak If QadeerDocument2 pagesAk If QadeerbwNorYNo ratings yet
- 0460 443 301 GB (Caddy TIG 2200i - Manual 2019)Document28 pages0460 443 301 GB (Caddy TIG 2200i - Manual 2019)maverick kitaroNo ratings yet
- Atom and The Location of Its Major ComponentsDocument11 pagesAtom and The Location of Its Major ComponentsAldenramosNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mechanism Design (Ue19Me544) : Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Conservation of EnergyDocument1 pageAdvanced Mechanism Design (Ue19Me544) : Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Conservation of EnergySyed Hafeez Peeran QuadriNo ratings yet
- EPTD W5 MidDocument14 pagesEPTD W5 MidJunied TazrianNo ratings yet
- Motores Paso A Paso SanyoDocument68 pagesMotores Paso A Paso SanyoRUBEN VALDIVIANo ratings yet
- The Effect of Geographical Setting in Detecting Stray Muon Particle Using Cloud ChamberDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Geographical Setting in Detecting Stray Muon Particle Using Cloud ChamberKathNo ratings yet
- NSEP 2023 Question Paper With Answerkey 26 11 2023Document12 pagesNSEP 2023 Question Paper With Answerkey 26 11 2023chitrakshgupta21No ratings yet
- Q3 P. Task 7 - ElectromagnetDocument2 pagesQ3 P. Task 7 - ElectromagnetJhonazel SandovalNo ratings yet
- Task 1-Eider Estrada Task 1-Eider EstradaDocument11 pagesTask 1-Eider Estrada Task 1-Eider EstradaMiGue DAzaNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: 270-E/F/G Full Digital AC Servo DriverDocument88 pagesInstruction Manual: 270-E/F/G Full Digital AC Servo DriverIgor Norante50% (2)
- Modern Physics Lecture Feb 2022Document20 pagesModern Physics Lecture Feb 2022taimoorNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Low Noise Pseudomorphic HEMT in A Surface Mount Plastic PackageDocument15 pagesData Sheet: Low Noise Pseudomorphic HEMT in A Surface Mount Plastic PackageÍtalo CésarNo ratings yet
- Eightfold Way Foiljlk, MDocument9 pagesEightfold Way Foiljlk, MMax TrackNo ratings yet
- PHY1010Document3 pagesPHY1010ms harshithaNo ratings yet
- 7-Element-Yagi-Uda-Beam-Pune Hams Tech TalkDocument18 pages7-Element-Yagi-Uda-Beam-Pune Hams Tech TalkVAS TECHNOLOGYNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine Drives: Dr. Arsalan ArifDocument10 pagesElectrical Machine Drives: Dr. Arsalan ArifFaraz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Seismic WavesDocument18 pagesSeismic WavesCyrex Kyle MacuhaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field Theories For Engineering by Md. Abdus SalamDocument321 pagesElectromagnetic Field Theories For Engineering by Md. Abdus SalamWalker BautistaNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Generator Construction & Modeling: D DR - Firas Mohamme Power Year Electrical 4Document19 pagesSynchronous Generator Construction & Modeling: D DR - Firas Mohamme Power Year Electrical 4Ahmad AliNo ratings yet
- Ws4-Physics Jonel Follero Quito Bsce-1eDocument1 pageWs4-Physics Jonel Follero Quito Bsce-1eJonel Follero QuitoNo ratings yet
- Emerson Digital Compressor ControllerDocument17 pagesEmerson Digital Compressor ControllerJamal Al AdwaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science LESSON 2 ORGDocument3 pagesGrade 8 Science LESSON 2 ORGAngel Rose DionisioNo ratings yet
- Refractive Index of Liquid Using Convex Lens and Plane MirrorDocument4 pagesRefractive Index of Liquid Using Convex Lens and Plane Mirroralekse100% (8)
- Design of A Controlled Solid State Device For Fault Current Limitation and Arc Flash SuppressionDocument6 pagesDesign of A Controlled Solid State Device For Fault Current Limitation and Arc Flash SuppressionAnwar HossanNo ratings yet
- Aula 7 - Física Dos DiodosDocument59 pagesAula 7 - Física Dos DiodosjacksonsssouzzaNo ratings yet
- II. Solve The Following Problems WITH COMPLETE SOLUTION. DO NOT ROUND Off Your Answers. Strictly No CheatingDocument1 pageII. Solve The Following Problems WITH COMPLETE SOLUTION. DO NOT ROUND Off Your Answers. Strictly No CheatingGilagidkidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. IntroductionDocument18 pagesChapter 1. IntroductionMerlin MendozaNo ratings yet
- EET202 - Ktu QbankDocument8 pagesEET202 - Ktu QbankJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet