Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ABAP Overview - 2hrs
0 ABAP Overview - 2hrs
Uploaded by
వంశీ యుCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
0 ABAP Overview - 2hrs
0 ABAP Overview - 2hrs
Uploaded by
వంశీ యుCopyright:
Available Formats
Beyond the Obvious Beyond the Obvious
SAP R/3 System Overview
&
ABAP/4 Programming
SAP R/3 System
Overview of R/3 System
Logical View of R/3 System
ABAP/4 - SAP R/3 PROGRAMMING
LANGUAGE
Advanced Business
Application Programming
ABAP/4
Fourth generation language
Event driven
All SAP R/3 applications and parts of Basis are
developed in ABAP
Verbose language
Topics of Discussion
ABAP Development Workbench
Data Dictionary
Reports
BDC
SAP Script
Module Pool
ABAP Development Workbench
ABAP Development Workbench
ABAP Development Workbench is a graphical
programming environment which enables us to create
new ABAP applications and change existing SAP
applications.
ABAP Workbench - Transaction code -S001
Tools -> ABAP Workbench
Repository Browser - Transaction code - SE80
Data Dictionary - SE11
Function Builder - SE37
Screen Painter - SE51
Creating a Program
Click the button ABAP Editor in the Workbench
Creating a program
The program attributes screen looks like this
... Debugging
Runtime Analysis
Tells us how long do specific operations take during
the run
Gives the trace list of subroutines that have been
processed
SQL trace helps to trace database calls to find out
the tables used by the application
Development class
A set of logically related development environment
objects.
A development class together with its objects is
transportable.
Each development class is under the administration
of one user.
Creating development class
Data Dictionary
Data Dictionary
ABAP Development workbench tool
Stores system wide data definition
Completely integrated with ABAP Workbench
Data Dictionary objects
Data Elements
Domains
Tables
Structures
Views
REPORTS
ABAP/4 Reporting
Objectives
Understand data declarations, commands, system
fields used in reports
Understand the selection screens
Understand the program level events, conditions &
loops
Understand the data retrieval from the tables and
Internal tables
Understand the modularization techniques,
field symbols and logical databases
Types of programs
Type 1
run on its own
Can be started it in the R/3 system without a
transaction code
Can be executed in background
Type M ( Module pool)
Program cannot run on its own and can be called via
a transaction code
Type I ( Include )
Program Selections
SELECT-OPTIONS Statement
SELECT-OPTIONS <Name> FOR <Table field>
NO EXTENSION
OBLIGATORY
LOWER CASE
SELECT-OPTIONS allows specification of multiple
values and ranges. This can only be declared for
fields within tables defined in the TABLES statement.
Example
SELECT
SELECT
-
-
OPTIONS: S_KUNNR FOR KNA1
OPTIONS: S_KUNNR FOR KNA1
-
-
KUNNR
KUNNR.
Program Selections
PARAMETERS Statement
PARAMETERS <Name> TYPE
LIKE
OBLIGATORY
AS CHECKBOX
DEFAULT
This statement allows entry of a single value on the
selection screen.
Example :
PARAMETER
PARAMETER :
P_KUNNR LIKE KNA1
P_KUNNR LIKE KNA1
-
-
KUNNR
KUNNR.
Blocking Selection Screen
A sample screen
SELECTION-SCREEN BEGIN OF BLOCK RAD1
WITH FRAME TITLE TEXT-002.
PARAMETERS R1 RADIOBUTTON GROUP GR1.
PARAMETERS R2 RADIOBUTTON GROUP GR1.
PARAMETERS R3 RADIOBUTTON GROUP GR1.
SELECTION-SCREEN END OF BLOCK RAD1.
DATA Definitions
TYPES Statement
TYPES <name> TYPE or LIKE
DECIMALS
SAP allows the creation of new user defined data types.
And this does not create a variable, just a new type
that can be used in creating a variable.
Example :
TYPES : CC LIKE BKPF
TYPES : CC LIKE BKPF
-
-
BUKRS
BUKRS
DATA : NEW_CC TYPE CC.
DATA : NEW_CC TYPE CC.
Data Definitions
Internal Tables
DATA : BEGIN OF <name> OCCURS x,
(variable definitions)
END OF <name>.
Internal Tables are defined as an extension of a
structure, with the addition of an OCCURS clause.
Example
DATA : BEGIN OF T_WRK,
DATA : BEGIN OF T_WRK,
T_KUNNR LIKE KNA1
T_KUNNR LIKE KNA1
-
-
KUNNR,
KUNNR,
SW TYPE C,
SW TYPE C,
END OF T_WRK.
END OF T_WRK.
Program Level Events
INITIALIZATION.
AT SELECTION-SCREEN
AT SELECTION-SCREEN OUTPUT
START-OF-SELECTION
END-OF-SELECTION
TOP-OF-PAGE
END-OF-PAGE
AT LINE-SELECTION
AT USER-COMMAND
IF Statement
CASE Statement
Modularization techniques
Defining Macros
Include program
Subroutines
Function Module
BDC
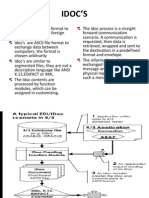
BDC - Batch Data Communication
To transfer data from non-SAP systems ( ie.
already available in electronic form )
Suitable for entering large amounts of data as it
executes the transactions automatically
Similar to entering the data in the transactions
manually
BDC Methods
Classical Method
Call Transaction
Call Dialog
Preparing a BDC Table
The BDC table should have five fields viz.,
1) Program name
2) Screen number
3) Screen begin
4) Field name
5) Field value
Preparing a BDC Table
For eg.
Prog Screen Scrn Field Field
name No begin name value
SAPMMO3M 0060 X
RM03M- MATNR mat.no
RM03M-MBRSH indu. sec
.
.
SAPMM03M 0080 X
RM03M-WERKS target pla
.
.
SAP Script
SAP Script
Objectives
Understand Forms, various components of forms
such as windows, pages, character format,
paragraph format etc.
Understand the control commands, symbols and
function modules in SAP Script.
Forms
Controls the page layout and text formatting
A form of the graphical Form Painter consists of
Header data
Page layout
Paragraph format
Character format
Documentation
SAP Script - Control commands
PERFORM Command
To Call an ABAP subroutine (form) from any program
Syntax
/: PERFORM <form> IN PROGRAM <prog>
/: USING &VAR1&
/: CHANGING &VAR2&
/: ENDPERFORM
Function Modules in SAP Script
Form functions
OPEN_FORM Opens the form output.
WRITE_FORM Calls a form element
CLOSE_FORM Ends the form output.
START_FORM Starts a new form.
Database
READ_TEXT Reads a text module and
passes
it to the specified work areas.
Module Pool
Creating Screens
Click screen painter button in Workbench
Structure of program
Flow logic
The flow logic of a screen drives the processing
sequence for that particular screen. Flow logic
describes how the program reacts to the user actions.
The events used for this purpose are,
Process before output (PBO)
Process after input (PAI)
Process on value request (POV)
Process on help request (POH)
You might also like
- SAP S/4HANA Retail: Processes, Functions, CustomisingFrom EverandSAP S/4HANA Retail: Processes, Functions, CustomisingRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- QT Forms Summary Qt1 Qt11Document1 pageQT Forms Summary Qt1 Qt11Muhammad Rafiq100% (2)
- Learn SAP The German WayDocument5 pagesLearn SAP The German WayKris TJ100% (1)
- Uploading Customer Master Extended Address Using BAPI MethodDocument3 pagesUploading Customer Master Extended Address Using BAPI Methodnet6351No ratings yet
- Outbound Delivery SettingsDocument5 pagesOutbound Delivery Settingslostrider_991100% (1)
- Change SAP Documents - CDHDR & CDPOSDocument4 pagesChange SAP Documents - CDHDR & CDPOSSquall LeeNo ratings yet
- SHD0Document3 pagesSHD0Gaurav HarimitterNo ratings yet
- Credit Management IN Sap SDDocument14 pagesCredit Management IN Sap SDRanjith SuddalaNo ratings yet
- OMRT - Account Key UssageDocument16 pagesOMRT - Account Key Ussageneelam618No ratings yet
- SHRM AssignmentDocument4 pagesSHRM AssignmentNaveen Pradhan100% (1)
- SAP interface programming with RFC and VBA: Edit SAP data with MS AccessFrom EverandSAP interface programming with RFC and VBA: Edit SAP data with MS AccessNo ratings yet
- BAPI Pricing Upload ProgramDocument3 pagesBAPI Pricing Upload ProgramSoumenNo ratings yet
- Pricing - Condition Base ValueDocument5 pagesPricing - Condition Base Valuemahesshbabum9231100% (1)
- Schedule Line CategoriesDocument3 pagesSchedule Line Categoriessushma_311819No ratings yet
- Text Determination IMG319081308573999Document18 pagesText Determination IMG319081308573999Anadi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Procedure To Schedule Batch Jobs in SAPDocument4 pagesStep by Step Procedure To Schedule Batch Jobs in SAPTim Nelson100% (1)
- E Invoice SystemDocument8 pagesE Invoice SystemSapSDNo ratings yet
- Sap SDDocument9 pagesSap SDSouvik_DasNo ratings yet
- SAP Output Condition Records TablesDocument5 pagesSAP Output Condition Records TablesDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- SAP Creating VOFM Custom RoutineDocument15 pagesSAP Creating VOFM Custom RoutineRamesh BalajiNo ratings yet
- BRF+ OutputDocument2 pagesBRF+ OutputKakarla ChanduNo ratings yet
- Pricing Requirements in Sap-Sd Sales Order ProcessingDocument3 pagesPricing Requirements in Sap-Sd Sales Order ProcessingLaxmi Narsimha Rao MamidalaNo ratings yet
- Beginner'S Guide To Ale and Idocs - A Step-By-Step ApproachDocument9 pagesBeginner'S Guide To Ale and Idocs - A Step-By-Step ApproachLokamNo ratings yet
- Idocs in Sap StepsDocument46 pagesIdocs in Sap StepsSyamal Babu N100% (1)
- Report - Sales Order Stock ReportDocument24 pagesReport - Sales Order Stock Reportrajeshec83100% (1)
- ALVgrid Example With CL - Gui - Alv - Grid and Screen PainterDocument6 pagesALVgrid Example With CL - Gui - Alv - Grid and Screen PainterHIRAGULROONo ratings yet
- SHD 0Document14 pagesSHD 0sandipsen198625No ratings yet
- FS - TS - e - PD758 Mnemonic - PDDocument14 pagesFS - TS - e - PD758 Mnemonic - PDSrinivasan NarasimmanNo ratings yet
- Sales Order ReportDocument16 pagesSales Order ReportJetendra MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- User ExitsDocument3 pagesUser Exitsvenkat100% (1)
- Sap SD - Basic Q & ADocument4 pagesSap SD - Basic Q & Ashekharsaseendran100% (1)
- Isrt SD Fs 005 in Pgi Block Auto-Removal v1.1Document4 pagesIsrt SD Fs 005 in Pgi Block Auto-Removal v1.1chetan100% (1)
- Returnable PackagingDocument11 pagesReturnable Packagingshailesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Sap QuestionaireDocument68 pagesSap QuestionaireLaxmi Vadlamudi100% (1)
- SAP SD Tables: Tables For Sales DocumentsDocument22 pagesSAP SD Tables: Tables For Sales DocumentsbeezusapNo ratings yet
- SAP Query IntroductionDocument7 pagesSAP Query Introductionkashram2001No ratings yet
- IDOCSDocument12 pagesIDOCSnaanakadaluNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Frequently Asked Questions1Document2 pagesSAP SD Frequently Asked Questions1Kamal BatraNo ratings yet
- Userexit Move Field To Vbakd951c031 524e 424b B7fa Bfd58ea6a412Document9 pagesUserexit Move Field To Vbakd951c031 524e 424b B7fa Bfd58ea6a412mm1979No ratings yet
- Differences Between Various Technologies in SAPDocument7 pagesDifferences Between Various Technologies in SAPnimi111100% (1)
- BDC Project Real TimeDocument14 pagesBDC Project Real Timerajesh98765No ratings yet
- SAP MM Stock TablesDocument19 pagesSAP MM Stock TablesrksamplaNo ratings yet
- Vics 856Document126 pagesVics 856EdNo ratings yet
- BRF+ ConfigDocument7 pagesBRF+ Configdeepankar senguptaNo ratings yet
- IDoc Basics For Functional ConsultantsDocument36 pagesIDoc Basics For Functional ConsultantsManoj JoshiNo ratings yet
- FI&SDIntegration (1) 20120529132458.211 XDocument66 pagesFI&SDIntegration (1) 20120529132458.211 XVikas ZurmureNo ratings yet
- Sample 850 EDI Specification PDFDocument33 pagesSample 850 EDI Specification PDFTejendra Soni100% (1)
- Sappress Abap Objects ApplicationDocument56 pagesSappress Abap Objects Applicationswap0lovein0% (1)
- How To Debug A Background SAP Workflow Method 1612299099Document5 pagesHow To Debug A Background SAP Workflow Method 1612299099Sajal RastogiNo ratings yet
- Data Migration in Sap Using LSMW: CA Swapnil ChavdaDocument62 pagesData Migration in Sap Using LSMW: CA Swapnil ChavdafharooksNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Consignment Sales Process.Document2 pagesSAP SD Consignment Sales Process.praveennbsNo ratings yet
- Material MasterDocument17 pagesMaterial Mastermic29100% (3)
- Cross Selling by Manoj Tony : Key Configuration DocumentDocument12 pagesCross Selling by Manoj Tony : Key Configuration DocumentAslam AnsariNo ratings yet
- BP in GLDocument35 pagesBP in GLMohammed Al SaaidiNo ratings yet
- Sap SD Route DeterminationDocument4 pagesSap SD Route Determinationsumit patilNo ratings yet
- AFS - Stock Allocations For New Demands and MRP's Behavior For Standard OrdersDocument22 pagesAFS - Stock Allocations For New Demands and MRP's Behavior For Standard OrdersSrinivas KotteNo ratings yet
- Usefull Sap SD NoteDocument3 pagesUsefull Sap SD NoteNarayanaNo ratings yet
- Saphelp Afs50 en 56 028e39b7b3972ce10000000a114084 ContentDocument49 pagesSaphelp Afs50 en 56 028e39b7b3972ce10000000a114084 ContentNirmal Kuruwita100% (2)
- Custom Fiori Applications in SAP HANA: Design, Develop, and Deploy Fiori Applications for the EnterpriseFrom EverandCustom Fiori Applications in SAP HANA: Design, Develop, and Deploy Fiori Applications for the EnterpriseNo ratings yet
- MidTerm Exam 2015 - Example To 2018Document7 pagesMidTerm Exam 2015 - Example To 2018kdhgxobjNo ratings yet
- Miniature Advanced Communication Engine (Mini-Ace) and Mini-Ace PlusDocument13 pagesMiniature Advanced Communication Engine (Mini-Ace) and Mini-Ace Plusgotcha75No ratings yet
- Pacing Guidelines For Java FundamentalsDocument1 pagePacing Guidelines For Java FundamentalsToram OnlineNo ratings yet
- Internal Cleaness ProcedureDocument26 pagesInternal Cleaness Procedureqamar qateebNo ratings yet
- Ff1 Cen Cim D v0 11Document17 pagesFf1 Cen Cim D v0 11Ankur KumarNo ratings yet
- Sample Reflection Paper After Seminar About ICT Integration in Teaching PDFDocument1 pageSample Reflection Paper After Seminar About ICT Integration in Teaching PDFSherwin Ian VillasenorNo ratings yet
- Jotun Facade New 21 - tcm132 91545Document5 pagesJotun Facade New 21 - tcm132 91545dnytan12345No ratings yet
- 7SG14 - Duobias M Complete Technical Manual PDFDocument142 pages7SG14 - Duobias M Complete Technical Manual PDFsteve_osullivanNo ratings yet
- TranscriptDocument3 pagesTranscriptrob51489No ratings yet
- Y205 EN2 05+IndAutomGuide2011 SensingDocument116 pagesY205 EN2 05+IndAutomGuide2011 SensingEnrique Palacín CarruescoNo ratings yet
- challanform9TH BIODocument1 pagechallanform9TH BIOferozabad schoolNo ratings yet
- Burners For Pyrolysis FurnacesDocument7 pagesBurners For Pyrolysis FurnacesAleem QureshiNo ratings yet
- Eeu 205 - Lesson Plan 5Document4 pagesEeu 205 - Lesson Plan 5api-434335837No ratings yet
- Siemens Sample Configurations - IEtoPB Link - June03Document15 pagesSiemens Sample Configurations - IEtoPB Link - June03Hhaabbde SybaritzNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Individual Complex Multi-Level Business Communication Development - Assignment 2 FACTSHEETDocument1 pageModule 4 - Individual Complex Multi-Level Business Communication Development - Assignment 2 FACTSHEETtarawneh92No ratings yet
- Boiler Heating SurfacesDocument12 pagesBoiler Heating SurfacesHai NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Open and Frugal LabwareDocument4 pagesThe Importance of Open and Frugal LabwareRomenick BelloNo ratings yet
- NATIONAL TESTING AGENCY JEE (Main) Session - 3Document7 pagesNATIONAL TESTING AGENCY JEE (Main) Session - 3SouravNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer White PaperDocument14 pagesHeat Transfer White PaperflitzzzNo ratings yet
- B767 IPC SupplementDocument133 pagesB767 IPC Supplementadonis hernandezNo ratings yet
- Bill of Quantity F G H (B2 Column 22F Slab) Include Form Work, Exclude Concrete and Rebar (Conventional Form Work)Document2 pagesBill of Quantity F G H (B2 Column 22F Slab) Include Form Work, Exclude Concrete and Rebar (Conventional Form Work)Phanint NgounNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae - Nicolaas Van Rensburg: Personal InformationDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae - Nicolaas Van Rensburg: Personal InformationArnouxNo ratings yet
- First Solar Series 3 Black Plus Module: User GuideDocument15 pagesFirst Solar Series 3 Black Plus Module: User GuideedsonleviNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and DesignDocument6 pagesSystem Analysis and DesignHoney Gambhir100% (1)
- EPM Products Broucher - IntroductionDocument8 pagesEPM Products Broucher - IntroductionKendra TerryNo ratings yet
- 09 Chapter 3Document41 pages09 Chapter 3Krishna GNo ratings yet
- Applying GAMP 5 To Validate An ERP SystemDocument8 pagesApplying GAMP 5 To Validate An ERP SystemTahir ZiaNo ratings yet