Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deflection: Moment Area Method (Mohr's Theorem, 1868) 1 Deformed Partial Beam
Deflection: Moment Area Method (Mohr's Theorem, 1868) 1 Deformed Partial Beam
Uploaded by
Dilon FernandoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Aer520 LabsDocument37 pagesAer520 LabsChristopher LauricoNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress StrainDocument141 pagesSimple Stress Strainjs kalyana ramaNo ratings yet
- KD Panels - Tds (En)Document4 pagesKD Panels - Tds (En)Dilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- KD Panels - Tds (En)Document4 pagesKD Panels - Tds (En)Dilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- 17 DeflectDocument11 pages17 DeflectDhurai KesavanNo ratings yet
- 12 Deflection 78707054Document12 pages12 Deflection 78707054manuel jimenezNo ratings yet
- 15 Flexure Section ModulusDocument12 pages15 Flexure Section ModulusAbu Bakar Siddke RumiNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials EngineerdogDocument150 pagesStrength of Materials EngineerdogEng-Mohammed Abu NuktaNo ratings yet
- Connections 3Document72 pagesConnections 3jrobert123321No ratings yet
- Ex3 LTBeamDocument27 pagesEx3 LTBeamYoussef AliNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialFormulas Short NotesDocument19 pagesStrength of MaterialFormulas Short NotesRavindra DevireddyNo ratings yet
- 2E4B BucklingDocument4 pages2E4B BucklingMohd Ridzuan Ahmad100% (1)
- Strength of Materials Important FormulasDocument19 pagesStrength of Materials Important FormulasSomrajNo ratings yet
- Unrestrained-Beam (STEEL PROJEK)Document11 pagesUnrestrained-Beam (STEEL PROJEK)AsmatSalSabilaNo ratings yet
- Deflection of BeamsDocument7 pagesDeflection of Beamsdipeshbarua55No ratings yet
- Shear WallDocument238 pagesShear Wallri olNo ratings yet
- Columnas Transicion Parabola JohnsonDocument7 pagesColumnas Transicion Parabola Johnsonjmam1992No ratings yet
- Strength of Material Formulas Short NoteDocument19 pagesStrength of Material Formulas Short NotePankaj pacharNo ratings yet
- Table: TABLE 6.1: Trial V I θ P (mW) Z R X L 1 2 3Document3 pagesTable: TABLE 6.1: Trial V I θ P (mW) Z R X L 1 2 3Klea OrosaNo ratings yet
- EM3 - Unit1Document11 pagesEM3 - Unit1P.V.RAMA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Steel Tension Member Design by Asd LRFD Steel Construct On ManualDocument20 pagesSteel Tension Member Design by Asd LRFD Steel Construct On Manual201087No ratings yet
- Experiment No.: 5 Test of Slender Column: 1. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperiment No.: 5 Test of Slender Column: 1. ObjectivesAsad UzzamanNo ratings yet
- Bending & Shearing Stresses: Lesson 2Document38 pagesBending & Shearing Stresses: Lesson 2dummya790No ratings yet
- Ejercicios - Resueltos - Diagramas de Momento y CortanteDocument11 pagesEjercicios - Resueltos - Diagramas de Momento y CortanteEstebanVasquezNo ratings yet
- 2008 - Shattuck - Thomas W. Shattuck Department of Chemistry Colby College Waterville, Maine 04901Document77 pages2008 - Shattuck - Thomas W. Shattuck Department of Chemistry Colby College Waterville, Maine 04901Barry SchizzelNo ratings yet
- Moment Distribution and Moment Re-DistributionDocument44 pagesMoment Distribution and Moment Re-DistributionJeff Sun100% (1)
- Bus Span & Deflection Help PDFDocument5 pagesBus Span & Deflection Help PDFarathi_rajeevNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document10 pagesLab Report 1abhishek kumar0% (1)
- Simple Stress StrainDocument141 pagesSimple Stress StrainvelavansuNo ratings yet
- WeldDocument43 pagesWeldAuggie AranzadoNo ratings yet
- Simply Supported Beam With Both Side Ovehang Help For Bending Moment and Shear Force, Engineering, Homework Help - TranstutorsDocument6 pagesSimply Supported Beam With Both Side Ovehang Help For Bending Moment and Shear Force, Engineering, Homework Help - TranstutorsMayur PatelNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #11 1.050 Solid Mechanics Fall 2004Document2 pagesProblem Set #11 1.050 Solid Mechanics Fall 2004Anthony HouseNo ratings yet
- Ce 308 - Slope-W DemonstrationDocument29 pagesCe 308 - Slope-W DemonstrationjanakaNo ratings yet
- Buckling TestDocument19 pagesBuckling TestMEjiNasRizNo ratings yet
- Unit V Moment Distribution MethodDocument28 pagesUnit V Moment Distribution MethodkarthipriyaNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structure Lecture Notes 2Document14 pagesCrystal Structure Lecture Notes 2Practical Piyangshu YTNo ratings yet
- Relation Between Load, Shear and Moments:: Example 1Document10 pagesRelation Between Load, Shear and Moments:: Example 1John August BigalbalNo ratings yet
- Deflection of BeamDocument9 pagesDeflection of BeamKirk S PhotongNo ratings yet
- Column BuckingDocument14 pagesColumn BuckingKoh Yong TengNo ratings yet
- Topic 16 FB (Weak Axis) and MNDocument16 pagesTopic 16 FB (Weak Axis) and MNangelica abanesNo ratings yet
- The Hong Kong Polytechnic UniversityDocument8 pagesThe Hong Kong Polytechnic University1214135360No ratings yet
- Lateral Torsional and Distortional Buckling of Channel-And Hat-SectionsDocument23 pagesLateral Torsional and Distortional Buckling of Channel-And Hat-SectionsThiago SilvaNo ratings yet
- Monorail 0.5 TonDocument9 pagesMonorail 0.5 TonAndreas HendiNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Beam (LRFD, Load and Resistance Factor Design)Document5 pagesDesign of Steel Beam (LRFD, Load and Resistance Factor Design)surajoffshoreNo ratings yet
- How To Determine Correct Number of Earthing Electrodes (Strips, Plates and Pipes) - Part 1Document12 pagesHow To Determine Correct Number of Earthing Electrodes (Strips, Plates and Pipes) - Part 1Burraq Engineering SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Experiment Code - J Solid Mechanics Lab: Shashank R - ME16B164 Shubham Jain-ME16B165Document10 pagesExperiment Code - J Solid Mechanics Lab: Shashank R - ME16B164 Shubham Jain-ME16B165Purvang ParmarNo ratings yet
- Slide Share BDocument42 pagesSlide Share BShakeel WaseemNo ratings yet
- Sample 3Document13 pagesSample 3Wesam MalehNo ratings yet
- Comp Chem 5Document39 pagesComp Chem 5esraamohamady790No ratings yet
- Prob Set 1Document8 pagesProb Set 1BlackmorphaNo ratings yet
- CCIP Errata Worked Examples To Eurocode 2 Jan2012Document13 pagesCCIP Errata Worked Examples To Eurocode 2 Jan2012fan_luc89No ratings yet
- MD2Document5 pagesMD2nagmajerald17No ratings yet
- Cantilever Beam Long ReportDocument21 pagesCantilever Beam Long ReportAbdul Azeez Ismaila ShuaibuNo ratings yet
- Deep BeamDocument31 pagesDeep BeamEngr Mohammed Ubaid QureshiNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Principles of Plasma Discharges and Materials ProcessingFrom EverandPrinciples of Plasma Discharges and Materials ProcessingNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesFrom Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Method of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsFrom EverandMethod of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- 2019door Controls Hardware Typical Product Catalogue PDFDocument151 pages2019door Controls Hardware Typical Product Catalogue PDFDilon Fernando75% (4)
- E8231PRL1F: Product DatasheetDocument2 pagesE8231PRL1F: Product DatasheetDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- All Type of Footing DesignDocument26 pagesAll Type of Footing DesignDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- L 787 DatasheetDocument2 pagesL 787 DatasheetDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Lovair L-966 Waste Bins 3D DatasheetDocument2 pagesLovair L-966 Waste Bins 3D DatasheetDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Lovair L-977 Waste Bins DatasheetDocument2 pagesLovair L-977 Waste Bins DatasheetDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Eumseong #1 Factory Eumseong #2 Factory Jincheon #1 FactoryDocument2 pagesEumseong #1 Factory Eumseong #2 Factory Jincheon #1 FactoryDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Tender Specification LOOP Type I Magnetic SystemDocument2 pagesTender Specification LOOP Type I Magnetic SystemDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Loop Type 1 Mounting InstructionsDocument8 pagesLoop Type 1 Mounting InstructionsDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Gold StarDocument3 pagesGold StarDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- White Star: White, Interior & Exterior Wall & Floor Tile / Stone AdhesiveDocument3 pagesWhite Star: White, Interior & Exterior Wall & Floor Tile / Stone AdhesiveDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Litokol X11 - Litokol X12Document4 pagesLitokol X11 - Litokol X12Dilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Elephant Gypsum Boards Specification - Moistbloc BoardDocument1 pageElephant Gypsum Boards Specification - Moistbloc BoardDilon Fernando0% (1)
- Loop Type 1 Mounting InstructionsDocument8 pagesLoop Type 1 Mounting InstructionsDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Under Tile & Stone PrimerDocument2 pagesUnder Tile & Stone PrimerDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- K10 GRS 2000Document2 pagesK10 GRS 2000Dilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- FC SSDocument2 pagesFC SSDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Modesty Panel PG 1 PDFDocument1 pageModesty Panel PG 1 PDFDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Zer Ve BoardDocument2 pagesZer Ve BoardDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Laticrete 252 TDSDocument5 pagesLaticrete 252 TDSDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Bar ScheduleDocument9 pagesBar ScheduleDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Weather BlocDocument4 pagesWeather BlocDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- 2008 08 21 Steel Piling Handbook Design EnglischDocument213 pages2008 08 21 Steel Piling Handbook Design EnglischIancu-Bogdan Teodoru100% (2)
Deflection: Moment Area Method (Mohr's Theorem, 1868) 1 Deformed Partial Beam
Deflection: Moment Area Method (Mohr's Theorem, 1868) 1 Deformed Partial Beam
Uploaded by
Dilon FernandoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Deflection: Moment Area Method (Mohr's Theorem, 1868) 1 Deformed Partial Beam
Deflection: Moment Area Method (Mohr's Theorem, 1868) 1 Deformed Partial Beam
Uploaded by
Dilon FernandoCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Deflection Prof Schierle 1
Deflection Prof Schierle 2
Deflection
Beamdeflectionmust belimitedto:
=L/ 360for LL
=L/ 240for combinedLL+DL.
Beamdeflectioniscausedbybothbendingandshear
Bendingdeflectiongoverns longbeams
Shear deflectiongoverns short beams,
but isvery small andusuallyignored
1 Simplebeamunder uniformload
2 Largebendingdeflectionof simplebeam
3 Small shear deflectionof simplebeam
4 Small bendingdeflectionof short cantilever beam
5 Large shear deflection of short cantilever beam
Deflection Prof Schierle 3
Moment Area Method (Mohrs Theorem, 1868)
http://www.scribd.com/doc/58608799/Mohrs-Theorems-1
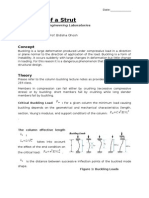
1 Deformed partial beam
AssumingGBis parallel toFO
ThenFG=AB, theunstressedlength
and GH/AB=, theunit strain.
Since E=f/ f=E f=EGH/AB.
Duetosimilar triangles
GH/AB=c/r f =Ec/r
Sincef=Mc/I Ec/r=Mc/I E/r=M/I 1/r =M/ EI
2 Elastic curve ABof partial beam
Assumingangles inradians:
Radial angled betweenm andn and
Tangent angle betweenA andB, yields:
dx=r d d/dx =1/r =M/ EI d=Mdx/ EI
=d =Mdx/ EI. Hence
= A
m
/ EI
A
m
=Mdx=bendingdiagramareabetweenAandB.
Slope Theorem
The angle between tangents at A and B on the
elastic curve of a beam is the moment diagram
area between A & B, divided by EI
A
m
2
Deflection Prof Schierle 4
A
m
=Mdx=bendingdiagramareabetweenAandB
x =lever armfromAtocentroidof bendingdiagram
xd =x d
Thus
=xd =Mdx/ EI, or
= x A
m
/ EI
Deflection Theorem
The displacement of the tangent at B on the
elastic curve equals the moment of the bending
diagram area between A and B times the lever-
arm x from its centroid to A, divided by EI.
A
m
Deflection Prof Schierle 5
Deflection formulas
=slopeof thetangent of theelasticcurve
=maximumdeflection.
1 Cantilever beamwithpoint load
=(PL)(L/2)/(EI) = 2/3L
= 1/2 PL
2
/(EI)
= 1/3 PL
3
/(EI)
2 Cantilever beamwithuniformload
=(WL/2)(L/3)/(EI) = 3/4L
= 1/6 WL
2
/(EI)
= 1/8 WL
3
/(EI)
3 Simplebeamwithpoint load
=(PL/4)(L/4)/(EI) = 1/3L
= 1/16 PL
2
/(EI)
= 1/48 PL
3
/(EI)
4 Simplebeamwithuniformload
=(WL/8)(2/3L/2)/(EI) = 5/16L
= 1/24 WL
2
/(EI)
= 5/384 WL
3
/(EI)
Deflection Prof Schierle 6
Beam formulas
The formulas include for common beams:
M= bending moment
V = shear
= deflection
3
Deflection Prof Schierle 7
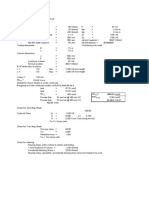
Steel beam with point load
Beamsupportsjoist point load(P=8k). Designfor stress
(F
b
=22ksi, checkdeflectionandredesignif required.
1 Beamdiagram
2 Loaddiagram(ignoreloadat supportswhichhasnoeffect
onshear, bending, or deflection)
Shear
V
a
=V
bl
=2(8)/2 V
a
=V
bl
=8k
V
br
=V
cl
=8-8 V
br
=V
cl
=0k
V
cr
=V
d
=R=0-8 V
cr
=V
d
=8k
Bending moment
M
max
=8(10) M
max
=80k
Required section modulus
S=M/F
b
=80k(12)/22ksi S=44in
3
TryW10x45, S=49.1in
3
49.1>44, ok
FromAISCtable I =248in
4
Deflection (L=30(12) =360)
=(23/648)PL
3
/EI
=(23/648)8(360
3
)/[(30000)248] =1.78
all
=360/240=1.5 1.5<1,78, not ok
TryW18x35, S=57.6in
3
, I =510in
4
Deflection
=[(23/648)8(360
3
)]/[(30000)510] =0.87
1.5>0.87, ok
Note: theW10x45of 36span/depthratioistooshallow;
whiletheW18x35hastherecommendedratioof 20, is
lighter andmoreeconomical.
Deflection Prof Schierle 8
Steel beam(with mixed load)
Steel beamsupports8kjoist load+0.4kfl uniformDL
(beam, fireproofing&finish), L=30(12) =360, F
b
=22ksi
1 Beamdiagram
2 Loaddiagram(ignoreloadat supports)
Shear
V
a
=R=[2(8)+0.4(30)]/2 V
a
=14k
V
bl
=14-0.4(10) V
bl
=10k
V
br
=10-8 V
br
=2k
V
cl
= 2-0.4(10) V
cl
=-2k
V
cr
=-2-8 V
cr
=-10k
V
d
=-10-0.4(10) V
d
=-14k
Bending moment
M=10(14+10)/2+5(2)/2 M=125k
Required Section modulus S
S=M/F
b
=125k(12)/22 ksi S=68in
3
TryW18x40, S=68.4in
3
68.4>68, ok
FromAISCtable I =612in
4
Deflection
W=wL=0.4(30) W=12k
max
=(23/684) PL
3
/(EI) +(5/384) WL
3
/(EI) *
* Combinedpoint loadanduniformload
max
=[(23/684)8(360)
3
+(5/384)12(360)
3
]/[(30000)612]
max
=1.1
all
=360/240=1.5in 1.5>1.1, ok
Deflection Prof Schierle 9
Deflection vs. span
Theformulas
V=wL
M=wL
2
/8
=(5/384) wL
4
/EI
reveal:
V increases linearly withL
M increases quadratic withL
increases tothe4
th
power withL
If Ldoubles increase16times !
1 Beamwith = 1
2 Double span with = 16
3 Short span: shear V governs
4 Mediumspan: bending Mgoverns
5 Long span: deflection governs
4
Deflection Prof Schierle 10
Deflection vs. I (moment of inertia)
64 1/64 4 Four boardsglued
8 1/8 3 Twinboardglued
2 1/2 2 Twinboard
1 1 1 Singleboard
I Typeof beam
Deflection Prof Schierle 11
You might also like
- Aer520 LabsDocument37 pagesAer520 LabsChristopher LauricoNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress StrainDocument141 pagesSimple Stress Strainjs kalyana ramaNo ratings yet
- KD Panels - Tds (En)Document4 pagesKD Panels - Tds (En)Dilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- KD Panels - Tds (En)Document4 pagesKD Panels - Tds (En)Dilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- 17 DeflectDocument11 pages17 DeflectDhurai KesavanNo ratings yet
- 12 Deflection 78707054Document12 pages12 Deflection 78707054manuel jimenezNo ratings yet
- 15 Flexure Section ModulusDocument12 pages15 Flexure Section ModulusAbu Bakar Siddke RumiNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials EngineerdogDocument150 pagesStrength of Materials EngineerdogEng-Mohammed Abu NuktaNo ratings yet
- Connections 3Document72 pagesConnections 3jrobert123321No ratings yet
- Ex3 LTBeamDocument27 pagesEx3 LTBeamYoussef AliNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialFormulas Short NotesDocument19 pagesStrength of MaterialFormulas Short NotesRavindra DevireddyNo ratings yet
- 2E4B BucklingDocument4 pages2E4B BucklingMohd Ridzuan Ahmad100% (1)
- Strength of Materials Important FormulasDocument19 pagesStrength of Materials Important FormulasSomrajNo ratings yet
- Unrestrained-Beam (STEEL PROJEK)Document11 pagesUnrestrained-Beam (STEEL PROJEK)AsmatSalSabilaNo ratings yet
- Deflection of BeamsDocument7 pagesDeflection of Beamsdipeshbarua55No ratings yet
- Shear WallDocument238 pagesShear Wallri olNo ratings yet
- Columnas Transicion Parabola JohnsonDocument7 pagesColumnas Transicion Parabola Johnsonjmam1992No ratings yet
- Strength of Material Formulas Short NoteDocument19 pagesStrength of Material Formulas Short NotePankaj pacharNo ratings yet
- Table: TABLE 6.1: Trial V I θ P (mW) Z R X L 1 2 3Document3 pagesTable: TABLE 6.1: Trial V I θ P (mW) Z R X L 1 2 3Klea OrosaNo ratings yet
- EM3 - Unit1Document11 pagesEM3 - Unit1P.V.RAMA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Steel Tension Member Design by Asd LRFD Steel Construct On ManualDocument20 pagesSteel Tension Member Design by Asd LRFD Steel Construct On Manual201087No ratings yet
- Experiment No.: 5 Test of Slender Column: 1. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperiment No.: 5 Test of Slender Column: 1. ObjectivesAsad UzzamanNo ratings yet
- Bending & Shearing Stresses: Lesson 2Document38 pagesBending & Shearing Stresses: Lesson 2dummya790No ratings yet
- Ejercicios - Resueltos - Diagramas de Momento y CortanteDocument11 pagesEjercicios - Resueltos - Diagramas de Momento y CortanteEstebanVasquezNo ratings yet
- 2008 - Shattuck - Thomas W. Shattuck Department of Chemistry Colby College Waterville, Maine 04901Document77 pages2008 - Shattuck - Thomas W. Shattuck Department of Chemistry Colby College Waterville, Maine 04901Barry SchizzelNo ratings yet
- Moment Distribution and Moment Re-DistributionDocument44 pagesMoment Distribution and Moment Re-DistributionJeff Sun100% (1)
- Bus Span & Deflection Help PDFDocument5 pagesBus Span & Deflection Help PDFarathi_rajeevNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document10 pagesLab Report 1abhishek kumar0% (1)
- Simple Stress StrainDocument141 pagesSimple Stress StrainvelavansuNo ratings yet
- WeldDocument43 pagesWeldAuggie AranzadoNo ratings yet
- Simply Supported Beam With Both Side Ovehang Help For Bending Moment and Shear Force, Engineering, Homework Help - TranstutorsDocument6 pagesSimply Supported Beam With Both Side Ovehang Help For Bending Moment and Shear Force, Engineering, Homework Help - TranstutorsMayur PatelNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #11 1.050 Solid Mechanics Fall 2004Document2 pagesProblem Set #11 1.050 Solid Mechanics Fall 2004Anthony HouseNo ratings yet
- Ce 308 - Slope-W DemonstrationDocument29 pagesCe 308 - Slope-W DemonstrationjanakaNo ratings yet
- Buckling TestDocument19 pagesBuckling TestMEjiNasRizNo ratings yet
- Unit V Moment Distribution MethodDocument28 pagesUnit V Moment Distribution MethodkarthipriyaNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structure Lecture Notes 2Document14 pagesCrystal Structure Lecture Notes 2Practical Piyangshu YTNo ratings yet
- Relation Between Load, Shear and Moments:: Example 1Document10 pagesRelation Between Load, Shear and Moments:: Example 1John August BigalbalNo ratings yet
- Deflection of BeamDocument9 pagesDeflection of BeamKirk S PhotongNo ratings yet
- Column BuckingDocument14 pagesColumn BuckingKoh Yong TengNo ratings yet
- Topic 16 FB (Weak Axis) and MNDocument16 pagesTopic 16 FB (Weak Axis) and MNangelica abanesNo ratings yet
- The Hong Kong Polytechnic UniversityDocument8 pagesThe Hong Kong Polytechnic University1214135360No ratings yet
- Lateral Torsional and Distortional Buckling of Channel-And Hat-SectionsDocument23 pagesLateral Torsional and Distortional Buckling of Channel-And Hat-SectionsThiago SilvaNo ratings yet
- Monorail 0.5 TonDocument9 pagesMonorail 0.5 TonAndreas HendiNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Beam (LRFD, Load and Resistance Factor Design)Document5 pagesDesign of Steel Beam (LRFD, Load and Resistance Factor Design)surajoffshoreNo ratings yet
- How To Determine Correct Number of Earthing Electrodes (Strips, Plates and Pipes) - Part 1Document12 pagesHow To Determine Correct Number of Earthing Electrodes (Strips, Plates and Pipes) - Part 1Burraq Engineering SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Experiment Code - J Solid Mechanics Lab: Shashank R - ME16B164 Shubham Jain-ME16B165Document10 pagesExperiment Code - J Solid Mechanics Lab: Shashank R - ME16B164 Shubham Jain-ME16B165Purvang ParmarNo ratings yet
- Slide Share BDocument42 pagesSlide Share BShakeel WaseemNo ratings yet
- Sample 3Document13 pagesSample 3Wesam MalehNo ratings yet
- Comp Chem 5Document39 pagesComp Chem 5esraamohamady790No ratings yet
- Prob Set 1Document8 pagesProb Set 1BlackmorphaNo ratings yet
- CCIP Errata Worked Examples To Eurocode 2 Jan2012Document13 pagesCCIP Errata Worked Examples To Eurocode 2 Jan2012fan_luc89No ratings yet
- MD2Document5 pagesMD2nagmajerald17No ratings yet
- Cantilever Beam Long ReportDocument21 pagesCantilever Beam Long ReportAbdul Azeez Ismaila ShuaibuNo ratings yet
- Deep BeamDocument31 pagesDeep BeamEngr Mohammed Ubaid QureshiNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Principles of Plasma Discharges and Materials ProcessingFrom EverandPrinciples of Plasma Discharges and Materials ProcessingNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesFrom Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Method of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsFrom EverandMethod of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- 2019door Controls Hardware Typical Product Catalogue PDFDocument151 pages2019door Controls Hardware Typical Product Catalogue PDFDilon Fernando75% (4)
- E8231PRL1F: Product DatasheetDocument2 pagesE8231PRL1F: Product DatasheetDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- All Type of Footing DesignDocument26 pagesAll Type of Footing DesignDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- L 787 DatasheetDocument2 pagesL 787 DatasheetDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Lovair L-966 Waste Bins 3D DatasheetDocument2 pagesLovair L-966 Waste Bins 3D DatasheetDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Lovair L-977 Waste Bins DatasheetDocument2 pagesLovair L-977 Waste Bins DatasheetDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Eumseong #1 Factory Eumseong #2 Factory Jincheon #1 FactoryDocument2 pagesEumseong #1 Factory Eumseong #2 Factory Jincheon #1 FactoryDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Tender Specification LOOP Type I Magnetic SystemDocument2 pagesTender Specification LOOP Type I Magnetic SystemDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Loop Type 1 Mounting InstructionsDocument8 pagesLoop Type 1 Mounting InstructionsDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Gold StarDocument3 pagesGold StarDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- White Star: White, Interior & Exterior Wall & Floor Tile / Stone AdhesiveDocument3 pagesWhite Star: White, Interior & Exterior Wall & Floor Tile / Stone AdhesiveDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Litokol X11 - Litokol X12Document4 pagesLitokol X11 - Litokol X12Dilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Elephant Gypsum Boards Specification - Moistbloc BoardDocument1 pageElephant Gypsum Boards Specification - Moistbloc BoardDilon Fernando0% (1)
- Loop Type 1 Mounting InstructionsDocument8 pagesLoop Type 1 Mounting InstructionsDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Under Tile & Stone PrimerDocument2 pagesUnder Tile & Stone PrimerDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- K10 GRS 2000Document2 pagesK10 GRS 2000Dilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- FC SSDocument2 pagesFC SSDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Modesty Panel PG 1 PDFDocument1 pageModesty Panel PG 1 PDFDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Zer Ve BoardDocument2 pagesZer Ve BoardDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Laticrete 252 TDSDocument5 pagesLaticrete 252 TDSDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Bar ScheduleDocument9 pagesBar ScheduleDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- Weather BlocDocument4 pagesWeather BlocDilon FernandoNo ratings yet
- 2008 08 21 Steel Piling Handbook Design EnglischDocument213 pages2008 08 21 Steel Piling Handbook Design EnglischIancu-Bogdan Teodoru100% (2)