Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sickle Cell Brochure
Sickle Cell Brochure
Uploaded by
api-2675051140 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
208 views2 pagesOriginal Title
sickle cell brochure
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
208 views2 pagesSickle Cell Brochure
Sickle Cell Brochure
Uploaded by
api-267505114Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Nursing Diagnosis:
1. Acute Pain related to sickle cell
crisis as evidence by a high pain
rating on the numeric scale.
2. Ineffective Peripheral Tissue
Perfusion related to red blood cell
sickling as evidence by infarction of
tissues.
3. Activity Intolerance related to
fatigue as evidence by decrease
activity
The job of a nurse is very important in
the role of treating a sickle cell anemia
patient. This is because it is his or her
job to keep the patient comfortable. It
becomes hard at times because the
amount of pain medications this type of
patient can tolerate is a lot more than
most patients bodies can safely
metabolize. It is then a hard decision on
whether or not it is safe to administer
the ordered amount of medications.
1. A Negroid-American, who is a sickle cell
carrier, is about to give birth to her first child.
What is the likelihood that this child will have
sickle cell?
A. 25% C. 75%
B. 50% D. 100%
2. A patient arrives in the emergency
department with a history of sickle cell
anemia and he is complaining of extreme pain
in abdomen and joints. What could be causing
this pain?
A. He is extremely constipated
B. He has a buildup of sickled cells in
multiple areas
C. He stopped taking his pain medicine
D. He is a male with sickle cell anemia
References:
Nursing Central. (2013) Unbound Medicine, Inc. (Version 2.2.48)
[Mobile application software]. Retrieved
from http://www.unboundmedicine.com/store/android
Facts About Sickle Cell Disease. (2014, January 16). Centers for
Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved July 2, 2014, from
http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/sicklecell/facts.html
Elise Chirco
NURS 300
Informational Brochure
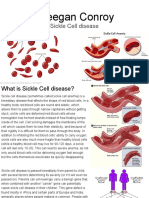
Sickle cell anemia is a recessive gene and all
too often it goes unnoticed by its carriers.
This is because as a recessive gene, the
disease does not typically show signs and
symptoms. So when two carriers of the
sickle cell gene procreate there is a 25%
chance the resulting child will be born with
the disease and there is a 50% chance that
their resulting child will only carry the sickle
cell anemia gene.
This disease does not have a gender
preference, boys and girls alike can receive
this life altering gene the same. The negroid
population is the one in which is most
devastated by sickle cell. According to the
Center for Disease Control, or CDC, 1 in 500
negroid-American births have sickle cell
anemia, as compared to, 1 in 36,000
hispanic-American births.
Children born with sickle cell anemia begin
showing signs and symptoms about five
months after birth according to the Center for
Disease Control. This is because it is at this age
is when the babys red blood cells began to
take on a sickled form. As pictured to the left,
a normal red blood cell is round and flexible
with a dip in the middle, for oxygen carrying
purposes, and a cell that has become sickled
looks like the letter C and has become rigid
and can no longer carry as much oxygen, if
any. Children with sickle cell will show
symptoms such as: swelling and pain in joints,
chest pain, and decreased energy and will
struggle to catch his or her breath. Delayed or
impaired growth can also be seen.
The average life expectancy of
a sickle cell patient is 42 years.
The sickled shape of the red blood cells
cause them to get stuck in joints. This leads
to extreme pain and joint immobility. The
extreme pain could also be a result of the
formation of a deep vein thrombosis. As
these patients age, the pain crisis will
increase with frequency and intensity. A
lack of oxygen being able to get past joints in
veins and arteries which can lead to tissue
necrosis and organ failure. Other symptoms
of this disease are pale or yellow skin,
fatigue, increased heart rate, enlarged liver
and spleen and eventually death.
The reason this form of the sickle cell disease
is called anemia is because there is a
decrease number of good red blood cells in
the body. Sickling of red blood cells occurs
quicker when the body has a decrease level
of oxygen. The liver filters out the bad red
blood cells faster than would a good blood
cell. A normal red blood cell will circulate
for about 120 days compared to a sickled
cells 20 days. The body cannot produce as
much and as fast as it is breaking down.
Jaundice tends to occur in these patients
because of this quick turn over in damaged
red blood cells.
As stated earlier sickled red blood cells are
not able to carry oxygen as well as normal
red blood cells. This causes a decrease in
amount of blood getting into the tissues and
organs, which can lead to organ failure.
When these organs do not receive enough
oxygen they send a message to the heart
saying the need is not being met, which will
lead to an increase in heart rate.
You might also like
- Gordon S Functional Health Pattern Assessment ToolDocument17 pagesGordon S Functional Health Pattern Assessment Toolmiss RN96% (45)
- Hospital Medicine: A Resource Guide On Commonly Encountered Inpatient Topics For Primary Care and Subspecialist FacultyDocument24 pagesHospital Medicine: A Resource Guide On Commonly Encountered Inpatient Topics For Primary Care and Subspecialist FacultyWilson LamNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project On Mendelian DisordersDocument42 pagesBiology Investigatory Project On Mendelian DisordersLalit Kumar93% (15)
- Biology Investigatory Project On Mendelian DisordersDocument42 pagesBiology Investigatory Project On Mendelian DisordersPrasaanth Rock86% (14)
- NCP Nasal PolypsDocument3 pagesNCP Nasal Polypsnickanel60% (5)
- Sickle Cell DiseaseDocument4 pagesSickle Cell DiseaseliacahyaNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell DiseaseDocument10 pagesSickle Cell DiseaseAlaa Elsaid Attia Ahmed Ahmed AlassalyNo ratings yet
- Anemia Bulan SabitDocument19 pagesAnemia Bulan SabitRyujin daughterNo ratings yet
- Sickel Cell AnemiaDocument15 pagesSickel Cell AnemiarajaNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument2 pagesSickle Cell AnemiaJosephine NievesNo ratings yet
- Lukes Presentation 1Document28 pagesLukes Presentation 1Lukes GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Disease DissertationDocument7 pagesSickle Cell Disease DissertationWritingPaperServicesUK100% (1)
- Sickle Cell Disease Is An Inherited Disorder in Which Red Blood CellsDocument5 pagesSickle Cell Disease Is An Inherited Disorder in Which Red Blood Cellsjhonnyboy33No ratings yet
- Sickle CellDocument9 pagesSickle CellmatekwaNo ratings yet
- ABC: Sickle-Cell Anemia, Shock, PoisoningDocument46 pagesABC: Sickle-Cell Anemia, Shock, Poisoningroneln100% (1)
- Sickle Cell AnaemiaDocument18 pagesSickle Cell AnaemiajhvjNo ratings yet
- Study of Sickle Cell Anemia NewDocument12 pagesStudy of Sickle Cell Anemia NewS.NagarajanNo ratings yet
- المستند (46) كتاب الجلوةDocument11 pagesالمستند (46) كتاب الجلوةManal HassanNo ratings yet
- Sickle CellDocument10 pagesSickle Cellapi-353439630No ratings yet
- Brief - Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument6 pagesBrief - Sickle Cell AnemiaJologs AggasidNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSickle Cell Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument18 pagesSickle Cell AnemiaArnim KumarNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument10 pagesSickle Cell AnemiaNader Smadi100% (1)
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument7 pagesSickle Cell AnemiakazelleNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument20 pagesSickle Cell AnemiaAnastasiafynn100% (1)
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument15 pagesSickle Cell AnemiakavitharavNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument3 pagesSickle Cell Anemiakarenkaren09No ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument13 pagesSickle Cell Anemiamayra100% (1)
- Sickle Cell DiseaseDocument7 pagesSickle Cell Diseasekarenkaren09100% (2)
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument5 pagesSickle Cell AnemiaBmoore Xtra XtraNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnaemiaDocument8 pagesSickle Cell AnaemiaBhargav DesaiNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument16 pagesUntitled DocumentDinesh DoraNo ratings yet
- hlth1020 SCDDocument7 pageshlth1020 SCDapi-302025926No ratings yet
- Wa0019.Document19 pagesWa0019.ibenazirbegamNo ratings yet
- Dock OendbDocument23 pagesDock OendbibenazirbegamNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Anemi1Document13 pagesSickle Cell Anemi109204445328No ratings yet
- Thesis Statement On Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument7 pagesThesis Statement On Sickle Cell Anemiacoawokugg100% (1)
- Sickle Cell IHCPDocument2 pagesSickle Cell IHCPMark Anthony YabresNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Anemia Term PaperDocument4 pagesSickle Cell Anemia Term Paperaflsmmmgx100% (1)
- Anmol's Investigatory Project 1Document7 pagesAnmol's Investigatory Project 1Anmol KatariaNo ratings yet
- Sickle CellDocument7 pagesSickle Cellmahmoudmustapha93No ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Disease: 100,000 $488 MILLIONDocument3 pagesSickle Cell Disease: 100,000 $488 MILLIONAtta U LlahNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Sickle Cell DiseaseDocument6 pagesTerm Paper Sickle Cell Diseasec5p64m3t100% (1)
- Sickle Cell DiseaseDocument8 pagesSickle Cell DiseaseShafieyah ShafiefieNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Anaemia by SALDocument4 pagesSickle Cell Anaemia by SALSahar Ahmed LaskarNo ratings yet
- Apex ProjectDocument12 pagesApex ProjectGajendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Anemia DissertationDocument4 pagesSickle Cell Anemia DissertationHelpWithWritingPaperCanada100% (1)
- Literature Review - Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument6 pagesLiterature Review - Sickle Cell Anemiaapi-549026840No ratings yet
- SicklecellanemiaDocument9 pagesSicklecellanemiaapi-357233301No ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Anemia Thesis StatementDocument4 pagesSickle Cell Anemia Thesis StatementStacy Vasquez100% (2)
- What Is Sickle Cell? Origin and Distribution of Sickle Cell DiseaseDocument27 pagesWhat Is Sickle Cell? Origin and Distribution of Sickle Cell DiseaseLuis PerazaNo ratings yet
- Anemia Sel Bulan Sabit 2Document2 pagesAnemia Sel Bulan Sabit 2Riskayati LatiefNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Disease Is The Most Common of The Hereditary Blood DisordersDocument4 pagesSickle Cell Disease Is The Most Common of The Hereditary Blood DisordersDaniel OkakaNo ratings yet
- Dissertation On Sickle Cell AnaemiaDocument7 pagesDissertation On Sickle Cell AnaemiaWhatIsTheBestPaperWritingServiceOverlandPark100% (1)
- Sickle Cell Anemia Research Paper OutlineDocument6 pagesSickle Cell Anemia Research Paper Outlineafeaxlaaa100% (1)
- Biology Investigatory Project On Mendelian DisordersDocument10 pagesBiology Investigatory Project On Mendelian DisordersWS ARYAN YTNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Disease, Epidemiology, Genetic History, Complication and ManagementDocument52 pagesSickle Cell Disease, Epidemiology, Genetic History, Complication and ManagementAnastasiafynnNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell DiseaseDocument3 pagesSickle Cell Diseasecindya13No ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument7 pagesSickle Cell Anemiaafsas rpNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Anemia Is One of A Group of Disorders Known As Sickle Cell DiseaseDocument6 pagesSickle Cell Anemia Is One of A Group of Disorders Known As Sickle Cell DiseaseAbduladheemNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Anemia: Yousef Ali Mohamed Abu-ElhejaDocument40 pagesSickle Cell Anemia: Yousef Ali Mohamed Abu-Elhejayouse864No ratings yet
- Low White Blood Cells, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLow White Blood Cells, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Castleman Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCastleman Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Management of The Ehlers Danlos SyndromesDocument7 pagesOrthopaedic Management of The Ehlers Danlos SyndromesGaspar ContrerasNo ratings yet
- 2021 American College of Rheumatology Vasculitis FoundationDocument10 pages2021 American College of Rheumatology Vasculitis FoundationVerónica Duménez JofréNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 Topic 6 VENIPUNCTURE EQUIPMENTSDocument29 pagesPMLS 2 Topic 6 VENIPUNCTURE EQUIPMENTSKeren Nathaniel AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Ped CardioDocument18 pagesPed CardioIdioness100% (1)
- Bed Site Teaching: Ridwan Permana (712014027) Preceptor: Dr. Rizal Daulay, SP - OT.,MARSDocument21 pagesBed Site Teaching: Ridwan Permana (712014027) Preceptor: Dr. Rizal Daulay, SP - OT.,MARSRidwan PermanaNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Implementation: Presented By: Ku Badlisyah Ku Aziz Lily Fairuz Md. YasanDocument21 pagesEvidence Based Implementation: Presented By: Ku Badlisyah Ku Aziz Lily Fairuz Md. YasanKu Badlisyah Ku AzizNo ratings yet
- Food AllergensDocument49 pagesFood AllergensBareera MunirNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Prospektif Kadar Neutrophil Gelatinase-: Associated Lipocalin Urin Dan Kreatinin SerumDocument7 pagesEvaluasi Prospektif Kadar Neutrophil Gelatinase-: Associated Lipocalin Urin Dan Kreatinin SerumJack Eugene LiowNo ratings yet
- White Paper: On Joint ReplacementDocument144 pagesWhite Paper: On Joint ReplacementCosme MejiaNo ratings yet
- Who, 2015Document59 pagesWho, 2015diahNo ratings yet
- None C9efb7c9Document6 pagesNone C9efb7c9liana iwiwNo ratings yet
- C11 SchizophreniaDocument22 pagesC11 SchizophreniaMaJoy OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- Kansas Physician Group Adds Two Cardiologists To PracticeDocument2 pagesKansas Physician Group Adds Two Cardiologists To PracticePR.comNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes Using.12Document9 pagesAssessment of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes Using.12Muhammad Rifki100% (1)
- Temporomandibular Joint DisorderDocument9 pagesTemporomandibular Joint DisorderTannels100% (1)
- Drug Study I MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesDrug Study I MetronidazoleKimberly Ann Aquino50% (2)
- Sabrina ManigoDocument2 pagesSabrina ManigoCOREY RICHNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plants What People Believe They Can Do What They Actually DoDocument2 pagesMedicinal Plants What People Believe They Can Do What They Actually DoAcua RioNo ratings yet
- Professional Development PlanDocument11 pagesProfessional Development Planapi-582896568No ratings yet
- System 5000 Electrosurgical Unit (ESU)Document4 pagesSystem 5000 Electrosurgical Unit (ESU)George VlNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Behavioural Therapy For ADHD in Adults Systematic ReviewDocument9 pagesCognitive Behavioural Therapy For ADHD in Adults Systematic ReviewDana Ben SimonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Risk ManagementDocument6 pagesClinical Risk ManagementJaparaj PeterNo ratings yet
- Efn Topic 10 - Sulfi Nurafifah 1020031181Document10 pagesEfn Topic 10 - Sulfi Nurafifah 1020031181Erdin TriansyahNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Mouth and Other Relevant Structures: Chapter OutlineDocument1 pageExamination of The Mouth and Other Relevant Structures: Chapter OutlineSofyan Al BaladiNo ratings yet
- Do You Symptoms?: 2 Jorge Basadre Grohmann National UniversityDocument4 pagesDo You Symptoms?: 2 Jorge Basadre Grohmann National UniversityDiana Vanessa Roque ChinoNo ratings yet
- Case Study SampleDocument1 pageCase Study SampleNhi UyênNo ratings yet
- Utah Medical Cannabis ActDocument28 pagesUtah Medical Cannabis ActLarryDCurtisNo ratings yet