Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Networks and Information System 1
Networks and Information System 1
Uploaded by
Kah Chun AlexCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- XTL2500 Detailed Service ManualDocument587 pagesXTL2500 Detailed Service ManualJohnNo ratings yet
- Service Publications: Number SubjectDocument60 pagesService Publications: Number SubjectJames100% (1)
- Basic Concept of CommunicationDocument9 pagesBasic Concept of CommunicationShuvodip Das100% (5)
- Hamdard-HIIT Communication SystemDocument13 pagesHamdard-HIIT Communication Systemshakr123No ratings yet
- 1 A) Draw The Basic Block Diagram of Communication SystemDocument29 pages1 A) Draw The Basic Block Diagram of Communication SystemBhargava GNo ratings yet
- Arab Open University - Bahrain Branch: T209 Revision Handout FALL 2004 - 2005Document17 pagesArab Open University - Bahrain Branch: T209 Revision Handout FALL 2004 - 2005api-26050323No ratings yet
- Chapter1 Int. To Comm. System 2018Document13 pagesChapter1 Int. To Comm. System 2018Abdi JoteNo ratings yet
- Data Comm and Comp Networking Lecture NoteDocument35 pagesData Comm and Comp Networking Lecture NoteMikiyas GetasewNo ratings yet
- Network Protocol and ArchitectureDocument84 pagesNetwork Protocol and ArchitectureKidus SeleshiNo ratings yet
- 0 - IntroductionDocument24 pages0 - IntroductionOmar AlzayatNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Note 1Document11 pagesData Communication Note 1Mohammad Saydul AlamNo ratings yet
- Communication PDFDocument0 pagesCommunication PDFwww.bhawesh.com.npNo ratings yet
- Principles of Communication Lecture 1Document29 pagesPrinciples of Communication Lecture 1Fariha Rahman NameerahNo ratings yet
- Topic 9-10 Data Communication and Computer NetworksDocument12 pagesTopic 9-10 Data Communication and Computer NetworksBENSON NGARI100% (1)
- Dgital Communication LecturesDocument202 pagesDgital Communication LecturesmgoldiieeeeNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Lecture 1Document29 pagesData Communication Lecture 1Blue BloodNo ratings yet
- Communication I1Document38 pagesCommunication I1Binod Pokhrel SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Communication: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Data Communication: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineeringআসিফ রেজাNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Communication: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Data Communication: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringpaimxtNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Data and Computer CommunicationsDocument26 pagesWilliam Stallings Data and Computer CommunicationsBagus FatkhurroziNo ratings yet
- DCN Chapter 1 - Part 1Document45 pagesDCN Chapter 1 - Part 1Esta AmeNo ratings yet
- What Does Communication (Or Telecommunication) Mean?Document5 pagesWhat Does Communication (Or Telecommunication) Mean?tasniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document26 pagesChapter 6Jason DelumenNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems I: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument11 pagesCommunication Systems I: Department of Electrical EngineeringAyad A. ABDULKAFINo ratings yet
- Chap1 Introd 2015Document19 pagesChap1 Introd 2015semakulaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Data CommDocument4 pagesIntro To Data CommChinchay GuintoNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital ModulationsDocument23 pagesAnalog and Digital ModulationsVu Phan NhatNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Lecture 1Document29 pagesData Communication Lecture 1Jinia S.No ratings yet
- Chapter One: Data Communication BasicsDocument46 pagesChapter One: Data Communication BasicsWiki EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CommunicationDocument21 pagesIntroduction To CommunicationAbdi JoteNo ratings yet
- The Key Elements of A Communication ModelDocument12 pagesThe Key Elements of A Communication ModelMD. SHAHIDUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Chapter I Data TransmissionDocument13 pagesChapter I Data TransmissionMohamedLashabNo ratings yet
- Notes 1 BIT3Document18 pagesNotes 1 BIT3Peter TsamwaNo ratings yet
- FoN - Chapter OneDocument36 pagesFoN - Chapter OneNasis DerejeNo ratings yet
- SDI ASI Encoder MultiplexerDocument41 pagesSDI ASI Encoder MultiplexerChristie MillerNo ratings yet
- Electronic Communication: Recap and Way ForwardDocument45 pagesElectronic Communication: Recap and Way ForwardShawn MoyoNo ratings yet
- Data Communication ConceptDocument29 pagesData Communication ConceptmysthicriousNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document64 pagesChapter 1abebemako302No ratings yet
- Ec 2004 (PDC) - CS - End - May - 2023Document24 pagesEc 2004 (PDC) - CS - End - May - 2023223UTKARSH TRIVEDINo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Networking: IncludesDocument19 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Networking: IncludesDawod YimerNo ratings yet
- S-72.1140 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (5 CR)Document46 pagesS-72.1140 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (5 CR)chinguetas_82600No ratings yet
- Diagram" Add With Power SupplyDocument2 pagesDiagram" Add With Power SupplyJonathan F. CardinalNo ratings yet
- Data Communications - A.K MhazoDocument158 pagesData Communications - A.K MhazoGloria Matope100% (1)
- Data CommunicationDocument114 pagesData CommunicationShikha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and MediaDocument17 pagesData Communication and MediaSameer SharmaNo ratings yet
- Telephone Network and DSL Technology: U.K.P. Mihiranga (MBA in MOT, B.Sc. Eng. (Hons), PMP-PMI (USA), AMIESL)Document37 pagesTelephone Network and DSL Technology: U.K.P. Mihiranga (MBA in MOT, B.Sc. Eng. (Hons), PMP-PMI (USA), AMIESL)Pathum MihirangaNo ratings yet
- SECA1303Document250 pagesSECA1303rqfkypprjtNo ratings yet
- Ee 346-Ln-Ch1-IiDocument61 pagesEe 346-Ln-Ch1-IisabitwebNo ratings yet
- EC301 Chapter 3 (3.1)Document45 pagesEC301 Chapter 3 (3.1)Ayu WafaNo ratings yet
- Notes Digital Communication Lecture 1Document61 pagesNotes Digital Communication Lecture 1Igho Silva0% (1)
- Notes Digital Communication Lecture 1 - 3Document63 pagesNotes Digital Communication Lecture 1 - 3dinkarbhombeNo ratings yet
- Notes Digital Communication Lecture 1 - 4Document63 pagesNotes Digital Communication Lecture 1 - 4dinkarbhombe100% (2)
- Communication ModelDocument3 pagesCommunication ModelSonaNoorNo ratings yet
- Ec 2252 Communication Theory Lecture NotesDocument120 pagesEc 2252 Communication Theory Lecture NotesAnonymous G4srxwO3jINo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Communication Systemmohd_anip9774No ratings yet
- ELEC 382 Notes 13 Wired Digital CommunicationDocument9 pagesELEC 382 Notes 13 Wired Digital CommunicationKenan BaltaciNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 11 Data Transmission Using Serial Communication AimDocument2 pagesExperiment No: 11 Data Transmission Using Serial Communication AimJose DahlsonNo ratings yet
- Information Technology: (Communication in IT)Document34 pagesInformation Technology: (Communication in IT)Hallasgo DanteNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Amateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileFrom EverandAmateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Software and Hardware RequirementsDocument31 pagesSoftware and Hardware RequirementsKah Chun AlexNo ratings yet
- Clinicpanel31 8 14Document85 pagesClinicpanel31 8 14Kah Chun AlexNo ratings yet
- IKEA - Information DensityDocument1 pageIKEA - Information DensityKah Chun AlexNo ratings yet
- The Inspiring Life Story of Alibaba Founder Jack MaDocument4 pagesThe Inspiring Life Story of Alibaba Founder Jack MaKah Chun AlexNo ratings yet
- Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM) Unauthorised Companies and Websites ListDocument4 pagesBank Negara Malaysia (BNM) Unauthorised Companies and Websites ListjackNo ratings yet
- Type of Organization1Document9 pagesType of Organization1Kah Chun AlexNo ratings yet
- RXM XXX ES Data GuideDocument11 pagesRXM XXX ES Data GuideAstrid PorticaNo ratings yet
- TV PDFDocument10 pagesTV PDFNarayan Krishan Vyas100% (1)
- Science, Technology and Society (Reviewer)Document8 pagesScience, Technology and Society (Reviewer)Irish CostalesNo ratings yet
- Experiment X VDocument4 pagesExperiment X VmarcelineNo ratings yet
- DC LabDocument149 pagesDC LabRavi Kumar MogilsettiNo ratings yet
- RF Interference Hunting Techniques AnDocument20 pagesRF Interference Hunting Techniques AnphieephieeNo ratings yet
- PRINCOMM ReviewerDocument4 pagesPRINCOMM Reviewerrick reyNo ratings yet
- Awp PPT L2 BKDocument11 pagesAwp PPT L2 BKNawaz MudassirNo ratings yet
- ZX Series: ZX500, ZX1000, ZX2000 & ZX3500Document162 pagesZX Series: ZX500, ZX1000, ZX2000 & ZX3500Refaat GhazyNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument103 pagesProject ReportChiragSinghalNo ratings yet
- Viva Voce Questions On Communication SystemsDocument3 pagesViva Voce Questions On Communication SystemsZealWolf100% (3)
- Nuts Volts - 2014 10Document84 pagesNuts Volts - 2014 10colin37100% (1)
- Four-Stage FM Transmitter: Pradee GDocument6 pagesFour-Stage FM Transmitter: Pradee GAmsalu SeteyNo ratings yet
- MEDICAMENTESCALARDocument5 pagesMEDICAMENTESCALARStere StereNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Radio SystemsDocument259 pagesAircraft Radio SystemsEdward Muriithi100% (2)
- Amateur Radio Technician Study Guide 2010Document38 pagesAmateur Radio Technician Study Guide 2010netlanuza3089100% (1)
- Vocational Training ReportDocument32 pagesVocational Training ReportAndrew CramerNo ratings yet
- Frictionless Bearing TSDocument16 pagesFrictionless Bearing TS4MH18CS086 Rakesh Mallika SNo ratings yet
- Cobra Electronics PR 900 DXDocument19 pagesCobra Electronics PR 900 DXAlexNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Using Lpda Antenna: Aditya - Satti D.Kushal Reddy E.Dilip RoyDocument90 pagesWireless Communication Using Lpda Antenna: Aditya - Satti D.Kushal Reddy E.Dilip RoymgitecetechNo ratings yet
- Sony UTX-B1Document28 pagesSony UTX-B1SeanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Service Manual EP450Document173 pagesDetailed Service Manual EP450serviciotecnicoafNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Far Field Antenna Measurements Without Anechoic ChamberDocument8 pagesTime Domain Far Field Antenna Measurements Without Anechoic ChamberNabil DakhliNo ratings yet
- WSN Unit-12Document21 pagesWSN Unit-12vnpprasunaNo ratings yet
- TM 11-615 Scr-609a and B, Scr-610a and BDocument110 pagesTM 11-615 Scr-609a and B, Scr-610a and BAdvocate100% (2)
- Radio TroubleshootingDocument14 pagesRadio TroubleshootingrolandNo ratings yet
- ANALOG COMMUNICATION LAB Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesANALOG COMMUNICATION LAB Questions and AnswersMurthyNo ratings yet
- Users Manual 324117Document18 pagesUsers Manual 324117guillermo quicenoNo ratings yet
Networks and Information System 1
Networks and Information System 1
Uploaded by
Kah Chun AlexOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Networks and Information System 1
Networks and Information System 1
Uploaded by
Kah Chun AlexCopyright:
Available Formats
NETWORKS AND INFORMATION SYSTEM 1 (MID TERM TIPS)
Tutorial 1
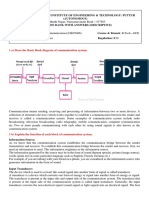
Key elements of communication model. (10 marks)
Source
o This devices generates the data to be transmitted (e.g.: telephone, personal
computer)
Transmitter
o Transform and encodes the information in such a way as to produce
electromagnetic signal that can be transmitted across some sort of transmission
system.
Transmission System
o This can be single transmission line or complex network connecting source
and destination
Receiver
o Accepts the signal from the transmission system and converts it into a form
that can be handled by the destination device
Destination
o Takes the incoming data from receiver.
Define the following transmission terminology (give examples) (10 marks)
a. Simplex
Signals transmitted in one direction (e.g. television)
b. Half duplex
Both stations transmits, but only one at a time (e.g. radio)
c. Full duplex
Simultaneous transmissions (e.g. telephone)
Data Signals
Entities that conveys meaning within a
computer or computer system
Electric or electromagnetic impulses used to
encode and transmit data
Example:
Computer files, music on CD, results from a
blood gas analysis machine
Example:
Telephone conversation, web page
download
Loss of Signal Strength (3 marks)
-8 dB + 10 dB + (-7 dB) = -5 dB
Given the message Hello, Goodbye, show the decimal arithmetic checksum that will be
generated (3 marks)
Transmitting Digital Data with Digital Signal (15 marks) each data 3 marks
Tutorial 3
Phase Shift Keying (draw 2 phases) 4 marks
Tutorial 4
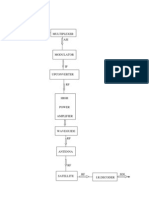
Show the sequence of Start Bit and Stop Bit, - NoiSe (5 marks)
No.11 (10 marks)
X
Y Z
-8 dB
+10 dB
-7 dB
You might also like
- XTL2500 Detailed Service ManualDocument587 pagesXTL2500 Detailed Service ManualJohnNo ratings yet
- Service Publications: Number SubjectDocument60 pagesService Publications: Number SubjectJames100% (1)
- Basic Concept of CommunicationDocument9 pagesBasic Concept of CommunicationShuvodip Das100% (5)
- Hamdard-HIIT Communication SystemDocument13 pagesHamdard-HIIT Communication Systemshakr123No ratings yet
- 1 A) Draw The Basic Block Diagram of Communication SystemDocument29 pages1 A) Draw The Basic Block Diagram of Communication SystemBhargava GNo ratings yet
- Arab Open University - Bahrain Branch: T209 Revision Handout FALL 2004 - 2005Document17 pagesArab Open University - Bahrain Branch: T209 Revision Handout FALL 2004 - 2005api-26050323No ratings yet
- Chapter1 Int. To Comm. System 2018Document13 pagesChapter1 Int. To Comm. System 2018Abdi JoteNo ratings yet
- Data Comm and Comp Networking Lecture NoteDocument35 pagesData Comm and Comp Networking Lecture NoteMikiyas GetasewNo ratings yet
- Network Protocol and ArchitectureDocument84 pagesNetwork Protocol and ArchitectureKidus SeleshiNo ratings yet
- 0 - IntroductionDocument24 pages0 - IntroductionOmar AlzayatNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Note 1Document11 pagesData Communication Note 1Mohammad Saydul AlamNo ratings yet
- Communication PDFDocument0 pagesCommunication PDFwww.bhawesh.com.npNo ratings yet
- Principles of Communication Lecture 1Document29 pagesPrinciples of Communication Lecture 1Fariha Rahman NameerahNo ratings yet
- Topic 9-10 Data Communication and Computer NetworksDocument12 pagesTopic 9-10 Data Communication and Computer NetworksBENSON NGARI100% (1)
- Dgital Communication LecturesDocument202 pagesDgital Communication LecturesmgoldiieeeeNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Lecture 1Document29 pagesData Communication Lecture 1Blue BloodNo ratings yet
- Communication I1Document38 pagesCommunication I1Binod Pokhrel SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Communication: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Data Communication: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineeringআসিফ রেজাNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Communication: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Data Communication: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringpaimxtNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Data and Computer CommunicationsDocument26 pagesWilliam Stallings Data and Computer CommunicationsBagus FatkhurroziNo ratings yet
- DCN Chapter 1 - Part 1Document45 pagesDCN Chapter 1 - Part 1Esta AmeNo ratings yet
- What Does Communication (Or Telecommunication) Mean?Document5 pagesWhat Does Communication (Or Telecommunication) Mean?tasniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document26 pagesChapter 6Jason DelumenNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems I: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument11 pagesCommunication Systems I: Department of Electrical EngineeringAyad A. ABDULKAFINo ratings yet
- Chap1 Introd 2015Document19 pagesChap1 Introd 2015semakulaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Data CommDocument4 pagesIntro To Data CommChinchay GuintoNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital ModulationsDocument23 pagesAnalog and Digital ModulationsVu Phan NhatNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Lecture 1Document29 pagesData Communication Lecture 1Jinia S.No ratings yet
- Chapter One: Data Communication BasicsDocument46 pagesChapter One: Data Communication BasicsWiki EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CommunicationDocument21 pagesIntroduction To CommunicationAbdi JoteNo ratings yet
- The Key Elements of A Communication ModelDocument12 pagesThe Key Elements of A Communication ModelMD. SHAHIDUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Chapter I Data TransmissionDocument13 pagesChapter I Data TransmissionMohamedLashabNo ratings yet
- Notes 1 BIT3Document18 pagesNotes 1 BIT3Peter TsamwaNo ratings yet
- FoN - Chapter OneDocument36 pagesFoN - Chapter OneNasis DerejeNo ratings yet
- SDI ASI Encoder MultiplexerDocument41 pagesSDI ASI Encoder MultiplexerChristie MillerNo ratings yet
- Electronic Communication: Recap and Way ForwardDocument45 pagesElectronic Communication: Recap and Way ForwardShawn MoyoNo ratings yet
- Data Communication ConceptDocument29 pagesData Communication ConceptmysthicriousNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document64 pagesChapter 1abebemako302No ratings yet
- Ec 2004 (PDC) - CS - End - May - 2023Document24 pagesEc 2004 (PDC) - CS - End - May - 2023223UTKARSH TRIVEDINo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Networking: IncludesDocument19 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Networking: IncludesDawod YimerNo ratings yet
- S-72.1140 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (5 CR)Document46 pagesS-72.1140 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (5 CR)chinguetas_82600No ratings yet
- Diagram" Add With Power SupplyDocument2 pagesDiagram" Add With Power SupplyJonathan F. CardinalNo ratings yet
- Data Communications - A.K MhazoDocument158 pagesData Communications - A.K MhazoGloria Matope100% (1)
- Data CommunicationDocument114 pagesData CommunicationShikha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and MediaDocument17 pagesData Communication and MediaSameer SharmaNo ratings yet
- Telephone Network and DSL Technology: U.K.P. Mihiranga (MBA in MOT, B.Sc. Eng. (Hons), PMP-PMI (USA), AMIESL)Document37 pagesTelephone Network and DSL Technology: U.K.P. Mihiranga (MBA in MOT, B.Sc. Eng. (Hons), PMP-PMI (USA), AMIESL)Pathum MihirangaNo ratings yet
- SECA1303Document250 pagesSECA1303rqfkypprjtNo ratings yet
- Ee 346-Ln-Ch1-IiDocument61 pagesEe 346-Ln-Ch1-IisabitwebNo ratings yet
- EC301 Chapter 3 (3.1)Document45 pagesEC301 Chapter 3 (3.1)Ayu WafaNo ratings yet
- Notes Digital Communication Lecture 1Document61 pagesNotes Digital Communication Lecture 1Igho Silva0% (1)
- Notes Digital Communication Lecture 1 - 3Document63 pagesNotes Digital Communication Lecture 1 - 3dinkarbhombeNo ratings yet
- Notes Digital Communication Lecture 1 - 4Document63 pagesNotes Digital Communication Lecture 1 - 4dinkarbhombe100% (2)
- Communication ModelDocument3 pagesCommunication ModelSonaNoorNo ratings yet
- Ec 2252 Communication Theory Lecture NotesDocument120 pagesEc 2252 Communication Theory Lecture NotesAnonymous G4srxwO3jINo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Communication Systemmohd_anip9774No ratings yet
- ELEC 382 Notes 13 Wired Digital CommunicationDocument9 pagesELEC 382 Notes 13 Wired Digital CommunicationKenan BaltaciNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 11 Data Transmission Using Serial Communication AimDocument2 pagesExperiment No: 11 Data Transmission Using Serial Communication AimJose DahlsonNo ratings yet
- Information Technology: (Communication in IT)Document34 pagesInformation Technology: (Communication in IT)Hallasgo DanteNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Amateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileFrom EverandAmateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Software and Hardware RequirementsDocument31 pagesSoftware and Hardware RequirementsKah Chun AlexNo ratings yet
- Clinicpanel31 8 14Document85 pagesClinicpanel31 8 14Kah Chun AlexNo ratings yet
- IKEA - Information DensityDocument1 pageIKEA - Information DensityKah Chun AlexNo ratings yet
- The Inspiring Life Story of Alibaba Founder Jack MaDocument4 pagesThe Inspiring Life Story of Alibaba Founder Jack MaKah Chun AlexNo ratings yet
- Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM) Unauthorised Companies and Websites ListDocument4 pagesBank Negara Malaysia (BNM) Unauthorised Companies and Websites ListjackNo ratings yet
- Type of Organization1Document9 pagesType of Organization1Kah Chun AlexNo ratings yet
- RXM XXX ES Data GuideDocument11 pagesRXM XXX ES Data GuideAstrid PorticaNo ratings yet
- TV PDFDocument10 pagesTV PDFNarayan Krishan Vyas100% (1)
- Science, Technology and Society (Reviewer)Document8 pagesScience, Technology and Society (Reviewer)Irish CostalesNo ratings yet
- Experiment X VDocument4 pagesExperiment X VmarcelineNo ratings yet
- DC LabDocument149 pagesDC LabRavi Kumar MogilsettiNo ratings yet
- RF Interference Hunting Techniques AnDocument20 pagesRF Interference Hunting Techniques AnphieephieeNo ratings yet
- PRINCOMM ReviewerDocument4 pagesPRINCOMM Reviewerrick reyNo ratings yet
- Awp PPT L2 BKDocument11 pagesAwp PPT L2 BKNawaz MudassirNo ratings yet
- ZX Series: ZX500, ZX1000, ZX2000 & ZX3500Document162 pagesZX Series: ZX500, ZX1000, ZX2000 & ZX3500Refaat GhazyNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument103 pagesProject ReportChiragSinghalNo ratings yet
- Viva Voce Questions On Communication SystemsDocument3 pagesViva Voce Questions On Communication SystemsZealWolf100% (3)
- Nuts Volts - 2014 10Document84 pagesNuts Volts - 2014 10colin37100% (1)
- Four-Stage FM Transmitter: Pradee GDocument6 pagesFour-Stage FM Transmitter: Pradee GAmsalu SeteyNo ratings yet
- MEDICAMENTESCALARDocument5 pagesMEDICAMENTESCALARStere StereNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Radio SystemsDocument259 pagesAircraft Radio SystemsEdward Muriithi100% (2)
- Amateur Radio Technician Study Guide 2010Document38 pagesAmateur Radio Technician Study Guide 2010netlanuza3089100% (1)
- Vocational Training ReportDocument32 pagesVocational Training ReportAndrew CramerNo ratings yet
- Frictionless Bearing TSDocument16 pagesFrictionless Bearing TS4MH18CS086 Rakesh Mallika SNo ratings yet
- Cobra Electronics PR 900 DXDocument19 pagesCobra Electronics PR 900 DXAlexNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Using Lpda Antenna: Aditya - Satti D.Kushal Reddy E.Dilip RoyDocument90 pagesWireless Communication Using Lpda Antenna: Aditya - Satti D.Kushal Reddy E.Dilip RoymgitecetechNo ratings yet
- Sony UTX-B1Document28 pagesSony UTX-B1SeanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Service Manual EP450Document173 pagesDetailed Service Manual EP450serviciotecnicoafNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Far Field Antenna Measurements Without Anechoic ChamberDocument8 pagesTime Domain Far Field Antenna Measurements Without Anechoic ChamberNabil DakhliNo ratings yet
- WSN Unit-12Document21 pagesWSN Unit-12vnpprasunaNo ratings yet
- TM 11-615 Scr-609a and B, Scr-610a and BDocument110 pagesTM 11-615 Scr-609a and B, Scr-610a and BAdvocate100% (2)
- Radio TroubleshootingDocument14 pagesRadio TroubleshootingrolandNo ratings yet
- ANALOG COMMUNICATION LAB Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesANALOG COMMUNICATION LAB Questions and AnswersMurthyNo ratings yet
- Users Manual 324117Document18 pagesUsers Manual 324117guillermo quicenoNo ratings yet