Professional Documents
Culture Documents
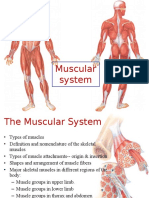
Chapter 7 Muscular System
Chapter 7 Muscular System
Uploaded by
Mycaela Archivido De AlvaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 Muscular System
Chapter 7 Muscular System
Uploaded by
Mycaela Archivido De AlvaCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 Muscular System
Major functions:
1. Movement of the body
2. Maintenance of posture
3. Respiration
4. Production of body heat
5. Communication
6. Constriction of organs and vessel
7. Contraction of heart
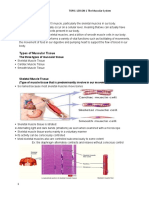
CHARACTERISTICS OF SKELETAL MUSCLE
Skeletal muscle
-Constitutes approx. 40% of body
weight
-Attached to the skeletal system
-Striated muscle because of
transverse bands or striations
Four Major Functional Characteristics:
1. Contractility- ability of skeletal to
shorten with force
2. Excitability- capacity of skeletal
muscle to respond to a stimulus
3. Extensibility- skeletal muscles stretch
4. Elasticity- ability to recoil to their
original resting length
Connective tissue coverings
Epimysium (muscular fascia)-
surrounds muscle
Perimysium- surrounds muscle
fasciculi
Endomysium- surrounds muscle
fibers
Muscle Fiber structure
Muscle fiber
- single cylindrical fiber, with several
nuclei located at its periphery
- largest human muscle fibers (30cm
and 0.15mm in diameter)
Sarcolemma
- cell membrane of the muscle fiber
Transverse tubules
- tube-like invaginations
- occur at regular intervals along the
muscle fiber and extend inward
- connect sarcolemma to
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
- highly organized smooth
endoplasmic reticulum
- has high concentration of Ca
2+
Sarcoplasm- cytoplasm
Myofibrils
- threadlike structures extend from
one end of muscle fiber to the other
- consists of two major proteins:
o Actin
o Myosin
Sarcomeres
- joined end to end to form myofibrils
You might also like
- Muscular SystemDocument26 pagesMuscular Systemlubnab75% (4)
- Determination of Percent Ethanol Using DistillationDocument4 pagesDetermination of Percent Ethanol Using DistillationMycaela Archivido De Alva100% (1)
- Muscular System Week 6 & 7Document3 pagesMuscular System Week 6 & 7Al SerenosoNo ratings yet
- SAKUNADocument19 pagesSAKUNAErika Lee ToretaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 (Muscular System)Document7 pagesUNIT 3 (Muscular System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6 Muscular SystemDocument17 pagesWEEK 6 Muscular SystemMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- M. M. College of Nursing Mullana Ambala: Topic: Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesM. M. College of Nursing Mullana Ambala: Topic: Muscular SystemBhawna PandhuNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument56 pagesMuscular SystemTrisha BawaNo ratings yet
- Muscle System kd13Document46 pagesMuscle System kd13Side PoorNo ratings yet
- Muscular 2Document9 pagesMuscular 2marygracetamborlnhsNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System NotesDocument32 pagesThe Muscular System NotesVivien Talavera0% (1)
- Muscular Tissue I Reading: Chapter 10Document34 pagesMuscular Tissue I Reading: Chapter 10Marc Andreo MalalaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6 Muscular SystemDocument18 pagesWEEK 6 Muscular SystemMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Final1Document33 pagesMuscular System Final1Karl Maurice ApogNo ratings yet
- Refined Muscular SystemDocument54 pagesRefined Muscular SystemogatojohnsonNo ratings yet
- ANPH-M2-CU5. Muscular SystemDocument27 pagesANPH-M2-CU5. Muscular SystemMary Grace MapulaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Reading MaterialsDocument17 pagesMuscular System Reading Materialsdelacruzchristinejoie.kldNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument110 pagesMuscular SystemJang WonyoungNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 (Muscles)Document5 pagesCHAPTER 11 (Muscles)eumarasiganNo ratings yet
- Zoology PPT Muscular SystemDocument68 pagesZoology PPT Muscular SystemDian O. Velasquez100% (2)
- The Muscular SystemDocument6 pagesThe Muscular SystemAya MojicaNo ratings yet
- MuscoDocument1 pageMuscoMarean NicholeNo ratings yet
- Muscular Tissue: Anatomy and Physiology LectureDocument25 pagesMuscular Tissue: Anatomy and Physiology LecturehanzNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissueDocument6 pagesMuscular TissueChezkaMayC.OliverosNo ratings yet
- 5.muscular System Yj1237291349853609678Document37 pages5.muscular System Yj1237291349853609678pandieswaran9489No ratings yet
- Lesson VI The Muscular SystemDocument13 pagesLesson VI The Muscular Systemmikaelladoles02No ratings yet
- Introduction To Body StructureDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Body StructureBrady DeNioNo ratings yet
- 6 Contraction of Skeletal MuscleDocument109 pages6 Contraction of Skeletal MuscleHaslinNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument23 pagesMuscular SystemAland BakrNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesLesson 5 Muscular SystemRodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- Module5 Muscular SystemDocument28 pagesModule5 Muscular Systemwilden ellorincoNo ratings yet
- Naw TrainingDocument34 pagesNaw Trainingganesh pNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument9 pagesDefinitionaimiorreNo ratings yet
- (Notes) Edped2 Midterm - Skeletal, Circulatory, Muscular, Respiratory, Reproductive, Nervous SystemDocument7 pages(Notes) Edped2 Midterm - Skeletal, Circulatory, Muscular, Respiratory, Reproductive, Nervous SystemaespaghettiiNo ratings yet
- Physiology U-4 Excitable Muscle TissueDocument154 pagesPhysiology U-4 Excitable Muscle Tissuesinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Embryology: Abdulrahman Uday AbdulfatahDocument27 pagesEmbryology: Abdulrahman Uday AbdulfatahAbdulrahman UdayNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Muscular System ReviewerDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 7 Muscular System ReviewerPhilline ReyesNo ratings yet
- Muscle 1Document29 pagesMuscle 1drpankaj28No ratings yet
- NefDn Muscular System SummDocument2 pagesNefDn Muscular System SummNefertitie DanaoNo ratings yet
- E. Muscular System RevisedDocument41 pagesE. Muscular System RevisedGenelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 AnaphyDocument19 pagesLesson 5 AnaphyKiane Dominique GarotNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesThe Muscular SystemKeiffer Ann LopezNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Muscular SystemDocument8 pages7.1 Muscular SystemEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Bs Pharma Muscular SystemDocument36 pagesBs Pharma Muscular SystemLawrenceNo ratings yet
- Muscle System Kd13Document46 pagesMuscle System Kd13patriciaperidot12No ratings yet
- MusclesDocument14 pagesMusclesmk.sabidoNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged 1 13Document13 pagesIlovepdf Merged 1 13Abdulrahman UdayNo ratings yet
- 3 Topic 3 MascleDocument62 pages3 Topic 3 Masclesamuel mergaNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY - Muscular SystemDocument11 pagesANAPHY - Muscular SystemSoleil RiegoNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Muscular SystemDocument76 pages6.0 Muscular System[R2A] Khadijah AzlanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: by DR - Ajish AbrahamDocument55 pagesAnatomy: by DR - Ajish AbrahamAjishAbrahamNo ratings yet
- CORRECHE Lei-AnnBelle CH10TopicOutlineDocument4 pagesCORRECHE Lei-AnnBelle CH10TopicOutlineleiannbellecorrecheNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 6 MuscleDocument12 pagesAnatomy Lec 6 Muscleidrimuha333No ratings yet
- Module 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocument20 pagesModule 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Types of Muscles: Muscular SystemDocument13 pagesTypes of Muscles: Muscular SystemHaru MatsubuchiNo ratings yet
- Functions of MusclesDocument5 pagesFunctions of MusclesJoseph RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Muscular SystemDocument54 pagesAnaphy Muscular SystemZosia SageNo ratings yet
- Physiology05 Muscle CellDocument37 pagesPhysiology05 Muscle CellsmpoojasubashNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Muscular ReviewerDocument7 pagesSkeletal and Muscular ReviewerJainessa SinsuatNo ratings yet
- Anatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyFrom EverandAnatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Reviewer PcolDocument3 pagesReviewer PcolMycaela Archivido De AlvaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates LabDocument6 pagesCarbohydrates LabMycaela Archivido De AlvaNo ratings yet
- Casein Protein Isolation and Characterization of Enzymatic Hydrolysate by Paper Chromatography and Qualitative Color ReactionsDocument5 pagesCasein Protein Isolation and Characterization of Enzymatic Hydrolysate by Paper Chromatography and Qualitative Color ReactionsMycaela Archivido De AlvaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 BiostatDocument2 pagesActivity 2 BiostatMycaela Archivido De AlvaNo ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument1 pageENGLISHMycaela Archivido De AlvaNo ratings yet
- EthanolDocument1 pageEthanolMycaela Archivido De AlvaNo ratings yet
- Detection of BasicDocument3 pagesDetection of BasicMycaela Archivido De AlvaNo ratings yet
- Practice of PharmacyDocument12 pagesPractice of PharmacyMycaela Archivido De AlvaNo ratings yet