Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SAP SD Definitions
SAP SD Definitions
Uploaded by
Sridharan RajagopalanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SAP SD Definitions
SAP SD Definitions
Uploaded by
Sridharan RajagopalanCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
CUSTOMER MASTER
Data which are to be used frequently with consistency and stored in long term view for the
business processes are called Master data.
Partner types:- identifies the nature of the partner and differentiates between the business
process.
Partner functions:- Identifies the role of the partner type within the business transaction.
Account group:- classifications of the master data according to the partner role. It controls the
fields in the CM, number assignments.
2.MATERIAL MASTER
Material master stores the data about the material required for the all the organizational units in
separate views.
Material group is the group of materials which has the same attributes.
Eg;- metal processing, electronics,etc.
Material type is the key which assigns the material to the group according to its functional role in
the business process.
Material type controls number assignment, quantity / value update in valuation area, views for
the Material master, default item category, account assignment.
Eg;- raw material, finished goods, trading goods.
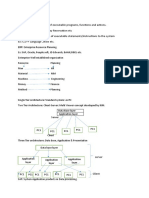
3.ENTERPRISE STRUCTURE
A Company Code :-is a organizational unit included in the balance sheet of a legally-independent
enterprise-the central organizational element of Financial Accounting.
Controlling Area :- is a cost-oriented organizational element used to represent a closed
system for cost accounting purposes.One controlling area can handle cost accounting for
several company codes
Sales Organisation :- Sales Organisation represents the selling unit as a legal entity ,is
responsible for the sale and distribution of goods or services and liable for product guarantees
and other rights to recourse.
Distributional Channel:- represents the channel through which saleable materials or services
reach customers.
Division:- is a collection of Product groups. A material belongs to exactly one division only.
Sales Area:- is the set-up that combines sales organisation, distributional channel and division.
Sales Office is the geographical aspects of the organization in business development and sales
Sales Group is the staff of a Sales office.Employees of a sales office can be assigned to sales
groups defined for each division or distribution channel.
Plant is the manufacturing facility where the goods are produced or the storage location in case
if there is no manufacturing concept.
Storage location is storage facility within a plant where the stock is physically stored. The storage
location has the where houses in proximity.
4.SALES DOCUMENTS
Different sales document represents the different business transactions in sales and thus provide
model for the entire sales order process.
Sales document basic functions:
Determining the delivering plant, Shipping point & Route automatically
Availability check & Transfer of requirements
Delivery Scheduling determines lead times for delivery processing.
Pricing- indicates how a price should be determined for the sales order item.
Sales Information System - dictates how the sales information system is updated
with sales order information to plan and control sales.
Checking Credit Limits
Sales header information:
Sold-to Party, Ship-to party
Purchase Order Number
Sales Area Data
Payment Terms
Pricing elements for the entire document
Order Status
Item line information:
Material number &Quantity
Pricing conditions for the individual items
Item level text
Item level status
Plant and storage location
Schedule lines
Schedule lines contains the qty and the delivery dates.
The item category controls what the item does in the sales document in terms of delivery , price
and billing and functions associated with that business transaction.
A quotation presents the customer with a legally binding offer for delivering a product or service
within certain fixed conditions, such as the validity period and the terms and conditions.
Inquiry Non-Binding Agreement- Information gained from these documents can be used to
gauge different markets, sales, inventory trends.
Contracts- Outline agreements that a customer promises to order over a specified period of
time, at a fixed quantity or value and the price involved, however without any mention about
schedule lines.
Schedule agreements- Outline agreements that a customer promises to order over a specified
period of time, at a fixed quantity or value and the price involved with determined schedule
lines.
Assortment Module: it is an order entry tool used in sales order that displays a list of materials
and services that can be released from a value contract. It has a validity date and a restriction
that only the materials and services that belong in the same sales organization and distribution
channel for which your release order is being made will be displayed.
Cash sale: It is special sales process in which the customer pays for the goods and picks up the
delivery .The sales order and the delivery is carried out at the same time. Normally the billing is
either sent after the delivery or not sent to the customer at all.
Rush order :is a special sales process carried out with immediate delivery option normally on
the same day, however the sales order , delivery and billing process takes place in the
sequence as in standard sales process.
Consignment refers to those goods which are stored at the customers location but are owned
by the business.
CONSIGNMENT FILLUP
CONSIGNMENT ISSUE
CONSIGNMENT RETURNS
CONSIGNMENT PICKUP
5. PRICING
( Pricing ) Procedure:- is set of process through which (the price for an item is) required
information is read among the permitted permutations and combinations, by following the
arithmetical and / logical operations in a predefined sequence.
Condition type:- is a arithmetic calculation or logic maintained in the procedure to arrive at the
value for the field.
Access sequence:- represents the search strategy to access the condition tables in a predefined
hierarchy to find the matching condition records.
Condition tables:-forms the accesses for the access sequence, contains key fields required to
find the suitable condition records.
Exclusive access indicators:- If the Exclusive access indicator is set, the system looks no further after it
finds the first valid condition record. In this case, the system cannot determine a best price.
Condition exclusion group:- the condition which result in the best/ worst value is selected and
others are deactivated.
Condition supplement:- the conditions which are to be accessed together in the procedure are
grouped in condition supplement.
Group condition:- the cumulative value of the quantity is taken as the condition base value for
scale point determination, but the rate for each item is taken from its individual condition record.
6.SHIPPING OUTBOUND DELIVERY
A shipping point:- is an independent organizational unit at a fixed location that processes and
monitors outbound deliveries as well as goods issue.
Shipping processing include:
Monitoring of deadlines for reference documents due for shipping (eg, customer
orders and PO)
Creating and processing outbound deliveries
Monitoring goods availability
Monitoring capacity situation in the warehouse
Support for picking (with link to the Warehouse Management System)
Packing the delivery
Printing and transmitting shipping documents
Processing goods issue
Controlling through overviews of:
- deliveries currently in process
- activities still to be performed
- possible bottlenecks
Outbound delivery is the process in which the goods are picked, packed and issued and the
relevant necessary documents are created at every stage.
Picking is the process of physically removing the goods from the source storage bin in the
storage location / warehouse complex to deliver goods on schedule.
Transfer Order is the document which is required for movement of the goods from the source
storage bin to destination bin within the warehouse complex.
Picking list is the output created for the picking personnel bin in the warehouse during the
outbound delivery, to give the information about the item, quantity, storage bin details.
Packing is the process of assigning delivery items to shipping materials. This produces shipping
units.
Packing material type:is the packaging material classified according to the delivery items to be
packed.
Pacing material group: is group defined for the set of delivery items which has similar packing
requirements.
Goods issue: is the process of releasing the goods for the shipment from the warehouse after
the necessary steps are carried out.
Goods issue functions:
Reduces the stock in the inventory
Updates the inventory balance sheet of the inventory accounting.
Creates the due list for the billing
Updates the sales information system
Updates the sales process status.
Reduces the delivery requirements in the material requirements planning.
Delivery document types provides the model for the business process to deliver the items for
fulfilling the
Sales order process.
Delivery document/ outbound delivery functions:
Availability check & TOR
Partner, text, output, material , Route determinations
Credit check
Listing & exclusion
Transportation planning
Delivery header information:
Ship-to party
warehouse no, picking ,loading status
shipping point ,Route
Delivery and transportation scheduling information
Delivery item category controls how the item is to be processed and handled in the
shipping process.
Item information:
Material
Quantity to be delivered
Plant and storage location
Transportation information
Picking Specifications
Movement type
7. TRANSPORTATION
Transport planning point is the location or group of people where the transport planning and
shipment completion process is carried out.
Individual Shipment :- can have more than one delivery , one point of departure , one
destination and only one mode of transport.
Collective Shipment:- can have more than one delivery ,multiple points of departure , many
destinations but only one mode of transport.
Transportation chain:- can have more than one delivery ,multiple points of departure , many
Destinations and multiple modes of transport.
The shipping document is the central element of transportation planning & shipment
Completion. It contains all the information necessary for carrying out transportation.
We can use shipment documents to:
Combine deliveries into one inbound or outbound shipment
Specify shipment stages
Legs
Border crossing points
Load transfer points
Assign goods to handling units
Assign service agents
Specify planned transportation deadlines
Record actual transportation deadlines
Specify output required for transportation (such as shipping papers or EDI messages)
Define transport-relevant texts
Shipment types contain all the essential control features for the shipment
document.
Shipping type is defined in combination with the mode of transport.
8. BILLING
Billing is the process of creating & sending the commercial document to the customer, normally
Bill- to party to collect the payment for the delivered materials.
An invoice is a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer, indicating the items,
quantities and agreed prices for products or services that the seller has already delivered to the
buyer.
Billing document functions:
Creation of invoices (and pro-forma invoices) on the basis of deliveries and
services
Transferring posting data to financial accounting
Creation of credit and debit memos on the basis of requests
Cancelling business transactions
Billing document header info:
Identification number of Payer
Billing Date
Net Value of entire Billing Document
Terms of Payment and Inco terms
Pricing Elements
Document Currency
Billing document item information:
Material number
Billing Quantity
Pricing for an individual item
Weight and Volume
Number of reference document for billing document.
Effects of billing processes:
Posting the values of receivables and deductions to the appropriate G/L account.
Other accounting documents in CO(CO PA, FI-LC) is automatically generated.
Updating the credit account, document flow status, statistics in sales information systems.
Billing plan: is special billing process in which the total value of the bill is distributed either
periodically at regular intervals or payments assigned to completion of stages.
Periodic billing: is the billing plan type in which the total value of the bill is distributed at certain
dates in regular intervals.
Mile stone billing: is the billing plan type in which the total value of the bill is distributed among
individual dates, according to the completion of specified tasks in the network called milestones.
Date category: date category has the control functions like fixed date, billing type,biling block and
billing rule.
Date proposal Maintenance: used for milestone billing, the reference billing plan no. specifies a
sequence of dates which can be used during order processing as a reference for date
determination.
Date rule: Date rules are needed in the billing plan to define start date and end date .The
foundation of date determination rule is the baseline
Billing rule: specifies the how the billing value is to be calculated in the billing plan type.
9.CREDIT / RISK MANAGEMENT
The credit control area is an organizational unit that specifies and controls the credit limit for
a customer.
Open order value : The value of all sales order items which have not yet delivered
Open delivery value : The value of all delivery items which are not yet billed
Open billing value : The value of all billing items which are not yet transferred to Accounting
Open Items: The value of billed items which are transferred to accounting (receivables)
Static Credit Check : Total value of open sales orders + open deliveries + open billing
documents + open items
Dynamic Credit Check: Total value of open deliveries + open billing documents + open items +
open sales orders for a specified horizon
The credit checks can also be done for,
Oldest open item
Critical fields
Next review date
Document value
High dunning level
In a centralized organization, company codes are combined into one credit control area for
Credit Management.
Total credit limit: Determine the credit limit allowed for a customer for all credit control areas.
Maximum individual credit limit: Restricts the credit limit for a specific credit control area.
Individual credit limit: Determine a specific credit limit for a customer within a credit control
area.
Credit groups combine different business processes that are to be treated in the same with
regards to the credit check.
Subsequent function blocked for credit check in sales order:
Order confirmation output
Confirmed Qty for avaialability check
Purchase requisition
Work list and delivery
Subsequent function blocked for credit check in delivery:
Picking
Packing
Shipping
Delivery note output
10.COPY CONTROL FUNCTIONS
Copy control is the function used to copy certain data from the preceding document to transfer it
to the subsequent document. Useful when the multiple entries of same data is required at
various stages of the sales transactions.
Data transfer routines: Control how fields are copied from the reference document.
Copying requirements: Requirements that are checked when you create a document with
reference.
Switches: switches for setting specific controls for each transaction.
11.BASIC FUNCTIONS
Partner determination : is the basic function to find the appropriate partner function in the
business transactions to whom the documents or deliveries is to be sent.
Account determination: is the basic function to find the appropriate G/L account to post the
revenues or deduction that arises from the sales transactions during sales process.
Account key: is assigned to the conditions types to post the values arising from the
pricing procedure to corresponding G/L account which is determined using the account
key as one of the criteria.
Delivery Scheduling includes Pick/Pack time and the Loading time.
The system uses the pick/pack time and the loading time to help determine the
material availability date and the loading date respectively.
Transportation scheduling includes the determination of the transportation lead time and
transit time
The system uses the transportation lead time and the transit time to help determine
the transportation planning date and the goods issue date respectively.
Output determination is the basic function to find to whom , how, when and what information is
to be sent.
Text determination is the function to find the appropriate text to be transferred from the
customer master record/ Material master record to the sales / delivery documents.
Incompletion procedure : specific control to ensure the requisite data is maintained at different
SD level . By highlighting/ warning the missing data in sales/delivery documents as well as sales
activities and partner functions in order.
Status groups are the group of the transactions allowed /not allowed, in case there is
a log of incompletion arises in the document creation.
Dynamic product proposal: is a list of products for a specific customer that is automatically
proposed during sales document processing.
Material determination: is the basic function to interchange the supply of the actual material
entered in the sales order with the alternate material, if the required material not available or to
push the stock of alternate material as sales promotion strategy.
Listing & Exclusion: Listing determines automatically which materials are allowed for the
customer to buy. Exclusion determines automatically which materials are not allowed.
Free goods: is a promotional deals wherein , one or more goods are supplied at free of cost ,if
certain materials are ordered at certain quantities.
Bonus buys :is a promotoional deal, which grants special prices, discounts or free articles, if
certain prerequisites and general conditions are fulfilled. In the Bonus Buy, Coupons can be
assigned as prerequisite.
Cross selling: is sales strategy , wherein when a given product is sold a suggestion is made for
another product or several other products or accessories.
A rebate is a special incentive offered for customer patronage, which is calculated based on
certain rebate basis in the relevant billing processes. Once the cumulative value called accrual
reaches certain value, it is settled by sending credit memo to a customer.
Material rebate
Customer rebate
Customer hierarchy rebate
Material group rebate
Independent of sales volume
12. MM MODULE
Warehouse: - is the location where the stocks of items that belong to one or more plants are
stored and physical movement of goods for inbound and outbound deliveries takes place. The
link between the MM to the inventory management takes place through the Warehouse number.
Storage type: The different warehouse areas, which differ with respect to their
organizational and technical features, are defined as storage types
Picking area: The picking area groups storage bins together in the storage type from
the picking viewpoint. It is the opposite of the storage section, which groups storage
bins together from the putaway viewpoint.
Picking area: The picking area groups storage bins together in the storage type from
the picking viewpoint.
Storage section, which groups storage bins together from the putaway viewpoint.
Door: A door within a warehouse can be used both for inbound delivery as well as
outbound delivery of goods
Material Requirement Planning :- is the process of forecasting,assesing and
maintaining the required optimum stock of the materials inorder to carry out the smooth
production process and to meet the demands of the customer.
Availability check :is the process of verifying the stock availability for a required
quantity of ordered material to deliver the same at the requested delivery date.
Check against Available To Promise: The ATP quantity is calculated from the
warehouse stock, the planned inward movements of stock (production orders,
purchase orders, planned orders) and the planned outward movements of stock (Sales
Orders, deliveries, reservations).
Check against Product allocation: facilitates period-based distribution of products
for certain customers or regions. Product allocation functionality allows to manage the
supply of scarce products to customers so that each customer receives an allocated
amount.
The check against planning: is performed against independent requirements which
are usually created for an anonymous market rather than being customer specific.
Transfer of requirements:- during the creation of sales order , for maintaining the
sufficient stock of the materials to be delivered and confirm the delivery date to the
customer ,the requirements are transferred to the MM and then to PP for the procurement
or for the inhouse production.
Checking group: It controls whether the system is to create individual or collective
requirements in sales and shipping processing.
Checking Rule: The use of Checking rule to control the scope of the availability check
for each transaction in sales and distribution.
Requirements Class: The requirements class contains all control features for planning.
In addition, it is specified at a global level whether an availability check is to take place for
the material in the sales and distribution documents on the basis of the ATP quantity
(ATP = available to promise) and whether requirements are to be passed on.
Requirements type: The requirements are identified by the requirements type. The
requirements type refers to the requirements class and its control features.
13. ABAP FOR SD MODULE
Presentation Layer: contains the software components that make up the SAPgui
(graphical user interface). This layer is the interface between the R/3 System and its
users.
Application Layer: consists of one or more application servers and a message server.
Each application server contains a set of services used to run the R/3 System.
Database Layer: consists of a central database system containing all of the data in the
R/3 System. The database system has two components - the database management
system (DBMS), and the database itself.
Reports are Executable Programs that reads data from the database, processes the
data and display the data to the required format.
Interface refers to the data transfer between two independent systems.
ALE (Application Link Enabling ) is a SAP terminology used mostly for SAP to
SAP communication in Distributed servers system.
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) is a technology in itself with its own set of
standards and used mostly for communication between any 2 systems on different
networks.
IDOC (Intermediate Document) is a Data container
Conversion programs helps in data transfer from an external system into the SAP R/3
System. In other words, this type of transfer refers to a one-time transfer from a legacy
system to the SAP system
Enhancements are plug points provided by SAP to add customer functionality to existing
SAP Transactions without modifying it.
User exits are routine which SAP allows you to add in additional customized
programs process without affecting the standard SAP programs
Forms are used for creating and maintaining the output for printing in SAP system.
SAPscript and Smartform are the tool that SAP provides for creating
layout sets.
Whenever new output type is created , 3 parameters are required.
They are :
- Smart form / SAP script Name
- Driver Program Name
- ENTRY routine name.
A data dictionary is a central source of information for application data.
You might also like
- SAP S/4HANA Retail: Processes, Functions, CustomisingFrom EverandSAP S/4HANA Retail: Processes, Functions, CustomisingRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- ARM Standard Configuration S4HANADocument11 pagesARM Standard Configuration S4HANAТетяна Яценко100% (1)
- s4270-SAP Advanced ATP (aATP) - 2020-3Document10 pagess4270-SAP Advanced ATP (aATP) - 2020-3董董董No ratings yet
- VT01N Config StepsDocument14 pagesVT01N Config Stepsmeti kota100% (2)
- Sap Afs VasDocument13 pagesSap Afs VasBarry Ho100% (1)
- Configuring CFOP On SAPDocument20 pagesConfiguring CFOP On SAPJuan PinaNo ratings yet
- Copy of SAP SD Tables Field Mapping Data PDFDocument229 pagesCopy of SAP SD Tables Field Mapping Data PDFKarthik KNo ratings yet
- Atpl - Exim Solution 2018Document23 pagesAtpl - Exim Solution 2018Mehul BazariaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Sap SD ModuleDocument20 pagesBasics of Sap SD ModuleSourav Daruka100% (1)
- BBP SDDocument62 pagesBBP SDJeevanNo ratings yet
- Incoterms in SapDocument7 pagesIncoterms in SapKhushal Chate100% (1)
- SAP Brazil Localization PortfolioDocument31 pagesSAP Brazil Localization Portfoliosatishkr14No ratings yet
- Customer Heirarchy in Sap - SDDocument2 pagesCustomer Heirarchy in Sap - SDvnkb100% (1)
- SD Workshop 1Document23 pagesSD Workshop 1Ngan PhamNo ratings yet
- Concept of SAPDocument22 pagesConcept of SAPramesh B100% (1)
- Customer Hierarchy in SAP SD PDFDocument9 pagesCustomer Hierarchy in SAP SD PDFمحمد شعيبNo ratings yet
- 05 Output DeterminationDocument11 pages05 Output Determinationmad13boy100% (1)
- ThirdPartySales SAP SDDocument14 pagesThirdPartySales SAP SDRaja ShekarNo ratings yet
- Issue in MiroDocument8 pagesIssue in MiroSUDHIRNo ratings yet
- Check List For Eway Bill Implementation Solution: 1. Edocument FrameworkDocument3 pagesCheck List For Eway Bill Implementation Solution: 1. Edocument FrameworkRakesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Kimsis Fiori AppsDocument37 pagesKimsis Fiori AppsPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- SAP AFS Online TrainingDocument2 pagesSAP AFS Online TrainingAnna CarolinaNo ratings yet
- Sales Order Reports: 1.list of Sales Orders VA05/VA05NDocument6 pagesSales Order Reports: 1.list of Sales Orders VA05/VA05Nabhilash eNo ratings yet
- SAP IS Oil Gas Functionalities PDFDocument1 pageSAP IS Oil Gas Functionalities PDFmohannaiduram0% (1)
- 03 S4HANA LogisticsDocument50 pages03 S4HANA LogisticsabidinalNo ratings yet
- SAP SD SUPORTE - LTMC S - 4 Hana Replacing LSMWDocument8 pagesSAP SD SUPORTE - LTMC S - 4 Hana Replacing LSMWSUBHOJIT BANERJEENo ratings yet
- Default Storage Location in Sales OrderDocument1 pageDefault Storage Location in Sales Orderabdelkader El alamiNo ratings yet
- Run Sap Like A Factory: RSLF Bpo - Nfe MonitoringDocument15 pagesRun Sap Like A Factory: RSLF Bpo - Nfe MonitoringEverton Araujo PadilhaNo ratings yet
- NFE 10.0 - Master Guide Version 1.4 For NFE 10.0 SP11Document28 pagesNFE 10.0 - Master Guide Version 1.4 For NFE 10.0 SP11Deivison FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Sap SD Configuration DocumentDocument109 pagesStep by Step Sap SD Configuration DocumentS JgNo ratings yet
- SAP Delivery/Shipping Reports: Name Business Requirement T-Code Menu PathDocument6 pagesSAP Delivery/Shipping Reports: Name Business Requirement T-Code Menu Pathabhilash eNo ratings yet
- Sub Contracting With DeliveryDocument11 pagesSub Contracting With Deliverysandip bhadaneNo ratings yet
- Localizacao CATT Procedimentos 46Document11 pagesLocalizacao CATT Procedimentos 46Alexandre OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Availability Check Against Product AllocationDocument4 pagesAvailability Check Against Product AllocationThiru ManiNo ratings yet
- ASN ProcessDocument35 pagesASN ProcessssyogendraNo ratings yet
- ALE Overview Too GoodDocument63 pagesALE Overview Too GoodShuvodeep Datta100% (1)
- B1-Sap SD TablesDocument5 pagesB1-Sap SD TablesShivaprakash Shastri HiremathNo ratings yet
- Message Customizing Incorrectly Maintained No SE729 1571547594Document9 pagesMessage Customizing Incorrectly Maintained No SE729 1571547594Ali Ehtsham GhummanNo ratings yet
- Business Partner - Customer-Vendor Integration S/4 HANADocument8 pagesBusiness Partner - Customer-Vendor Integration S/4 HANAJoão Douglas Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- BAdI Calculation of ICMS DIFAL Base For Consumption Goods or AssetsDocument8 pagesBAdI Calculation of ICMS DIFAL Base For Consumption Goods or AssetsRodrigoNo ratings yet
- SAP TablesDocument25 pagesSAP TablesFercho Canul CentenoNo ratings yet
- Redefining Business Partner in SAP S 4HADocument4 pagesRedefining Business Partner in SAP S 4HAAlexNo ratings yet
- Sap SCNDocument91 pagesSap SCNramesh BNo ratings yet
- Third-Party Process Overview - SAP BlogsDocument23 pagesThird-Party Process Overview - SAP BlogsManas Kumar SahooNo ratings yet
- Sap SD DemoDocument16 pagesSap SD DemoAnjan KumarNo ratings yet
- Vofm Routines in Sales & Distribution: Part 1: Copying RequirementsDocument20 pagesVofm Routines in Sales & Distribution: Part 1: Copying RequirementsnathaanmaniNo ratings yet
- Custom Invoic Template SapDocument41 pagesCustom Invoic Template Sapsimplepunjabi100% (1)
- Idoc For FunctionalDocument28 pagesIdoc For FunctionalsharadapurvNo ratings yet
- Sales Scheduling Agreements (3NR - GB) - Test ScriptDocument32 pagesSales Scheduling Agreements (3NR - GB) - Test ScriptFernando MillanNo ratings yet
- AFS - Stock Allocations For New Demands and MRP's Behavior For Standard OrdersDocument22 pagesAFS - Stock Allocations For New Demands and MRP's Behavior For Standard OrdersSrinivas KotteNo ratings yet
- Sap AfsDocument156 pagesSap Afstest100% (1)
- Sap SD Functional Consultant 1588517277Document2 pagesSap SD Functional Consultant 1588517277Kiran BharatiNo ratings yet
- Project SAP S4 HANA Implementation: Functional SpecificationsDocument4 pagesProject SAP S4 HANA Implementation: Functional SpecificationsPrashant Kumar100% (1)
- SAP SD Questions and AnswersDocument16 pagesSAP SD Questions and Answerserlend2012No ratings yet
- SAP SD Interview QuestionsDocument10 pagesSAP SD Interview QuestionsPrasad BudhwaniNo ratings yet
- Profile Synopsis: SAP-Sales & Distribution Experienced ProfessionalDocument8 pagesProfile Synopsis: SAP-Sales & Distribution Experienced ProfessionalSourav SinghNo ratings yet
- Copy Controls in SAP SD 1703256598Document13 pagesCopy Controls in SAP SD 1703256598Kavi JaganNo ratings yet